Tailoring Self-Supervision for Supervised Learning
- 摘要
- 文章思路
- 一些值得读的参考文献和技术:
- 值得一读的高引文献
- 可视化技术
摘要
近期,在监督学习中部署一个合适的自监督学习来提高监督学习的性能是一个具有前景的方式。然而,因为之前的前置任务主要为了无监督的表征学习而设计,所以自监督的优点没有被完全利用起来。这里,我们首先为自监督辅助监督目标,提出三点要求。第一,这些任务需要指导模型学习丰富的(互补)表征。第二,自监督中涉及的变换不应该严重修改训练的数据分布。第三,这些任务应该轻量和高适用。随后,为了满足这三点要求,我们提出一个简单的辅助自监督任务,预测局部旋转(predicting localizable rotation, LoRot)。我们用多个实验来验证所提方法在鲁棒性和泛化性方面的性能。代码https://github.com/wjun0830/Localizable-Rotation。
文章思路
已证明在监督学习中引入自监督学习可以提升模型的鲁棒性1 2,但之前引入的自监督都是为无监督表征学习设计的。
作者认为在监督学习下使用自监督,应该满足三点要求才能把它的优点发挥出来。
第一,自监督应该相比于主要任务(监督任务)学习到更多的物体特征,依据有二:1、监督学习有捷径3 4,2、自监督通过之前的前置任务能够学习物体的通用特征5 6 7 8 9 。
第二,因为目标是为了辅助监督学习,所以加上自监督的话就是多个训练目标,多任务学习的训练方式能够胜任10 11,但条件是变换函数引起的数据分布不能太大,否则在现实中12会妨碍主要任务(监督任务)13 14。
第三,辅助监督学习的自监督引起的计算和修改的开销应小,保证使用时的轻量和高适用性。而之前的自监督为了微乎其微的性能提升,带来了很大的时空开销。
为何其他的自监督方法不用,偏偏使用旋转7?
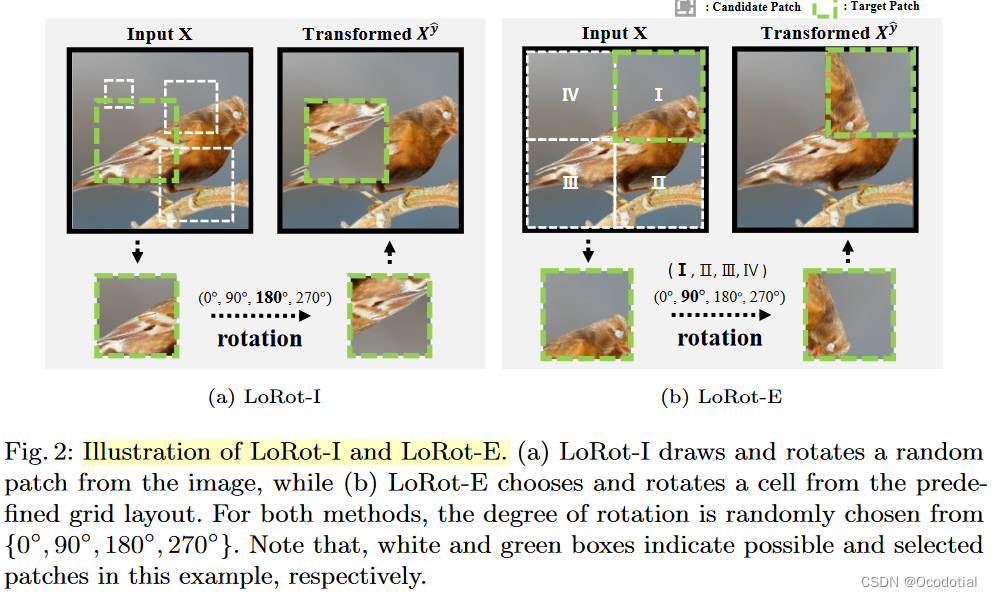
因为其通过旋转操作将模型的注意力分散到图像的各个部分学习高判别性语义特征,再加上局部的增强策略15 16 17 18
。
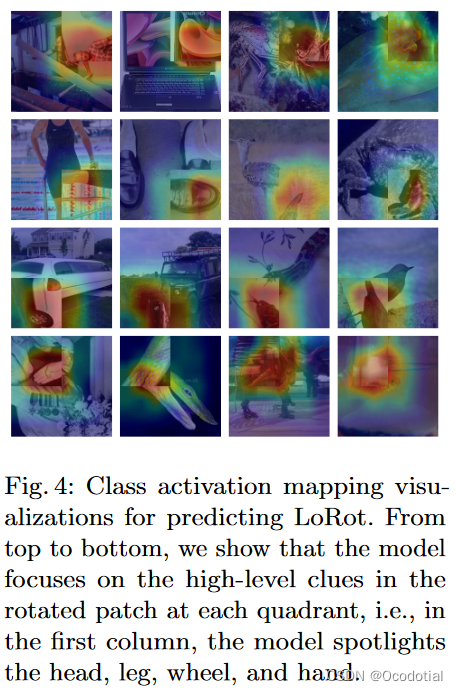
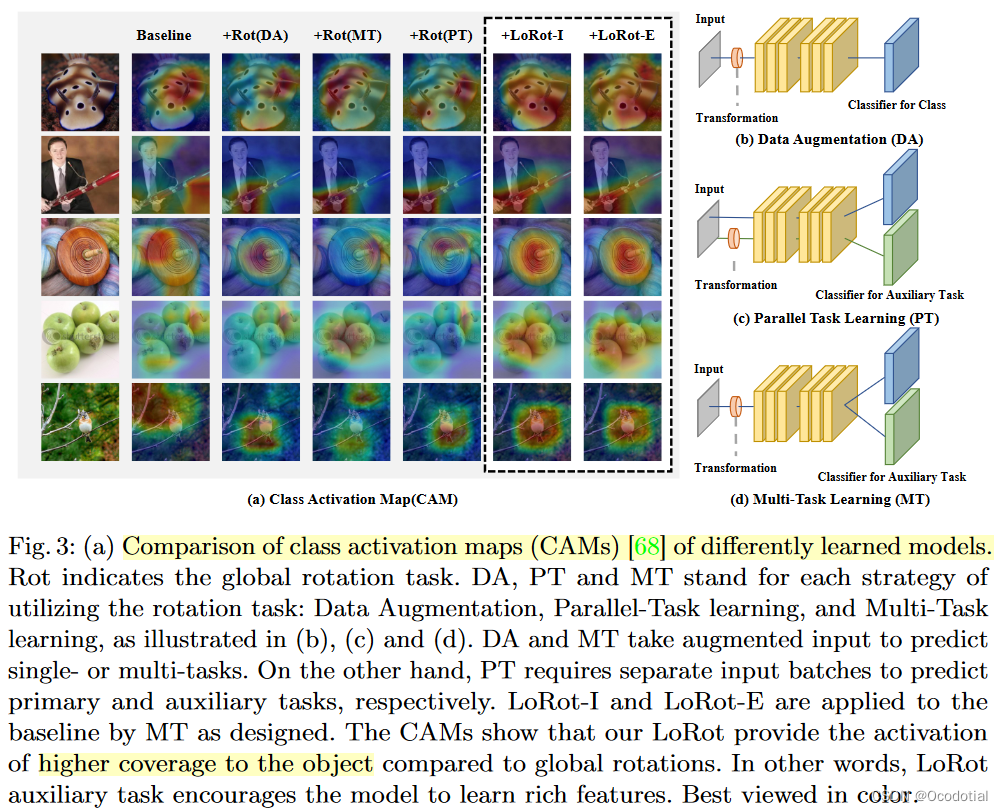

这样局部旋转后,迫使模型先完成定位任务,从而让注意力放到局部内。然后为了正确的预测旋转,让模型学习块内丰富的语义特征,使得最终相比于监督学习,能够让模型习得更多的特征。
一些值得读的参考文献和技术:
值得一读的高引文献
Deep residual learning for image recognition19
Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning20
Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning21
Benchmarking adversarial robustness on image classification22
Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database23
Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space24
Exploring simple siamese representation learning25
Autoaugment: Learning augmentation strategies from data26
Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments27
Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features28
Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss29
A Bayesian/information theoretic model of learning to learn via multiple task sampling30
Obfuscated gradients give a false sense of security: Circumventing defenses to adversarial examples31
可视化技术

t-SNE32
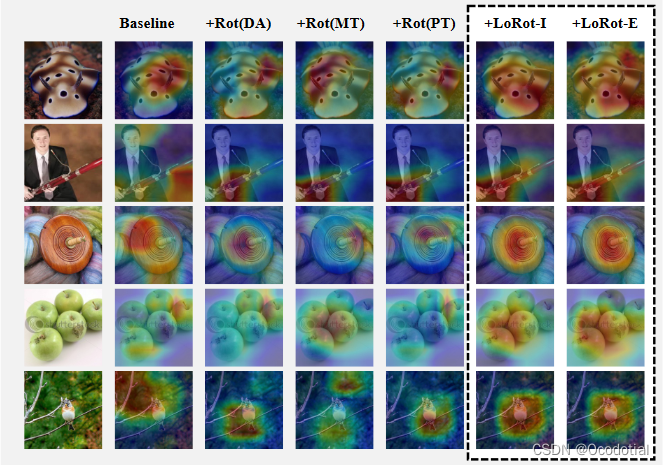
Comparison of class activation maps (CAMs)33
Carlucci F M, D’Innocente A, Bucci S, et al. Domain generalization by solving jigsaw puzzles[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 2229-2238. ↩︎
Hendrycks D, Mazeika M, Kadavath S, et al. Using self-supervised learning can improve model robustness and uncertainty[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2019, 32. ↩︎
Geirhos R, Jacobsen J H, Michaelis C, et al. Shortcut learning in deep neural networks[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2020, 2(11): 665-673. ↩︎
Nguyen A, Yosinski J, Clune J. Deep neural networks are easily fooled: High confidence predictions for unrecognizable images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2015: 427-436. ↩︎
Doersch C, Gupta A, Efros A A. Unsupervised visual representation learning by context prediction[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2015: 1422-1430. ↩︎
Dosovitskiy A, Springenberg J T, Riedmiller M, et al. Discriminative unsupervised feature learning with convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2014, 27. ↩︎
Gidaris S, Singh P, Komodakis N. Unsupervised representation learning by predicting image rotations[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.07728, 2018. ↩︎ ↩︎
Noroozi M, Favaro P. Unsupervised learning of visual representations by solving jigsaw puzzles[C]//European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham, 2016: 69-84. ↩︎
Noroozi M, Vinjimoor A, Favaro P, et al. Boosting self-supervised learning via knowledge transfer[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018: 9359-9367. ↩︎
Caruana R. Multitask learning[J]. Machine learning, 1997, 28(1): 41-75. ↩︎
Ruder S. An overview of multi-task learning in deep neural networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05098, 2017. ↩︎
Mallat S. Understanding deep convolutional networks[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2016, 374(2065): 20150203. ↩︎
Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2020: 1597-1607. ↩︎
Lee H, Hwang S J, Shin J. Self-supervised label augmentation via input transformations[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2020: 5714-5724. ↩︎
DeVries T, Taylor G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04552, 2017. ↩︎
Yun S, Han D, Oh S J, et al. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. 2019: 6023-6032. ↩︎
Zhang H, Cisse M, Dauphin Y N, et al. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.09412, 2017. ↩︎
Zhong Z, Zheng L, Kang G, et al. Random erasing data augmentation[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 2020, 34(07): 13001-13008. ↩︎
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 770-778. ↩︎
He K, Fan H, Wu Y, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2020: 9729-9738. ↩︎
Grill J B, Strub F, Altché F, et al. Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2020, 33: 21271-21284. ↩︎
Dong Y, Fu Q A, Yang X, et al. Benchmarking adversarial robustness on image classification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 321-331. ↩︎
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, et al. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Ieee, 2009: 248-255. ↩︎
Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Shlens J, et al. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 2020: 702-703. ↩︎
Chen X, He K. Exploring simple siamese representation learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2021: 15750-15758. ↩︎
Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Mane D, et al. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation strategies from data[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 113-123. ↩︎
Caron M, Misra I, Mairal J, et al. Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 9912-9924. ↩︎
Caron M, Bojanowski P, Joulin A, et al. Deep clustering for unsupervised learning of visual features[C]//Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV). 2018: 132-149. ↩︎
Cao K, Wei C, Gaidon A, et al. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2019, 32. ↩︎
Baxter J. A Bayesian/information theoretic model of learning to learn via multiple task sampling[J]. Machine learning, 1997, 28(1): 7-39. ↩︎
Athalye A, Carlini N, Wagner D. Obfuscated gradients give a false sense of security: Circumventing defenses to adversarial examples[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2018: 274-283. ↩︎
Van der Maaten L, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of machine learning research, 2008, 9(11). ↩︎
Zhou B, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 2921-2929. ↩︎