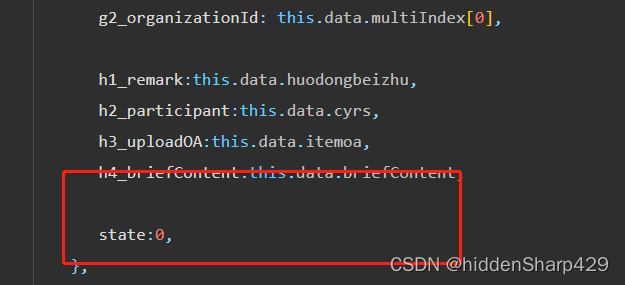
数组和函数
文章目录
- 数组和函数
- 一、数组
- 1.普通数组
- 2.关联数组
- 3.数组和循环
- 二、函数
- 1.定义函数
- 2.调用函数

一、数组
变量:用一个固定的字符串,代替一个不固定字符串。
数组:用一个固定的字符串,代替多个不固定字符串。
1.普通数组
1、定义数组:
方法一: 一次赋一个值
数组名[ 下标 ]=变量值
[root@nfs ~]# array1[0]=apple
[root@nfs ~]# array1[1]=orange
[root@nfs ~]# array1[2]=pear
[root@nfs ~]# declare -a
declare -a BASH_ARGC='()'
declare -a BASH_ARGV='()'
declare -a BASH_LINENO='()'
declare -a BASH_SOURCE='()'
declare -ar BASH_VERSINFO='([0]="4" [1]="2" [2]="46" [3]="2" [4]="release" [5]="x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu")'
declare -a DIRSTACK='()'
declare -a FUNCNAME='()'
declare -a GROUPS='()'
declare -a PIPESTATUS='([0]="0")'
declare -a array1='([0]="apple" [1]="orange" [2]="pear")'
[root@nfs ~]# declare -a | grep array1 //查看数组
declare -a array1='([0]="apple" [1]="orange" [2]="pear")'
[root@nfs ~]# echo $array1 //默认返回数组第一个值
apple
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array1[1]}
orange
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array1[2]}
pear
方法二: 一次赋多个值
[root@nfs ~]# array2=(luo guan tom)
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array2[@]}
luo guan tom
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${!array2[@]}
0 1 2
[root@nfs ~]# declare -a | grep array2
declare -a array2='([0]="luo" [1]="guan" [2]="tom")'
[root@nfs ~]# array3=(`cat /etc/passwd`)
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array3[0]}
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
[root@nfs ~]# array4=(`ls /home`)
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array4[@]}
guan Guan guanguan Guanguan luo luo1 luo2 luo3 user0013 user3 userA userA1 userA2 userA3 userB userB1 userB2 userB3 userB4 userB5 userC userD
#" " 里面包含的字符串在数组中被看做一个元素
[root@nfs ~]# array5=(guan luo tom "hello word")
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array5[0]}
guan
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array5[1]}
luo
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array5[2]}
tom
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array5[3]}
hello word
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${array5[@]}
guan luo tom hello word元素可以是变量
#数组里的
[root@nfs ~]# student1=guan
[root@nfs ~]# student2=luo
[root@nfs ~]# students=($student1 $student2)
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${students[*]}
guan luo
2、访问数组元素:
#echo ${array[0]}:访问数组中的第一个元素
#echo ${array[@]}:访问数组中所有元素,等同于 echo ${array[*]}
#echo ${#array[@]}:统计数组元素的个数
#echo ${!array[@]}:获取数组元素的索引
#echo ${array[@]:1}:从数组下标1开始
#echo ${array[@]:1:2}:从数组下标1开始,访问两个元素
2.关联数组
注意:先声明关联数组
1、方法一:一次赋一个值
数组名[索引]=变量值
[root@nfs ~]# declare -A ass_array1
[root@nfs ~]# ass_array1[index1]=guan
[root@nfs ~]# ass_array1[index2]=luo
[root@nfs ~]# ass_array1[index3]=tom
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${ass_array1[*]}
guan luo tom
2、方法二:一次赋多个值
[root@nfs ~]# declare -A ass_array2
[root@nfs ~]# ass_array2=([index1]=tom [index2]=guan [index3]=luo [index4]="hello word")
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${ass_array2[*]}
hello word tom guan luo
[root@nfs ~]# echo ${!ass_array2[*]}
index4 index1 index2 index3
3.数组和循环
1、通过循环定义和显示数组
例子1:while 脚本快速定义数组
[root@nfs test]# vim test21.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash test21.sh
循环完成,输出数组
192.168.200.2 up 192.168.200.184 up 192.168.200.182 up
[root@nfs test]# vim test21.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash test21.sh
循环完成,输出数组
1: 192.168.200.2 up
2: 192.168.200.184 up
3: 192.168.200.182 up
[root@nfs test]# vim test21.sh
[root@nfs test]# cat test21.sh
#!/bin/bash
#循环读取文件,定义数组
while read line
do
#hosts:数组名
#[++i]:索引递增,++i是从1开始,i++是从0开始的
#$line:值,即文件中的内容
hosts[++i]=$line
done < /root/test/up.txt
echo "循环完成,输出数组"
for i in ${!hosts[*]}
do
echo "索引序号是:$i: 取值 ${hosts[$i]}"
done
[root@nfs test]# cat up.txt
192.168.200.2 up
192.168.200.184 up
192.168.200.182 up
例子2:for脚本快速定义数组
[root@nfs test]# vim test22.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash test22.sh
0: 127.0.0.1
1: localhost
2: localhost.localdomain
3: localhost4
4: localhost4.localdomain4
5: ::1
6: localhost
7: localhost.localdomain
8: localhost6
9: localhost6.localdomain6
10: 192.168.200.182
11: nfs
12: 192.168.200.183
13: wbe3
14: 192.168.200.184
15: web1
16: 192.168.200.185
17: wbe2
18: 192.168.200.186
19: mycat
[root@nfs test]# cat test22.sh
#!/bin/bash
for line in `cat /etc/hosts`
do
hosts[i++]=$line
done
for i in ${!hosts[*]}
do
echo "$i: ${hosts[$i]}"
done
[root@nfs test]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.200.182 nfs
192.168.200.183 wbe3
192.168.200.184 web1
192.168.200.185 wbe2
192.168.200.186 mycat
[root@nfs test]#
[root@nfs test]# vim test22.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash test22.sh
0: 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
1: ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
2: 192.168.200.182 nfs
3: 192.168.200.183 wbe3
4: 192.168.200.184 web1
5: 192.168.200.185 wbe2
6: 192.168.200.186 mycat
[root@nfs test]# cat test22.sh
#!/bin/bash
IFS=$'\n' //定义以换行符为分隔符
for line in `cat /etc/hosts`
do
hosts[i++]=$line
done
for i in ${!hosts[*]}
do
echo "$i: ${hosts[$i]}"
done
[root@nfs test]#
2、通过数组统计数据
例子1:数组统计性别
[root@nfs test]# vim sex.txt
[root@nfs test]# vim sex.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash sex.sh
f:1
m:2
[root@nfs test]# cat sex.sh
#!/bin/bash
declare -A sex
while read line
do
type=`echo $line | awk '{print $2}'`
let sex[$type]++
done < sex.txt
for i in ${!sex[*]}
do
echo "$i:${sex[$i]}"
done
[root@nfs test]# cat sex.txt
guan m
luo f
tom m
例子2:数组统计,用户shell 的类型和数量
[root@nfs test]# vim shell.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash shell.sh
/sbin/nologin:42
/bin/sync:1
/bin/bash:20
/sbin/shutdown:1
/sbin/halt:1
[root@nfs test]# cat shell.sh
#!/bin/bash
declare -A shells
while read ll
do
type=`echo $ll | awk -F: '{print $NF}'`
let shells[$type]++
done < /etc/passwd
for i in ${!shells[*]}
do
echo "$i:${shells[$i]}"
done
二、函数
1.定义函数
方法一:
函数名(){
函数要实现的功能代码
}
方法二:
function 函数名 {
函数要实现的功能代码
}
例子1
编写脚本,实现如下菜单的功能
provide these tools:
show disk info(d)
show mem info(m)
show cpu info(c)
quit(q)
[root@nfs test]# vim tool.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash tool.sh
provide these tools:
show disk info(d)
show mem info(m)
show cpu info(c)
quit(q)
:d
-------------disk info------------------
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 17G 8.4G 8.7G 50% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 894M 0 894M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 910M 22M 889M 3% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 179M 836M 18% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 182M 4.0K 182M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs tmpfs 182M 4.0K 182M 1% /run/user/0
provide these tools:
show disk info(d)
show mem info(m)
show cpu info(c)
quit(q)
:m
---------------mem info------------------
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1819 452 73 21 1294 1124
Swap: 2047 0 2047
provide these tools:
show disk info(d)
show mem info(m)
show cpu info(c)
quit(q)
:c
-----------------cpu info------------------
19:23:03 up 8:09, 2 users, load average: 1.02, 1.09, 1.13
provide these tools:
show disk info(d)
show mem info(m)
show cpu info(c)
quit(q)
:q
----------------- exit ---------------------
[root@nfs test]# cat tool.sh
#!/bin/bash
menu () {
cat << EOF
provide these tools:
show disk info(d)
show mem info(m)
show cpu info(c)
quit(q)
EOF
}
#cat << EOF
#provide these tools:
#show disk info(d)
#show mem info(m)
#show cpu info(c)
#quit(q)
#EOF
menu
while :
do
read -p ":" choice
case $choice in
d)
echo "-------------disk info------------------"
df -hT
;;
m)
echo "---------------mem info------------------"
free -m
;;
c)
echo "-----------------cpu info------------------"
uptime
;;
q)
echo "----------------- exit ---------------------"
exit
;;
*)
#cat << EOF
#provide these tools:
#show disk info(d)
#show mem info(m)
#show cpu info(c)
#quit(q)
#EOF
menu
esac
done
[root@nfs test]#
2.调用函数
语法:
函数名
函数名 参数1 参数2
例子2
数的阶乘
[root@nfs test]# vim fac.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash fac.sh
请输入你想阶乘结果的数:9
9阶乘的结果为:362880
[root@nfs test]# cat fac.sh
#!/bin/bash
#定义函数名fun
read -p "请输入你想阶乘结果的数:" num
fun () {
#初值为1
fac=1
#使用阶乘循环
for((i=1;i<=$num;i++))
do
#阶乘公式
fac=$[$fac*$i]
done
echo "$num阶乘的结果为:$fac"
}
fun
[root@nfs test]# vim fac.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash fac.sh
6阶乘的结果为:720
7阶乘的结果为:5040
8阶乘的结果为:40320
[root@nfs test]# cat fac.sh
#!/bin/bash
#定义函数名fun
fun () {
#初值为1
fac=1
#使用阶乘循环
for((i=1;i<=$1;i++))
do
#阶乘公式
fac=$[$fac*$i]
done
echo "$1阶乘的结果为:$fac"
}
fun $1 //传参
fun $2
fun $3
[root@nfs test]# bash fac.sh 10 11 12
10阶乘的结果为:3628800
11阶乘的结果为:39916800
12阶乘的结果为:479001600
[root@nfs test]# vim test23.sh
[root@nfs test]# bash test23.sh
输出加工后的数组
6 7 8
[root@nfs test]# cat test23.sh
#!/bin/bash
num=(1 2 3)
array () {
for i in $*
do
outarray[j++]=$[$i+5]
done
echo "输出加工后的数组"
echo ${outarray[*]}
}
result=`array ${num[*]}`
echo ${result[*]}






![[Python从零到壹] 六十一.图像识别及经典案例篇之基于纹理背景和聚类算法的图像分割](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dbe8e250f7004ee1b3b120ae0974280c.png#pic_center)