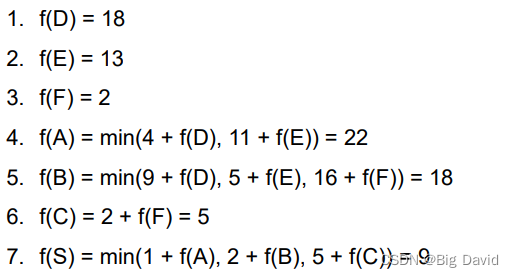本文将讲解BFS,Dijstra,A*,动态规划的算法原理,不正之处望读者指正,希望有兴趣的读者能在评论区提出一些这些算法的面试考点,共同学习,一起进步
0 图论基础
图有三种:无向图、有向图、带权重的图
无向图

有向图

带权重的图

1 BFS
广度优先搜索算法
利用队列queue数据结构实现:先进先出
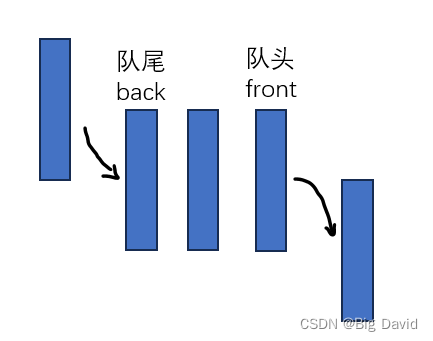
算法流程(伪代码):
BFS(G, start, goal):
let Q be queue;
Q.push(start);
mark start as visited;
while (!Q.empty())
{
v = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (v is the goal) return v;
for all neighbours n of v in G
Q.push(n);
n->parent = v;
mark n as visited;
}
BFS总结:
(1)相同探索所有的方向
(2)如果所有边权重为1,那么用BFS搜索出来的路径是cost最优的
(3)在不同的场景中,不能保证所有的边权重为1,对于这些场景,BFS受限
2 Dijstra
核心思想:
(1)相比BFS,Dijstra维护一个新变量g(n),g(n)表示从起始节点到当前节点的累积成本
(2)从openset(Min-priority queue)中访问累积成本g最低的节点
算法流程(伪代码):
Dijstra(G, start, goal):
let open_list be priority_queue;
open_list.push(start, 0);
g[start] = 0;
while (!open_list.empty())
{
current = open_list.pop();
mark current as visited;
if (current is the goal) return current;
for (all unvisited neightbours next of current in G)
{
next_cost = g[current] + cost(current, next);
if (next is not in open_list)
open_list.push(next, next_cost);
else {
if (g[next] > next_cost)
g[next] = next_cost;
}
}
}
优点:
(1)Dijstra算法能找到从起始节点到图上所有其他节点的最短路径
(2)Dijstra算法满足最优性
缺点:每次都会从open_list寻找代价最少的节点,但是并不知道终点在哪,如果用这个算法做图中特定两个点的最短路径,是比较低效的
3 A*算法
A*算法手撕版本见手撕A算法(详解A算法)
核心思想:
(1)相比Dijstra,A*将目标点的成本估计为启发式信息以提高效率
(2)启发式函数h(n):表示从节点n到目标的估计成本
(3)评估每个节点的成本函数:f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
(4)从open_list选择f-score最低的节点,而不是Dijstra算法中的g-score
算法流程(伪代码):
Astar(G, start, goal):
let open_list be priority_queue;
g[start] = 0;
f[start] = g[start] + h[start];
open_list.push(start, f[start]);
while (!open_list.empty())
{
current = open_list.pop();
mark current as visited;
if (current is the goal) return current;
for all unvisited neighbours next of current in G
next_cost = g[current] + cost(current, next);
if (next is not in open_list)
open_list.push(next, next_cost + h[next]);
else
{
if (g[next] > next_cost) {
g[next] = next_cost;
f[next] = next_cost + h[next];
}
}
}
启发式函数设计
在路径搜索过程中,没有唯一启发函数设计原则,需要根据特定的任务来设计,如果最优性和距离相关,则可以计算节点之间的直线距离来估计
三种常用的距离:
起点:
(
p
1
,
p
2
)
(p_1, p_2)
(p1,p2) 终点:
(
q
1
,
q
2
)
(q_1, q_2)
(q1,q2)
(1)Euclidian distance
d
(
p
,
q
)
=
(
q
1
−
p
1
)
2
+
(
q
2
−
p
2
)
2
d(p,q)=\sqrt{(q_1-p_1)^2+(q_2-p_2)^2}
d(p,q)=(q1−p1)2+(q2−p2)2
(2)Manhattan distance
d
(
p
,
q
)
=
∣
q
1
−
p
1
∣
+
∣
q
2
−
p
2
∣
d(p,q)=|q_1 - p_1|+|q_2 - p_2|
d(p,q)=∣q1−p1∣+∣q2−p2∣
(3)Great circle distance

△
σ
=
a
r
c
c
o
s
(
s
i
n
ϕ
1
s
i
n
ϕ
2
+
c
o
s
ϕ
1
c
o
s
ϕ
2
c
o
s
(
△
λ
)
)
\bigtriangleup \sigma =arccos(sin\phi _1sin\phi_2+cos\phi_1cos\phi_2cos(\bigtriangleup\lambda ))
△σ=arccos(sinϕ1sinϕ2+cosϕ1cosϕ2cos(△λ))
d = r △ σ d = r\bigtriangleup \sigma d=r△σ
最优性
启发式函数
h
(
n
)
<
c
o
s
t
(
n
,
g
o
a
l
)
h(n)<cost(n,goal)
h(n)<cost(n,goal)
只要启发式函数提供了小于实际成本的估计,A*将始终找到最优路径,并且通常比Dijstra快
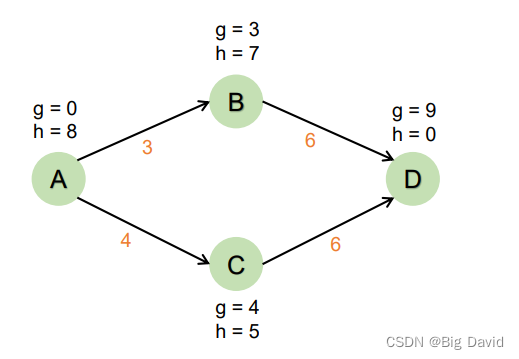
实际上A->B->D是最短路径
因为B的启发式函数高估了对目标的成本
这种高估导致搜索算法相信节点C总成本低于节点B,使得节点C在节点B之前访问,导致结果不是最优路径
在gridmap中如何设计启发式函数

使用8连接,曼哈顿距离启发式高估了成本
欧几里得距离总是可以接受
A*算法的精度和效率

(1) h ( n ) = 0 h(n)=0 h(n)=0:A退化为Dijstra
(2) h ( n ) < c o s t ( n , g o a l ) h(n)<cost(n,goal) h(n)<cost(n,goal):A满足最优性,效率比Dijstra更高
(3) h ( n ) = c o s t ( n , g o a l ) h(n)=cost(n,goal) h(n)=cost(n,goal):A满足最优性,并且有最高的效率
(4) h ( n ) > c o s t ( n , g o a l ) h(n)>cost(n,goal) h(n)>cost(n,goal):A不满足最优性,高估实际成本
BFS、Dijstra、A*总结:
| BFS | Dijstra | A* |
|---|---|---|
| (1)BFS算法会朝着周围等价扩展 | (1)相比BFS,Dijstra倾向于累积成本最小化,不是平等地搜索所有可能的路径,能在加权图中满足最优性 | (1)A*是Dijstra的修改,添加了启发式函数h(n)提高搜索效率 |
| (2)如果每条边权重为1,BFS搜索出来的path也是最优解 | (2)如果每条边权重为1,BFS=Dijstra | (3)启发式函数的设计会影响效率和准确性 |
搜索算法可视化参考:http://qiao.github.io/PathFinding.js/visual/
4 动态规划
- 定义:
一种计算机编程方式,首先把算法问题分解为子问题,求解这些子问题,并把这些结果保存下来,然后优化子问题找到整个问题的最优解
- 动态规划的性质:
(1)最优子结构
面对一个大问题可以分解为一系列子问题。如果能找到每个小问题的最优解,并且能够把小问题拼成大的问题。这种问题就叫最优子结构
(2)重复的子问题
动态规划不会重新计算重复的子问题,会事先保存结果
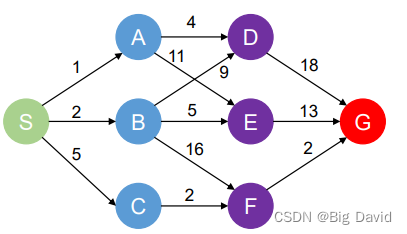
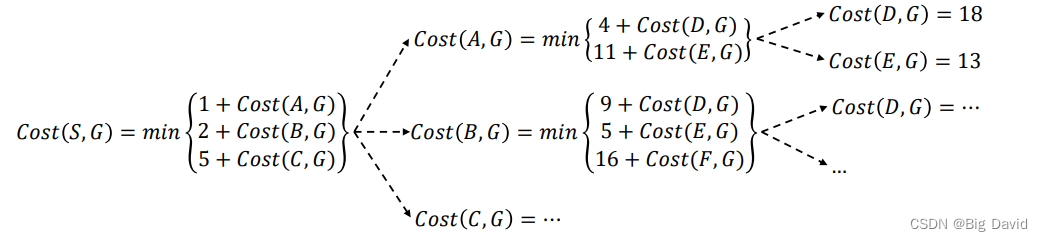
3. 计算方法
(1)前向法
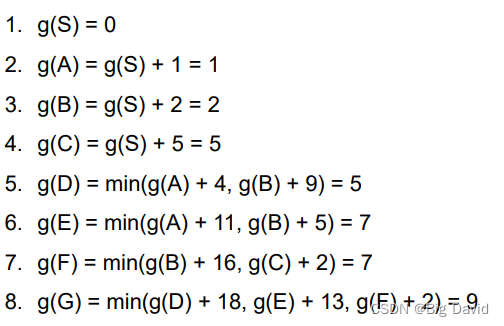
(2)逆向法