目录
一、导入
二、对象声明
三、对象属性
1.声明对象属性
2.信号属性
3.方法属性
4.附加属性略
5.枚举属性
6.对象属性赋值
四、自定义对象
一、导入
- 模块导入
语法:import <ModuleIdentifier> [<Version.Number>] [as <Qualifier>]例:
import QtQuickimport QtQuick 2.10import QtQuick as Quick - 目录导入
语法:import "<DirectoryPath>" [as <Qualifier>]例:
import "../privateComponents" import "../textwidgets" as MyModule
二、对象声明
- 对象
对象声明由其对象类型的名称组成,后跟一组大括号。然后,所有属性和子对象都在这些大括号内声明。例:import QtQuick 2.0 Rectangle { width: 100 height: 100 color: "red" } - 对象树中的子对象
任何对象声明都可以通过嵌套对象声明定义子对象。这样,任何对象声明都会隐式声明可能包含任意数量的子对象的对象树。例:import QtQuick 2.0 Rectangle { width: 100 height: 100 gradient: Gradient { GradientStop { position: 0.0; color: "yellow" } GradientStop { position: 1.0; color: "green" } } } - 视觉场景中的子对象
视觉场景中父子关系的概念由模块中的 Item 类型提供,这是大多数 QML 类型的基本类型,因为大多数 QML 对象都是要直观呈现的。例如,“矩形”和“文本”都是基于Item的类型import QtQuick 6.2 Rectangle { width: 200 height: 200 color: 'red' data: [ Text { anchors.centerIn: parent text: qsTr("Hello QML") } ] }简写形式
import QtQuick 6.2 Rectangle { width: 200 height: 200 color: 'red' Text { anchors.centerIn: parent text: qsTr("Hello QML") } } - 坐标
Qt Quick中使用的默认视觉坐标系统是项目坐标。这是一个笛卡尔坐标系,(0,0) 位于项目的左上角。x 轴向右增长,y 轴向下增长,因此项目的右下角位于坐标(宽度、高度)处。坐标数值是指在其父容器中的坐标。例:Rectangle { width: 200 height: 200 color: "red" Rectangle { x: 100 y: 100 width: 100 height: 100 color: "blue" Rectangle { width: 50 height: 50 color: "green" } } }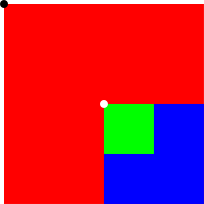
- 堆叠
Qt Quick 项目使用递归绘制算法来确定在发生碰撞时将哪些项目绘制在顶部。通常,项目按照创建顺序(或在 QML 文件中指定z属性:低于0的z值将堆叠在父级下方)绘制在其父项目之上。z值的越大,优先级越高,但仅限于同父级比较,如果父级优先级低于其他父级,即使子级z值极大,也不会比其他父级要高。 - 注释
单行注释以 // 开头,在行尾结束。
多行注释以 /* 开头,以 */ 结尾
例:Text { text: "Hello world!" //a basic greeting /* We want this text to stand out from the rest so we give it a large size and different font. */ font.family: "Helvetica" font.pointSize: 24 }
三、对象属性
1.声明对象属性
除枚举类型(用int代替)之外的任何 QML 值类型都可以用作自定义属性类型
语法:
[default] [required] [readonly] property <propertyType> <propertyName>例:
Item {
property int someNumber
property string someString
property url someUrl
property color previousColor
//var 值类型是一个通用占位符类型,可以保存任何类型的值,包括列表和对象
property var someNumber: 1.5
property Rectangle someRectangle
states: [
State { name: "loading" },
State { name: "running" },
State { name: "stopped" }
]
// 如果list只有一个项,则可以省略[]
states: State { name: "running" }
property list<Rectangle> siblingRects
property list<Rectangle> childRects: [
Rectangle { color: "red" },
Rectangle { color: "blue"}
]
}分组属性
Text {
//dot notation
font.pixelSize: 12
font.b: true
}
Text {
//group notation
font { pixelSize: 12; b: true }
}默认属性:使用default标注为默认属性,使用时可以不用声明key
// MyLabel.qml
import QtQuick 2.0
Text {
default property var someText
text: "Hello, " + someText.text
}使用时,而这效果相同
MyLabel {
Text { text: "world!" }
}
MyLabel {
someText: Text { text: "world!" }
}on 语法:
<PropertyModifierTypeName> on <propertyName> {
// attributes of the object instance
}目前有两种使用方式:
- 属性值写入侦听器
目前主要用于监听动画属性,例:import QtQuick 2.0 Item { width: 400 height: 50 Rectangle { width: 50 height: 50 color: "red" NumberAnimation on x { from: 0 to: 350 loops: Animation.Infinite duration: 2000 } } }
- 属性值源
2.信号属性
信号是来自对象的通知,指示发生了某些事件:例如,属性已更改、动画已启动或停止,或者图像已下载。例如,鼠标区域类型具有当用户在鼠标区域内单击时发出的单击信号。
每当发出特定信号时,都可以通过信号处理程序通知对象。信号处理程序使用语法 on<Signal 声明>其中 <Signal> 是信号的名称,第一个字母大写。信号处理程序必须在发出信号的对象的定义中声明,并且处理程序应包含调用信号处理程序时要执行的 JavaScript 代码块。
例如,下面的 onClicked 信号处理程序是在 MouseArea 对象定义中声明的,并在单击 MouseArea 时调用,从而导致打印控制台消息:
import QtQuick 2.0
Item {
width: 100; height: 100
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
console.log("Click!")
}
}
}语法:
signal <signalName>[([<parameterName>: <parameterType>[, ...]])]例:
import QtQuick 2.0
Item {
// 无参数可省略括号
signal clicked
signal hovered()
// 指定参数
signal actionPerformed(action: string, actionResult: int)
} 发出信号:
直接通过id调用信号即可
id.actionPerformed("something", 1)处理信号:
on<Signal>:fun即可
onDeactivated: console.log("Deactivated!")属性更改信号处理器:
on<Property>Changed例:
import QtQuick 2.0
TextInput {
text: "Change this!"
onTextChanged: console.log("Text has changed to:", text)
}
3.方法属性
语法:
function <functionName>([<parameterName>[: <parameterType>][, ...]]) [: <returnType>] { <body> }例1:
import QtQuick 2.0
Rectangle {
id: rect
function calculateHeight() : real {
return rect.width / 2;
}
width: 100
height: calculateHeight()
}例2:
import QtQuick 2.0
Item {
width: 200; height: 200
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: (mouse)=> label.moveTo(mouse.x, mouse.y)
}
Text {
id: label
function moveTo(newX: real, newY: real) {
label.x = newX;
label.y = newY;
}
text: "Move me!"
}
}4.附加属性
略
5.枚举属性
枚举提供一组固定的命名选项。它们可以使用关键字在 QML 中声明:enum
// MyText.qml
Text {
enum TextType {
Normal,
Heading
}
property int textType: MyText.TextType.Normal
font.bold: textType == MyText.TextType.Heading
font.pixelSize: textType == MyText.TextType.Heading ? 24 : 12
}6.对象属性赋值
- 初始化时的值赋值
<propertyName> : <value>import QtQuick 2.0 Rectangle { color: "red" property color nextColor: "blue" // combined property declaration and initialization } - 命令式值赋值
[<objectId>.]<propertyName> = valueimport QtQuick 2.0 Rectangle { id: rect Component.onCompleted: { rect.color = "red" } }
四、自定义对象
现在我们定义一个消息框对象:MessageLabel
新建QML文件:MessageLabel.qml
// MessageLabel.qml
import QtQuick
Rectangle {
height: 50
//声明消息内容:message
property string message: "debug message"
//声明消息类型:msgType(debug、warning、critical)
property string msgType: "debug"
Column {
anchors.fill: parent
Text {
text: msgType.toString().toUpperCase() + ":"
font.bold: msgType === "critical"
color: msgType === "warning" || msgType === "critical" ? "red" : "blue"
//动画
ColorAnimation on color {
running: msgType === "critical"
from: "red"
to: "black"
duration: 1000
loops: msgType === "critical" ? Animation.Infinite : 1
}
}
Text {
text: message
color: msgType === "warning" || msgType === "critical" ? "red" : "blue"
}
}
}
使用:
// application.qml
import QtQuick
Column {
width: 180
height: 180
padding: 1.5
topPadding: 10.0
bottomPadding: 10.0
spacing: 5
MessageLabel{
width: parent.width - 2
msgType: "debug"
}
MessageLabel {
width: parent.width - 2
message: "This is a warning!"
msgType: "warning"
}
MessageLabel {
width: parent.width - 2
message: "A critical warning!"
msgType: "critical"
}
}
![[操作系统]进程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ec1451ae832140d9baff0dfb6b373485.png)