1.容器接口
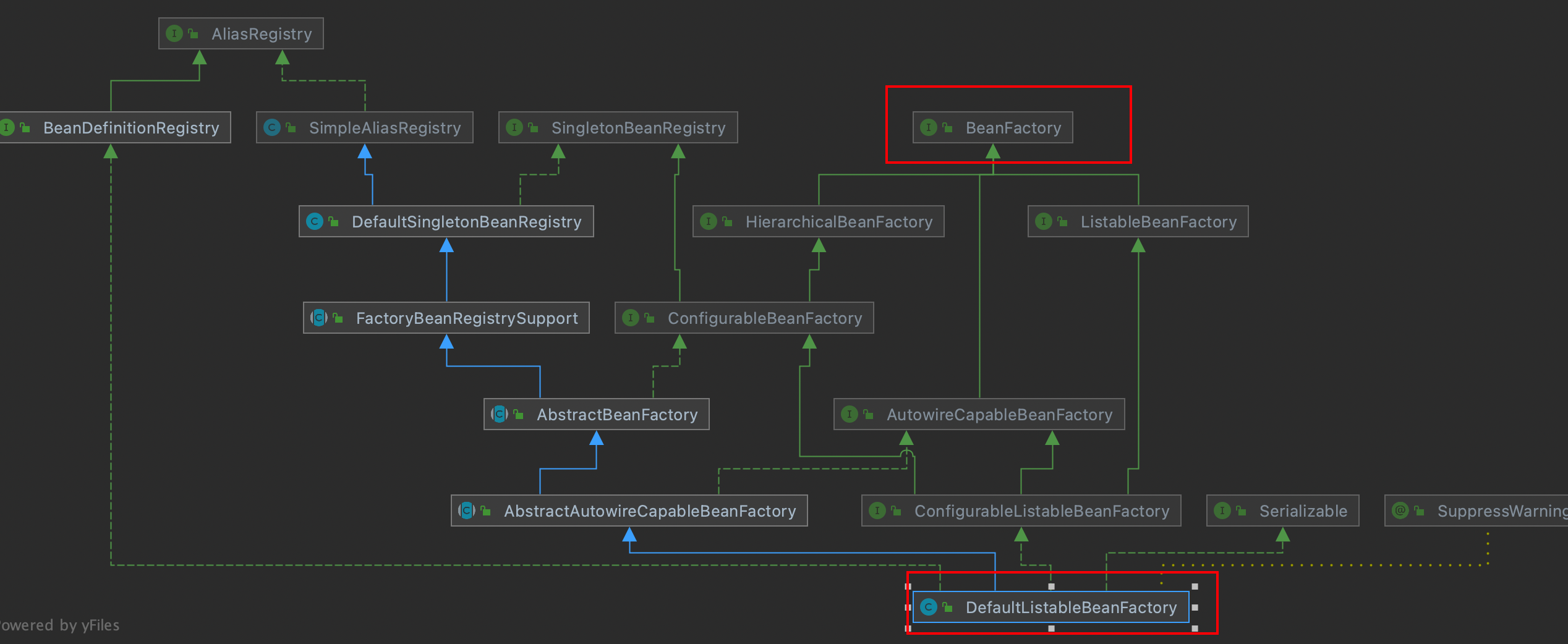
1.BeanFactory能做哪些事
1.什么是beanFactory
-
它是spring的核心容器
-
是ApplicationContext的父接口
-
ApplicationContext扩展实现都【组合了】beanFactory
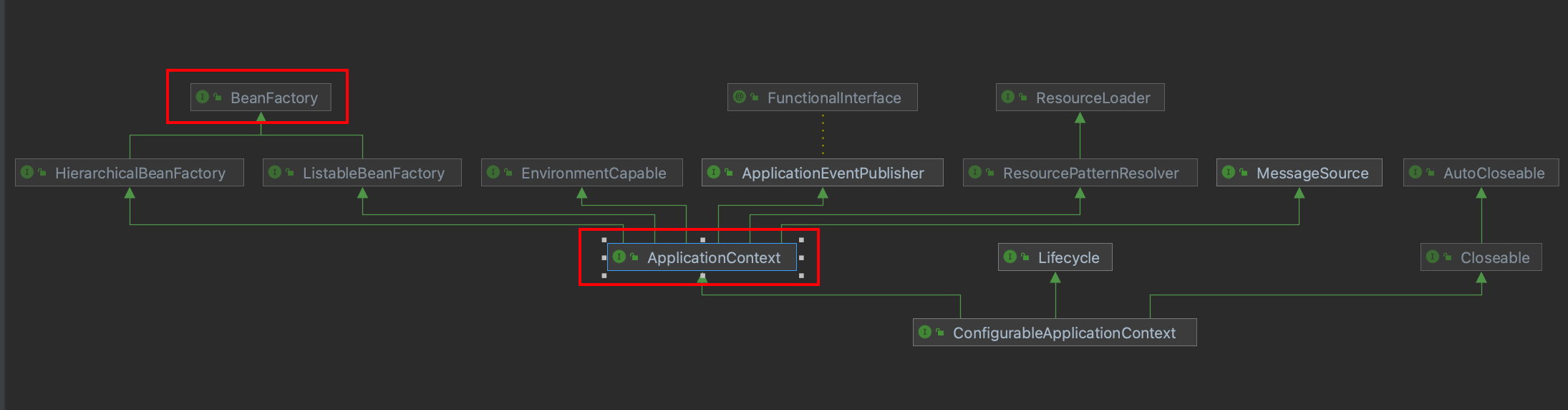
2.BeanFactory的功能
- 明面上只有getBean()方法
- 实际上控制反转、依赖注入、bean生命周期的各种功能都是由它的实现类提供
-
演示一下通过子实现类获取单例bean
// BeanFactory的子实现类 获取所有单例bean对象 Field field = DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.class.getDeclaredField("singletonObjects"); // 暴力反射 field.setAccessible(true); BeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = (Map<String, Object>) field.get(beanFactory); singletonObjects.entrySet().stream().filter(entry -> entry.getKey().startsWith("comentDemo")) .forEach(entry -> System.out.println("key="+entry.getKey()+"-value="+entry.getValue()));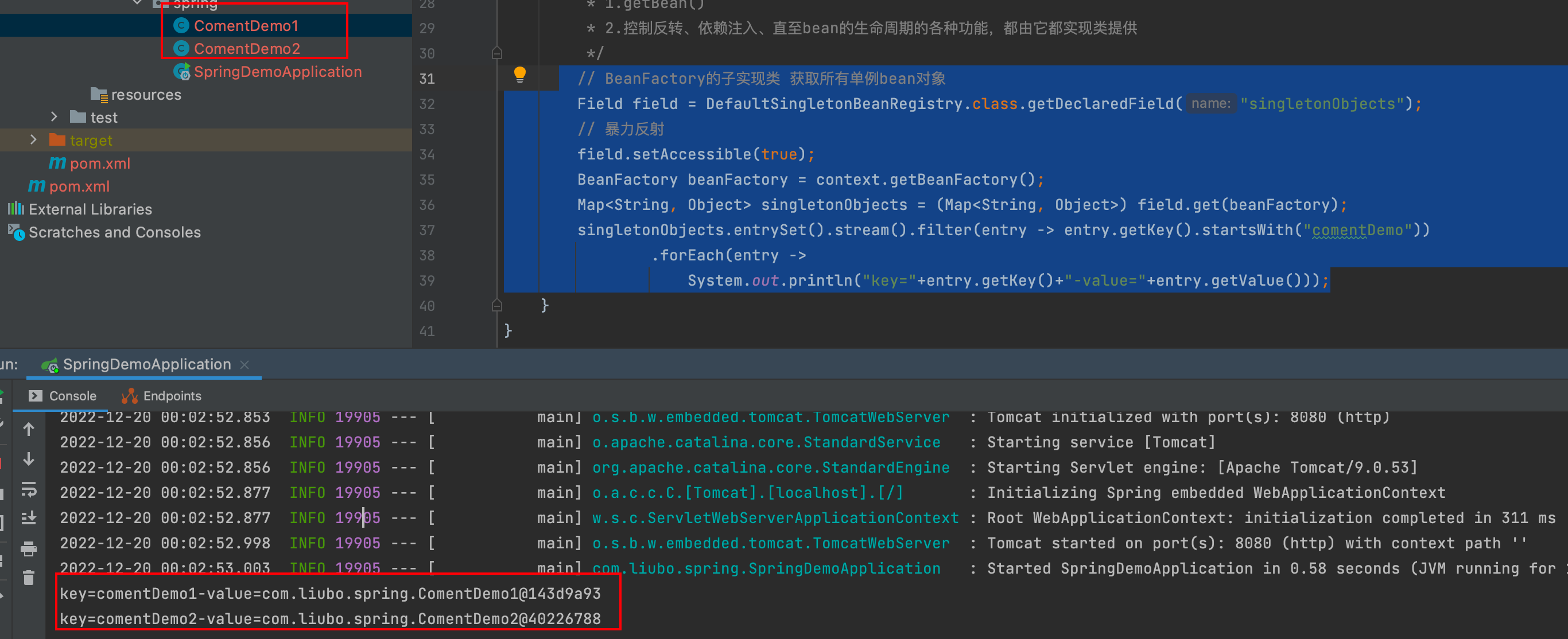
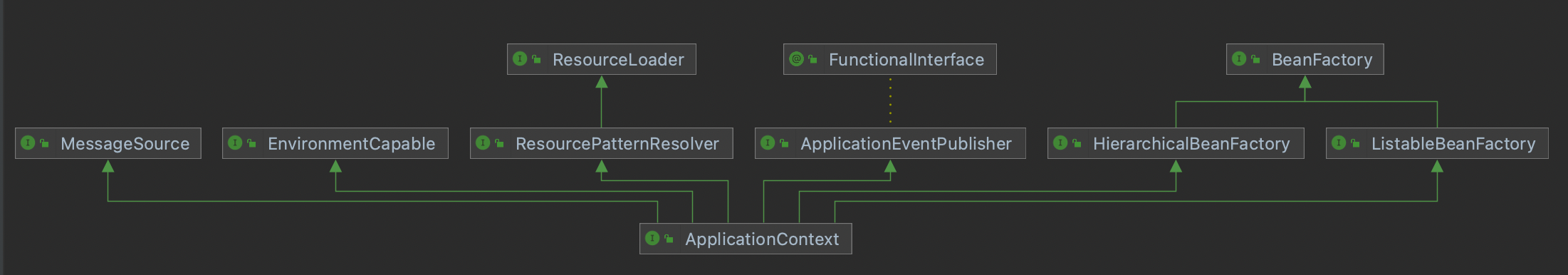
2.ApplicationContext有哪些扩展功能
-
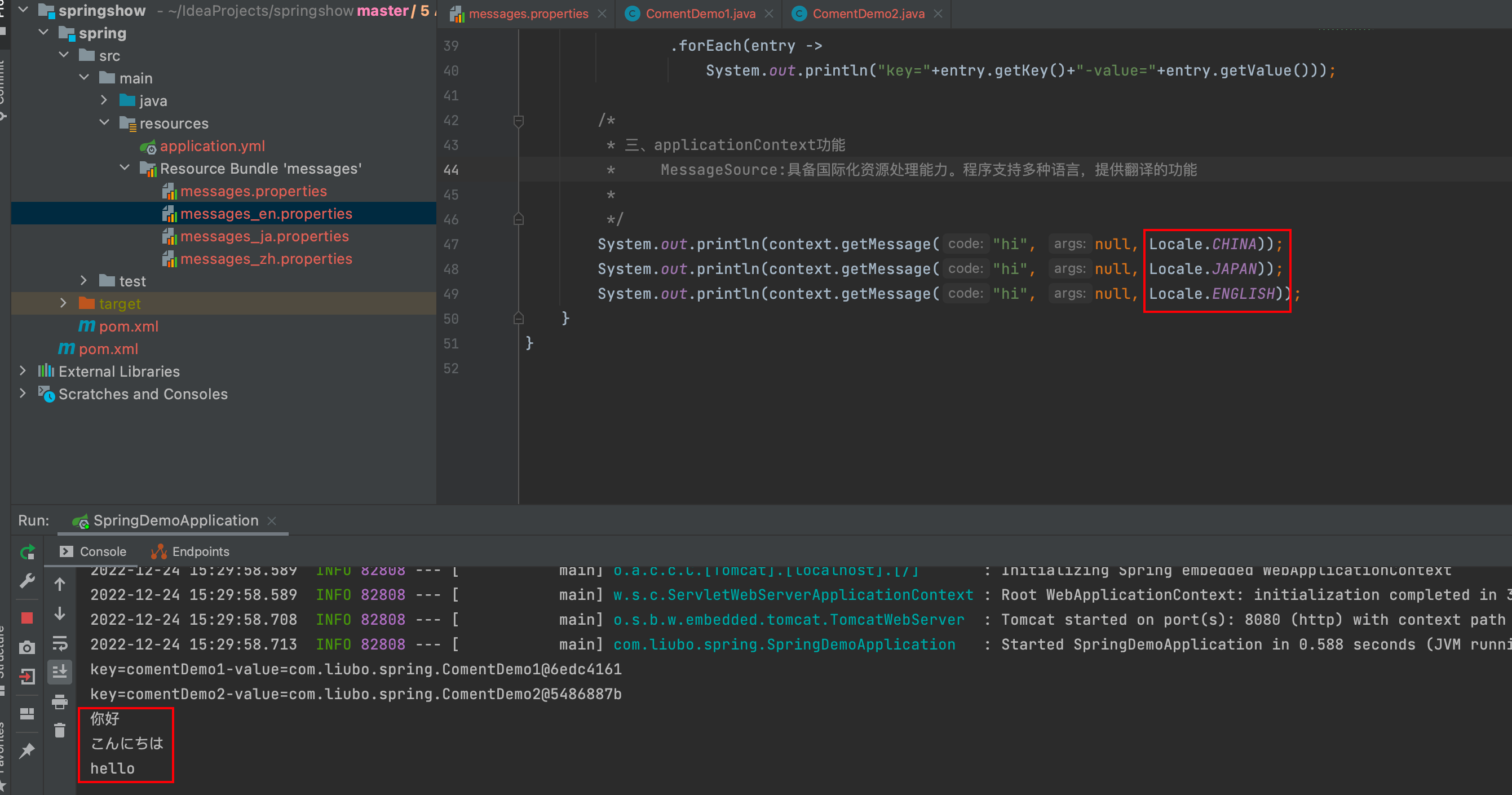
MessageSource:资源国际化功能(具备处理国际化资源的能力,程序支持多种语言,提供一种翻译的能力)
-
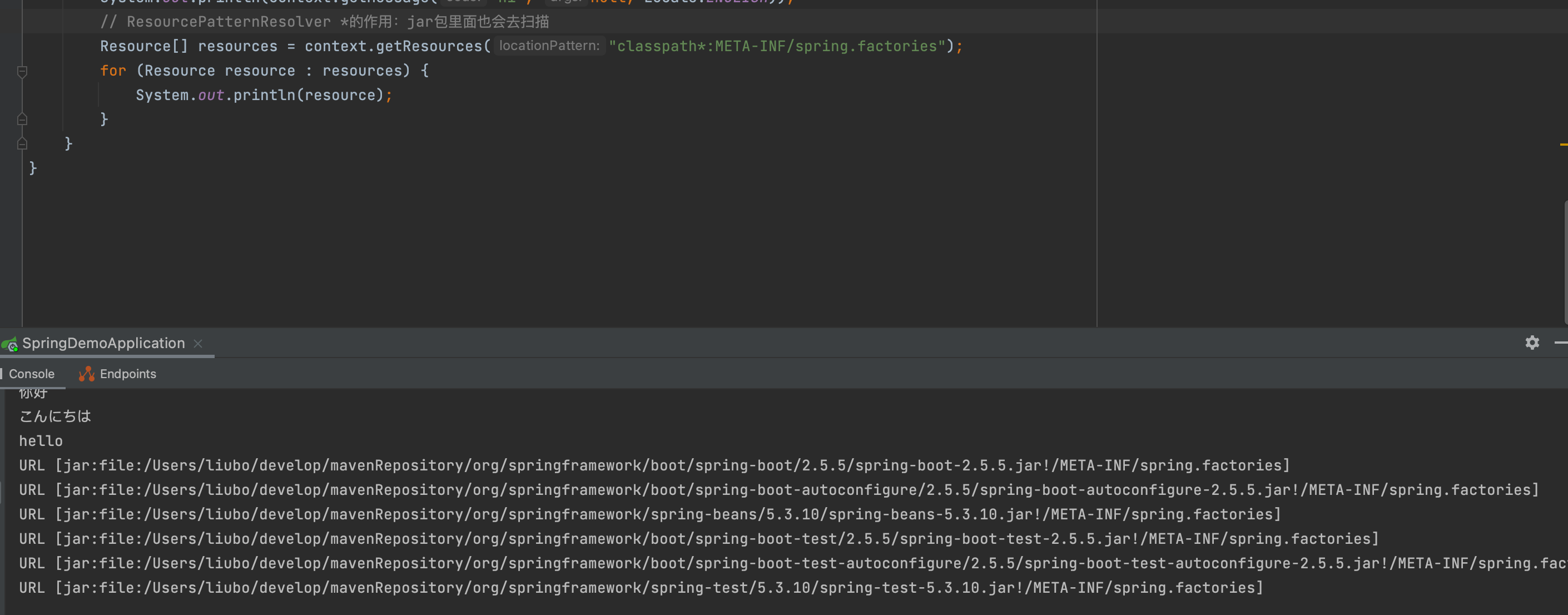
ResourcePatternResolver:根据通配符匹配资源(类路径、磁盘路径)的能力
-
EnvironmentCapable:获取系统变量和配置变量
System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("server.port")); -
ApplicationEventPublisher:发布事件
context.publishEvent(new ComentDemo1()); @EventListener public void comentDemo(Object event){ System.out.println("监听到事件"+event); }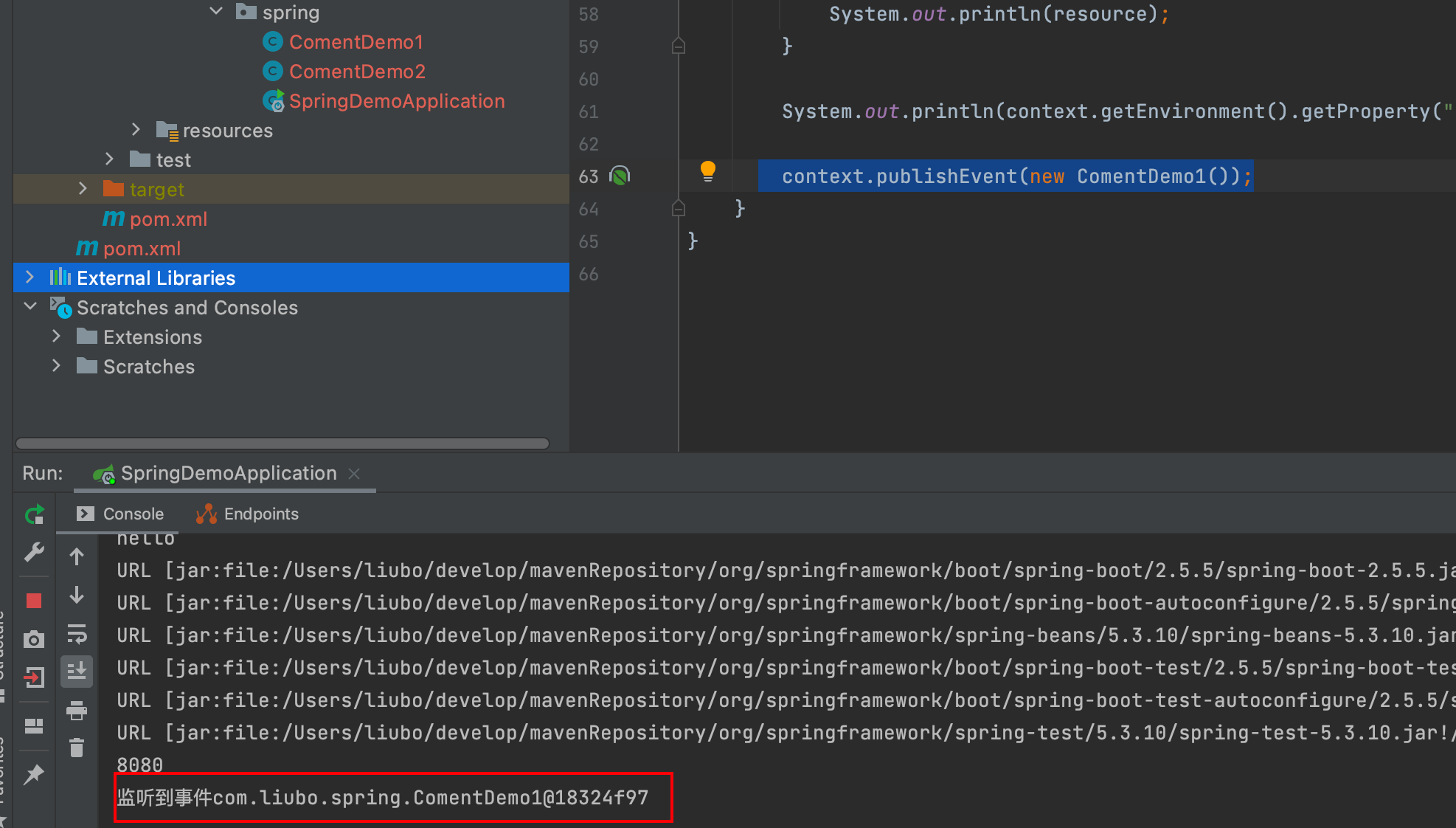
2.容器实现
1.BeanFactory实现
public class TestBeanFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// bean的定义
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition =
BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Config.class).setScope("singleton").getBeanDefinition();
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("config", beanDefinition);
// beanFactory添加后置处理器 (无法获取bean1,bean2 所以需要添加后置处理器处理解析@Configuration和@Bean)
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory);
// 执行处理器,就能对beanFactory做出扩展
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanFactoryPostProcessor ->
beanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory));
// bean后置处理器 针对bean的生命周期的各个阶段提供扩展,例如@Autowired@Resource
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class).values().stream()
.sorted(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator()) // 比较器
.forEach(beanFactory::addBeanPostProcessor);
// 打印bean1、bean2
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); // 准备好所有的单例
// System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean(Bean1.class).getBean2());
System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean(Bean1.class).getInter());
}
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2() {
return new Bean2();
}
@Bean
public Bean3 bean3() {
return new Bean3();
}
@Bean
public Bean4 bean4() {
return new Bean4();
}
}
interface Inter{}
static class Bean3 implements Inter{}
static class Bean4 implements Inter{}
static class Bean1 {
public Bean1() {
System.out.println("bean1 构造器");
}
@Autowired
private Bean2 bean2;
@Autowired
@Resource(name = "bean3") // 到底使用bean3还是bean4? 为什么是bean4呢? 因为Resource后处理器的优先级比Autowired低
private Inter bean4;
public Inter getInter() {
return bean4;
}
public Bean2 getBean2() {
return bean2;
}
}
static class Bean2 {
public Bean2() {
System.out.println("bean2 构造器");
}
}
}
2.ApplicationContext实现
public class TestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// testClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
// testFileSystemApplicationContext();
// testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
testAnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
/* classpath或者磁盘实现原理
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
System.out.println("读取之前");
for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader definitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
definitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("a02.xml"));
System.out.println("读取之后");
for (String name : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);*/
}
/**
* 基于classpath下的xml格式的配置文件来创建
*/
public static void testClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("a02.xml");
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
/**
* 基于磁盘路径下的xml格式的配置文件来创建
*/
public static void testFileSystemApplicationContext() {
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/main/resources/a02.xml");
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
/**
* 基于java配置类来创建
*/
public static void testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
/**
* 基于java配置类来创建,用于web环境
*/
public static void testAnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(WebConfig.class);
}
@Configuration
static class WebConfig{
// tomcatweb服务器
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory(){
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
// dispatcherServlet
@Bean
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet(){
return new DispatcherServlet();
}
// DispatcherServlet注册到tomcat
@Bean
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistrationBean(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet){
return new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,"/");
}
@Bean("/hello")
public Controller controller(){
return (request, response) ->{
response.getWriter().println("hello");
return null;
};
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1(){
return new Bean1();
}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2(Bean1 bean1){
Bean2 bean2 = new Bean2();
bean2.setBean1(bean1);
return bean2;
}
}
static class Bean1 {
}
static class Bean2 {
private Bean1 bean1;
public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1) {
this.bean1 = bean1;
}
public Bean1 getBean1() {
return bean1;
}
}
}





![[机器学习-概念新] 什么是欧式距离、标准化欧式距离、马氏距离、余弦距离](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200703235519658.png)