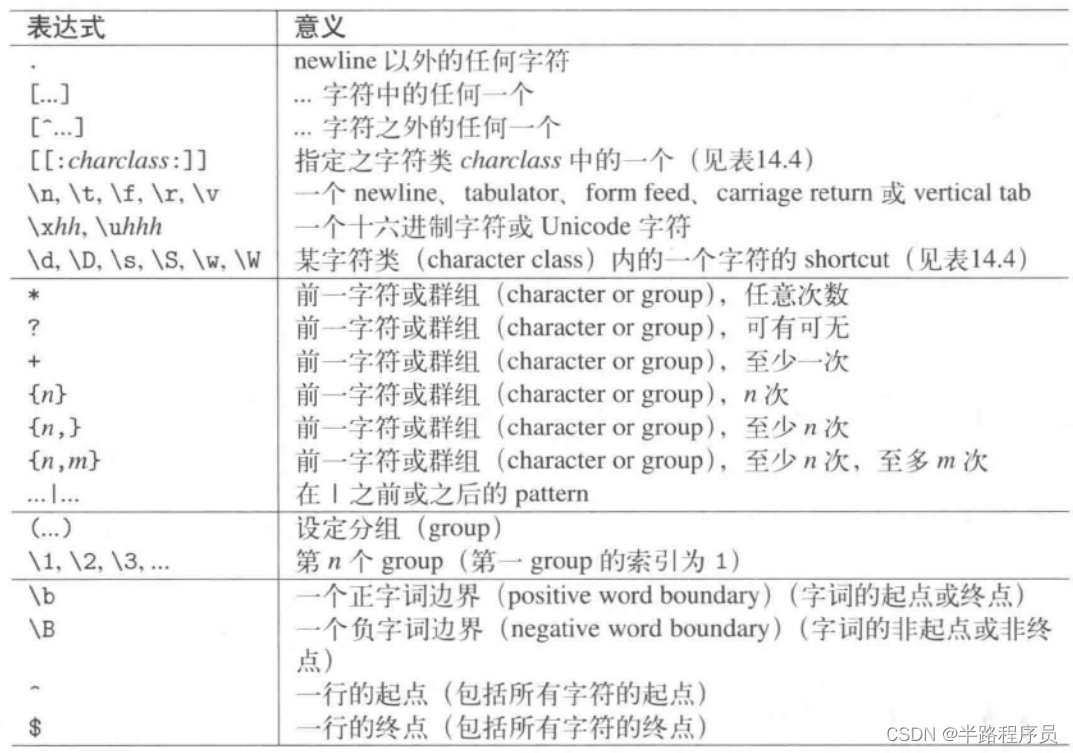
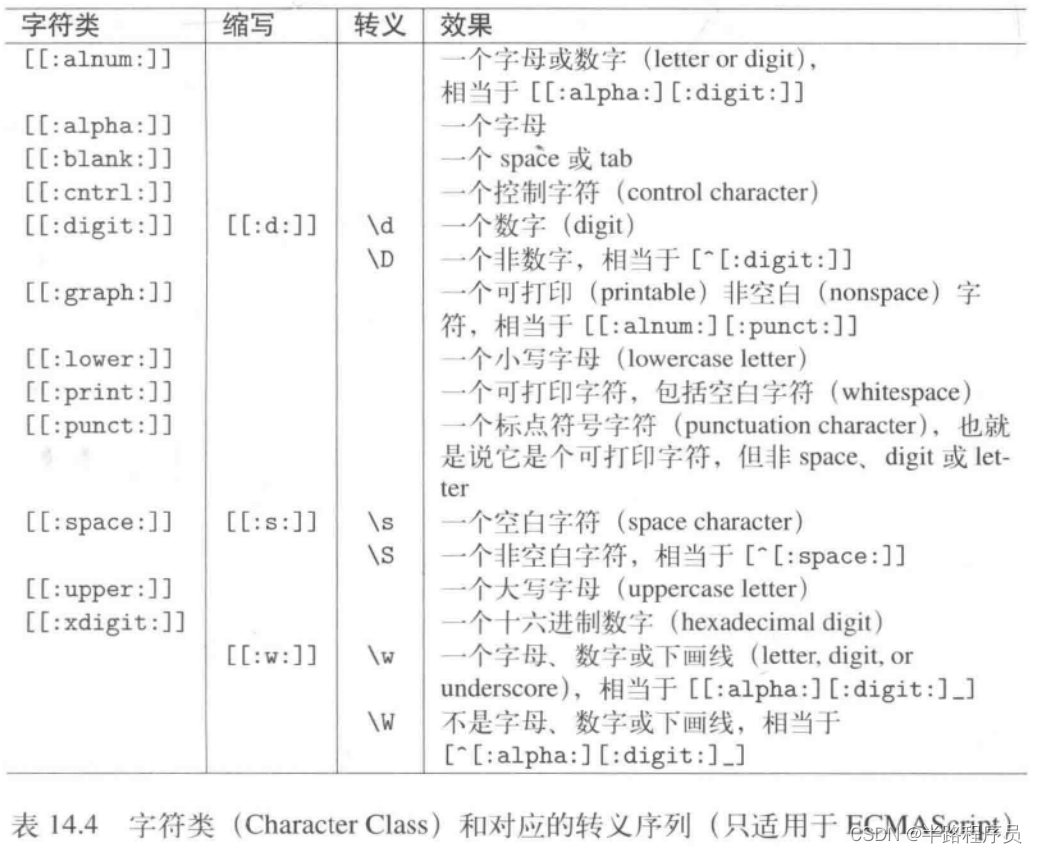
1、正则表达式
(1)regex的匹配和查找接口
#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void out (bool b)
{
cout << ( b ? "found" : "not found") << endl;
}
int main()
{
// find XML/HTML-tagged value (using default syntax):
regex reg1("<.*>.*</.*>");
bool found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", // data
reg1); // regular expression
out(found);
// find XML/HTML-tagged value (tags before and after the value must match):
regex reg2("<(.*)>.*</\\1>");
found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", // data
reg2); // regular expression
out(found);
// find XML/HTML-tagged value (using grep syntax):
regex reg3("<\\(.*\\)>.*</\\1>",regex_constants::grep);
found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", // data
reg3); // regular expression
out(found);
// use C-string as regular expression (needs explicit cast to regex):
found = regex_match ("<tag>value</tag>", // data
regex("<(.*)>.*</\\1>")); // regular expression
out(found);
cout << endl;
// regex_match() versus regex_search():
found = regex_match ("XML tag: <tag>value</tag>",
regex("<(.*)>.*</\\1>")); // fails to match
out(found);
found = regex_match ("XML tag: <tag>value</tag>",
regex(".*<(.*)>.*</\\1>.*")); // matches
out(found);
found = regex_search ("XML tag: <tag>value</tag>",
regex("<(.*)>.*</\\1>")); // matches
out(found);
found = regex_search ("XML tag: <tag>value</tag>",
regex(".*<(.*)>.*</\\1>.*")); // matches
out(found);
}
输出:
found
found
found
found
not found
found
found
foundregex_match()检验是否整个字符序列匹配某个正则表达式。
regex_search()检验是否部分字符序列匹配某个正则表达式。
regex_match(data, regex(pattern))
总是等价于
regex_search(data, regex("(.|\n)*" + pattern + "(.|\n)*")),其中(.|\n)*指任何数量和任意字符,.意指换行之外的任意字符,|表示or。
(2)处理次表达式
#include <string>
#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string data = "XML tag: <tag-name>the value</tag-name>.";
cout << "data: " << data << "\n\n";
smatch m; // for returned details of the match
bool found = regex_search (data,
m,
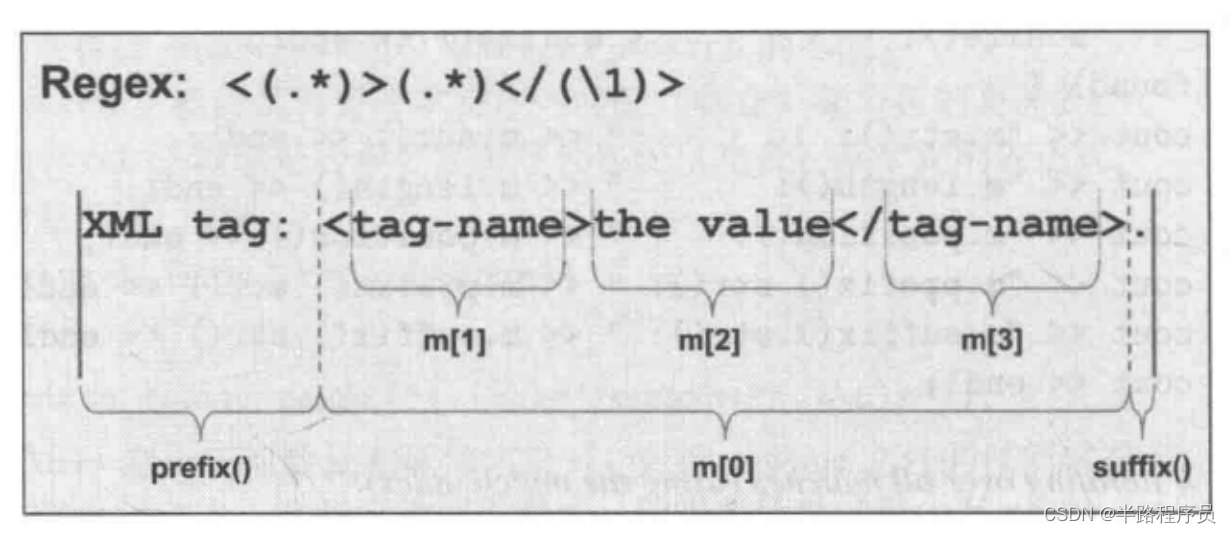
regex("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>")); //出现\1则是代表与第一个小括号中要匹配的内容相同。
// print match details:
cout << "m.empty(): " << boolalpha << m.empty() << endl;
cout << "m.size(): " << m.size() << endl;
if (found) {
cout << "m.str(): " << m.str() << endl;
cout << "m.length(): " << m.length() << endl;
cout << "m.position(): " << m.position() << endl;
cout << "m.prefix().str(): " << m.prefix().str() << endl;
cout << "m.suffix().str(): " << m.suffix().str() << endl;
cout << endl;
// iterating over all matches (using the match index):
for (int i=0; i<m.size(); ++i) {
cout << "m[" << i << "].str(): " << m[i].str() << endl;
cout << "m.str(" << i << "): " << m.str(i) << endl;
cout << "m.position(" << i << "): " << m.position(i)
<< endl;
}
cout << endl;
// iterating over all matches (using iterators):
cout << "matches:" << endl;
for (auto pos = m.begin(); pos != m.end(); ++pos) {
cout << " " << *pos << " ";
cout << "(length: " << pos->length() << ")" << endl;
}
}
}
输出:
data: XML tag: <tag-name>the value</tag-name>.
m.empty(): false
m.size(): 4
m.str(): <tag-name>the value</tag-name>
m.length(): 30
m.position(): 9
m.prefix().str(): XML tag:
m.suffix().str(): .
m[0].str(): <tag-name>the value</tag-name>
m.str(0): <tag-name>the value</tag-name>
m.position(0): 9
m[1].str(): tag-name
m.str(1): tag-name
m.position(1): 10
m[2].str(): the value
m.str(2): the value
m.position(2): 19
m[3].str(): tag-name
m.str(3): tag-name
m.position(3): 30
matches:
<tag-name>the value</tag-name> (length: 30)
tag-name (length: 8)
the value (length: 9)
tag-name (length: 8)smatch:针对“匹配string”而设计
cmatch:针对“匹配C-string(const char*)”而设计
wsmatch:针对“匹配wstring”而设计
wcmatch:针对“匹配wide C-string(const wchar_t*)”而设计
出现\1则是代表与第一个小括号中要匹配的内容相同。注意:\1必须与小括号配合使用
(3)regex iterator
#include <string>
#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string data = "<person>\n"
" <first>Nico</first>\n"
" <last>Josuttis</last>\n"
"</person>\n";
regex reg("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>");
// iterate over all matches (using a regex_iterator):
sregex_iterator pos(data.cbegin(),data.cend(),reg);
sregex_iterator end;
for ( ; pos!=end ; ++pos ) {
cout << "match: " << pos->str() << endl;
cout << " tag: " << pos->str(1) << endl;
cout << " value: " << pos->str(2) << endl;
}
// use a regex_iterator to process each matched substring as element in an algorithm:
sregex_iterator beg(data.cbegin(),data.cend(),reg);
for_each (beg,end,[](const smatch& m) {
cout << "match: " << m.str() << endl;
cout << " tag: " << m.str(1) << endl;
cout << " value: " << m.str(2) << endl;
});
}
输出:
match: <first>Nico</first>
tag: first
value: Nico
match: <last>Josuttis</last>
tag: last
value: Josuttis
match: <first>Nico</first>
tag: first
value: Nico
match: <last>Josuttis</last>
tag: last
value: Josuttis(4)regex token iterator
#include <string>
#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string data = "<person>\n"
" <first>Nico</first>\n"
" <last>Josuttis</last>\n"
"</person>\n";
regex reg("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>");
// iterate over all matches (using a regex_token_iterator):
sregex_token_iterator pos(data.cbegin(),data.cend(), // sequence
reg, // token separator
{0,2}); // 0: full match, 2: second substring
sregex_token_iterator end;
for ( ; pos!=end ; ++pos ) {
cout << "match: " << pos->str() << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string names = "nico, jim, helmut, paul, tim, john paul, rita";
regex sep("[ \t\n]*[,;.][ \t\n]*"); // separated by , ; or . and spaces
sregex_token_iterator p(names.cbegin(),names.cend(), // sequence
sep, // separator
-1); // -1: values between separators
sregex_token_iterator e;
for ( ; p!=e ; ++p ) {
cout << "name: " << *p << endl;
}
}
输出:
match: <first>Nico</first>
match: Nico
match: <last>Josuttis</last>
match: Josuttis
name: nico
name: jim
name: helmut
name: paul
name: tim
name: john paul
name: rita(5)用于替换的正则表达式
#include <string>
#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string data = "<person>\n"
" <first>Nico</first>\n"
" <last>Josuttis</last>\n"
"</person>\n";
regex reg("<(.*)>(.*)</(\\1)>");
cout << regex_replace(data,
reg,
"<$1 value=\"$2\"/>") << endl; //replacement
cout << regex_replace(data,
reg,
"<\\1 value=\"\\2\"/>",
regex_constants::format_sed) << endl;
string res2;
regex_replace(back_inserter(res2),
data.begin(), data.end(),
reg,
"<$1 value=\"$2\"/>",
regex_constants::format_no_copy | regex_constants::format_first_only);
cout << res2 << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
<person>
<first value="Nico"/>
<last value="Josuttis"/>
</person>
<person>
<first value="Nico"/>
<last value="Josuttis"/>
</person>
<first value="Nico"/>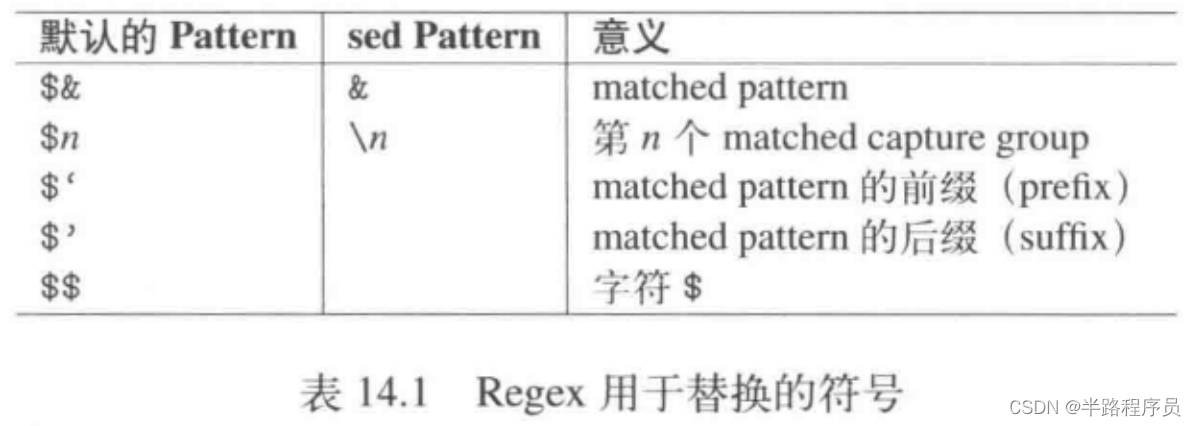
(6)regex flag
#include <string>
#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// case-insensitive find LaTeX index entries
string pat1 = R"(\\.*index\{([^}]*)\})"; // first capture group
string pat2 = R"(\\.*index\{(.*)\}\{(.*)\})"; // 2nd and 3rd capture group
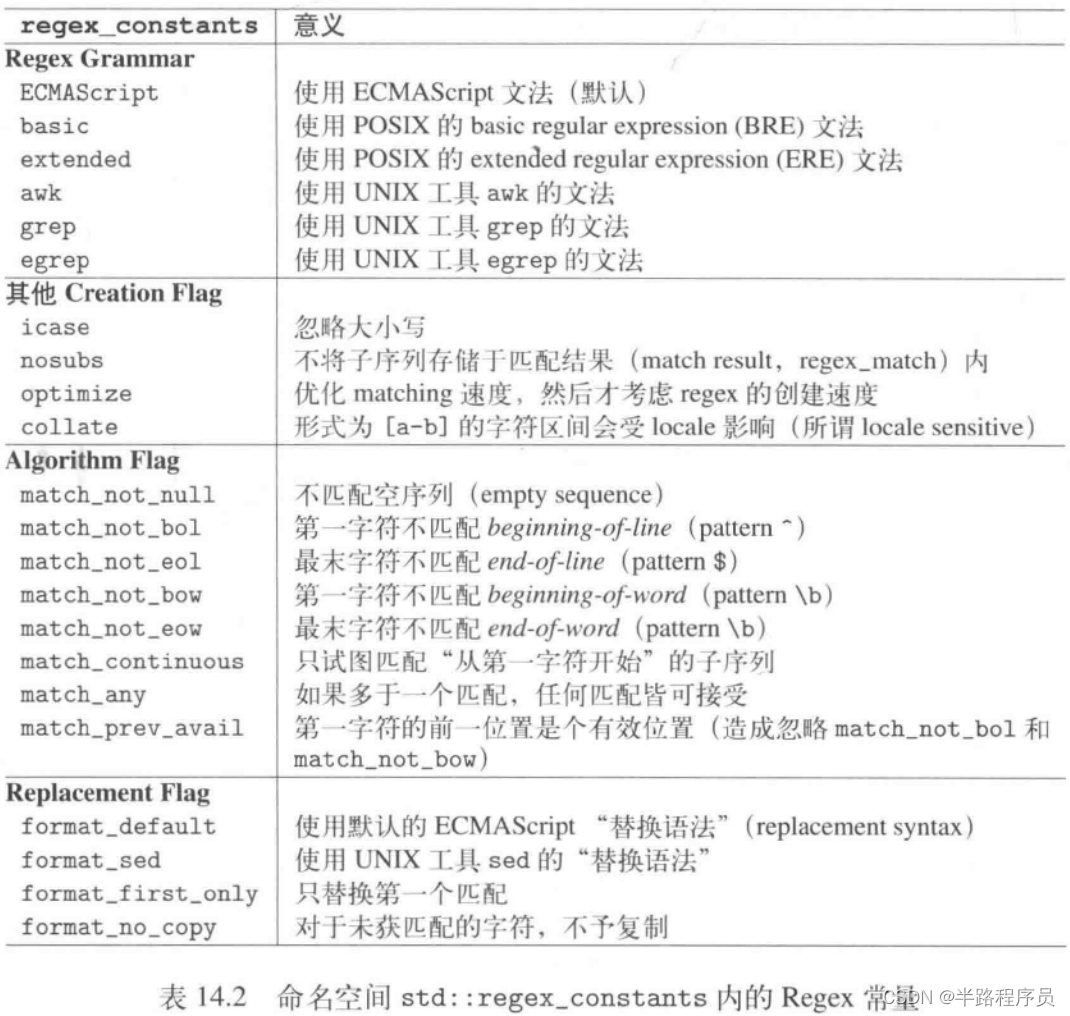
regex pat (pat1+"\n"+pat2,
regex_constants::egrep|regex_constants::icase);
// initialize string with characters from standard input:
string data((istreambuf_iterator<char>(cin)),
istreambuf_iterator<char>());
// search and print matching index entries:
smatch m;
auto pos = data.cbegin();
auto end = data.cend();
for ( ; regex_search (pos,end,m,pat); pos=m.suffix().first) {
cout << "match: " << m.str() << endl;
cout << " val: " << m.str(1)+m.str(2) << endl;
cout << " see: " << m.str(3) << endl;
}
}
(7)regex 异常
#include <regex>
#include <string>
template <typename T>
std::string regexCode (T code)
{
switch (code) {
case std::regex_constants::error_collate:
return "error_collate: "
"regex has invalid collating element name";
case std::regex_constants::error_ctype:
return "error_ctype: "
"regex has invalid character class name";
case std::regex_constants::error_escape:
return "error_escape: "
"regex has invalid escaped char. or trailing escape";
case std::regex_constants::error_backref:
return "error_backref: "
"regex has invalid back reference";
case std::regex_constants::error_brack:
return "error_brack: "
"regex has mismatched '[' and ']'";
case std::regex_constants::error_paren:
return "error_paren: "
"regex has mismatched '(' and ')'";
case std::regex_constants::error_brace:
return "error_brace: "
"regex has mismatched '{' and '}'";
case std::regex_constants::error_badbrace:
return "error_badbrace: "
"regex has invalid range in {} expression";
case std::regex_constants::error_range:
return "error_range: "
"regex has invalid character range, such as '[b-a]'";
case std::regex_constants::error_space:
return "error_space: "
"insufficient memory to convert regex into finite state";
case std::regex_constants::error_badrepeat:
return "error_badrepeat: "
"one of *?+{ not preceded by valid regex";
case std::regex_constants::error_complexity:
return "error_complexity: "
"complexity of match against regex over pre-set level";
case std::regex_constants::error_stack:
return "error_stack: "
"insufficient memory to determine regex match";
}
return "unknown/non-standard regex error code";
}#include <regex>
#include <iostream>
#include "regexexception.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
try {
// initialize regular expression with invalid syntax:
regex pat ("\\\\.*index\\{([^}]*)\\}",
regex_constants::grep|regex_constants::icase);
//...
}
catch (const regex_error& e) {
cerr << "regex_error: \n"
<< " what(): " << e.what() << "\n"
<< " code(): " << regexCode(e.code()) << endl;
}
}(8)regex ECMAScript文法