1、string字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
const string delims(" \t,.;");
string line;
// for every line read successfully
while (getline(cin,line)) {
string::size_type begIdx, endIdx;
// search beginning of the first word
begIdx = line.find_first_not_of(delims);
// while beginning of a word found
while (begIdx != string::npos) {
// search end of the actual word
endIdx = line.find_first_of (delims, begIdx);
if (endIdx == string::npos) {
// end of word is end of line
endIdx = line.length();
}
// print characters in reverse order
for (int i=endIdx-1; i>=static_cast<int>(begIdx); --i) {
cout << line[i];
}
cout << ' ';
// search beginning of the next word
begIdx = line.find_first_not_of (delims, endIdx);
}
cout << endl;
}
}
输入:ajsdk12345e.asfa \jkawefa
输出:e54321kdsja afsa afewakj\
(1)string各项操作

(2)构造函数和析构函数

data() 和 c_str()以字符数组的形式返回string内容,并且在该数组位置[size()]上有一个'\0'结束字符。copy()将string内容复制到调用者提供的字符数组中,其末尾不添加'\0'字符,注意,data()和c_str()返回的字符数组由该string拥有,也就是说,调用者不可以改动它或者释放其内存。
例如:
std::string s("12345");
atoi(s.c_str())
f(s.data, s.length())
char buffer[100];
s.copy(buffer, 100); //copy at most 100 characters os s into buffer
s.copy(buffer, 200, 2); //copy at most 100 characters of s into buffer
//starting with the third character of s一般而言,整个程序你应该坚持使用string,直到你必须将其内容转化为char*时,注意c_str()和data()的返回值的有效期在下一次调用non-const 成员函数时即告终止。
std::string s;
...
foo(s.c_str()); //s.c_str() is valid during the whole statement
const char* p;
p = s.c_str(); //p refers to the contents of s as a C-string
foo(p); //OK (p is still valid)
s += "ext"; //invalidates p
foo(p); //ERROR: argument p is not valid
(3)赋值操作
const std::string aString("othello");
std::string s;
s = aString;
s = "two\nlines";
a = ' ';
s.assign(aString);
s.assign(aString, 1, 3);
s.assign(aString, 2, std::string::npos);
s.assign("two\nlines");
s.assign("nico", 5);
s.assign(5, 'x');(4)安插和移除字符
const std::string aString("othello");
std::string s;
s += aString;
s += "two\nlines";
s += '\n';
s += {'o', 'k'};
s.append(aString);
s.append(aString, 1, 3); //append "the"
s.append(aString, 2, std::string::npos); // append "hello"
s.append("two\nlines");
s.append("nico", 5); //append character array 'n' 'i' 'c' '0' '\0'
s.append(5, 'x'); //append five characters 'x' 'x' 'x' 'x' 'x'
s.push_back('\n');
s.insert(1, aString);
//注意,成员函数insert()不接受索引+单字符的实参组合,必须传入一个string或者加上一个额外数字
s.insert(0, ' '); //ERROR
s.insert(0, " "); //OK
//你也可以这样尝试
s.insert(0, 1,' '); // ERROR : ambiguous
// 由于insert()具有以下重载形式,上一行会导致令人厌烦的歧义
insert(size_type idx, size_type num, charT c); //position is index
insert(iterator pos, size_type num, charT c); //position is iterator
string的size_type通常被定义为unsigned,string的iterator通常被定义为char*。
于是第一实参0有两种转换可能,不分优劣,为了获得正确的操作,必须使用如下:
s.insert((std::string::size_tpye)0, 1, ' '); //OKstd::string s = "i18n"; //s:i18n
s.replace(1, 2, "nternationalizatio"); //s:internationalization
s.erase(13); //s:international
s.erase(7, 5); //s:internal
s.pop_back(); //s:interna(since C++11)
s.replace(0, 2, "ex"); //s:externa(5)子字符串和字符串拼接
std::string s("interchangeability");
s.substr() //returns a copy of s
s.substr(11) //returns string("ability")
s.substr(5, 6); //returns string("change")
s.substr(s.find('c')); //returns string("changeability")(6)getline()
读取一行字符,包括前导空白字符,遇到换行或者end-of-file,分行符会被读取出来,但是不会添加到结果上,默认分行符是换行符号,也可以自定义任意符号作为分行符。
while(std::getline(std::cin,s)) {}
while(std::getline(std::cin, s, ':')){}如果自定义了分行符,则换行符就被当做普通字符。
(7)搜索查找
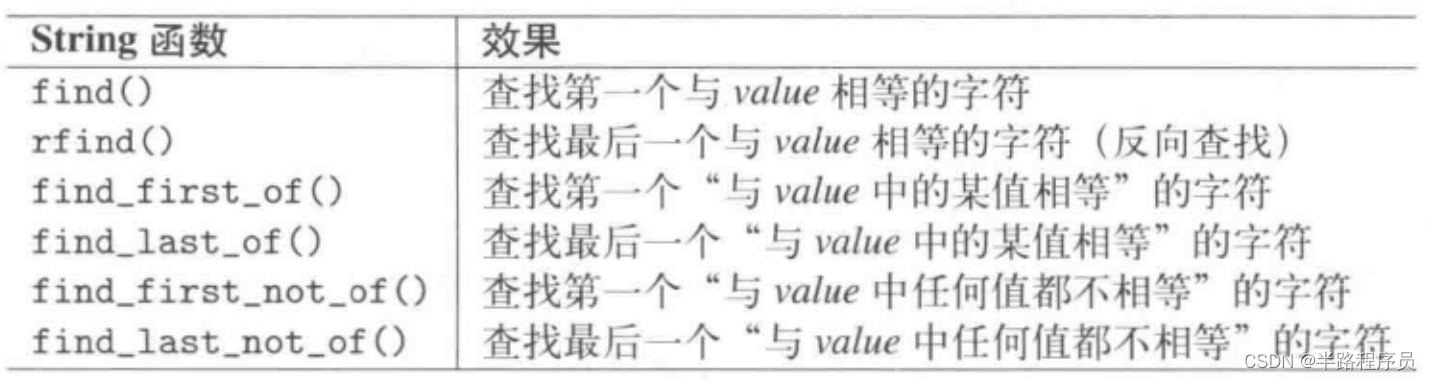
std::string s("Hi Bill, I'm ill, so please pay the bill");
s.find("il"); //returns 4
s.find("il", 10); //returns 13
s.rfind("il"); //returns 37
s.find_first_of("il"); //returns 1
s.find_last_of("il"); //returns 39
s.find_first_not_of("il"); //returns 0
s.find_last_not_of("il"); //returns 36
s.find("hi"); //returns npos(8)npos的意义
如果查找失败,会返回string::npos,使用string的npos值及其类型时要格外小心,若要检查函数返回值,一定要使用类型string::size_type,不能使用int或unsigned作为返回值类型,否则返回值与string::npos之间的比较可能无法正确执行,这是因为npos被设置为-1。
事实上(unsigned long)-1与(unsigned short)-1不同,因此对于下列表达式:
idx == std::string::npos,如果idx的值为-1,由于idx和string::npos类型不同,比较结果可能会是false。
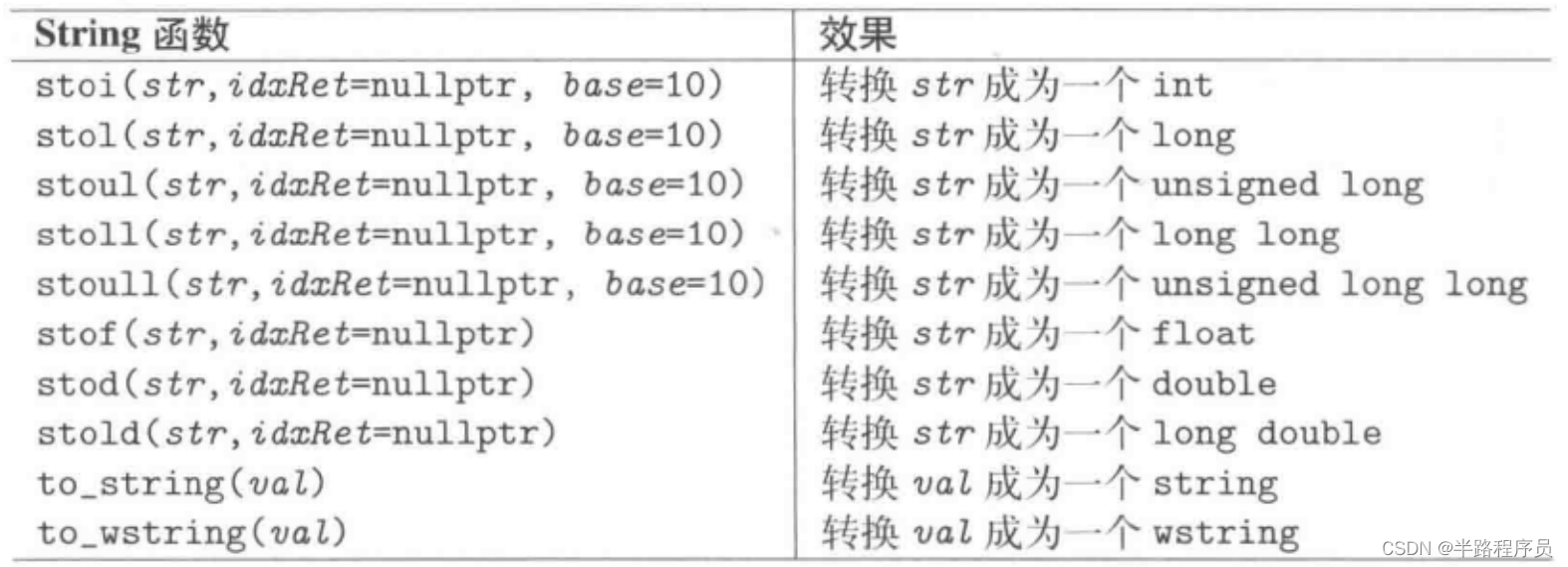
(9)数值转换
自C++11起,C++标准库提供了一些便捷函数,用来将string转换为数值或者反向转换,但是只适用于类型string或者wstring类型,不适用于u16string和u32string。
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <exception>
int main()
{
try {
// convert to numeric type
std::cout << std::stoi (" 77") << std::endl;
std::cout << std::stod (" 77.7") << std::endl;
std::cout << std::stoi ("-0x77") << std::endl;
// use index of characters not processed
std::size_t idx;
std::cout << std::stoi (" 42 is the truth", &idx) << std::endl;
std::cout << " idx of first unprocessed char: " << idx << std::endl;
// use bases 16 and 8
std::cout << std::stoi (" 42", nullptr, 16) << std::endl;
std::cout << std::stol ("789", &idx, 8) << std::endl;
std::cout << " idx of first unprocessed char: " << idx << std::endl;
// convert numeric value to string
long long ll = std::numeric_limits<long long>::max();
std::string s = std::to_string(ll); // converts maximum long long to string
std::cout << s << std::endl;
// try to convert back
std::cout << std::stoi(s) << std::endl; // throws out_of_range
}
catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
输出:
77
77.7
0
42
idx of first unprocessed char: 4
66
7
idx of first unprocessed char: 1
9223372036854775807
stoistd::stoi("-0x77")只会解析-0,std::stol("789", &idx, 8)只解析7,因为8在8进制中是一个无效字符。
(10)string iterator使用实例

#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <regex>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// create a string
string s("The zip code of Braunschweig in Germany is 38100");
cout << "original: " << s << endl;
// lowercase all characters
transform (s.cbegin(), s.cend(), // source
s.begin(), // destination
[] (char c) { // operation
return tolower(c);
});
cout << "lowered: " << s << endl;
// uppercase all characters
transform (s.cbegin(), s.cend(), // source
s.begin(), // destination
[] (char c) { // operation
return toupper(c);
});
cout << "uppered: " << s << endl;
// search case-insensitive for Germany
string g("Germany");
string::const_iterator pos;
pos = search (s.cbegin(),s.cend(), // source string in which to search
g.cbegin(),g.cend(), // substring to search
[] (char c1, char c2) { // comparison criterion
return toupper(c1) == toupper(c2);
});
if (pos != s.cend()) {
cout << "substring \"" << g << "\" found at index "
<< pos - s.cbegin() << endl;
}
}
输出:
original: The zip code of Braunschweig in Germany is 38100
lowered: the zip code of braunschweig in germany is 38100
uppered: THE ZIP CODE OF BRAUNSCHWEIG IN GERMANY IS 38100
substring "Germany" found at index 32
(11)为string打造trait class,允许以大小写无关的方式操作字符
#ifndef ICSTRING_HPP
#define ICSTRING_HPP
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
// replace functions of the standard char_traits<char>
// so that strings behave in a case-insensitive way
struct ignorecase_traits : public std::char_traits<char> {
// return whether c1 and c2 are equal
static bool eq(const char& c1, const char& c2) {
return std::toupper(c1)==std::toupper(c2);
}
// return whether c1 is less than c2
static bool lt(const char& c1, const char& c2) {
return std::toupper(c1)<std::toupper(c2);
}
// compare up to n characters of s1 and s2
static int compare(const char* s1, const char* s2,
std::size_t n) {
for (std::size_t i=0; i<n; ++i) {
if (!eq(s1[i],s2[i])) {
return lt(s1[i],s2[i])?-1:1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// search c in s
static const char* find(const char* s, std::size_t n,
const char& c) {
for (std::size_t i=0; i<n; ++i) {
if (eq(s[i],c)) {
return &(s[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
};
// define a special type for such strings
typedef std::basic_string<char,ignorecase_traits> icstring;
// define an output operator
// because the traits type is different from that for std::ostream
inline
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& strm, const icstring& s)
{
// simply convert the icstring into a normal string
return strm << std::string(s.data(),s.length());
}
#endif // ICSTRING_HPP#include "icstring.hpp"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
icstring s1("hallo");
icstring s2("otto");
icstring s3("hALLo");
cout << std::boolalpha;
cout << s1 << " == " << s2 << " : " << (s1==s2) << endl;
cout << s1 << " == " << s3 << " : " << (s1==s3) << endl;
icstring::size_type idx = s1.find("All");
if (idx != icstring::npos) {
cout << "index of \"All\" in \"" << s1 << "\": "
<< idx << endl;
}
else {
cout << "\"All\" not found in \"" << s1 << endl;
}
}
输出:
hallo == otto : false
hallo == hALLo : true
index of "All" in "hallo": 1





![力扣第2题-判断一个数值是否是回文数[简单]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/59ca728e9229c0ce33e329f14bba1f02.png)