文章目录
- 前言
- 一、准备好我们的后处理基础脚本
- 1、C#:
- 2、Shader:
- 二、开始逐语句对ShaderToy进行转化
- 1、首先,找到我们的主函数 mainImage
- 2、其余的方法全部都是在 mainImage 函数中调用的方法
- 3、替换后的代码(已经没报错了,但是效果不对)
- 三、我们来调试一下Shader,看看问题出在了哪?
- 1、return float4(col, 1.0);
- 2、black or fire
- 3、getDepth函数
- 四、修改 STEPS 的数值出错问题
- 法1:在属性面板增加 STEPS 参数,赋予初始值4
- 法2:使用#define 预定义一个常量
- 五、最终代码
前言
在上一篇文章中,我们讲解了基础的ShaderToy怎么转化为Unity中的Shader。我们在这篇文章中,复刻一个复杂的ShaderToy效果卡通火。
-
Unity中的ShaderToy
-
卡通火
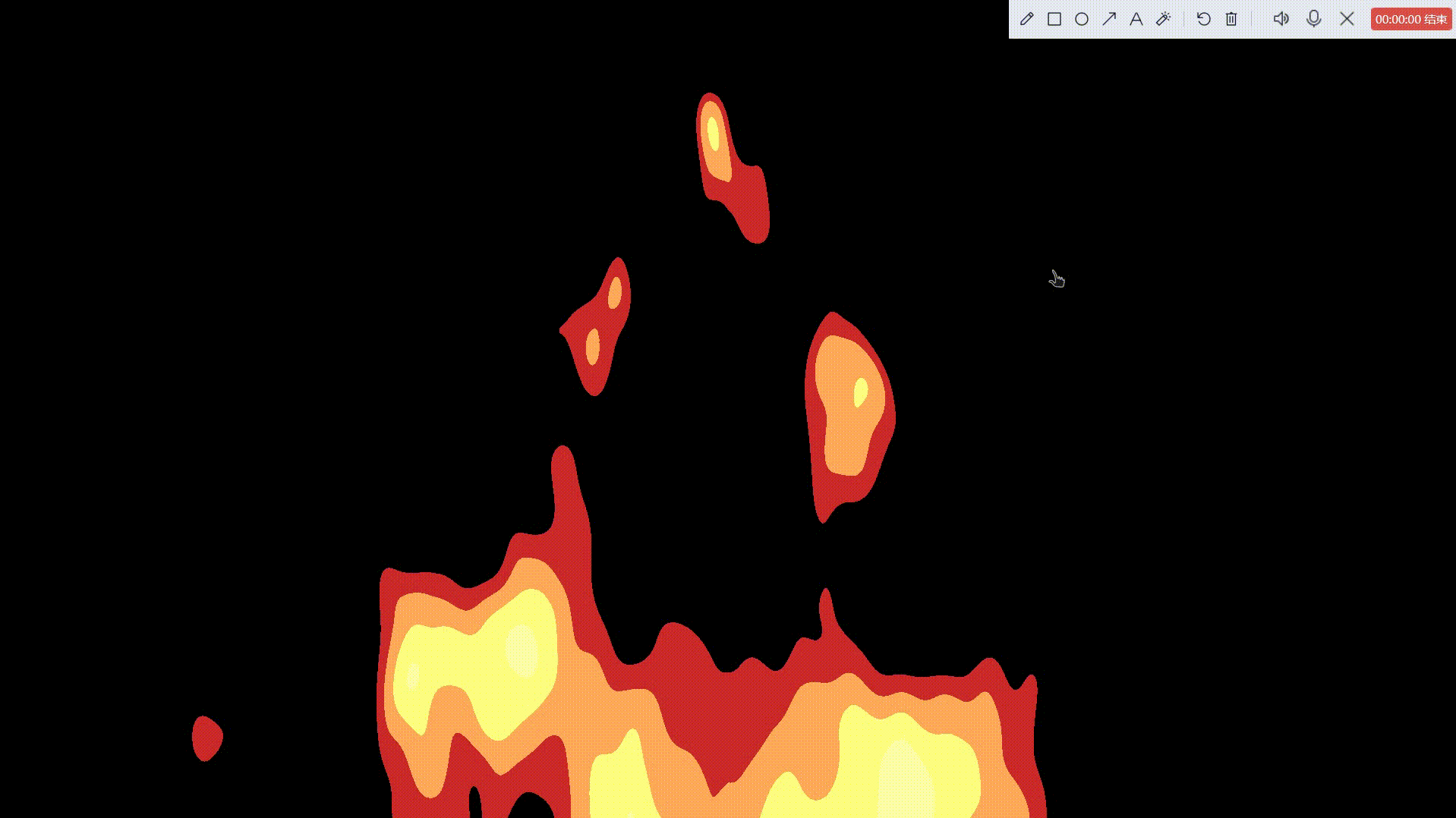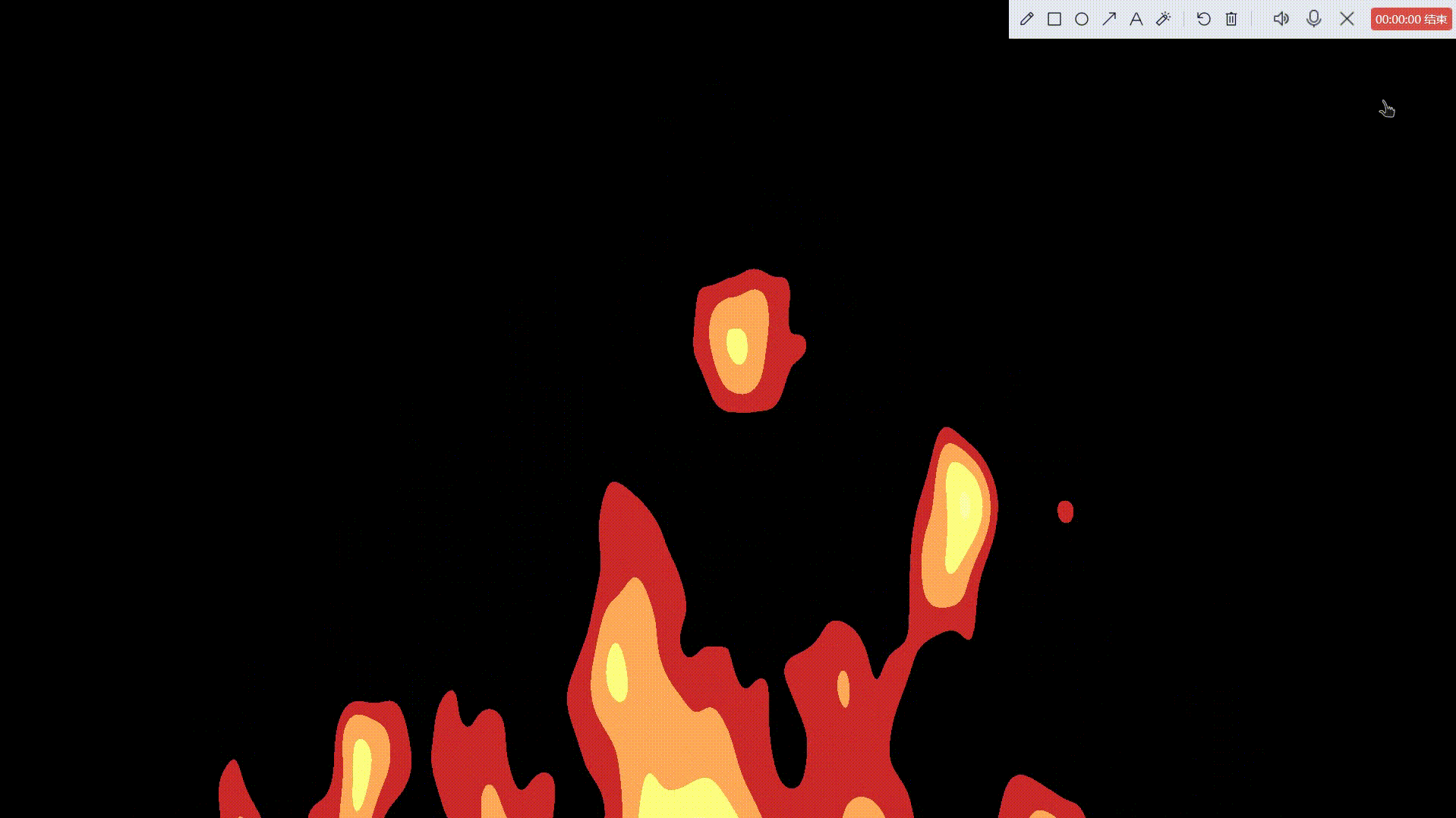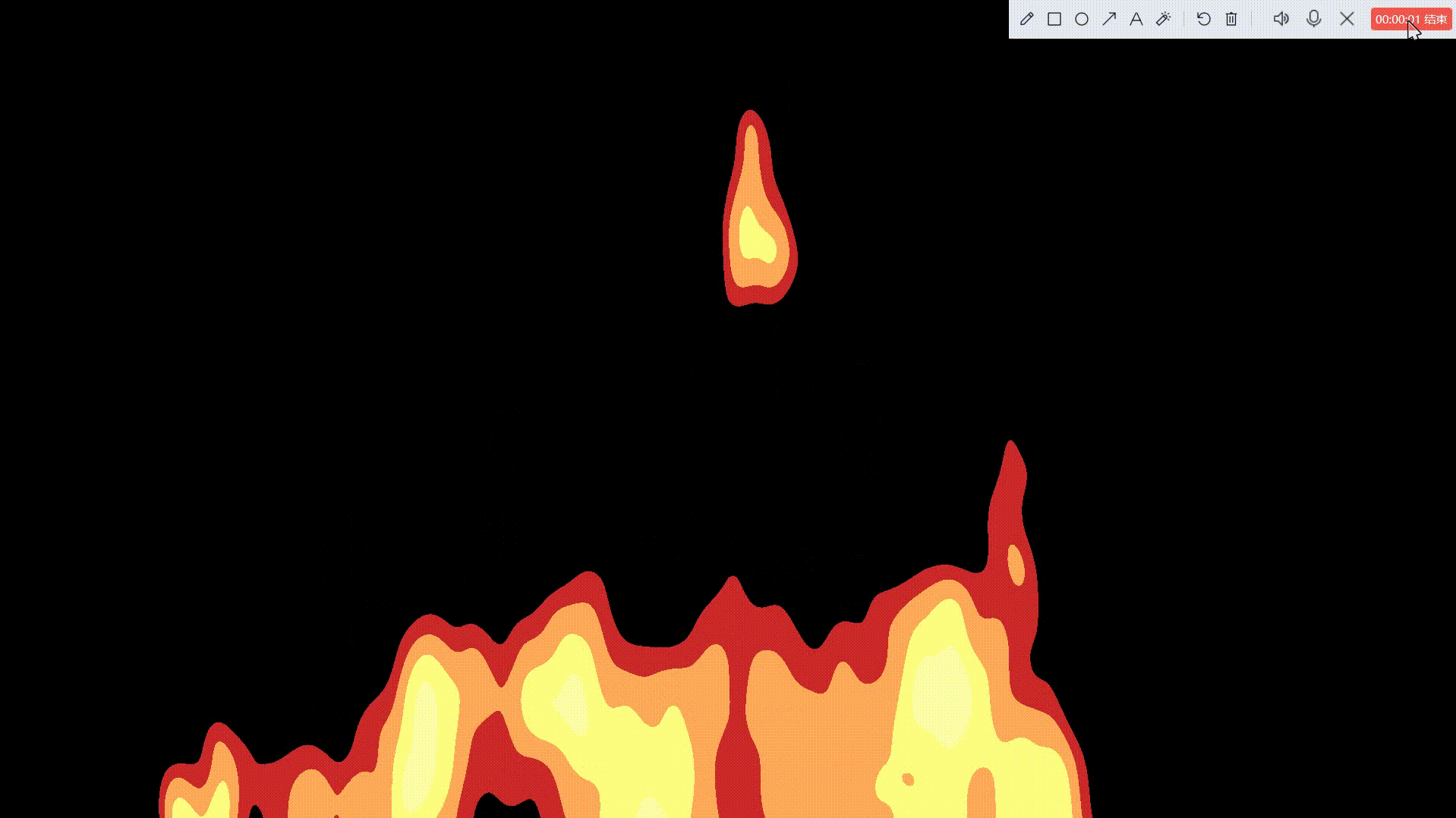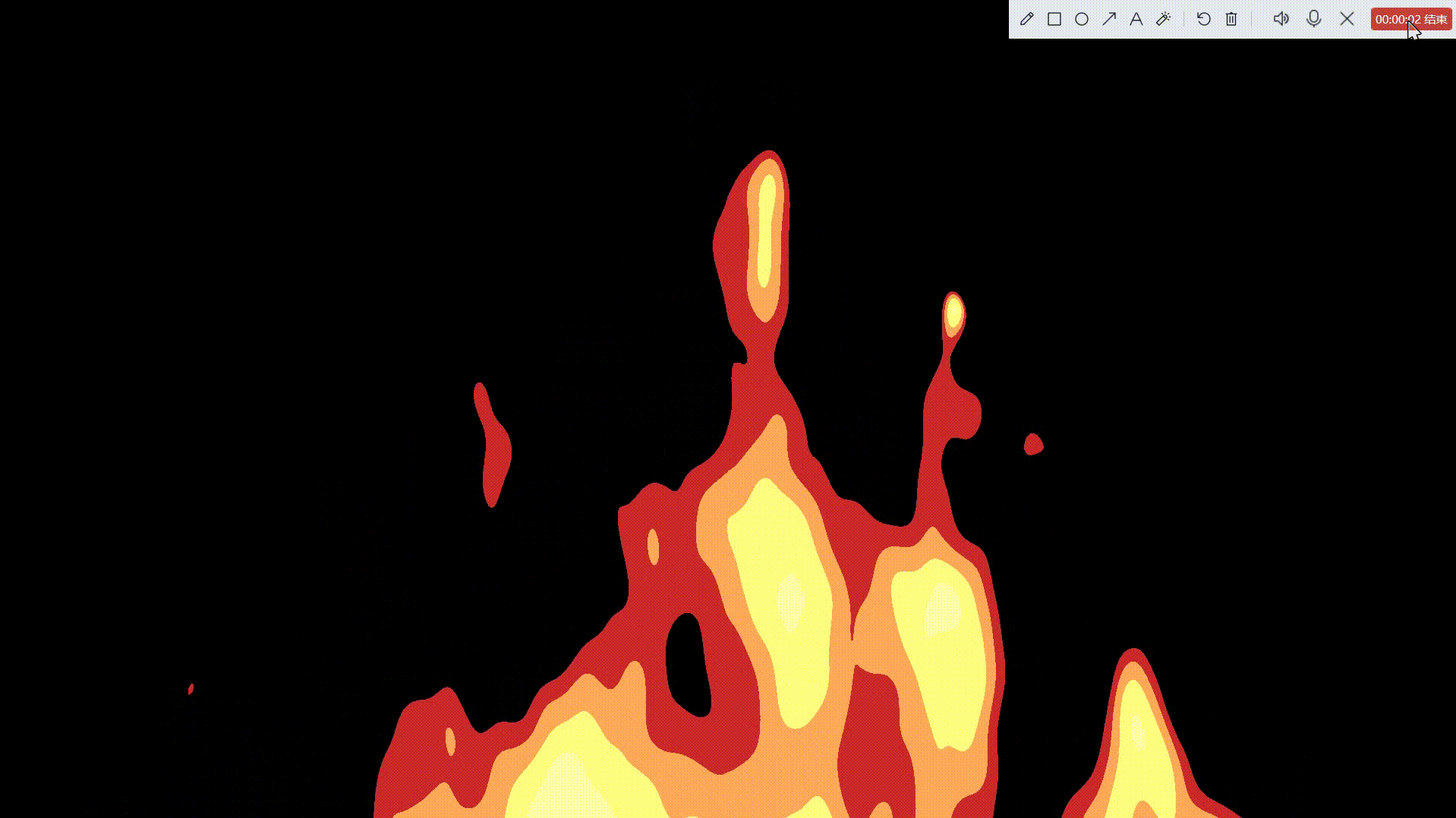
一、准备好我们的后处理基础脚本
1、C#:
using UnityEngine;
//后处理脚本
[ExecuteInEditMode]
public class P2_9 : MonoBehaviour
{
public Shader PostProcessingShader;
private Material mat;
public Material Mat
{
get
{
if (PostProcessingShader == null)
{
Debug.LogError("没有赋予Shader");
return null;
}
if (!PostProcessingShader.isSupported)
{
Debug.LogError("当前Shader不支持");
return null;
}
//如果材质没有创建,则根据Shader创建材质,并给成员变量赋值存储
if (mat == null)
{
Material _newMaterial = new Material(PostProcessingShader);
_newMaterial.hideFlags = HideFlags.HideAndDontSave;
mat = _newMaterial;
return _newMaterial;
}
return mat;
}
}
private void OnRenderImage(RenderTexture source, RenderTexture destination)
{
Graphics.Blit(source,destination,Mat);
}
}
2、Shader:
Shader "MyShader/P2_9"
{
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert_img
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
fixed4 frag (v2f_img i) : SV_Target
{
return 1;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
二、开始逐语句对ShaderToy进行转化
1、首先,找到我们的主函数 mainImage
void mainImage( out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord )
{
vec2 uv = fragCoord.xy / iResolution.xy;
uv.x *= 4.0;
float t = iTime * 3.0;
vec3 col = vec3(0);
float noise = getNoise(uv, t);
//shape cutoff to get higher further up the screen
CUTOFF = uv.y;
//and at horiz edges
CUTOFF += pow(abs(uv.x*0.5 - 1.),1.0);
//debugview cutoff field
//fragColor = vec4(vec3(CUTOFF),1.0);
if (noise < CUTOFF){
//black
col = vec3(0.);
}else{
//fire
float d = pow(getDepth(noise),0.7);
vec3 hsv = vec3(d *0.17,0.8 - d/4., d + 0.8);
col = hsv2rgb(hsv);
}
fragColor = vec4(col,1.0);
}
2、其余的方法全部都是在 mainImage 函数中调用的方法
因此,我们可以直接使用把这些方法复制到 我们片元着色器的上方,把参数类型转化为CG中的参数类型,即可直接使用
- vec2 :float2
- vec3 :float3
- vec4 :float4
- float4(0,0) : 0
- fract(x) : frac(x) (取 x 的小数部分)
- mix(a,b,x) :lerp(a,b,x) (线性插值)
选中需要转化的变量名,使用快捷键 Ctrl + F,进行全部替换
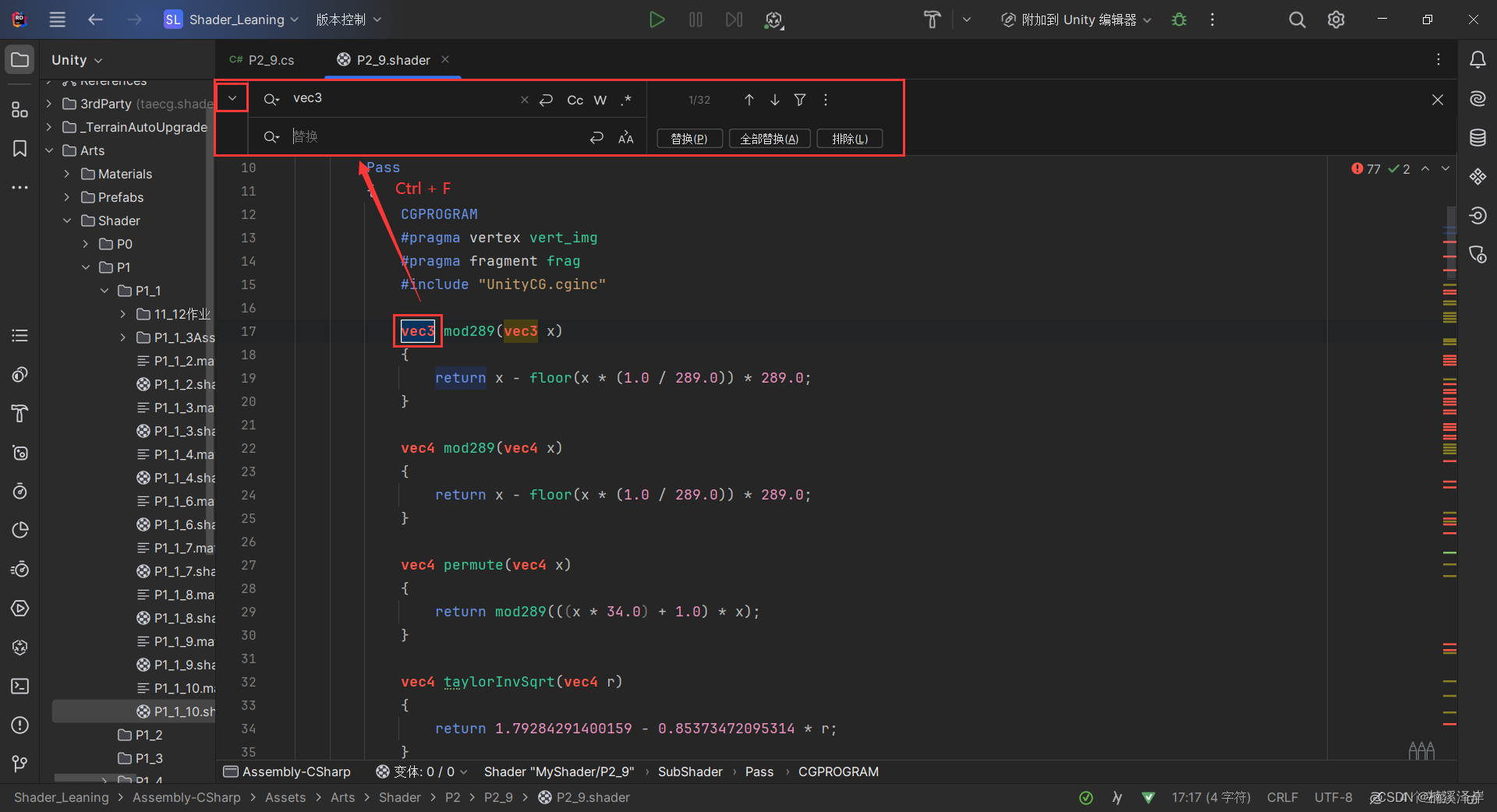
3、替换后的代码(已经没报错了,但是效果不对)
//https://www.shadertoy.com/view/lsscWr
Shader "MyShader/P2_9"
{
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert_img
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
float3 mod289(float3 x)
{
return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
}
float4 mod289(float4 x)
{
return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
}
float4 permute(float4 x)
{
return mod289(((x * 34.0) + 1.0) * x);
}
float4 taylorInvSqrt(float4 r)
{
return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r;
}
float snoise(float3 v)
{
const float2 C = float2(1.0 / 6.0, 1.0 / 3.0);
const float4 D = float4(0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0);
// First corner
float3 i = floor(v + dot(v, C.yyy));
float3 x0 = v - i + dot(i, C.xxx);
// Other corners
float3 g = step(x0.yzx, x0.xyz);
float3 l = 1.0 - g;
float3 i1 = min(g.xyz, l.zxy);
float3 i2 = max(g.xyz, l.zxy);
// x0 = x0 - 0.0 + 0.0 * C.xxx;
// x1 = x0 - i1 + 1.0 * C.xxx;
// x2 = x0 - i2 + 2.0 * C.xxx;
// x3 = x0 - 1.0 + 3.0 * C.xxx;
float3 x1 = x0 - i1 + C.xxx;
float3 x2 = x0 - i2 + C.yyy; // 2.0*C.x = 1/3 = C.y
float3 x3 = x0 - D.yyy; // -1.0+3.0*C.x = -0.5 = -D.y
// Permutations
i = mod289(i);
float4 p = permute(permute(permute(
i.z + float4(0.0, i1.z, i2.z, 1.0))
+ i.y + float4(0.0, i1.y, i2.y, 1.0))
+ i.x + float4(0.0, i1.x, i2.x, 1.0));
// Gradients: 7x7 points over a square, mapped onto an octahedron.
// The ring size 17*17 = 289 is close to a multiple of 49 (49*6 = 294)
float n_ = 0.142857142857; // 1.0/7.0
float3 ns = n_ * D.wyz - D.xzx;
float4 j = p - 49.0 * floor(p * ns.z * ns.z); // mod(p,7*7)
float4 x_ = floor(j * ns.z);
float4 y_ = floor(j - 7.0 * x_); // mod(j,N)
float4 x = x_ * ns.x + ns.yyyy;
float4 y = y_ * ns.x + ns.yyyy;
float4 h = 1.0 - abs(x) - abs(y);
float4 b0 = float4(x.xy, y.xy);
float4 b1 = float4(x.zw, y.zw);
//float4 s0 = float4(lessThan(b0,0.0))*2.0 - 1.0;
//float4 s1 = float4(lessThan(b1,0.0))*2.0 - 1.0;
float4 s0 = floor(b0) * 2.0 + 1.0;
float4 s1 = floor(b1) * 2.0 + 1.0;
float4 sh = -step(h, 0);
float4 a0 = b0.xzyw + s0.xzyw * sh.xxyy;
float4 a1 = b1.xzyw + s1.xzyw * sh.zzww;
float3 p0 = float3(a0.xy, h.x);
float3 p1 = float3(a0.zw, h.y);
float3 p2 = float3(a1.xy, h.z);
float3 p3 = float3(a1.zw, h.w);
//Normalise gradients
float4 norm = taylorInvSqrt(float4(dot(p0, p0), dot(p1, p1), dot(p2, p2), dot(p3, p3)));
p0 *= norm.x;
p1 *= norm.y;
p2 *= norm.z;
p3 *= norm.w;
// Mix final noise value
float4 m = max(0.6 - float4(dot(x0, x0), dot(x1, x1), dot(x2, x2), dot(x3, x3)), 0.0);
m = m * m;
return 42.0 * dot(m * m, float4(dot(p0, x0), dot(p1, x1),
dot(p2, x2), dot(p3, x3)));
}
//END ASHIMA /
const float STEPS = 4.;
float CUTOFF = 0.15; //depth less than this, show black
float3 hsv2rgb(float3 c)
{
float4 K = float4(1.0, 2.0 / 3.0, 1.0 / 3.0, 3.0);
float3 p = abs(frac(c.xxx + K.xyz) * 6.0 - K.www);
return c.z * lerp(K.xxx, clamp(p - K.xxx, 0.0, 1.0), c.y);
}
float getNoise(float2 uv, float t)
{
//given a uv coord and time - return a noise val in range 0 - 1
//using ashima noise
//add time to y position to make noise field move upwards
float TRAVEL_SPEED = 1.5;
//octave 1
float SCALE = 2.0;
float noise = snoise(float3(uv.x * SCALE, uv.y * SCALE - t * TRAVEL_SPEED, 0));
//octave 2 - more detail
SCALE = 6.0;
noise += snoise(float3(uv.x * SCALE + t, uv.y * SCALE, 0)) * 0.2;
//move noise into 0 - 1 range
noise = (noise / 2. + 0.5);
return noise;
}
float getDepth(float n)
{
//given a 0-1 value return a depth,
//remap remaining non-cutoff region to 0 - 1
float d = (n - CUTOFF) / (1. - CUTOFF);
//step it
d = floor(d * STEPS) / STEPS;
return d;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f_img i) : SV_Target
{
float2 uv = i.uv;
uv.x *= 4.0;
float t = _Time.y * 3.0;
float3 col = 0;
float noise = getNoise(uv, t);
//shape cutoff to get higher further up the screen
CUTOFF = uv.y;
//and at horiz edges
CUTOFF += pow(abs(uv.x * 0.5 - 1.), 1.0);
//debugview cutoff field
//fragColor = float4(float3(CUTOFF),1.0);
if (noise < CUTOFF)
{
//black
col = 0;
}
else
{
//fire
float d = pow(getDepth(noise), 0.7);
float3 hsv = float3(d * 0.17, 0.8 - d / 4., d + 0.8);
col = hsv2rgb(hsv);
}
return float4(col, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
三、我们来调试一下Shader,看看问题出在了哪?
我们在调试Shader时,因为主要效果是在 片元着色器 中实现的。
所以,我们调试Shader一般 从 输出 倒着 来调试
1、return float4(col, 1.0);
在 ShaderToy中,已经规定了透明值为 1 。所以,最终效果为黑色,不是透明值导致的。我们应该顺着 col 去找bug。
2、black or fire
if (noise < CUTOFF)
{
//black
col = 0;
}
else
{
//fire
float d = pow(getDepth(noise), 0.7);
float3 hsv = float3(d * 0.17, 0.8 - d / 4., d + 0.8);
col = hsv2rgb(hsv);
}
-
我们修改black中的col。发现黑色的背景变白了,说明这不是使col最终全为 0 的原因
col = 1;

-
我们修改 fire 中的 col 分别为 hsv 、d 和 getDepth(noise); (没有变化,说明这也不是原因所在)
col = hsv; / col = d; / col = getDepth(noise);
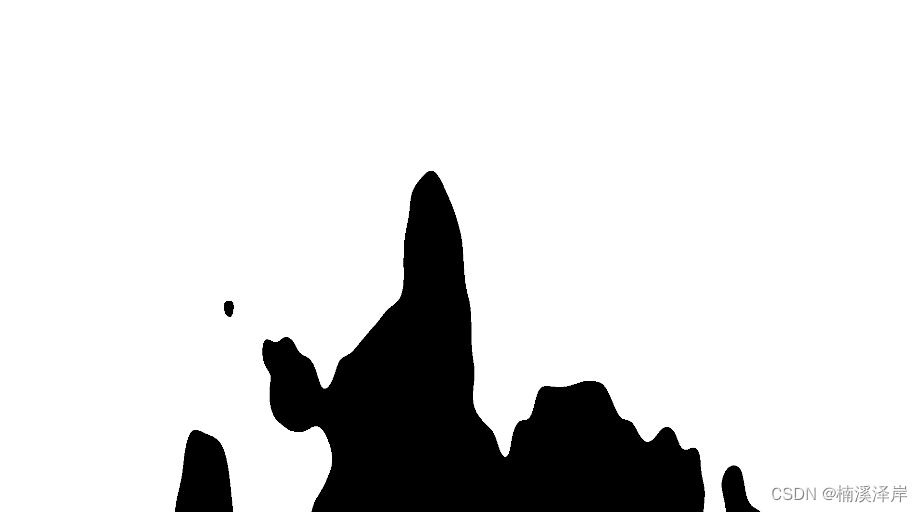

-
我们修改 fire 中的 col 为 noise 后,我们的火出现了变化(可以锁定getDepth函数出现了问题)
col = noise;
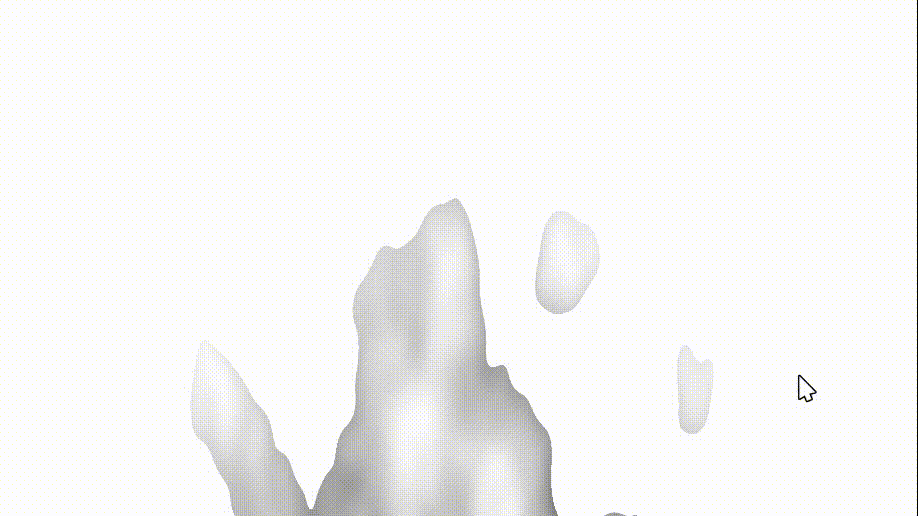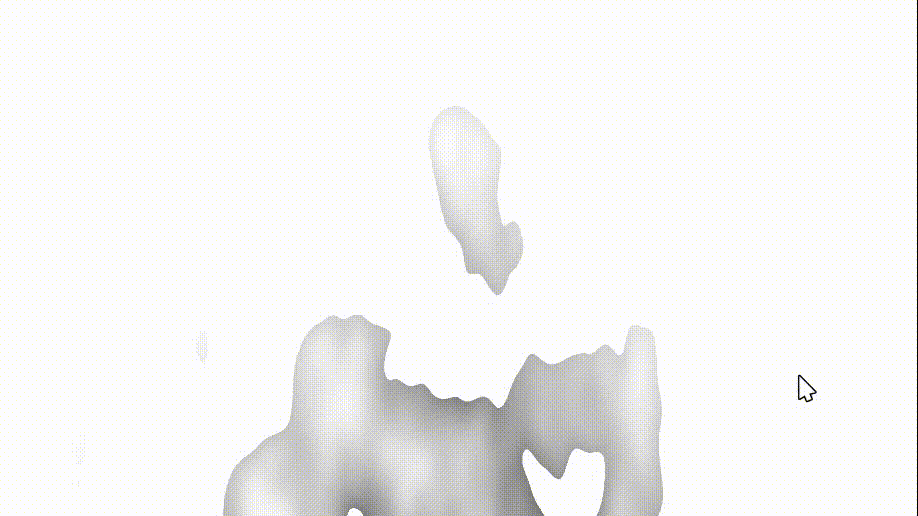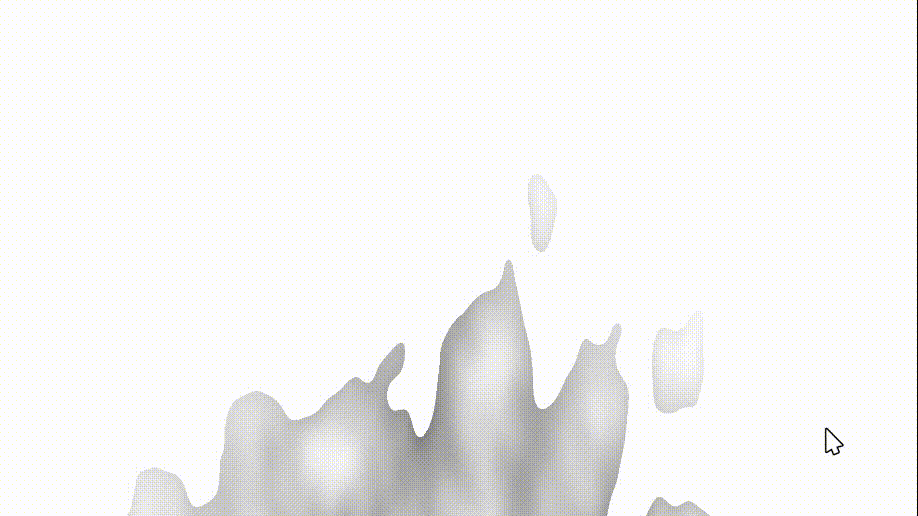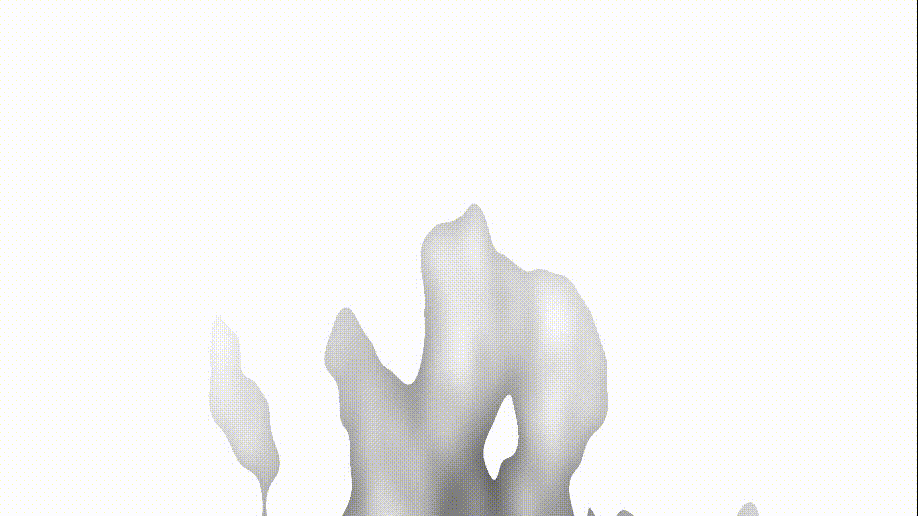
3、getDepth函数
float getDepth(float n)
{
//given a 0-1 value return a depth,
//remap remaining non-cutoff region to 0 - 1
float d = (n - CUTOFF) / (1. - CUTOFF);
//step it
d = floor(d * STEPS) / STEPS;
return d;
}
- 在归一化(remap remaining non-cutoff region to 0 - 1)之后,返回一个d。(我们可以看出火有了大致的颜色,说明问题处在了d = floor(d * STEPS) / STEPS;这句话)

- 而 d 我们已经返回过了。所以,最终问题在 STEPS 参数上
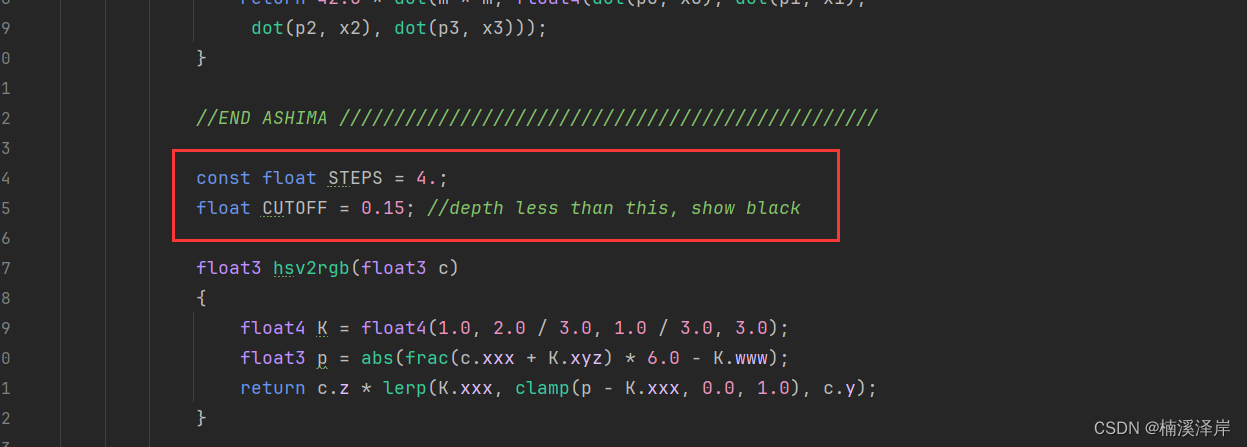
四、修改 STEPS 的数值出错问题
在Unity的Shader中,如果我们的常量直接定义在Pass中
不管初始值为多少,Unity都会默认为0。
如果我们想这样使用参数,必须在属性块定义一个变量给定初始值
法1:在属性面板增加 STEPS 参数,赋予初始值4
- 在这样定义后,修改对应的变量名后即可使用
Properties
{
_Steps("STEPS",float) = 4
}
法2:使用#define 预定义一个常量
#define STEPS 4
- 可以看出,我们效果正确了

五、最终代码
//https://www.shadertoy.com/view/lsscWr
Shader "MyShader/P2_9"
{
Properties
{
_Steps("STEPS",float) = 4
_CUTOFF("CUTOFF",float) = 0.15
}
SubShader
{
// No culling or depth
Cull Off ZWrite Off ZTest Always
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert_img
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
float3 mod289(float3 x)
{
return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
}
float4 mod289(float4 x)
{
return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
}
float4 permute(float4 x)
{
return mod289(((x * 34.0) + 1.0) * x);
}
float4 taylorInvSqrt(float4 r)
{
return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r;
}
float snoise(float3 v)
{
const float2 C = float2(1.0 / 6.0, 1.0 / 3.0);
const float4 D = float4(0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0);
// First corner
float3 i = floor(v + dot(v, C.yyy));
float3 x0 = v - i + dot(i, C.xxx);
// Other corners
float3 g = step(x0.yzx, x0.xyz);
float3 l = 1.0 - g;
float3 i1 = min(g.xyz, l.zxy);
float3 i2 = max(g.xyz, l.zxy);
// x0 = x0 - 0.0 + 0.0 * C.xxx;
// x1 = x0 - i1 + 1.0 * C.xxx;
// x2 = x0 - i2 + 2.0 * C.xxx;
// x3 = x0 - 1.0 + 3.0 * C.xxx;
float3 x1 = x0 - i1 + C.xxx;
float3 x2 = x0 - i2 + C.yyy; // 2.0*C.x = 1/3 = C.y
float3 x3 = x0 - D.yyy; // -1.0+3.0*C.x = -0.5 = -D.y
// Permutations
i = mod289(i);
float4 p = permute(permute(permute(
i.z + float4(0.0, i1.z, i2.z, 1.0))
+ i.y + float4(0.0, i1.y, i2.y, 1.0))
+ i.x + float4(0.0, i1.x, i2.x, 1.0));
// Gradients: 7x7 points over a square, mapped onto an octahedron.
// The ring size 17*17 = 289 is close to a multiple of 49 (49*6 = 294)
float n_ = 0.142857142857; // 1.0/7.0
float3 ns = n_ * D.wyz - D.xzx;
float4 j = p - 49.0 * floor(p * ns.z * ns.z); // mod(p,7*7)
float4 x_ = floor(j * ns.z);
float4 y_ = floor(j - 7.0 * x_); // mod(j,N)
float4 x = x_ * ns.x + ns.yyyy;
float4 y = y_ * ns.x + ns.yyyy;
float4 h = 1.0 - abs(x) - abs(y);
float4 b0 = float4(x.xy, y.xy);
float4 b1 = float4(x.zw, y.zw);
//float4 s0 = float4(lessThan(b0,0.0))*2.0 - 1.0;
//float4 s1 = float4(lessThan(b1,0.0))*2.0 - 1.0;
float4 s0 = floor(b0) * 2.0 + 1.0;
float4 s1 = floor(b1) * 2.0 + 1.0;
float4 sh = -step(h, 0);
float4 a0 = b0.xzyw + s0.xzyw * sh.xxyy;
float4 a1 = b1.xzyw + s1.xzyw * sh.zzww;
float3 p0 = float3(a0.xy, h.x);
float3 p1 = float3(a0.zw, h.y);
float3 p2 = float3(a1.xy, h.z);
float3 p3 = float3(a1.zw, h.w);
//Normalise gradients
float4 norm = taylorInvSqrt(float4(dot(p0, p0), dot(p1, p1), dot(p2, p2), dot(p3, p3)));
p0 *= norm.x;
p1 *= norm.y;
p2 *= norm.z;
p3 *= norm.w;
// Mix final noise value
float4 m = max(0.6 - float4(dot(x0, x0), dot(x1, x1), dot(x2, x2), dot(x3, x3)), 0.0);
m = m * m;
return 42.0 * dot(m * m, float4(dot(p0, x0), dot(p1, x1),
dot(p2, x2), dot(p3, x3)));
}
//END ASHIMA /
float _Steps;
float _CUTOFF; //depth less than this, show black
float3 hsv2rgb(float3 c)
{
float4 K = float4(1.0, 2.0 / 3.0, 1.0 / 3.0, 3.0);
float3 p = abs(frac(c.xxx + K.xyz) * 6.0 - K.www);
return c.z * lerp(K.xxx, clamp(p - K.xxx, 0.0, 1.0), c.y);
}
float getNoise(float2 uv, float t)
{
//given a uv coord and time - return a noise val in range 0 - 1
//using ashima noise
//add time to y position to make noise field move upwards
float TRAVEL_SPEED = 1.5;
//octave 1
float SCALE = 2.0;
float noise = snoise(float3(uv.x * SCALE, uv.y * SCALE - t * TRAVEL_SPEED, 0));
//octave 2 - more detail
SCALE = 6.0;
noise += snoise(float3(uv.x * SCALE + t, uv.y * SCALE, 0)) * 0.2;
//move noise into 0 - 1 range
noise = (noise / 2. + 0.5);
return noise;
}
float getDepth(float n)
{
//given a 0-1 value return a depth,
//remap remaining non-_CUTOFF region to 0 - 1
float d = (n - _CUTOFF) / (1. - _CUTOFF);
//step it
d = floor(d * _Steps) / _Steps;
return d;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f_img i) : SV_Target
{
float2 uv = i.uv;
uv.x *= 4.0;
float t = _Time.y * 3.0;
float3 col = 0;
float noise = getNoise(uv, t);
//shape _CUTOFF to get higher further up the screen
_CUTOFF = uv.y;
//and at horiz edges
_CUTOFF += pow(abs(uv.x * 0.5 - 1.), 1.0);
//debugview _CUTOFF field
//fragColor = float4(float3(_CUTOFF),1.0);
if (noise < _CUTOFF)
{
//black
col = 0;
}
else
{
//fire
float d = pow(getDepth(noise), 0.7);
float3 hsv = float3(d * 0.17, 0.8 - d / 4., d + 0.8);
col = hsv2rgb(hsv);
}
return float4(col, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
}