文章目录
- 什么是阻塞队列
- 阻塞队列的特点
- BlockingQueue不是新的东西
- 学会使用队列
- 阻塞队列四组API
- SynchronousQueue 同步队列
什么是阻塞队列
阻塞队列本质上还是一种队列,遵循先进先出,后进后出的原则,在此基础上,如果出队时阻塞队列为空,则会使当前线程陷入阻塞,直到入队新元素时通知线程继续执行,如果入队时阻塞队列为满,则会使当前线程陷入阻塞,直到出队旧元素时才通知线程进行执行。
阻塞队列的特点

BlockingQueue不是新的东西
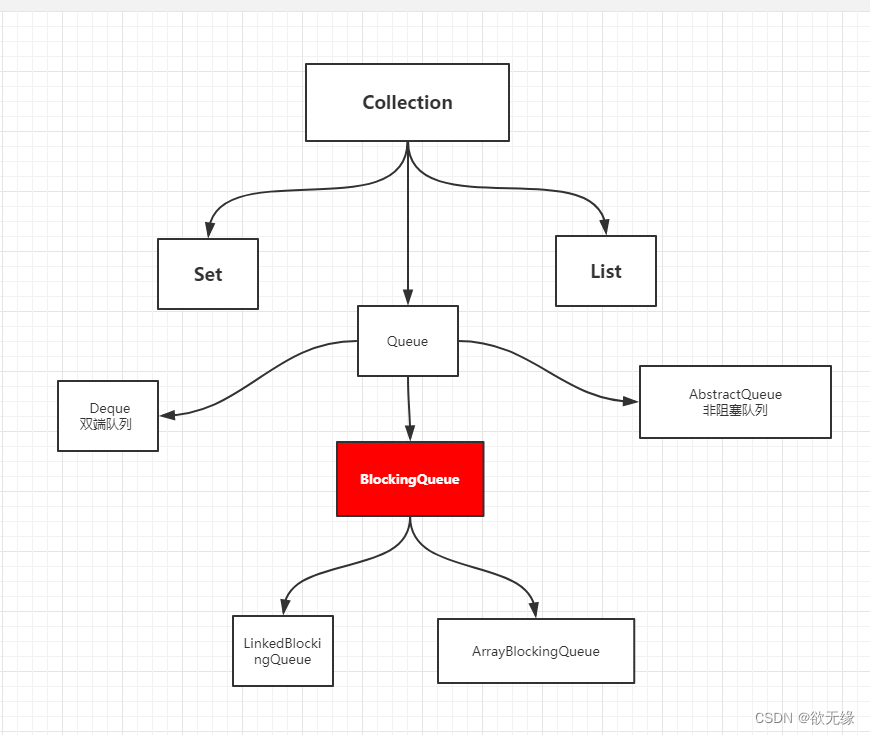
学会使用队列
阻塞队列四组API
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 有返回值,不抛出异常 | 阻塞 等待 | 超时等待 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 添加 | add(E e) | offer(E e) | put() | offer(E e,Time,TimeUnit) |
| 移除 | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(Time,TimeUnit) |
| 检测队首元素 | element() | peek | 无 | 无 |
-
抛出异常是指当队列满时,再次插入会抛出异常(如果队列未满,插入返回值未true);
-
返回布尔是指当队列满时,再次插入会返回false;
-
阻塞是指当队列满时,再次插入会被阻塞,直到队列取出一个元素,才能插入。
-
超时是指当一个时限过后,才会插入或者取出。
抛出异常
/**
* 抛出异常
*/
public static void test1(){
// 队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
// IllegalStateException: Queue full 抛出异常!
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
// java.util.NoSuchElementException 抛出异常!
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
}
有返回值,没有异
/**
* 有返回值,没有异常
*/
public static void test2(){
// 队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d")); // false 不抛出异常!
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll()); // null 不抛出异常!
}
等待,阻塞(一直阻塞)
/**
* 等待,阻塞(一直阻塞)
*/
public static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
// 队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
// 一直阻塞
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
// blockingQueue.put("d"); // 队列没有位置了,一直阻塞
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take())
}
等待,阻塞(等待超时
/**
* 等待,阻塞(等待超时)
*/
public static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
// 队列的大小
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
blockingQueue.offer("a");
blockingQueue.offer("b");
blockingQueue.offer("c");
// blockingQueue.offer("d",2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 等待超过2秒就退出
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
SynchronousQueue 同步队列
- 和其他的BlockingQueue 不一样, SynchronousQueue 不存储元素
- put了一个元素,必须从里面先take取出来,否则不能在put进去值!
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>(); // 同步队
// new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" put 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"T1").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"T2").start();
}
}