目录
单源最短路径问题
Dijkstra算法
原理
获得最短路径长度的Dijkstra代码实现
时间复杂度
算法优化
优先队列优化后的代码实现
时间复杂度
可以具体获得最短路径的Dijkstra代码实现
Bellman-Ford算法
原理
代码实现
Floyed算法
原理
代码实现
单源最短路径问题
我们的起始点是固定点,从起始点出发到达其他各顶点的最短路径。
Dijkstra算法
此算法不能处理负权边,由于大量的应用不依赖负权边,所以这个算法有非常广泛的应用。
原理 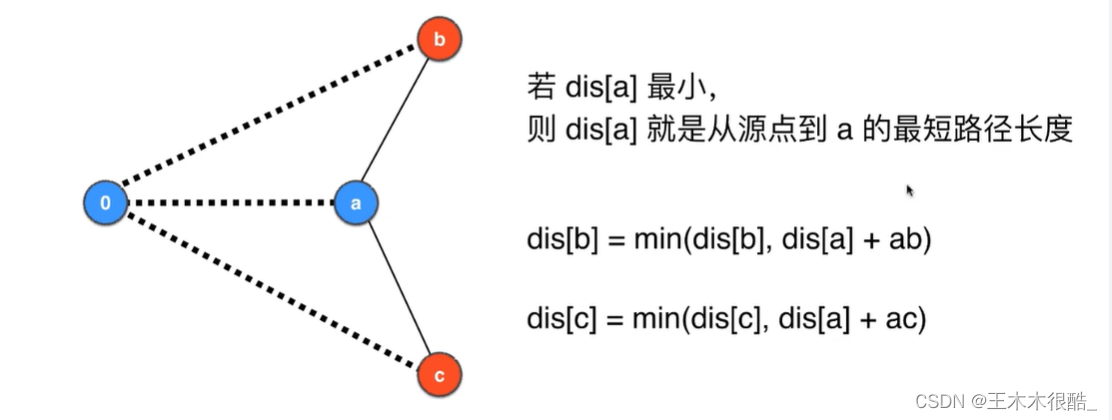

获得最短路径长度的Dijkstra代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Dijkstra {
private WeightedGraph G;
private int s;//源点s
private int[] dis;//整型数组表示源点s到某个顶点的距离
private boolean[] visited;//找到还没确定最短距离的顶点
public Dijkstra(WeightedGraph G, int s){
this.G = G;
G.validateVertex(s);//验证合法性
this.s = s;
dis = new int[G.V()];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);//赋初值
dis[s] = 0;//赋初值为0
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
while(true){
//循环的第一轮找到的必是源点s
int cur = -1;//最小的dis值对应的顶点是谁
int curdis = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//当前找到的最小的dis值
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(!visited[v] && dis[v] < curdis){
curdis = dis[v];
cur = v;
}
if(cur == -1) break;//代表当前所有的顶点都访问过了,可以退出咯
visited[cur] = true;//哪些顶点的dis值已经求出来了
for(int w: G.adj(cur))
if(!visited[w]){
if(dis[cur] + G.getWeight(cur, w) < dis[w])
dis[w] = dis[cur] + G.getWeight(cur, w);
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int v){//判断顶点和源点的连通性
G.validateVertex(v);
return visited[v];
}
public int distTo(int v){//从源点s到顶点v对应的最短路径的长度
G.validateVertex(v);
return dis[v];
}
static public void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Dijkstra dij = new Dijkstra(g, 0);
for(int v = 0; v < g.V(); v ++)
System.out.print(dij.distTo(v) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}时间复杂度
算法优化

我们可以用优先队列获得v这个顶点对应的dis值,不再是v这个顶点序号的最小值了。我们的优先队列取出来的是顶点的序号,但比较起来是比较的dis值。
优先队列优化后的代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Dijkstra {
private WeightedGraph G;
private int s;
private int[] dis;
private boolean[] visited;
private class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
public int v, dis;
public Node(int v, int dis){
this.v = v;
this.dis = dis;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node another){
return dis - another.dis;
}
}
public Dijkstra(WeightedGraph G, int s){
this.G = G;
G.validateVertex(s);
this.s = s;
dis = new int[G.V()];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dis[s] = 0;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<Node>();
pq.add(new Node(s, 0));
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
int cur = pq.remove().v;
if(visited[cur]) continue;
visited[cur] = true;
for(int w: G.adj(cur))
if(!visited[w]){
if(dis[cur] + G.getWeight(cur, w) < dis[w]){
dis[w] = dis[cur] + G.getWeight(cur, w);
pq.add(new Node(w, dis[w]));
}
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int v){
G.validateVertex(v);
return visited[v];
}
public int distTo(int v){
G.validateVertex(v);
return dis[v];
}
static public void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Dijkstra dij = new Dijkstra(g, 0);
for(int v = 0; v < g.V(); v ++)
System.out.print(dij.distTo(v) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}时间复杂度

可以具体获得最短路径的Dijkstra代码实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Dijkstra {
private WeightedGraph G;
private int s;
private int[] dis;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
private class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
public int v, dis;
public Node(int v, int dis){
this.v = v;
this.dis = dis;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node another){
return dis - another.dis;
}
}
public Dijkstra(WeightedGraph G, int s){
this.G = G;
G.validateVertex(s);
this.s = s;
dis = new int[G.V()];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
pre = new int[G.V()];
Arrays.fill(pre, -1);
dis[s] = 0;
pre[s] = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<Node>();
pq.add(new Node(s, 0));
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
int cur = pq.remove().v;
if(visited[cur]) continue;
visited[cur] = true;
for(int w: G.adj(cur))
if(!visited[w]){
if(dis[cur] + G.getWeight(cur, w) < dis[w]){
dis[w] = dis[cur] + G.getWeight(cur, w);
pq.add(new Node(w, dis[w]));
pre[w] = cur;
}
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int v){
G.validateVertex(v);
return visited[v];
}
public int distTo(int v){
G.validateVertex(v);
return dis[v];
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
static public void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Dijkstra dij = new Dijkstra(g, 0);
for(int v = 0; v < g.V(); v ++)
System.out.print(dij.distTo(v) + " ");
System.out.println();
System.out.println(dij.path(3));
}
}Bellman-Ford算法
原理
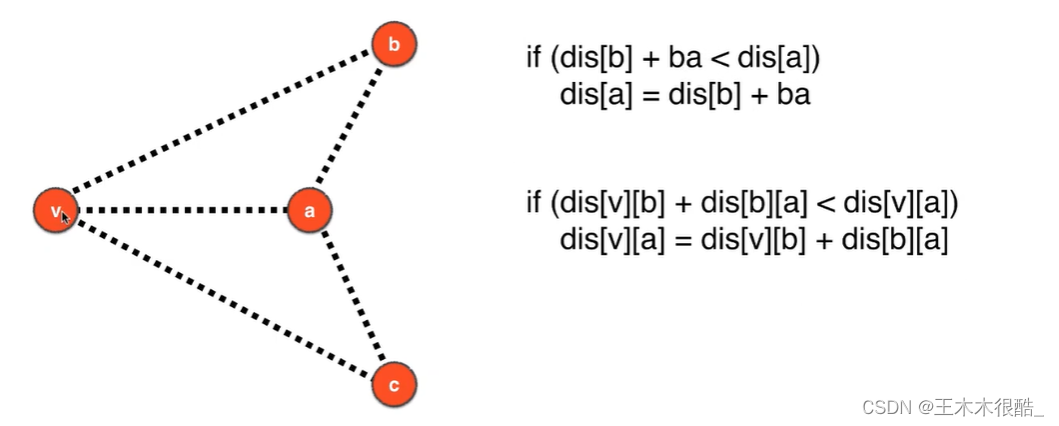
松弛操作有方向性,相当于拐个弯到达某个端点是不是比直接到达某个端点更近。此算法在有向图无向图也成立。




代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BellmanFord {
private WeightedGraph G;
private int s;
private int[] dis;
private boolean hasNegCycle = false;
public BellmanFord(WeightedGraph G, int s){
this.G = G;
G.validateVertex(s);
this.s = s;
dis = new int[G.V()];
Arrays.fill(dis, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dis[s] = 0;
for(int pass = 1; pass < G.V(); pass ++){
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(dis[v] != Integer.MAX_VALUE &&
dis[v] + G.getWeight(v, w) < dis[w])
dis[w] = dis[v] + G.getWeight(v, w);
}
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
for(int w : G.adj(v))
if(dis[v] != Integer.MAX_VALUE &&
dis[v] + G.getWeight(v, w) < dis[w])
hasNegCycle = true;
}
public boolean hasNegativeCycle(){
return hasNegCycle;
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int v){
G.validateVertex(v);
return dis[v] != Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public int distTo(int v){
G.validateVertex(v);
if(hasNegCycle) throw new RuntimeException("exist negative cycle.");
return dis[v];
}
static public void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
BellmanFord bf = new BellmanFord(g, 0);
if(!bf.hasNegativeCycle()){
for(int v = 0; v < g.V(); v ++)
System.out.print(bf.distTo(v) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
else
System.out.println("exist negative cycle.");
WeightedGraph g2 = new WeightedGraph("g2.txt");
BellmanFord bf2 = new BellmanFord(g2, 0);
if(!bf2.hasNegativeCycle()){
for(int v = 0; v < g2.V(); v ++)
System.out.print(bf2.distTo(v) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
else
System.out.println("exist negative cycle.");
}
}Floyed算法
原理

可以包含负权边,也可以包含负权环。
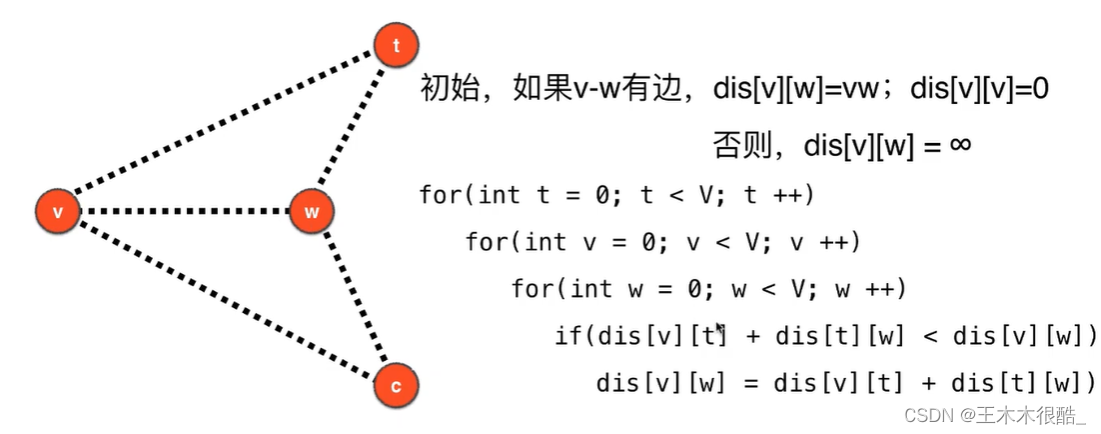
代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Floyed {
private WeightedGraph G;
private int[][] dis;
private boolean hasNegCycle = false;
public Floyed(WeightedGraph G){
this.G = G;
dis = new int[G.V()][G.V()];
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
Arrays.fill(dis[v], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++){
dis[v][v] = 0;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
dis[v][w] = G.getWeight(v, w);
}
for(int t = 0; t < G.V(); t ++)
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
for(int w = 0; w < G.V(); w ++)
if(dis[v][t] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dis[t][w] != Integer.MAX_VALUE
&& dis[v][t] + dis[t][w] < dis[v][w])
dis[v][w] = dis[v][t] + dis[t][w];
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(dis[v][v] < 0)
hasNegCycle = true;
}
public boolean hasNegativeCycle(){
return hasNegCycle;
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return dis[v][w] != Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public int distTo(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return dis[v][w];
}
static public void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Floyed floyed = new Floyed(g);
if(!floyed.hasNegativeCycle()){
for(int v = 0; v < g.V(); v ++){
for(int w = 0; w < g.V(); w ++)
System.out.print(floyed.distTo(v, w) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
else
System.out.println("exist negative cycle.");
WeightedGraph g2 = new WeightedGraph("g2.txt");
Floyed floyed2 = new Floyed(g2);
if(!floyed2.hasNegativeCycle()){
for(int v = 0; v < g.V(); v ++){
for(int w = 0; w < g.V(); w ++)
System.out.print(floyed2.distTo(v, w) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
else
System.out.println("exist negative cycle.");
}
}