一、有效的括号
20.有效的括号(题目链接)

思路:
1)括号的顺序匹配:用栈实现,遇到左括号入,遇到右括号出(保证所出的左括号与右括号对应),否则顺序不匹配。
2)括号的数量匹配:
1>左括号大于右括号:用栈实现,遇到左括号入,遇到右括号出,遍历完字符数组,此时栈不为空,则说明左括号数量大于右括号;
2>右括号大于左括号:遇到右括号出时,判断栈是否为空,若此时栈为空,说明右括号数量大于左括号;
typedef char SDateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
SDateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化栈和销毁栈
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void DestoryStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//出栈和入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, SDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SDateType* tmp = (SDateType*)realloc( ps->a,newcapacity * sizeof(SDateType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//尾插
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//只少有一个元素,才能删除
ps->top--;
}
//栈的有效个数和栈顶元素
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
int StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int isValid(char* s) {
Stack ps;
InitStack(&ps);
while (*s)
{
if (*s == '[' || *s == '(' || *s == '{')
{
StackPush(&ps, *s);
s++;
}
else
{
if (StackEmpty(&ps))
{
return false;
}
char tmp = StackTop(&ps);
StackPop(&ps);
if ((*s == ']' && tmp != '[') ||
(*s == '}' && tmp != '{') ||
(*s == ')' && tmp != '('))
{
return false;
}
s++;
}
}
if (!StackEmpty(&ps))
{
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
DestoryStack(&ps);
}二、用队列实现栈
225. 用队列复制栈(题目链接)

思路: 栈是后进先出,队列是先进先出。
用俩队列实现栈
1)入栈时,选择有数据的队列入数据;
2)出栈时,将有数据队列中前k-1个数据出队列,并入到空队列中,返回并出有数据队列的最后一个数据

typedef int QDateType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDateType val;
struct QueueNode * next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QueueNode *head;
QueueNode *tail;
QDateType size;
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDateType x)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* node = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
node->val = x;
node->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = node;
pq->size++;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = node;
pq->tail = node;
pq->size++;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head != NULL);//只少保证一个节点
QueueNode* del = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->head->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
pq->size--;
if (pq->head == NULL)//只有一个节点处理
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}
}
// 返回队头和队尾
QDateType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head->val;
}
QDateType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->tail->val;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head==NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QueueNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
return obj;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));
Queue * empty=&obj->q1;
Queue * nonempty=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(empty))
{
empty=&obj->q2;
nonempty=&obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(nonempty)!=1)
{
int tmp= QueueFront(nonempty);
QueuePush(empty,tmp);
QueuePop(nonempty);
}
int tmp= QueueFront(nonempty);
QueuePop(nonempty);
return tmp;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(!myStackEmpty(obj));
Queue * empty=&obj->q1;
Queue * nonempty=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(empty))
{
empty=&obj->q2;
nonempty=&obj->q1;
}
return QueueBack(nonempty);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
三、用栈实现队列
225. 用栈实现队列(题目链接)

思路: 栈是后进先出,队列是先进先出。
1)入队列:s1栈用来在栈顶入数据;
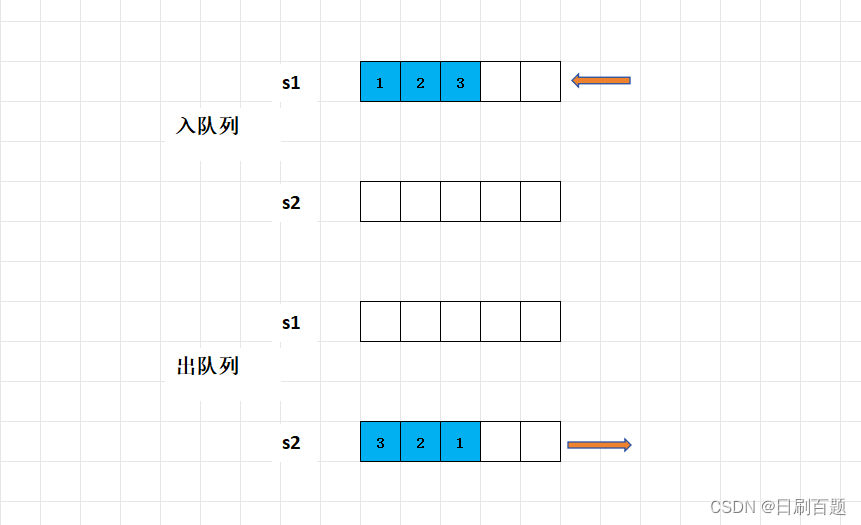
2)出队列:s2栈用来出栈顶数据,如果s2为空,则从s1出数据入到s2中去(比如;s1中的数据为1,2,3,入到s2变为3,2,1),再出s2的栈顶数据,这样就满足队列的性质了
typedef int SDateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
SDateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化栈和销毁栈
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void DestoryStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//出栈和入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, SDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SDateType* tmp = (SDateType*)realloc( ps->a,newcapacity * sizeof(SDateType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//尾插
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);//只少有一个元素,才能删除
ps->top--;
}
//栈的有效个数和栈顶元素
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
int StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
typedef struct {
Stack s1;
Stack s2;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue* )malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
InitStack(&obj->s1);
InitStack(&obj->s2);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
StackPush(&obj->s1,x);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return StackEmpty(&obj->s1)&&StackEmpty(&obj->s2);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));
if(StackEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
int tmp= StackTop(&obj->s1);
StackPush(&obj->s2,tmp);
StackPop(&obj->s1);
}
}
int tmp= StackTop(&obj->s2);
StackPop(&obj->s2);
return tmp;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));
if(StackEmpty(&obj->s2))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->s1))
{
int tmp= StackTop(&obj->s1);
StackPush(&obj->s2,tmp);
StackPop(&obj->s1);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->s2);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
DestoryStack(&obj->s1);
DestoryStack(&obj->s2);
free(obj);
}
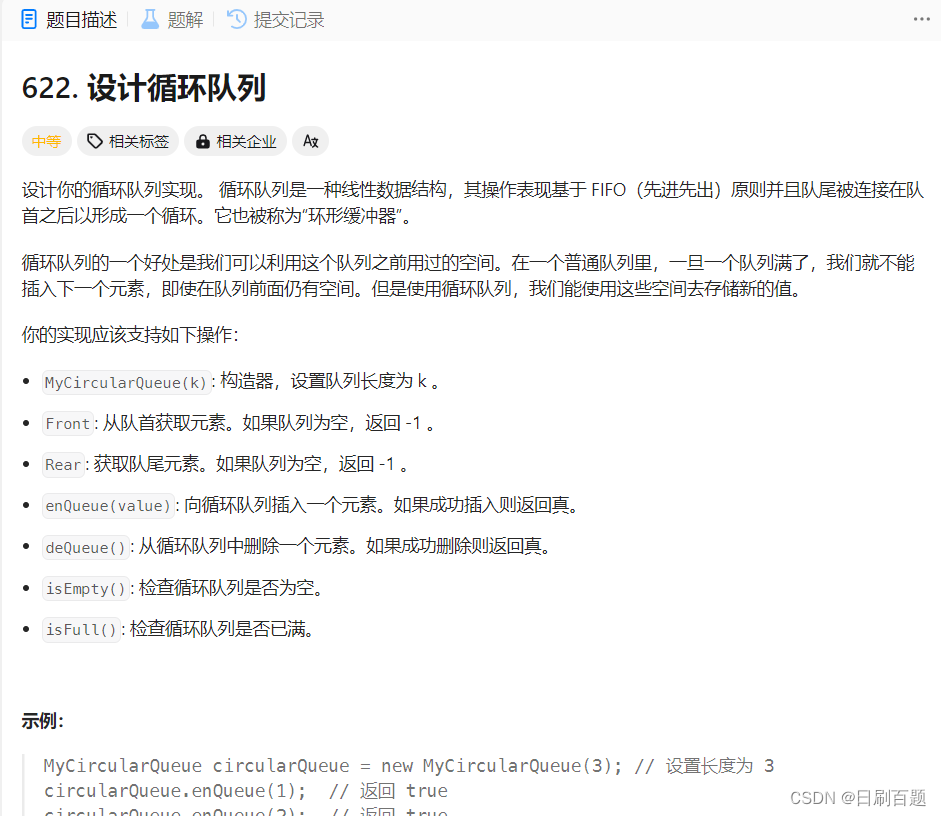
四、设计循环队列
622.设计循环队列(题目链接)
思路一:数组
以front为队列头下标,tail为队列尾下一个元素下标,一共k个数据,开辟k+1个整型大小空间,方便区分队列为空、为满以及一个元素的情况
1)队列为空,front=tail
2)队列为1个元素,front+1=tail
3) 队列为满,(tail+1)%(k+1)==front

typedef struct {
int *a;
int front;
int rear;
int n;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
int * tmp=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->a=tmp;
obj->front=0;
obj->rear=0;
obj->n=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if((obj->rear+1)%(obj->n+1)==obj->front)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull( obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->rear]=value;
obj->rear++;
obj->rear=obj->rear%(obj->n+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(obj->front==obj->rear)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty( obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->front++;
obj->front=obj->front%(obj->n+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty( obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty( obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[(obj->rear-1+obj->n+1)%(obj->n+1)];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}
思路二:单向循环链表
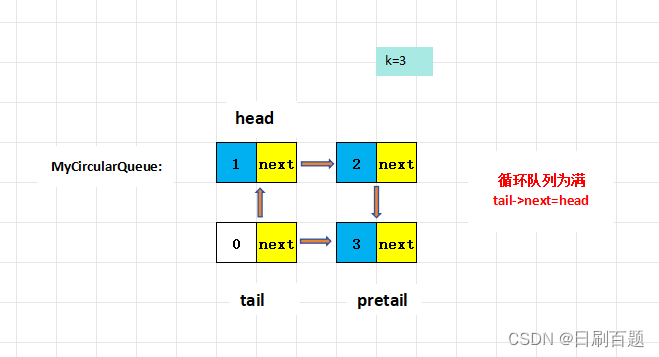
以head为队列头节点,tail为队列尾尾节点的下一个节点,一共k个数据,开辟k+1个节点的循环单向链表,方便区分队列为空、为满以及一个元素的情况
1)队列为空,head=tail
2)队列为1个元素,head->next=tail
3) 队列为满,tail->next=head

typedef struct QueueNode
{
int val;
struct QueueNode * next;
}QueueNode;
QueueNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
QueueNode* node=(QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
node->val=x;
node->next=NULL;
return node;
}
typedef struct MyCircularQueue{
QueueNode *head;
QueueNode *tail;
QueueNode * pretail;
int n;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
QueueNode* node=BuyNode(0);
obj->pretail=NULL;
obj->head=obj->tail=node;
obj->n=(k+1);
QueueNode* cur=obj->tail;
while(k--)
{
QueueNode* node=BuyNode(0);
cur->next=node;
cur= cur->next;
}
cur->next=obj->head;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(obj->tail->next==obj->head)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull( obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->tail->val=value;
obj->pretail=obj->tail;
obj->tail=obj->tail->next;
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(obj->head==obj->tail)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty( obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->head=obj->head->next;
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty( obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->head->val;
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty( obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->pretail->val;
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
while(obj->n--)
{
QueueNode*next=obj->head->next;
free(obj->head);
obj->head=next;
}
obj->head=NULL;
free(obj);
}