目录
1.next_permutation函数的定义
2.简单使用
2.1普通数组全排列
2.2结构体全排列
2.3string
3.补充

1.next_permutation函数的定义
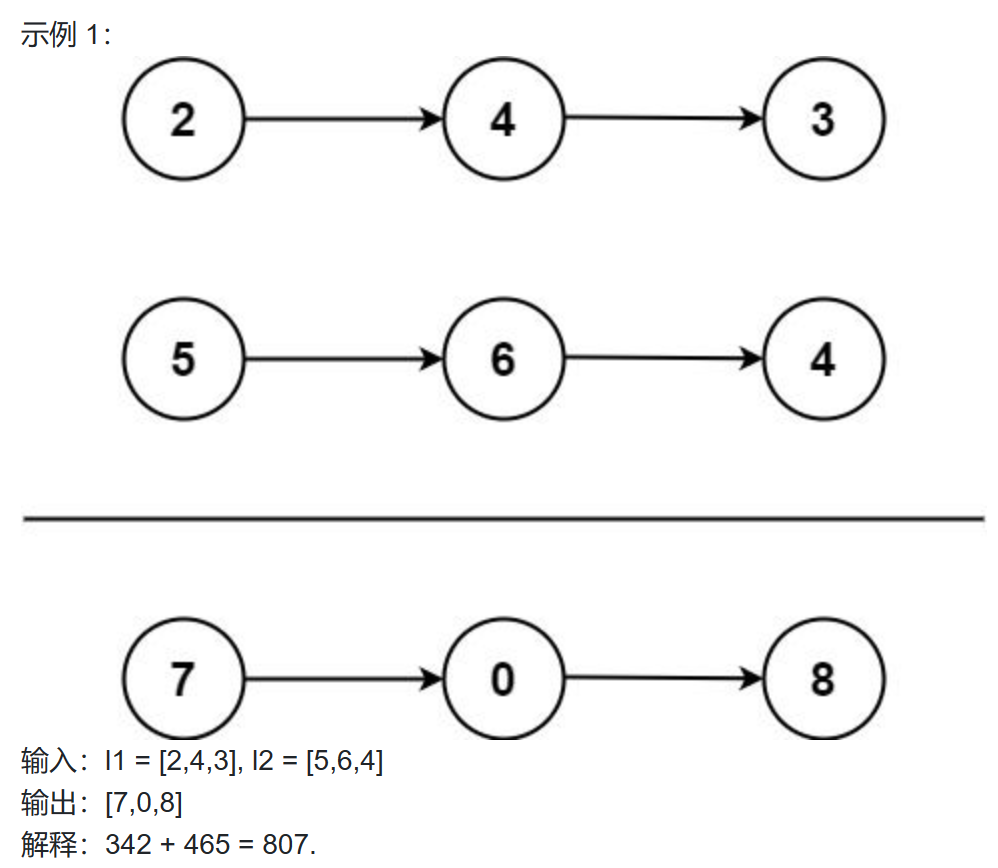
next_permutation函数会按照字母表顺序生成给定序列的下一个较大的排列,直到整个序列为降序为止。与其相对的还有一个函数——prev_permutation函数。
next_permutaion(起始地址,末尾地址+1)
next_permutaion(起始地址,末尾地址+1,自定义排序)
注:next_permutation只能获得上一个排列,如果要获得全排列,那么就需要先对数组进行升序排序
2.简单使用
2.1普通数组全排列
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
do {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(arr, arr + 4));
return 0;
}运行结果:
1 2 3 4
1 2 4 3
1 3 2 4
1 3 4 2
1 4 2 3
1 4 3 2
2 1 3 4
2 1 4 3
2 3 1 4
2 3 4 1
2 4 1 3
2 4 3 1
3 1 2 4
3 1 4 2
3 2 1 4
3 2 4 1
3 4 1 2
3 4 2 1
4 1 2 3
4 1 3 2
4 2 1 3
4 2 3 1
4 3 1 2
4 3 2 12.2结构体全排列
由于结构体默认不能比较大小,所以就不能使用默认的next_permutation()排列比较函数,需要使用自定义排列比较函数。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct
{
int test;
bool operator < (const fyd& a)
{
return test < a.test;
}
}fyd;
fyd arr[4];
int main()
{
arr[0].test = 2;
arr[1].test = 1;
arr[2].test = 4;
arr[3].test = 3;
do {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
cout << arr[i].test << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(arr, arr + 4));
return 0;
}运行结果:
1 2 3 4
1 2 4 3
1 3 2 4
1 3 4 2
1 4 2 3
1 4 3 2
2 1 3 4
2 1 4 3
2 3 1 4
2 3 4 1
2 4 1 3
2 4 3 1
3 1 2 4
3 1 4 2
3 2 1 4
3 2 4 1
3 4 1 2
3 4 2 1
4 1 2 3
4 1 3 2
4 2 1 3
4 2 3 1
4 3 1 2
4 3 2 12.3string
string等数据结构不能直接用名字代表地址,只能够使用自带的迭代器begin()、end()实现全排列。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
do{
cout << s << endl;
}while (next_permutation(s.begin(), s.end()));
return 0;
}运行结果:
abc //input
abc
acb
bac
bca
cab
cba3.补充
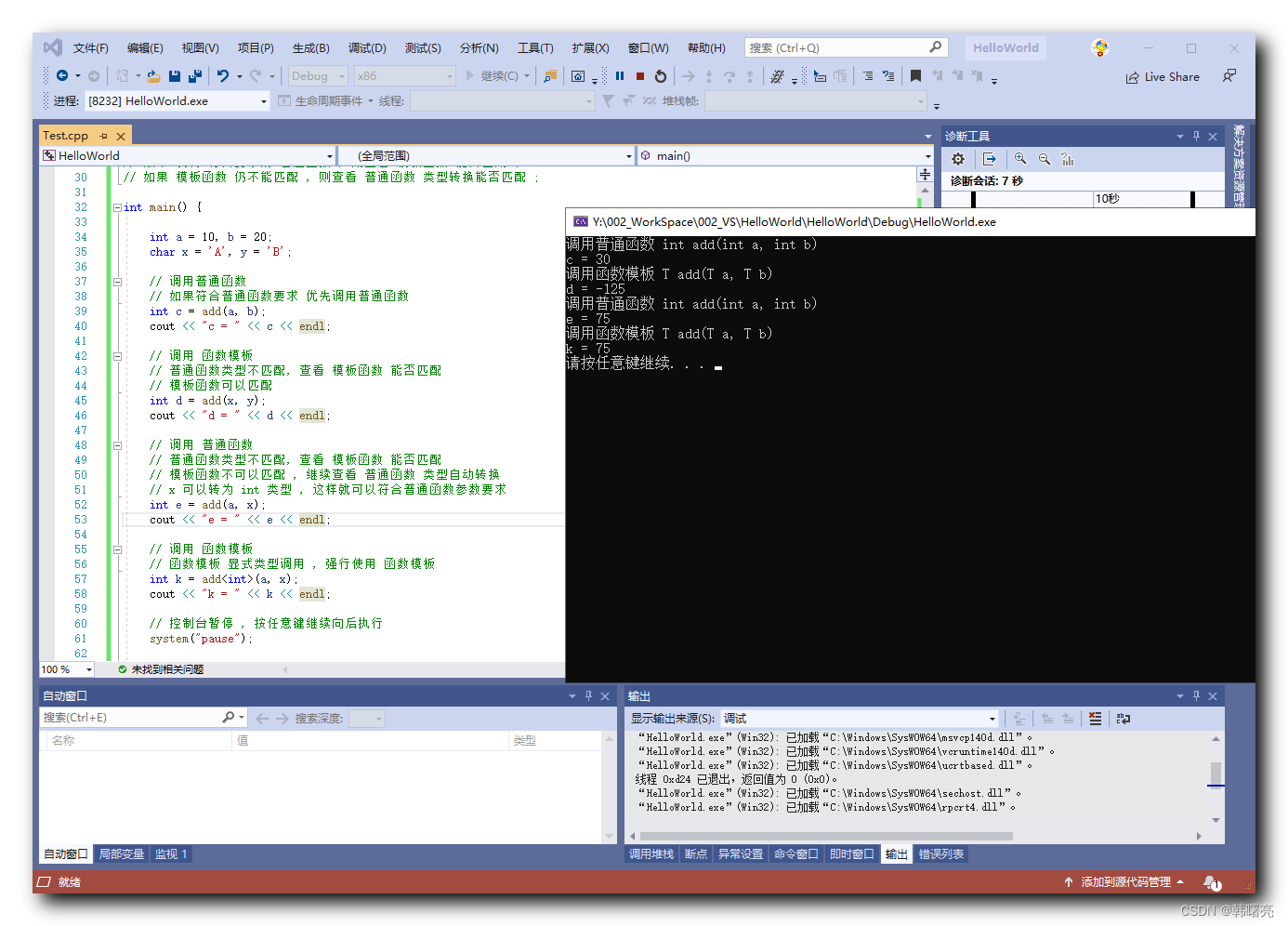
推荐大家使用:cplusplus.com - The C++ Resources Network
可以查询到对应函数对应的头文件、底层代码及使用方式等。
例如:
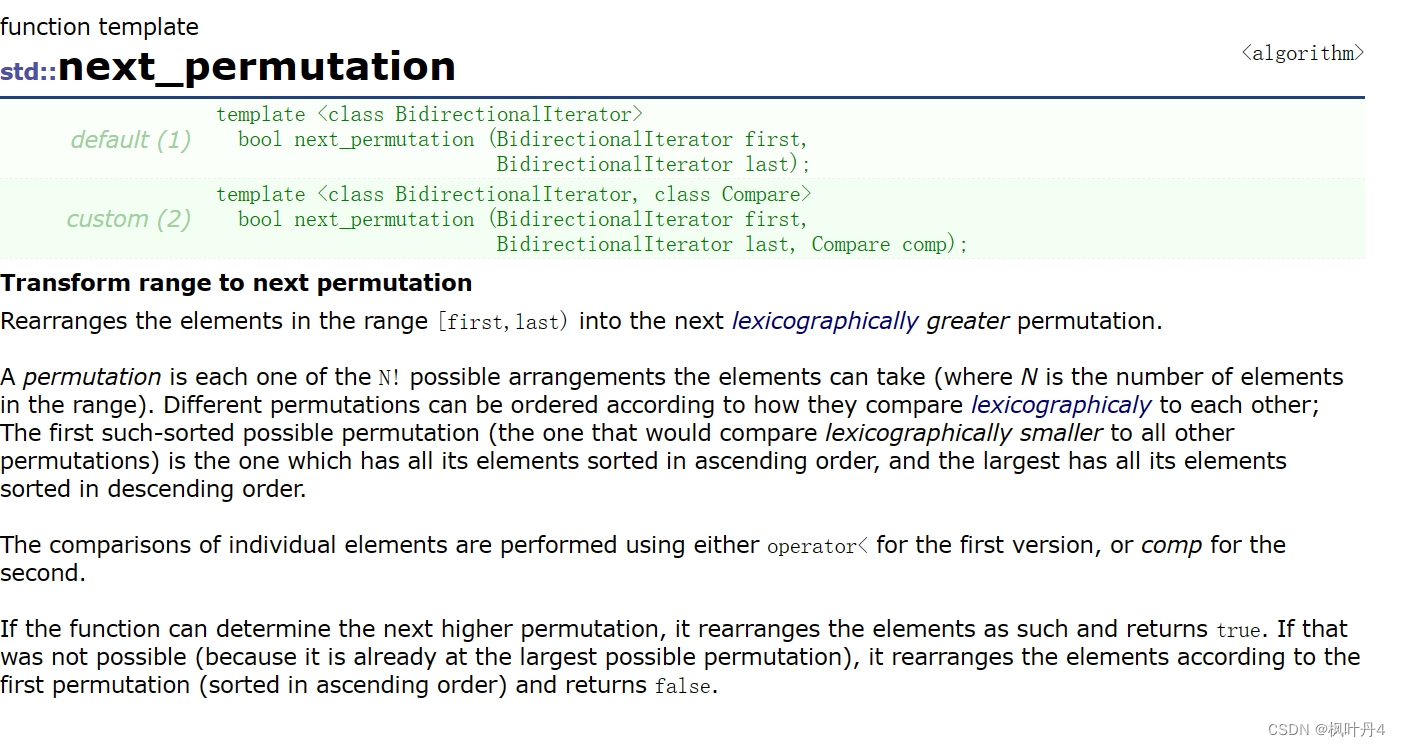
剩下的就不多说啦!自己探索叭!