转载:线程池详解(通俗易懂超级好)_拉格朗日(Lagrange)的博客-CSDN博客_线程池
目录
基本概念
什么是线程池
线程池优点
线程池源码
ThreadPoolExecutor
参数解释
具体使用
线程池的工作原理
线程池的参数
任务队列(workQueue)
线程工厂(threadFactory)
拒绝策略(handler)
功能线程池
定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
对比
总结
自定义线程池
实现步骤
任务类
线程类
线程池类
测试类
总结
线程池总结
其他
使用无界队列的线程池会导致内存飙升吗
基本概念
什么是线程池
线程池也是一种多线程的方式,处理过程就是将任务放到队列里面,通过线程池中的线程执行这些任务
线程池优点
(1)降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。
(2)提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。
(3)提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
线程池源码
ThreadPoolExecutor
线程池的真正实现类是 ThreadPoolExecutor,其构造方法有如下4种:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
threadFactory, defaultHandler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}参数解释
- corePoolSize(必需):核心线程数。默认情况下,核心线程会一直存活,但是当将 allowCoreThreadTimeout 设置为 true 时,核心线程也会超时回收。
- maximumPoolSize(必需):线程池所能容纳的最大线程数。当活跃线程数达到该数值后,后续的新任务将会阻塞。
- keepAliveTime(必需):线程闲置超时时长。如果超过该时长,非核心线程就会被回收。如果将 allowCoreThreadTimeout 设置为 true 时,核心线程也会超时回收。
- unit(必需):指定 keepAliveTime 参数的时间单位。常用的有:TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS(毫秒)、TimeUnit.SECONDS(秒)、TimeUnit.MINUTES(分)。
- workQueue(必需):任务队列。通过线程池的 execute() 方法提交的 Runnable 对象将存储在该参数中。其采用阻塞队列实现。
- threadFactory(可选):线程工厂。用于指定为线程池创建新线程的方式。
- handler(可选):拒绝策略。当达到最大线程数时需要执行的饱和策略。
具体使用
// 创建线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
sPoolWorkQueue,
sThreadFactory);
// 向线程池提交任务
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
... // 线程执行的任务
}
});
// 关闭线程池
threadPool.shutdown(); // 设置线程池的状态为SHUTDOWN,然后中断所有没有正在执行任务的线程
threadPool.shutdownNow(); // 设置线程池的状态为 STOP,然后尝试停止所有的正在执行或暂停任务的线程,并返回等待执行任务的列表线程池的工作原理
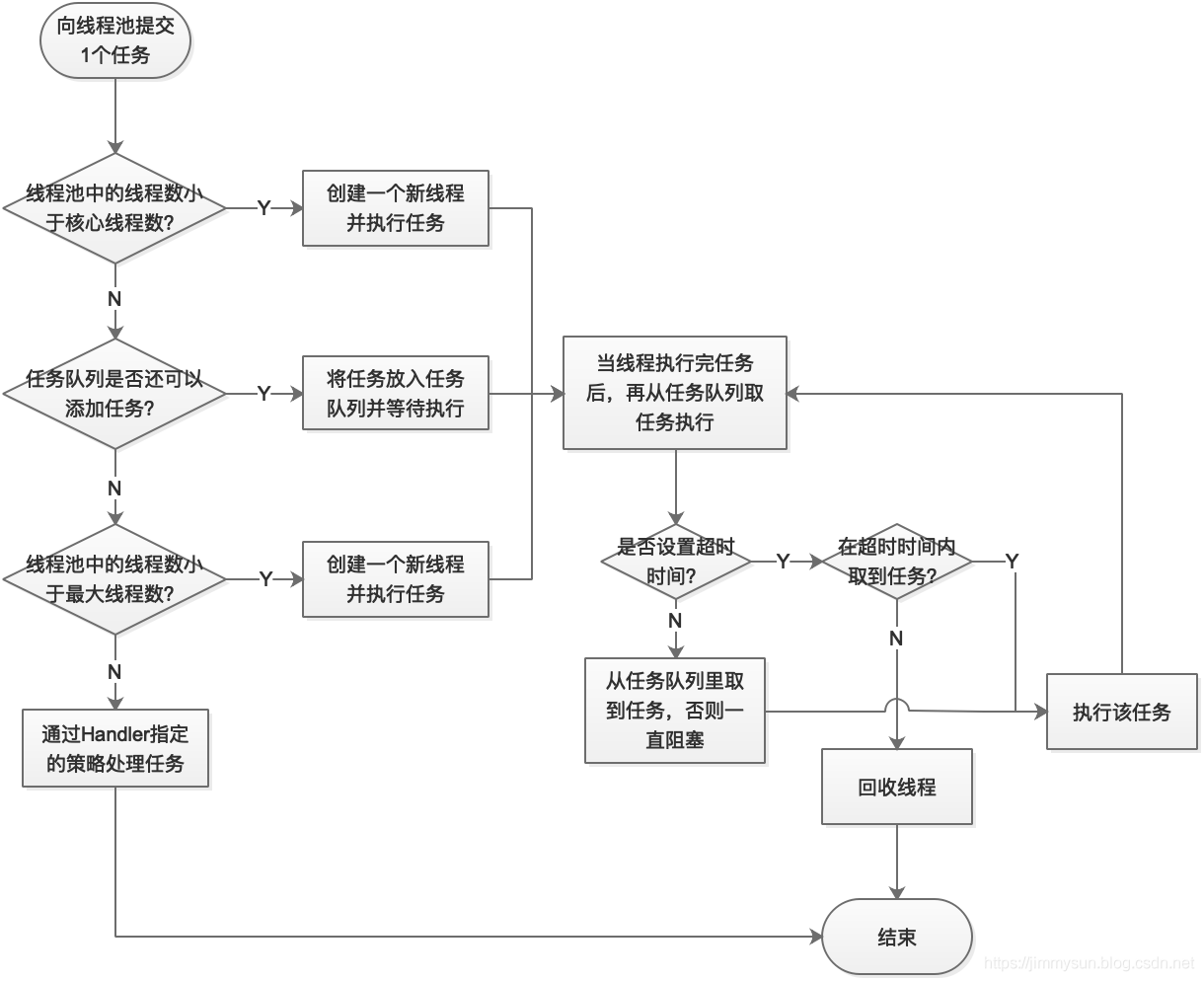
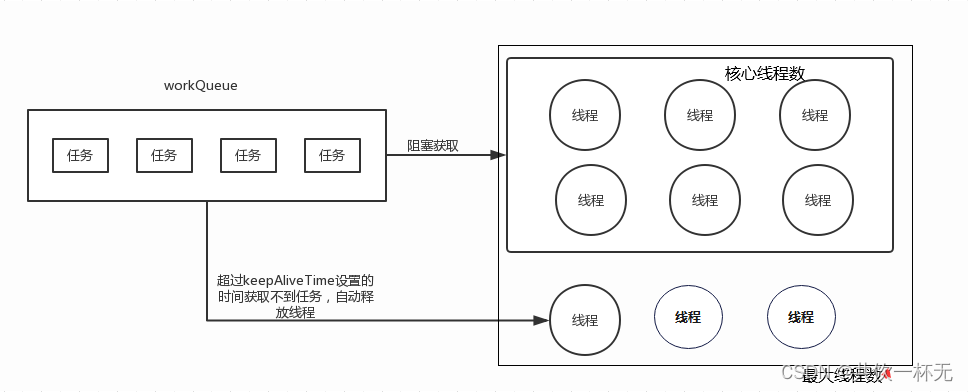
线程池的参数
任务队列(workQueue)
任务队列是基于阻塞队列实现的,即采用生产者消费者模式,在 Java 中需要实现 BlockingQueue 接口。但 Java 已经为我们提供了 7 种阻塞队列的实现:
- ArrayBlockingQueue:一个由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列(数组结构可配合指针实现一个环形队列)。
- LinkedBlockingQueue: 一个由链表结构组成的有界阻塞队列,在未指明容量时,容量默认为 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
- PriorityBlockingQueue: 一个支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列,对元素没有要求,可以实现 Comparable 接口也可以提供 Comparator 来对队列中的元素进行比较。跟时间没有任何关系,仅仅是按照优先级取任务。
- DelayQueue:类似于PriorityBlockingQueue,是二叉堆实现的无界优先级阻塞队列。要求元素都实现 Delayed 接口,通过执行时延从队列中提取任务,时间没到任务取不出来。
- SynchronousQueue: 一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,消费者线程调用 take() 方法的时候就会发生阻塞,直到有一个生产者线程生产了一个元素,消费者线程就可以拿到这个元素并返回;生产者线程调用 put() 方法的时候也会发生阻塞,直到有一个消费者线程消费了一个元素,生产者才会返回。
- LinkedBlockingDeque: 使用双向队列实现的有界双端阻塞队列。双端意味着可以像普通队列一样 FIFO(先进先出),也可以像栈一样 FILO(先进后出)。
- LinkedTransferQueue: 它是ConcurrentLinkedQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue 和 SynchronousQueue 的结合体,但是把它用在 ThreadPoolExecutor 中,和 LinkedBlockingQueue 行为一致,但是是无界的阻塞队列。
注意有界队列和无界队列的区别:如果使用有界队列,当队列饱和时并超过最大线程数时就会执行拒绝策略;而如果使用无界队列,因为任务队列永远都可以添加任务,所以设置 maximumPoolSize 没有任何意义。
线程工厂(threadFactory)
线程工厂指定创建线程的方式,需要实现 ThreadFactory 接口,并实现 newThread(Runnable r) 方法。该参数可以不用指定,Executors 框架已经为我们实现了一个默认的线程工厂:
/**
* The default thread factory.
*/
private static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}拒绝策略(handler)
当线程池的线程数达到最大线程数时,需要执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略需要实现 RejectedExecutionHandler 接口,并实现 rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) 方法。不过 Executors 框架已经为我们实现了 4 种拒绝策略:
- AbortPolicy(默认):丢弃任务并抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常。
- CallerRunsPolicy:由调用线程处理该任务。
- DiscardPolicy:丢弃任务,但是不抛出异常。可以配合这种模式进行自定义的处理方式。
- DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃队列最早的未处理任务,然后重新尝试执行任务。
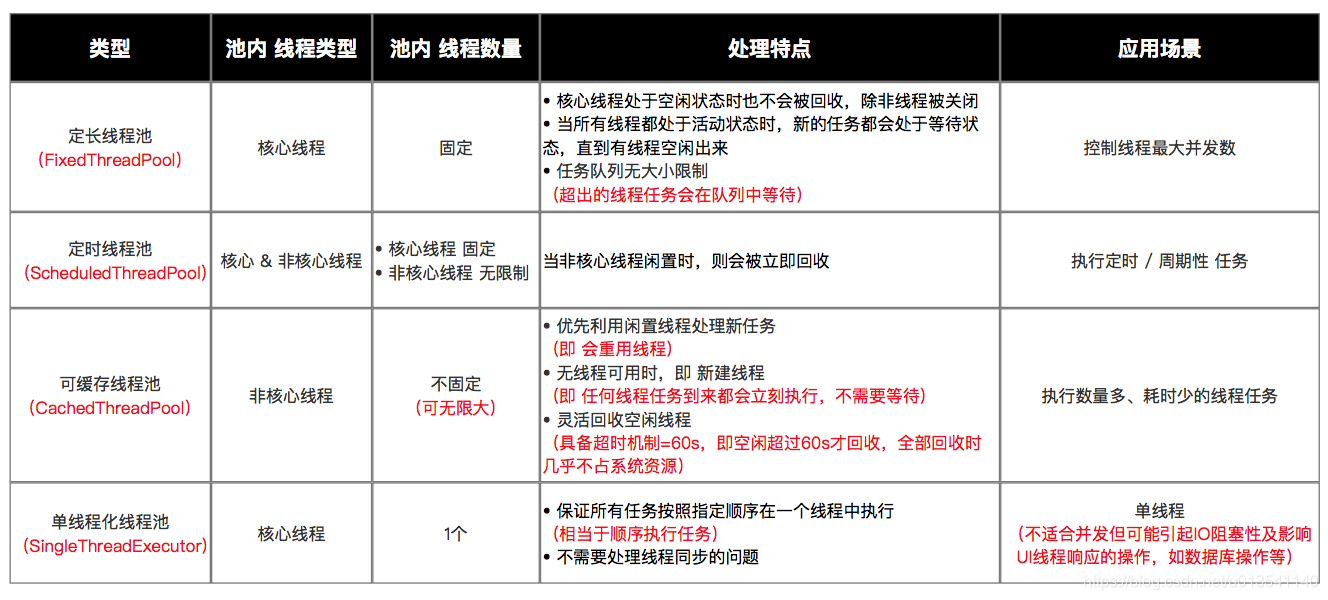
功能线程池
嫌上面使用线程池的方法太麻烦?其实Executors已经为我们封装好了 4 种常见的功能线程池,如下:
- 定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
- 定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
- 可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
- 单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
定长线程池(FixedThreadPool)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}- 特点:只有核心线程,线程数量固定,执行完立即回收,任务队列为链表结构的有界队列。
- 应用场景:控制线程最大并发数。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建定长线程池对象 & 设置线程池线程数量固定为3
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
fixedThreadPool.execute(task);定时线程池(ScheduledThreadPool )
创建方法的源码:
private static final long DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS = 10L;
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(
int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}- 特点:核心线程数量固定,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置 10ms 后回收,任务队列为延时阻塞队列。
- 应用场景:执行定时或周期性的任务。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建 定时线程池对象 & 设置线程池线程数量固定为5
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
scheduledThreadPool.schedule(task, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 延迟1s后执行任务
scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(task,10,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);// 延迟10ms后、每隔1000ms执行任务可缓存线程池(CachedThreadPool)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}- 特点:无核心线程,非核心线程数量无限,执行完闲置 60s 后回收,任务队列为不存储元素的阻塞队列。
- 应用场景:执行大量、耗时少的任务。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建可缓存线程池对象
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
cachedThreadPool.execute(task);单线程化线程池(SingleThreadExecutor)
创建方法的源码:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));
}- 特点:只有 1 个核心线程,无非核心线程,执行完立即回收,任务队列为链表结构的有界队列。
- 应用场景:不适合并发但可能引起 IO 阻塞性及影响 UI 线程响应的操作,如数据库操作、文件操作等。
使用示例:
// 1. 创建单线程化线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 2. 创建好Runnable类线程对象 & 需执行的任务
Runnable task =new Runnable(){
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行任务啦");
}
};
// 3. 向线程池提交任务
singleThreadExecutor.execute(task);对比
获取ExecutorService可以利用JDK中的Executors 类中的静态方法,常用获取方式如下:
static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() 创建一个默认的线程池对象,里面的线程可重用,且在第一次使用时才创建
static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
线程池中的所有线程都使用ThreadFactory来创建,这样的线程无需手动启动,自动执行;
static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) 创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池
static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池且线程池中的所有线程都使用ThreadFactory来创建。
static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor()
创建一个使用单个 worker 线程的 Executor,以无界队列方式来运行该线程。
static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
创建一个使用单个 worker 线程的 Executor,且线程池中的所有线程都使用ThreadFactory来创建。
总结
Executors 的 4 个功能线程池虽然方便,但现在已经不建议使用了,而是建议直接通过使用 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。
- FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadExecutor:主要问题是堆积的请求处理队列均采用 LinkedBlockingQueue,可能会耗费非常大的内存,甚至 OOM。
- CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool:主要问题是线程数最大数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建数量非常多的线程,甚至 OOM。
自定义线程池
实现步骤
1:编写任务类(MyTask),实现Runnable接口;
2:编写线程类(MyWorker),用于执行任务,需要持有所有任务;
3:编写线程池类(MyThreadPool),包含提交任务,执行任务的能力;
4:编写测试类(MyTest),创建线程池对象,提交多个任务测试;
任务类
package com.itheima.demo01;
/*
需求:
自定义线程池练习,这是任务类,需要实现Runnable;
包含任务编号,每一个任务执行时间设计为0.2秒
*/
public class MyTask implements Runnable{
private int id;
//由于run方法是重写接口中的方法,因此id这个属性初始化可以利用构造方法完成
public MyTask(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("线程:"+name+" 即将执行任务:"+id);
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程:"+name+" 完成了任务:"+id);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTask{" +
"id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
线程类
package com.itheima.demo01;
import java.util.List;
/*
需求:
编写一个线程类,需要继承Thread类,设计一个属性,用于保存线程的名字;
设计一个集合,用于保存所有的任务;
*/
public class MyWorker extends Thread{
private String name;//保存线程的名字
private List<Runnable> tasks;
//利用构造方法,给成员变量赋值
public MyWorker(String name, List<Runnable> tasks) {
super(name);
this.tasks = tasks;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//判断集合中是否有任务,只要有,就一直执行任务
while (tasks.size()>0){
Runnable r = tasks.remove(0);
r.run();
}
}
}
线程池类
package com.itheima.demo01;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/*
这是自定义的线程池类;
成员变量:
1:任务队列 集合 需要控制线程安全问题
2:当前线程数量
3:核心线程数量
4:最大线程数量
5:任务队列的长度
成员方法
1:提交任务;
将任务添加到集合中,需要判断是否超出了任务总长度
2:执行任务;
判断当前线程的数量,决定创建核心线程还是非核心线程
*/
public class MyThreadPool {
// 1:任务队列 集合 需要控制线程安全问题
private List<Runnable> tasks = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList<>());
//2:当前线程数量
private int num;
//3:核心线程数量
private int corePoolSize;
//4:最大线程数量
private int maxSize;
//5:任务队列的长度
private int workSize;
public MyThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maxSize, int workSize) {
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.workSize = workSize;
}
//1:提交任务;
public void submit(Runnable r){
//判断当前集合中任务的数量,是否超出了最大任务数量
if(tasks.size()>=workSize){
System.out.println("任务:"+r+"被丢弃了...");
}else {
tasks.add(r);
//执行任务
execTask(r);
}
}
//2:执行任务;
private void execTask(Runnable r) {
//判断当前线程池中的线程总数量,是否超出了核心数,
if(num < corePoolSize){
new MyWorker("核心线程:"+num,tasks).start();
num++;
}else if(num < maxSize){
new MyWorker("非核心线程:"+num,tasks).start();
num++;
}else {
System.out.println("任务:"+r+" 被缓存了...");
}
}
}
测试类
package com.itheima.demo01;
/*
测试类:
1: 创建线程池类对象;
2: 提交多个任务
*/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1:创建线程池类对象;
MyThreadPool pool = new MyThreadPool(2,4,20);
//2: 提交多个任务
for (int i = 0; i <30 ; i++) {
//3:创建任务对象,并提交给线程池
MyTask my = new MyTask(i);
pool.submit(my);
}
}
}
总结
主要还是线程池中的逻辑,定义阻塞队列,每当有任务执行的时候,添加到队列中,如果当前线程数量小于核心线程数,就被核心线程执行,如果小于最大线程数,就被新创建的线程执行,否则的话缓存在队列里面,队列里面满了的话,就执行拒绝策略
线程池总结
1:利用Executors工厂类的静态方法,创建线程池对象;
2:编写Runnable或Callable实现类的实例对象;
3:利用ExecutorService的submit方法或ScheduledExecutorService的schedule方 法提交并执行线程任务
4:如果有执行结果,则处理异步执行结果(Future)
5:调用shutdown()方法,关闭线程池
其他
使用无界队列的线程池会导致内存飙升吗
LinkedBlockingQueue默认的最大任务数量是Integer.MAX_VALUE,非常大,可以理解为无限大吧;但是存在这种情况,当每个线程获取到一个任务后,执行时间比较长,导致workQueue里积压的任务越来越多,机器的内存使用不停的飙升,最后也会导致OOM