广播机制
1.广播机制
1.1概述
1.1.1引入
1.广播的生活案例
- 记得以前读书的时候,每个班级都会有一个挂在墙上的大喇叭,用来广播一些通知,比如,开学要去搬书,广播: "每个班级找几个同学教务处拿书",发出这个广播后,所有同学都会在同一时刻收到这条广播通知,收到,但不是每个同学都会去搬书,一般去搬书的都是班里的"大力士",这群"大力士"接到这条广播后就会动身去把书搬回可是!——好吧,上面这个就是一个广播传递的一个很形象的例子:
- 大喇叭--> 发送广播 --> 所有学生都能收到广播 --> 大力士处理广播
2.生活中广播特点
(1)广播发送者
- 发一个或者多个
- 不关心谁接收
- 实时性
(2)广播接收者
- 接收一个或者多个
- 执行相应操作
- 不关心谁发的
- 实时性
3.广播的好处
- 广播的发送者和接收者事先是不需要知道对方的存在的,这样带来的好处便是:系统的各个组件可以松耦合地组织在一起,这样系统就具有高度的可扩展性,容易与其它系统进行集成。
1.1.2Android中的广播
1.安卓中的广播
- 如:手机接到一条短信,就会产生一个收到短消息的事件。接到一个电话,就会产生一个接到电话的事件。拍摄照片后就会产生一个拍摄照片的事件。
- 在Android中,有一些操作完成以后,会发送广播,比如说发出一条短信,或打出一个电话,比如电池的使用状态,电话的接收和短信的接收都会产生一个广播。Android系统内部产生这些事件后广播这些事件,至于广播接收对象是否关心这些事件,以及它们如何处理这些事件,都由广播接收对象自己决定。

2.系统广播
- 电池的状态(如:电量不足)
- 短信的接收和发送
- 电话的接听和拨打
- 系统闹钟
- 系统垃圾文件占用内存过多
3.广播的原理

4.广播机制
- 检查注册时候的IntentFilter中的Action是不是和广播Intent中的action是一致的
- 一致的话使用onReceive相匹配
1.1.3广播接收器
1.BroadcastReceiver
- 监听系统或者是应用广播
2.BroadcastReceiver介绍
- 安卓中四大组件之一
- 本质:全局的监听器(OnXxxListener是程序级别的事件监听器)
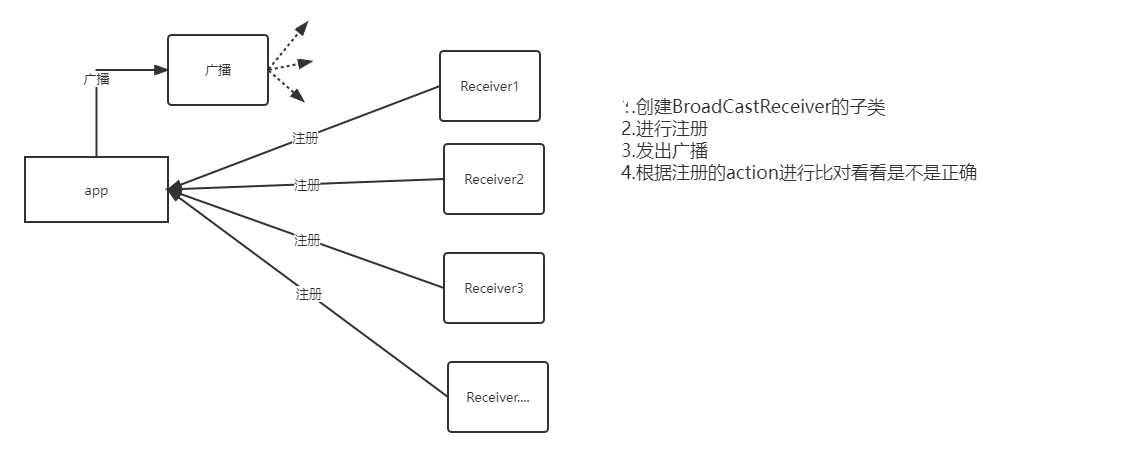
3.如何接收广播?
- 先注册,注册方式有多种
4.系统广播接收器创建步骤
关键是注册
- 创建BroadcaseReceiver的子类,重写onReceive方法
- 注册,编写intentfilter标签设置action的值
- 广播发出后,对比intentfilter中的action的值是不是一致的,一致就调用onReceive方法创建接收器对象否则不创建
总之,接收的事件处理逻辑放到onReceive方法中就可以。调用完onReceive方法之后就失效了。
5.发送本地广播的创建方式
- 创建BroadcaseReceiver的子类,重写onReceive方法
- 注册,编写intentfilter标签设置action的值
- 创建Intent,设置action属性,使用sendBroadcast(intent)发送广播
- 广播发出后,对比intentfilter中的action的值是不是一致的,一致就调用onReceive方法创建接收器对象否则不创建
1.1.4自定义广播接收器
- Intent就相当于无线电的信号,里面有很多正要的信息。
//第一个广播 接收器
public class MyBroadcastReceiver1 extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
}
}
1.1.5常见的系统权限
发短信要有发短信的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_SMS“/>
接收开机广播的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>

1.1.6常见的广播Action

1.1.7发送系统级广播
1.广播类型
- 标准广播
- 异步执行,不一定哪个先接收到,几乎是同时
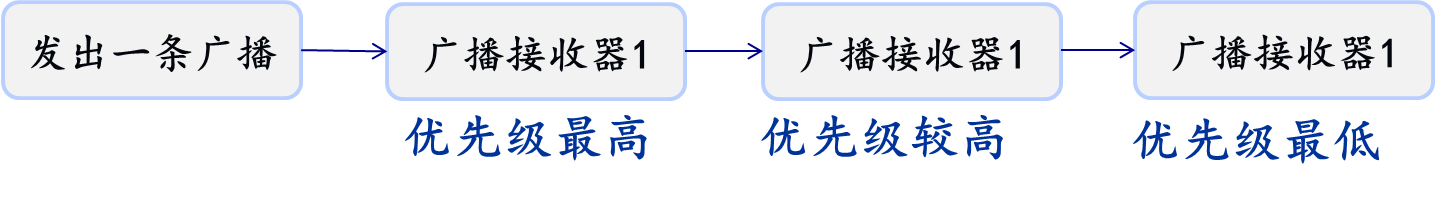
- 有序广播
- 根据优先级和注册的顺序一个一个的接收,只有接受并处理完了才可以继续往下传播
2.创建方式
- 标准广播:context的sendBroadcast(Intent)
- 有序广播:context的sendOrderedBroadcast(Intent,str)
- <intent-filter>元素的android:priority属性中设置
- 在IntentFilter对象的setPriority()设置
- 取值范围:-1000到1000,数越大,优先级越高
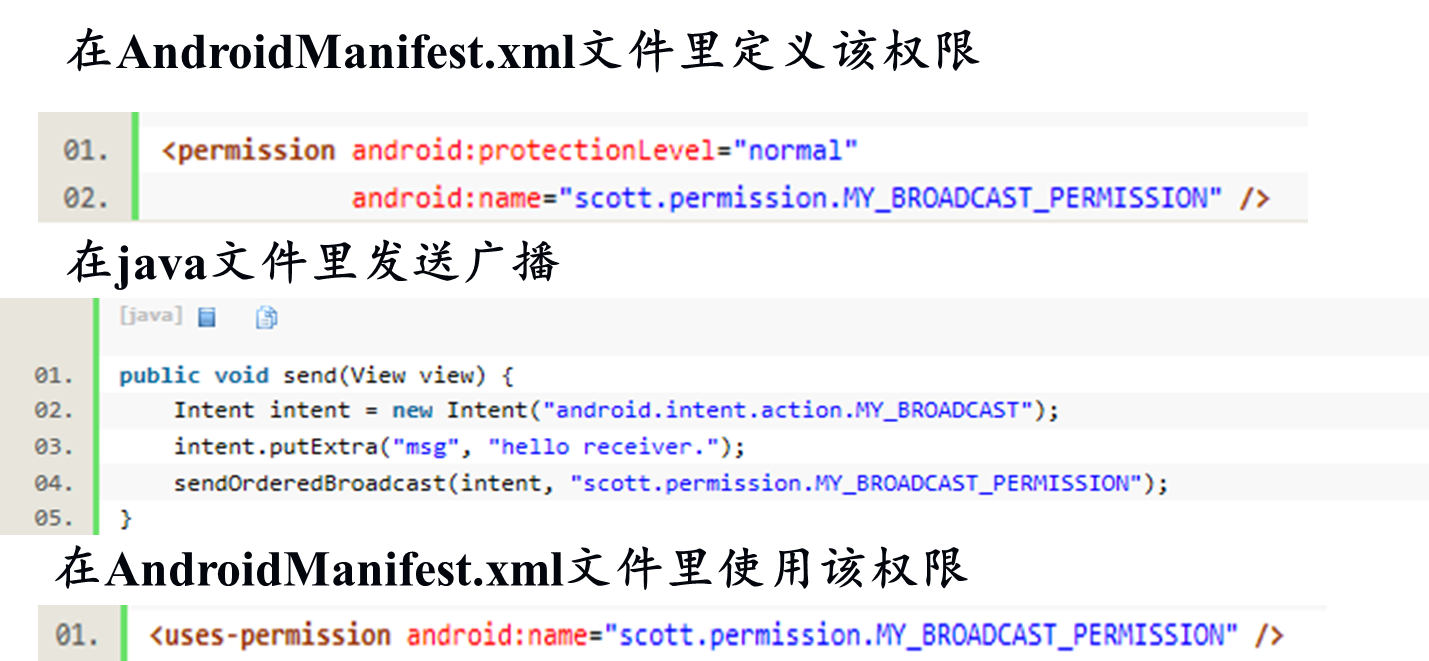
- str,权限参数,如果为null则表示不要求接收者声明指定的权限,如果不为null,则表示接收者若要接收此广播,需声明指定权限。
3.有序广播接收器
- setResultExtras(Bundle)方法将一个Bundle对象设置为结果集对象,传给下一个接收者。
- 下一个接收者通过getResultExtras()可以获取上一个接收者存入的数据
public final Bundle getResultExtras(boolean makeMap)
makeMap如果为true,如果当前的Bundle为null,将创建一个空的Bundle对象;否则需要准备好接收一个空Bundle对象。用的时候设置成true就行了
- abortBroadcast(),阻断广播不往下传播
4.有序和无序的比较
| 标准 | 有序 |
| 异步 | 反之 |
| 不可以终止 | 反之 |
| 无法传递结果 | 反之 |
| 发送方式是sendBroadcast(intent) | 反之 |
1.1.8本地广播(重点)
1.优缺点
- 高效
- 防止泄露
- 安全性更高
2.如何创建
- 只能采用动态的注册方式
- 必须在一个包下
3.LocalBroadcastManager
- 局部通知管理器,这种通知的好处是安全性高,效率也高,适合局部通信。
4.获取LocalBroadcastManager的实例对象
LocalBroadcastManager localBManager =
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance( this ) ;
5.注册方式
- LocalBroadcastManager对象的registerReceiver()注册广播
6.创建步骤(重点)
- 创建intent,设置action
- 可选,设置intent的数据
- 创建IntentFilter,设置action
- 创建自定义的BroadCastReceiver对象
- 获取LocalBroadcastManager对象
- 根据LocalBroadcastManager对象调用registerBroadcast(接收器对象,intentfilter)注册
- LocalBroadcastManager对象的sendBroadcast(intent)发送广播
注意:
- 和一般的不同的就在于5,6,7步
- 本地广播无法通过静态注册来接收
- 本地广播相比系统全局广播更加高效
7.取消注册的方法
- LocalBroadcastManager对象的unregisterReceiver(localReceiver);方法
1.2注册方式
两种注册方式:
- 动态注册:在代码里注册(万能)
- 静态注册:在AndroidManifest.xml中注册;
1.2.1静态注册
1.注册方式
- AndroidManifest.xml中注册。
- action指定要接收的广播事件
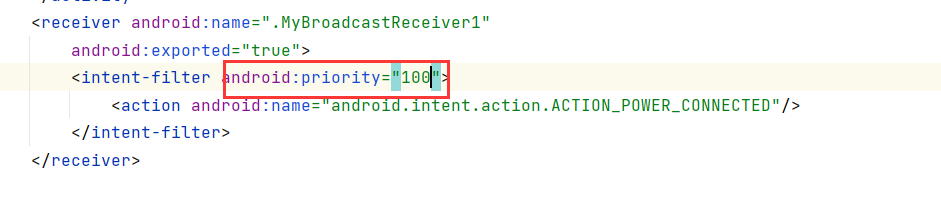
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver1"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.ACTION_POWER_CONNECTED"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
扩展:在顺序广播中可以指定优先级
2.优缺点
优点:不用启动程序就可以
1.2.2动态注册
1.注册方式
- 有两种代码的方式
- IntentFilter设置要监听的广播
- registerReceiver注册广播

2.IntentFilter的方法
| No | 方法 | 类型 | 描述 |
| 1 | public IntentFilter() | 构造 | 创建一个空的IntentFilter对象 |
| 2 | public IntentFilter(String action) | 构造 | 创建一个IntentFilter对象,并指定Action |
| 3 | public final void addAction(String action) | 普通 | 增加一个要过滤的Action |
| 4 | public final void addCategory(String category) | 普通 | 增加一个要过滤的Category |
| 5 | public final boolean hasAction(String action) | 普通 | 判断指定的Action是否存在 |
| 6 | public final boolean hasCategory(String category) | 普通 | 判断指定的Category是否存在 |
3.取消注册
- 一定要设置取消注册,不然的话在Activity或者是Service销毁的时候没有取消注册会报错的。

4.优缺点
优点:注册方式灵活,根据需要注册,常用于更新UI。
缺点:需要程序启动才可以接收广播,假如我们需要程序 没有启动,但是还是能接收广播的话,那么就需要注册静态广播了!
也就是广播接收器必须是启动着的。
1.2.3静态注册案例-接收开机广播
1.案例:接收开机的广播
- 创建自定义的BroadcastReceiver用于处理监听到的系统广播。
//接收系统开机的广播事件
public class BootCompleteReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "开机成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
- 注册广播接收器。
<receiver android:name=".BootCompleteReceiver"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
- 开启权限。
<!--接收开机广播的权限-->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
- 重启手机。
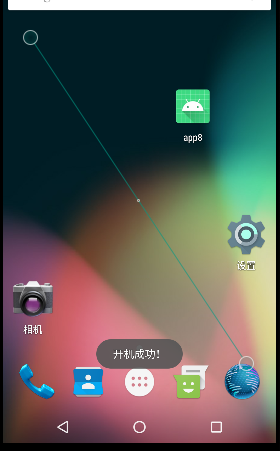
1.2.4静/动态注册案例-发送广播
1.动态注册的方式发送标准广播
- 发送标准广播
- 设置要发送的数据
- 不带权限
(1)布局文件
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送标准广播"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:onClick="sendBroadcast" />
(2)Java代码
//点击按钮发送标准广播
public void sendBroadcast(View view) {
//设置发送的数据
Intent intent =new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.lxz.app8");
intent.putExtra("code","我是张三!");
//动态注册
IntentFilter filter=new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction("com.lxz.app8");
BroadcastReceiver1 receiver=new BroadcastReceiver1();
registerReceiver(receiver,filter);
//发送广播
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
(3)自定义广播接收器
//接收标准广播
public class BroadcastReceiver1 extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
(4)效果图

2.在1的基础上设置权限
(1)manifest中定义和设置权限
<!--定义权限-->
<permission android:name="com.lxz.app.permission"/>
<!--设置权限-->
<uses-permission android:name="com.lxz.app.permission"/>
(2)布局文件
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送标准广播(带权限)"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:onClick="sendBroadcast2" />
(3)发送广播的Java代码
//点击按钮发送标准广播(带权限)
public void sendBroadcast2(View view) {
//设置发送的数据
Intent intent =new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.lxz.app8");
intent.putExtra("code","我是张三!有权限!");
//动态注册
IntentFilter filter=new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction("com.lxz.app8");
BroadcastReceiver1 receiver=new BroadcastReceiver1();
registerReceiver(receiver,filter);
//设置权限
String str="com.lxz.app.permission";
//发送广播
sendBroadcast(intent,str);
}
(4)广播接收器
//接收标准广播
public class BroadcastReceiver1 extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
(5)效果图

3.有序广播的测试
- 采用静态注册的方式
- 设置优先级
(1)布局文件
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送有序广播"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:onClick="sendOrderBroadcast1" />
(2)发送有序广播的方法
//点击按钮发送有序广播
public void sendOrderBroadcast1(View view) {
//设置发送的数据
Intent intent =new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.lxz.app8");
intent.putExtra("code","请依次报号!");
//发送广播-参数2代表的是自定义的权限
sendOrderedBroadcast(intent,null);
}
(3)注册代码
<!--注册广播-->
<receiver android:name=".BroadcastOrderReceiver"
android:exported="true"
>
<intent-filter android:priority="0">
<action android:name="com.lxz.app8"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name=".BroadcastOrderReceiver1"
android:exported="true"
>
<intent-filter android:priority="1">
<action android:name="com.lxz.app8"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name=".BroadcastOrderReceiver2"
android:exported="true"
>
<intent-filter android:priority="2">
<action android:name="com.lxz.app8"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
<receiver android:name=".BroadcastOrderReceiver3"
android:exported="true"
>
<intent-filter android:priority="3">
<action android:name="com.lxz.app8"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
(4)广播接收者
- 注册顺序从上到下
- 优先级从下到上
- 响应的时候从下到上
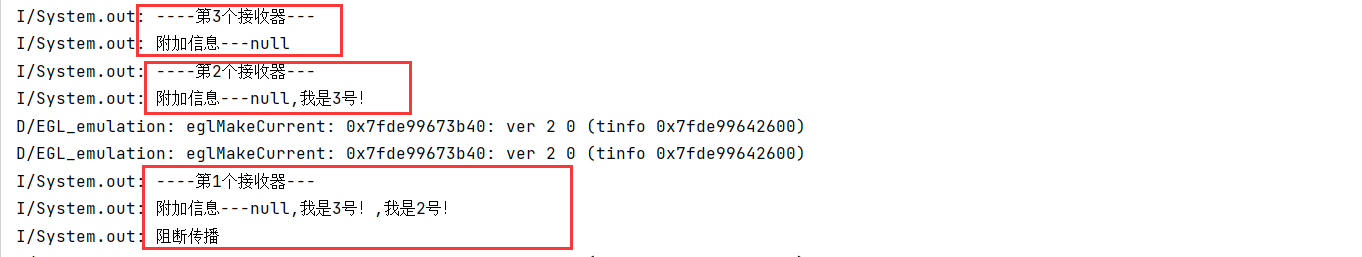
- 代码从下到上依次为
public class BroadcastOrderReceiver3 extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code")+"我是3号", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Bundle bundle=getResultExtras(true);
System.out.println("----第3个接收器---");
System.out.println("附加信息---"+bundle.getString("other"));
bundle.putString("other",bundle.getString("other")+",我是3号!");
setResultExtras(bundle);
}
}
public class BroadcastOrderReceiver2 extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code")+"我是2号", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Bundle bundle=getResultExtras(true);
System.out.println("----第2个接收器---");
System.out.println("附加信息---"+bundle.getString("other"));
bundle.putString("other",bundle.getString("other")+",我是2号!");
setResultExtras(bundle);
}
}
public class BroadcastOrderReceiver1 extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code")+"我是1号", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Bundle bundle=getResultExtras(true);
System.out.println("----第1个接收器---");
System.out.println("附加信息---"+bundle.getString("other"));
bundle.putString("other",bundle.getString("other")+",我是1号!");
setResultExtras(bundle);
//停止广播的传递
abortBroadcast();
System.out.println("阻断传播");
}
}
public class BroadcastOrderReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code")+"我是0号", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Bundle bundle=getResultExtras(true);
System.out.println("----第0个接收器---");
System.out.println("附加信息---"+bundle.getString("other"));
}
}
(5)效果图

1.2.5本地广播案例-简单的发送和接收
1.参考代码
(1)布局文件代码
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送本地广播"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:onClick="localBroadcast" />
(2)发送本地广播的Java代码
//发送本地广播
public void localBroadcast(View view) {
//设置数据
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.lxz.localapp");
intent.putExtra("code","我是本地广播");
//动态注册
LocalBroadReceiver receiver=new LocalBroadReceiver();
IntentFilter filter=new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction("com.lxz.localapp");
LocalBroadcastManager manager=LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(getApplicationContext());
manager.registerReceiver(receiver,filter);
//发送广播
manager.sendBroadcast(intent);
}
(3)本地广播接收者的代码
//接收本地广播
public class LocalBroadReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(context, "接收信息:"+intent.getStringExtra("code"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
(4)效果图

1.2.6本地广播案例-仿qq下线
待实现
1.案例要求
- 像QQ一样,正在运行的QQ,如果我们用别的手机再次登陆自己的账号,前面这个是会提醒账户在别的终端登录,然后把我们打开的app都关掉,然后回到登陆页面。LoginActivity.java
- 注意:需要在模拟器中设置—应用-左上角— —打开应用信息—设置出现在其它应用上
2.参考代码
(1)项目目录结构
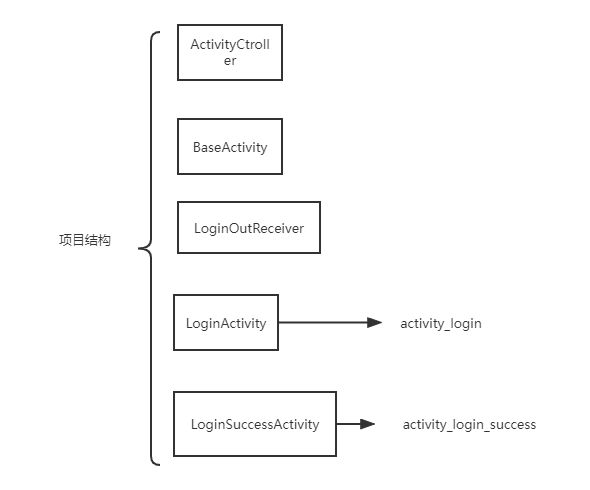
(2)ActivityCtroller代码。
- 用于管理所有的Activity
//Activity管理类
public class ActivityController {
//保存Activity
private static List<Activity> list=new ArrayList<>();
//添加Activity
public static void addActivity(Activity activity){
list.add(activity);
}
//删除Activity
public static void removeActivity(Activity activity){
list.remove(activity);
}
//结束所有的Activity
public static void finishAllActivity(){
for (Activity a:list){
if (!a.isFinishing()){
a.finish();
}
}
}
}
(3)BaseActivity,是登录成功界面的基类,可以注册BroadcastReceiver。
- 注意必须添加
- android.intent.category.DEFAULT
public class BaseActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private LoginOutReceiver receiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ActivityController.addActivity(this);
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
//注册广播
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction("com.lxz.loginout");
filter.addCategory("android.intent.category.DEFAULT");
receiver = new LoginOutReceiver();
registerReceiver(receiver, filter);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
if (receiver!=null){
unregisterReceiver(receiver);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}
(4)登录界面的Activity。
//仿qq下线
public class LoginActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_login);
}
//方法:登录
public void login(View view) {
EditText account=findViewById(R.id.account);
EditText password=findViewById(R.id.password);
System.out.println(account+","+password);
if (account.getText().toString().equals("root")&&password.getText().toString().equals("123456")){
Toast.makeText(this, "登录成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setClass(getApplicationContext(),LoginSuccessActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
finish();
}
else{
Toast.makeText(this, "账号或密码错误!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
(5)登录界面activity对应的布局文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".LoginActivity">
<TableLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:stretchColumns="1">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="text"
android:text="账号:"
android:textSize="30dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/account"
android:text="root"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="账号(root)"
android:inputType="text"
android:maxLines="1"
android:textSize="30dp" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="text"
android:text="密码:"
android:textSize="30dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="密码(123456)"
android:inputType="text"
android:maxLines="1"
android:text="123456"
android:textSize="30dp" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="login"
android:text="登录"
android:textSize="30dp" />
</LinearLayout>
(6)登录成功Activity,LoginSuccessActivity的代码。
- 发送广播
//登录成功后的界面
public class LoginSuccessActivity extends BaseActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_login_success);
//当登录后的Activity添加到管理类中去
ActivityController.addActivity(this);
}
//方法:强制下线(发布广播)
public void outlogin(View view) {
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.lxz.loginout");
intent.addCategory("android.intent.category.DEFAULT");
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}
(7)activity_login_success布局文件代码。
- 有一个强制下线的按钮。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".LoginSuccessActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="outlogin"
android:text="强制下线"
android:textSize="30dp" />
</LinearLayout>
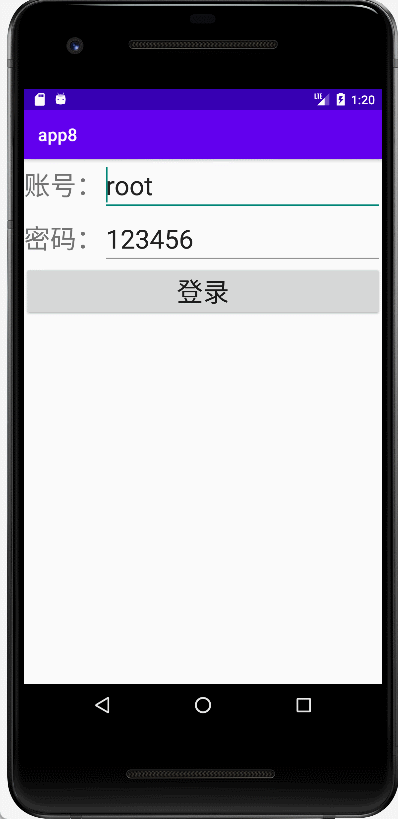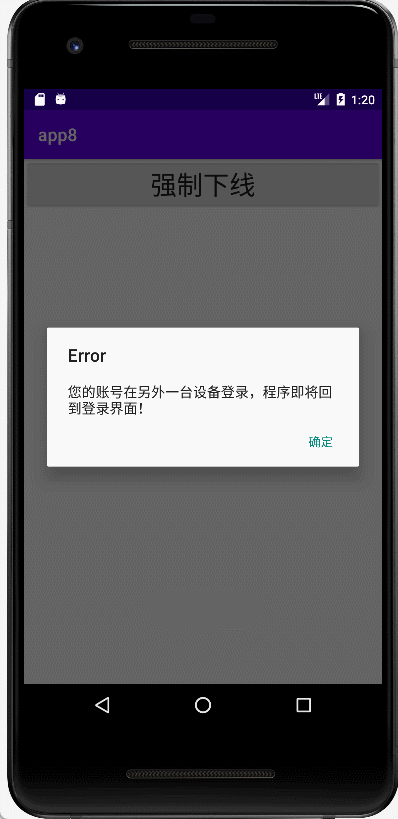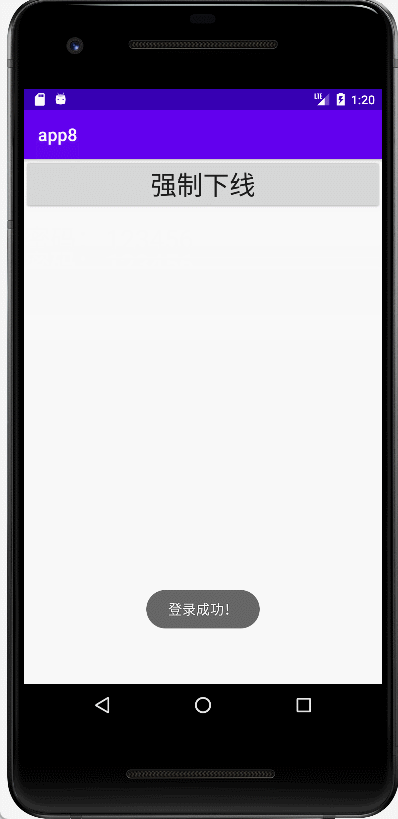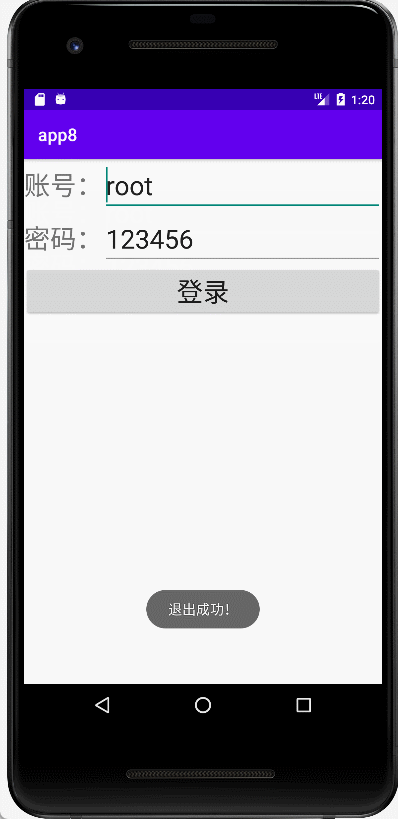
(8)LoginOutReceiver广播接收器代码。
- 设置一个Dialog用于弹窗
- 我目前测试了本地广播和系统广播发现本地广播的context会报错,可能是因为进程号不统一导致的。
//强制下线的界面
public class LoginOutReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder=new AlertDialog.Builder(context);
builder.setTitle("Error")
.setMessage("您的账号在另外一台设备登录,程序即将回到登录界面!")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) {
ActivityController.finishAllActivity();
Toast.makeText(context, "退出成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Intent intent1=new Intent();
intent1.setClass(context,LoginActivity.class);
context.startActivity(intent1);
}
})
;
builder.create().show(); }
}
(9)效果图
1.3生命周期
1.3.1生命周期图
1.3.2onReceive注意事项
onReceive方法中不能加入比较耗时的操作,否则系统会认为程序无响应,不要在广播里添加过多逻辑或者进行任何耗时操作,因为在广播中是不允许开辟线程的, 当onReceiver( )方法运行较长时间(超过10秒)还没有结束的话,那么程序会报错(ANR), 广播更多的时候扮演的是一个打开其他组件的角色,比如启动Service,Notification提示, Activity等。如果需要完成一项比较耗时的工作,可以通过发送Intent给Activity或Service,由Activity或Service来完成。