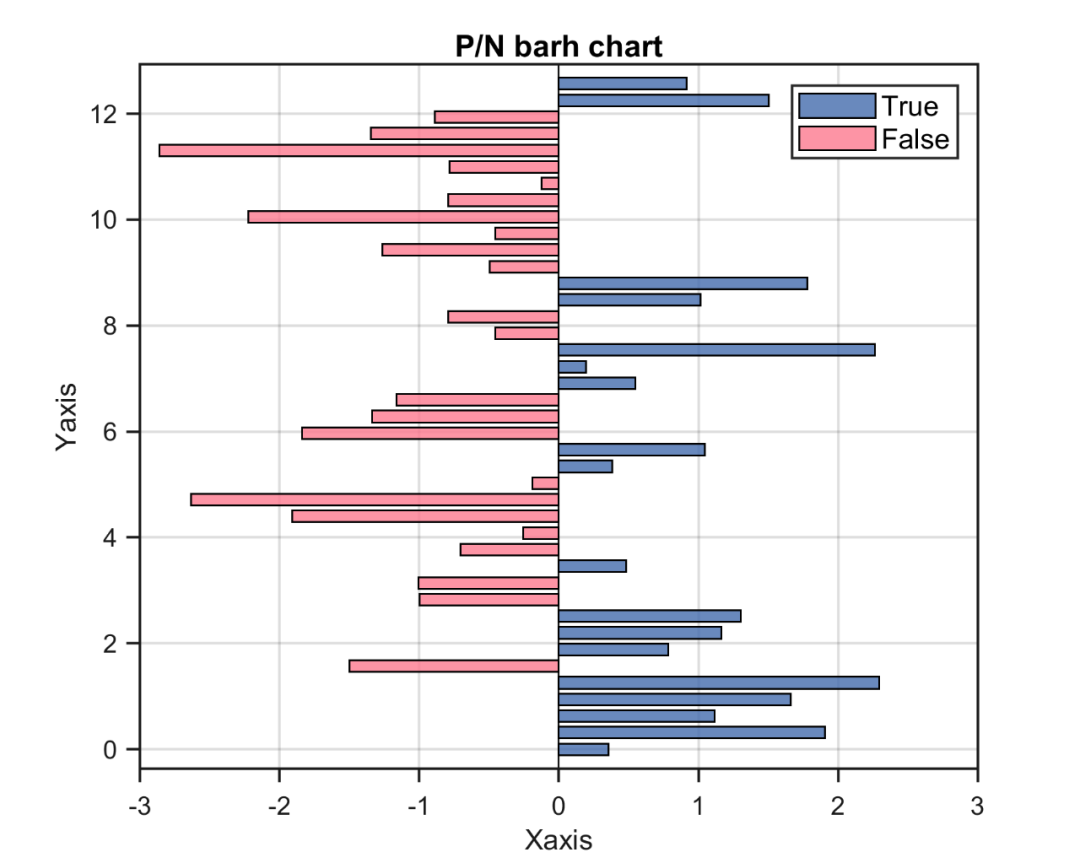
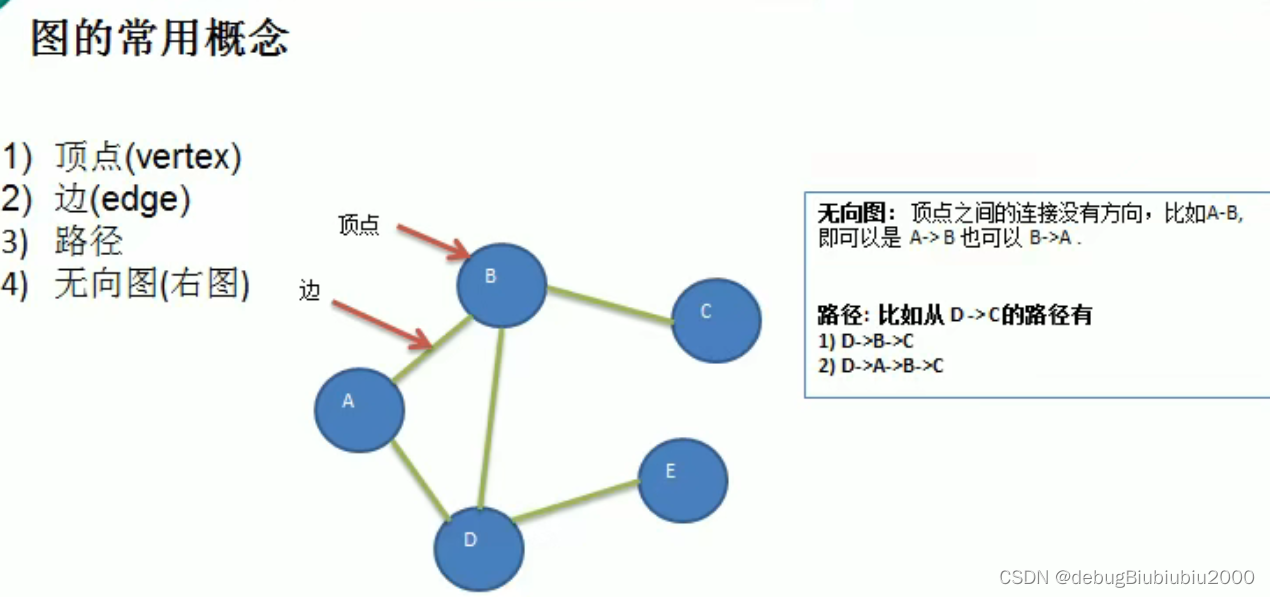
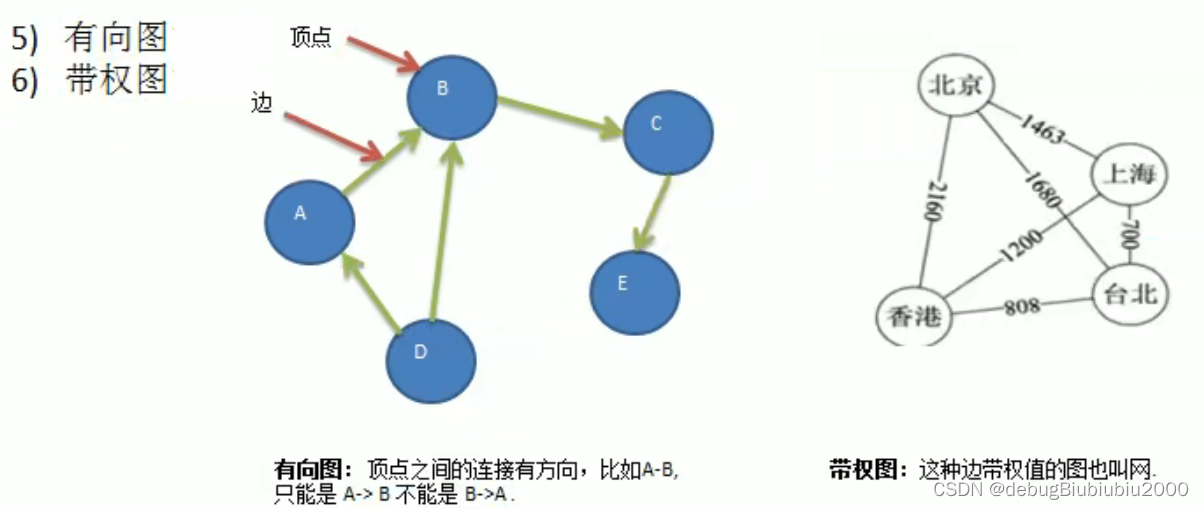
图
基本介绍

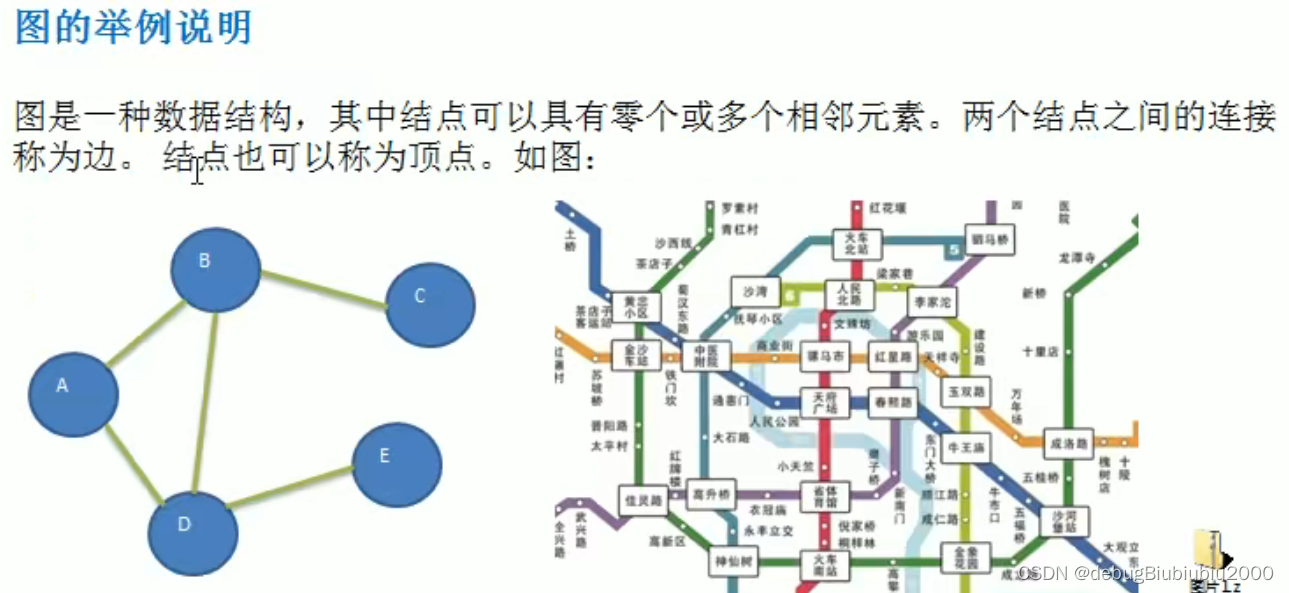
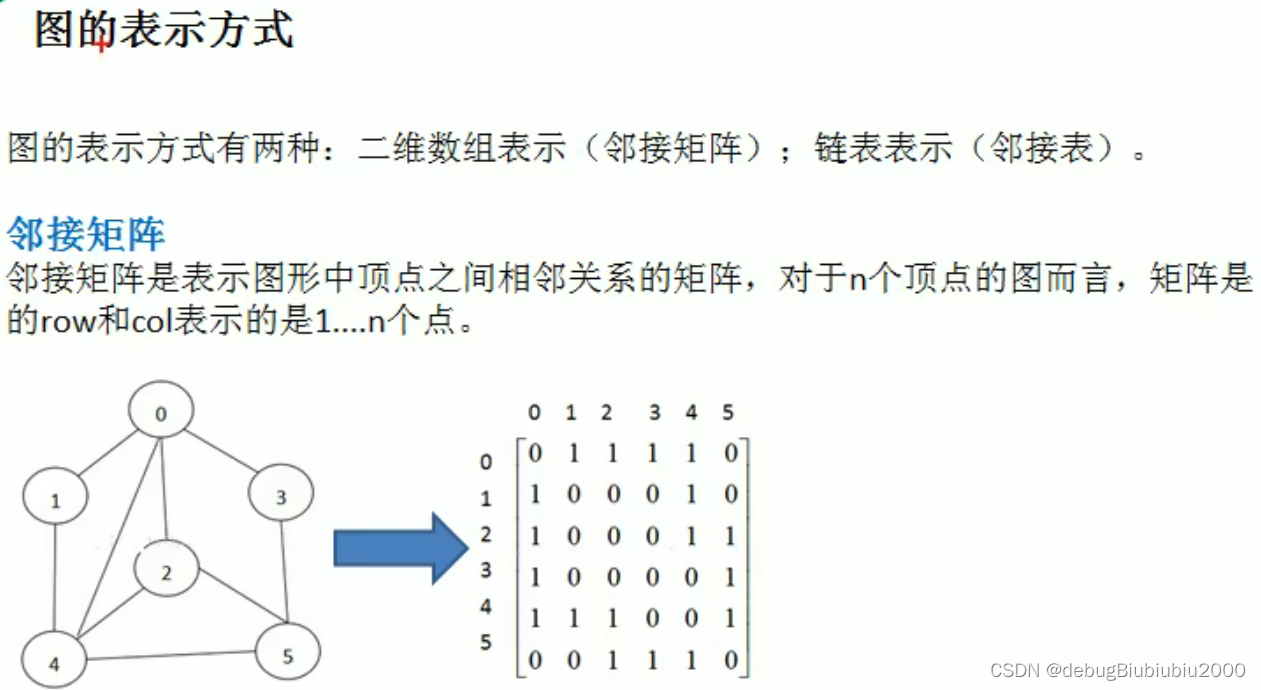
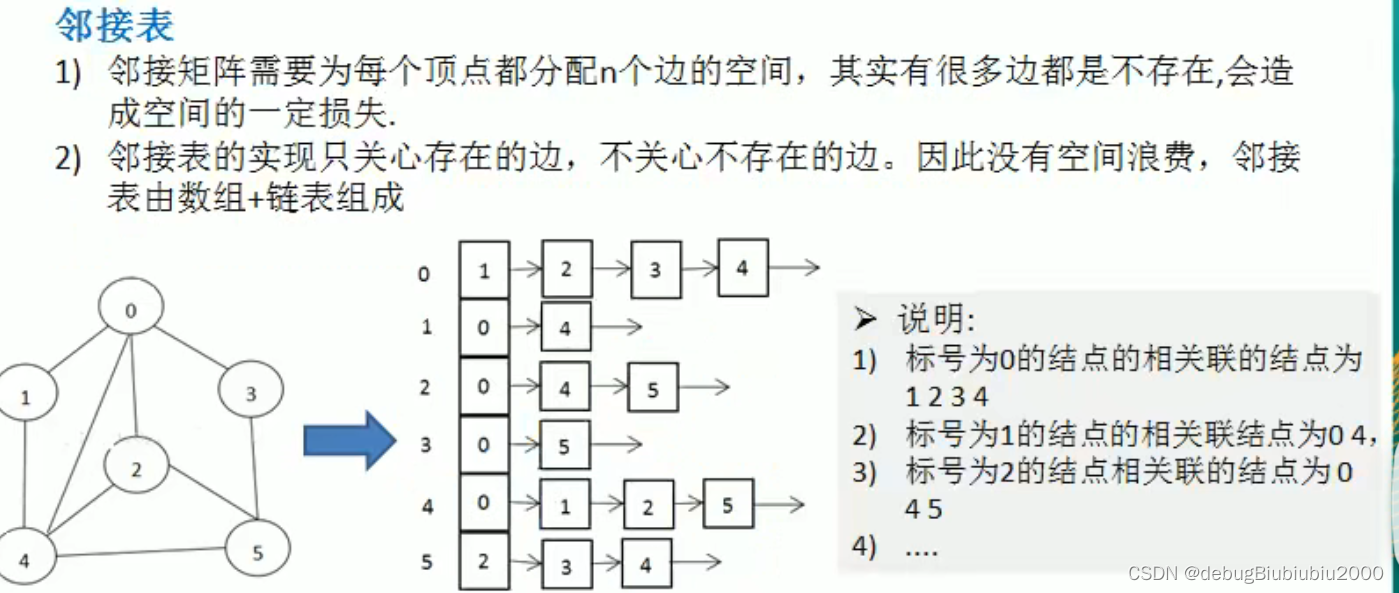
表示方式
图的创建
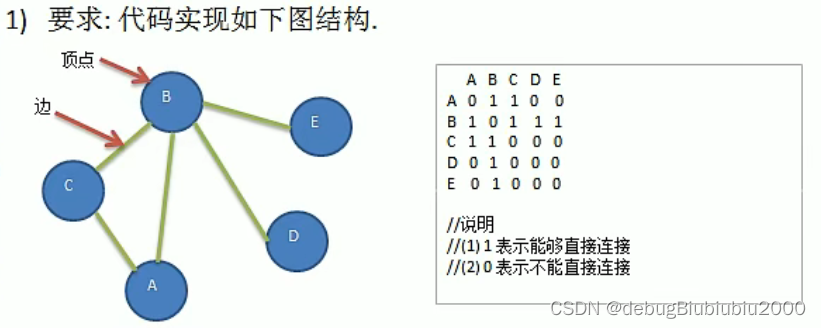
from typing import List
class Graph:
vertex_list: List[str] = [] # 存储顶点的数组
edges: List[list] = [] # 存储图中各条边的邻接矩阵
num_edges: int = 0 # 边的数总数
def __init__(self, n: int):
"""
根据传入的顶点个数初始化顶点数组和邻接矩阵
n: 图中的顶点个数
"""
for i in range(n):
arr = []
for j in range(n):
arr.append(0)
self.edges.append(arr)
def insert_vertex(self, vertex_val: str):
"""
添加顶点
vertex_val: 顶点的值
"""
self.vertex_list.append(vertex_val)
def insert_edge(self, v1: int, v2: int, weight: int = 0):
"""
添加边
v1: 边的起始顶点的下标,从0开始
v2: 边的结束顶点的下标,从0开始
weight: 权值,为1表示两个顶点之间存在边,为0表示两个顶点没有边
如 A——B ,v1 表示顶点A的下标0,v2表示顶点B的下标1,
AB之间存在边,所以weight=1
"""
# 因为是无向图,所以两个顶点对应的位置都要设置边
self.edges[v1][v2] = weight
self.edges[v2][v1] = weight
self.num_edges += 1 # 边的数量加1
def show_graph(self):
"""
遍历邻接矩阵
"""
for arr in self.edges:
for i in arr:
print(i, end=' ')
print()
def get_num_vertex(self) -> int:
"""
返回图中的顶点个数
"""
return len(self.vertex_list)
def get_num_edge(self) -> int:
"""
返回图中边的数量
"""
return self.num_edges
def get_vertex_val_by_index(self, i: int) -> str:
"""
根据顶点下标返回顶点的值
如传入下标0,返回A
"""
return self.vertex_list[i]
def get_weight(self, v1: int, v2: int) -> int:
"""
返回两个顶点之间边的权值
"""
return self.edges[v1][v2]
def test_graph():
n = 5
vertex_arr = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
graph = Graph(n)
# 向图中循环添加顶点
for i in vertex_arr:
graph.insert_vertex(i)
# 添加边
graph.insert_edge(0, 1, 1)
graph.insert_edge(0, 2, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 2, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 3, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 4, 1)
# 显示图的邻接矩阵
graph.show_graph()
test_graph()
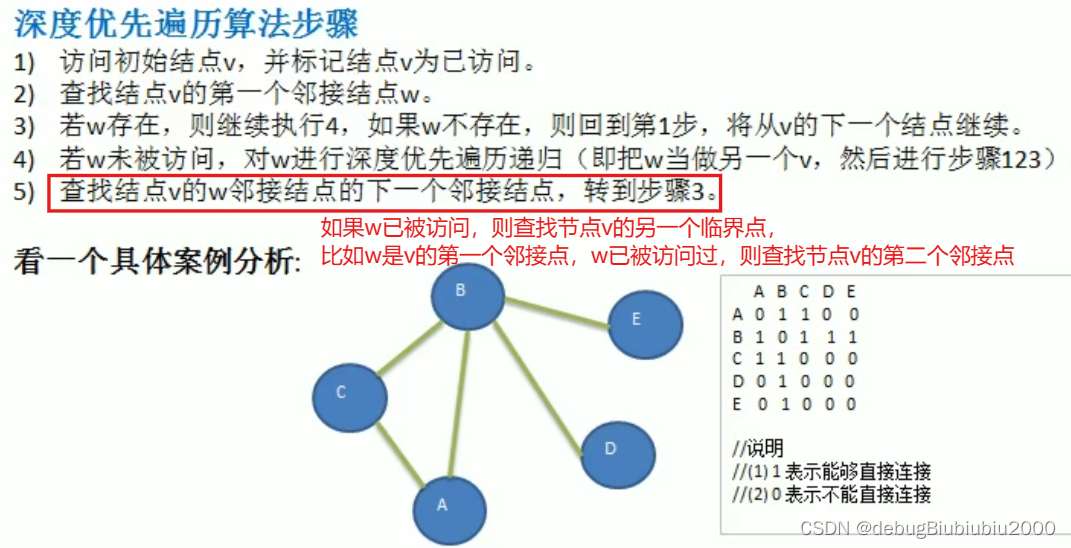
图的深度优先遍历
基本介绍

代码实现
from typing import List
class Graph:
vertex_list: List[str] = [] # 存储顶点的数组
edges: List[list] = [] # 存储图中各条边的邻接矩阵
num_edges: int = 0 # 边的数总数
is_visited: List[bool] = [] # 标记一个节点是否被访问
def __init__(self, n: int):
"""
根据传入的顶点个数初始化顶点数组和邻接矩阵
n: 图中的顶点个数
"""
for i in range(n):
arr = []
for j in range(n):
arr.append(0)
self.edges.append(arr)
self.is_visited.append(False)
def get_first_neighbor(self, index: int):
"""
返回节点第一个邻接节点的下标,如果节点没有邻接节点则返回-1
"""
for i in range(len(self.vertex_list)):
if self.edges[index][i] > 0:
return i
return -1
def get_next_neighbor(self, v1: int, v2: int):
"""
根据节点v1的前一个邻接节点的下标v2获取节点v1的下一个邻接节点的下标
"""
for i in range(v2 + 1, len(self.vertex_list)):
if self.edges[v1][i] > 0:
return i
return -1
def dfs(self, i: int):
"""
深度优先遍历
:param i: 从节点i开始遍历
:return:
"""
# 访问节点i,即输出它
print(self.vertex_list[i], end=' -> ')
self.is_visited[i] = True
# 获取节点i的下一个邻接节点
w = self.get_first_neighbor(i)
# 如果节点i的下一个邻接节点w存在
while w != -1:
if not self.is_visited[w]: # 如果w没有被访问过,则从节点w开始继续深度遍历
self.dfs(w)
# 如果w已经被访问过,则从节点i的另一个邻接点开始遍历
w = self.get_next_neighbor(i, w)
# 如果w不存在,则回退到节点v,遍历节点v的下一个邻接点
# 所谓的回溯,就是返回到调用dfs()的地方继续执行
def for_dfs(self):
"""
遍历所有顶点,看是否存在没有访问过的节点
"""
for i in range(self.get_num_vertex()):
if not self.is_visited[i]: # 存在没有访问过的节点,以该节点进行深度优先遍历
self.dfs(i)
def insert_vertex(self, vertex_val: str):
"""
添加顶点
vertex_val: 顶点的值
"""
self.vertex_list.append(vertex_val)
def insert_edge(self, v1: int, v2: int, weight: int = 0):
"""
添加边
v1: 边的起始顶点的下标,从0开始
v2: 边的结束顶点的下标,从0开始
weight: 权值,为1表示两个顶点之间存在边,为0表示两个顶点没有边
如 A——B ,v1 表示顶点A的下标0,v2表示顶点B的下标1,
AB之间存在边,所以weight=1
"""
# 因为是无向图,所以两个顶点对应的位置都要设置边
self.edges[v1][v2] = weight
self.edges[v2][v1] = weight
self.num_edges += 1 # 边的数量加1
def show_graph(self):
"""
遍历邻接矩阵
"""
for arr in self.edges:
for i in arr:
print(i, end=' ')
print()
def get_num_vertex(self) -> int:
"""
返回图中的顶点个数
"""
return len(self.vertex_list)
def test_graph():
n = 5
vertex_arr = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
graph = Graph(n)
# 向图中循环添加顶点
for i in vertex_arr:
graph.insert_vertex(i)
# 添加边
graph.insert_edge(0, 1, 1)
graph.insert_edge(0, 2, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 2, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 3, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 4, 1)
# 显示图的邻接矩阵
graph.show_graph()
print("深度优先遍历:", end='')
graph.for_dfs()
test_graph()
图的广度优先遍历
基本介绍

代码实现
from typing import List
class Graph:
vertex_list: List[str] = [] # 存储顶点的数组
edges: List[list] = [] # 存储图中各条边的邻接矩阵
num_edges: int = 0 # 边的数总数
is_visited: List[bool] = [] # 标记一个节点是否被访问
def __init__(self, n: int):
"""
根据传入的顶点个数初始化顶点数组和邻接矩阵
n: 图中的顶点个数
"""
for i in range(n):
arr = []
for j in range(n):
arr.append(0)
self.edges.append(arr)
self.is_visited.append(False)
def get_first_neighbor(self, index: int):
"""
返回节点第一个邻接节点的下标,如果节点没有邻接节点则返回-1
"""
for i in range(len(self.vertex_list)):
if self.edges[index][i] > 0:
return i
return -1
def get_next_neighbor(self, v1: int, v2: int):
"""
根据节点v1的前一个邻接节点的下标v2获取节点v1的下一个邻接节点的下标
"""
for i in range(v2 + 1, len(self.vertex_list)):
if self.edges[v1][i] > 0:
return i
return -1
def bfs(self, i: int):
"""
对一个节点进行广度优先遍历
:param i: 节点的下标
"""
que = [] # 用列表模拟队列,存储已访问过的节点
# 输出节点信息
print(self.vertex_list[i], end=' -> ')
# 标记节点为已访问
self.is_visited[i] = True
que.append(i) # 将已访问过的节点的下标加入队列
while que: # 队列不为空,对节点i的广度优先遍历就继续
# 取出队头节点的下标u
u = que.pop(0)
# 获取节点u的第一个邻接节点的下标w
w = self.get_first_neighbor(u)
# 如果节点w存在
while w != -1:
# 如果节点w未被访问,则访问并将节点w入队
if not self.is_visited[w]:
print(self.vertex_list[w], end=' -> ')
self.is_visited[w] = True
que.append(w)
# 查找节点u继节点w后的另一个邻接节点
w = self.get_next_neighbor(u, w)
def for_bfs(self):
"""
遍历所有顶点,看还有哪一个没有访问过,如果有,则从没有访问过的顶点开始广度优先遍历
:return:
"""
for i in range(len(self.vertex_list)):
if not self.is_visited[i]:
self.bfs(i)
def insert_vertex(self, vertex_val: str):
"""
添加顶点
vertex_val: 顶点的值
"""
self.vertex_list.append(vertex_val)
def insert_edge(self, v1: int, v2: int, weight: int = 0):
"""
添加边
v1: 边的起始顶点的下标,从0开始
v2: 边的结束顶点的下标,从0开始
weight: 权值,为1表示两个顶点之间存在边,为0表示两个顶点没有边
如 A——B ,v1 表示顶点A的下标0,v2表示顶点B的下标1,
AB之间存在边,所以weight=1
"""
# 因为是无向图,所以两个顶点对应的位置都要设置边
self.edges[v1][v2] = weight
self.edges[v2][v1] = weight
self.num_edges += 1 # 边的数量加1
def show_graph(self):
"""
遍历邻接矩阵
"""
for arr in self.edges:
for i in arr:
print(i, end=' ')
print()
def test_graph():
n = 5
vertex_arr = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
graph = Graph(n)
# 向图中循环添加顶点
for i in vertex_arr:
graph.insert_vertex(i)
# 添加边
graph.insert_edge(0, 1, 1)
graph.insert_edge(0, 2, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 2, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 3, 1)
graph.insert_edge(1, 4, 1)
# 显示图的邻接矩阵
graph.show_graph()
print("广度优先遍历:", end='')
graph.for_bfs()
test_graph()