一、概述
众所周知在办公的时候两台电脑之间经常倒数据资料非常麻烦,而NAS可以很好的解决这个问题。树莓派搭建NAS方法有很多,我们之前也拍过直接用Samba、FTP这些来实现NAS功能,但是这些需要你会在命令行进行配置,而且对于新手用起来并不直观方便对于一个NAS系统来说功能也不全,故我们这次用开源的OMV来搭建NAS系统!
目前网上普遍的OMV搭建NAS的教程都比较老了,照着做会出现各种问题,而我们本期教程是在最新树莓派官方系统上做的,大家照着做完全不会有问题,本期的精简视频教程在B站-杨坤树莓派爱好者基地中可以看到,VLOG全程记录视频可以在B站-玩派VLOG看到,欢迎大家三连~
视频教程地址:
哔哩哔哩bilibili:树莓派爱好者基地
视频VLOG记录:
哔哩哔哩bilibili:玩派VLOG
二、教程内容
1、树莓派安装系统
这里我们用到的是最新的树莓派官方精简版系统(不能使用带桌面的版本!)

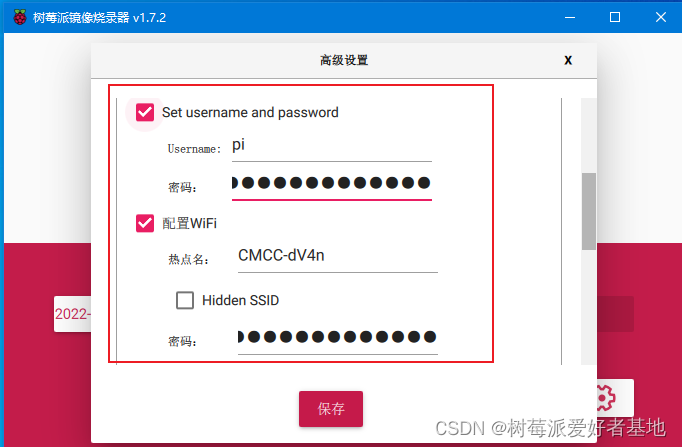
记得点这个设置,在里面需要开启SSH、设置pi账户的密码、配置WIFI的账号和密码


2、固定静态IP
打开路由器后台查看树莓派IP地址

在ssh软件中输入下面命令,配置DHCP文件
sudo nano /etc/dhcpcd.conf
文件中这个位置按照你自己的情况进行修改

然后重启树莓派
sudo reboot
3、换源
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
把原来的注视掉,把下面的复制进去
deb http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/raspbian/raspbian/ bullseye main non-free contrib rpi
deb-src http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/raspbian/raspbian/ bullseye main non-free contrib rpi

继续
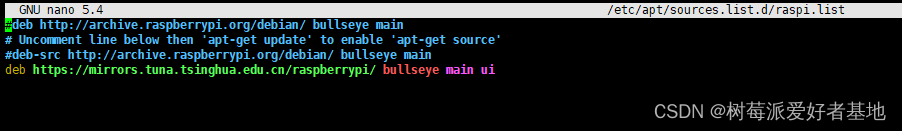
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list.d/raspi.list
把原来的注视掉,把下面的复制进去
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/raspberrypi/ bullseye main ui
然后记得更新一下
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
4、安装OMV
wget https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/OpenMediaVault-Plugin-Developers/installScript@master/install
chmod +x install
sudo ./install -n
5、配置OMV
浏览器输入树莓派IP地址就可以进入NAS系统了。
用户名默认为admin,密码为openmediavault
首先在系统设置-工作台里面设置一下登出时间,之前的太短了

把硬盘插在树莓派上,然后快速擦除磁盘
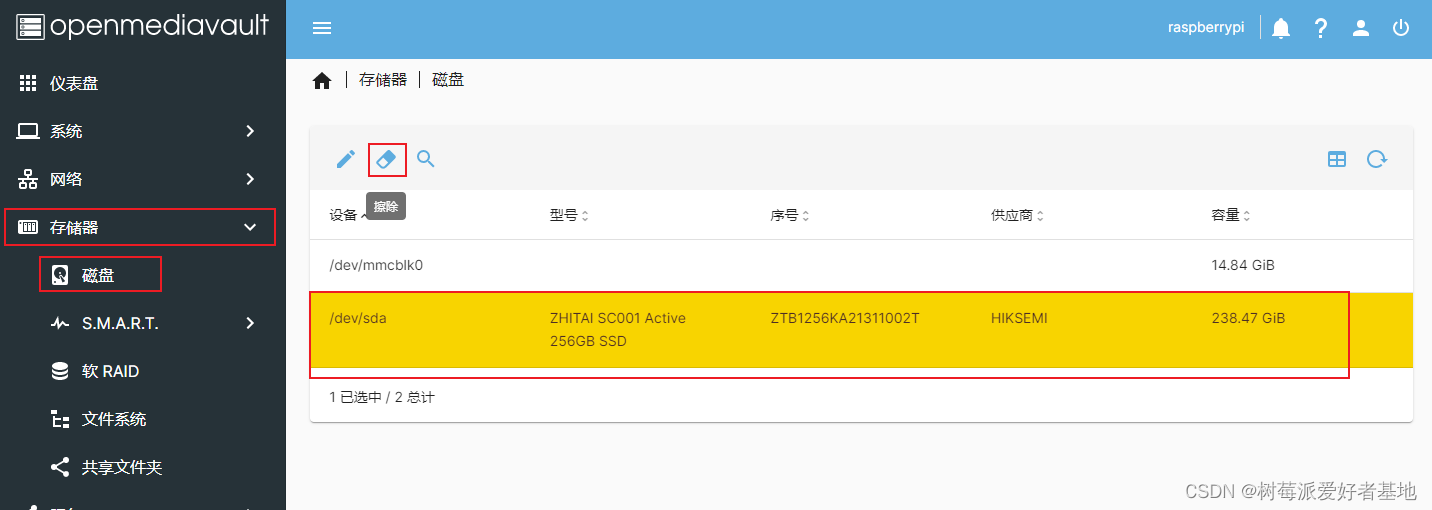
创建文件系统

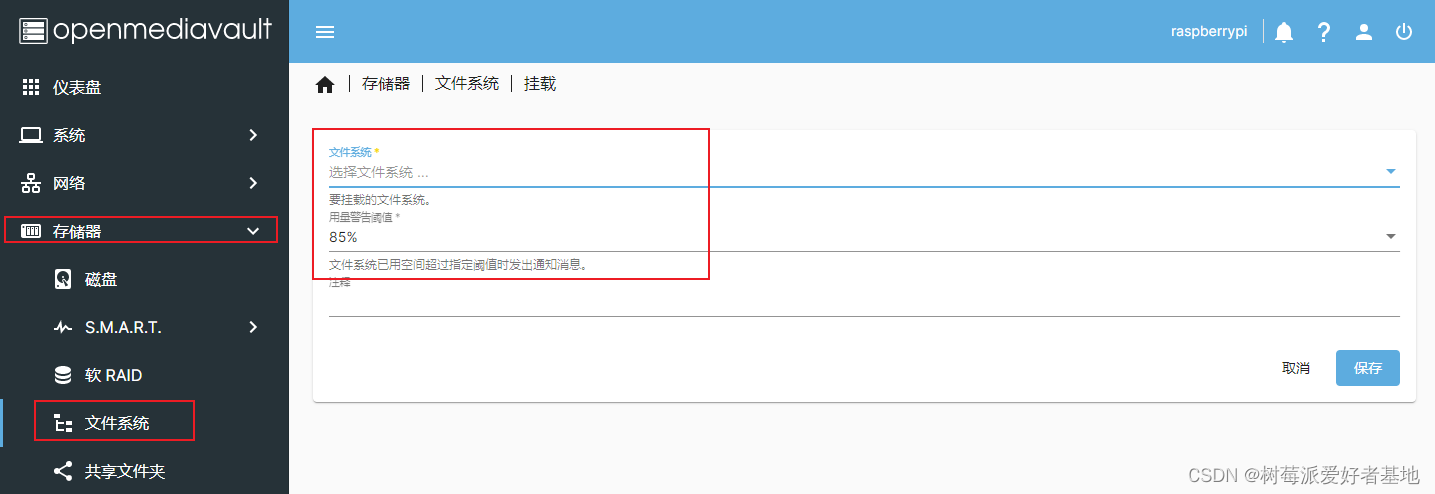
挂载
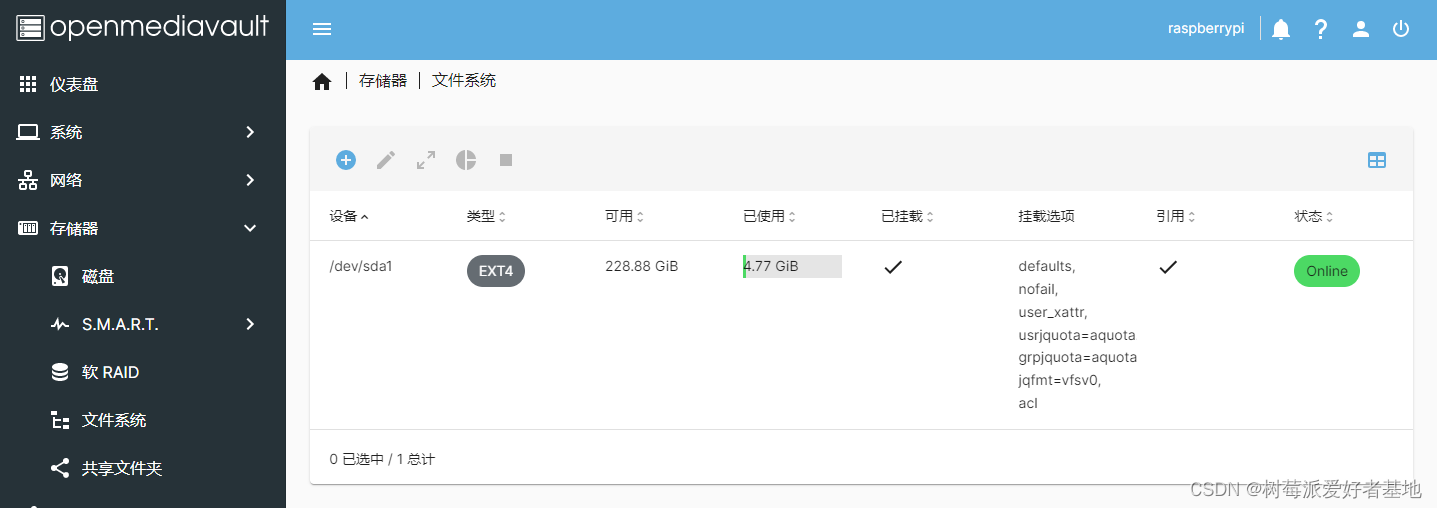
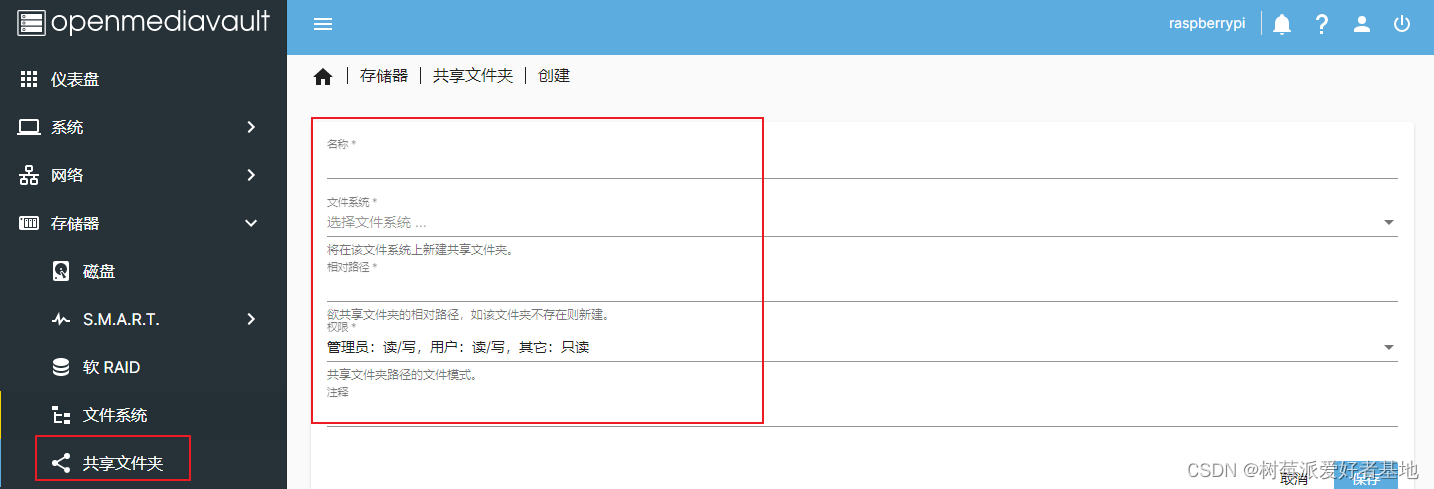
创建共享文件夹
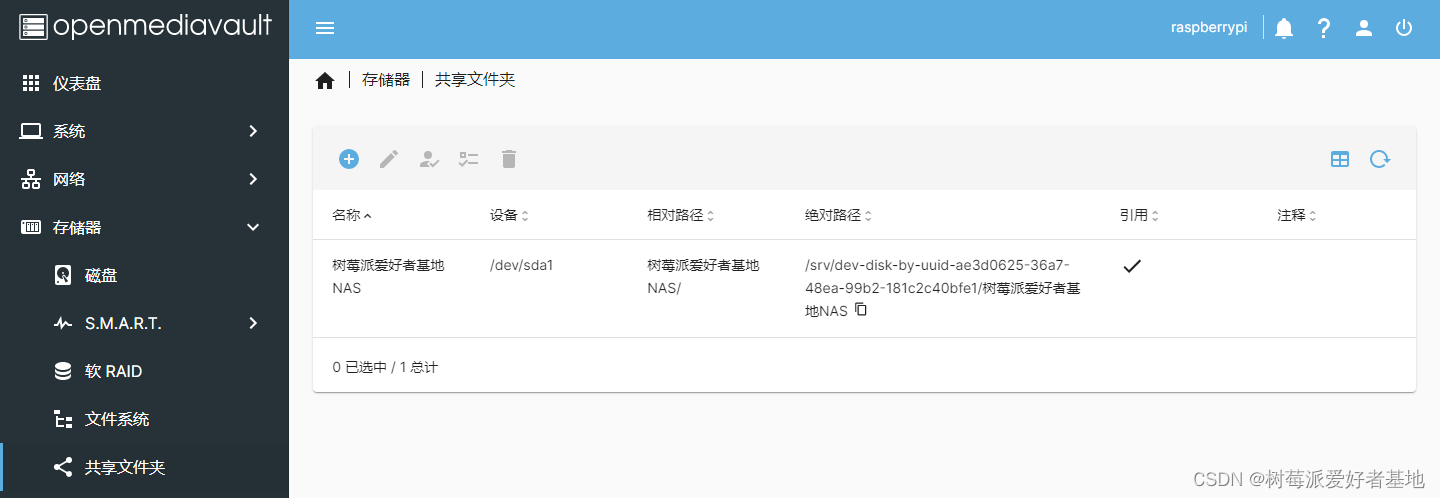
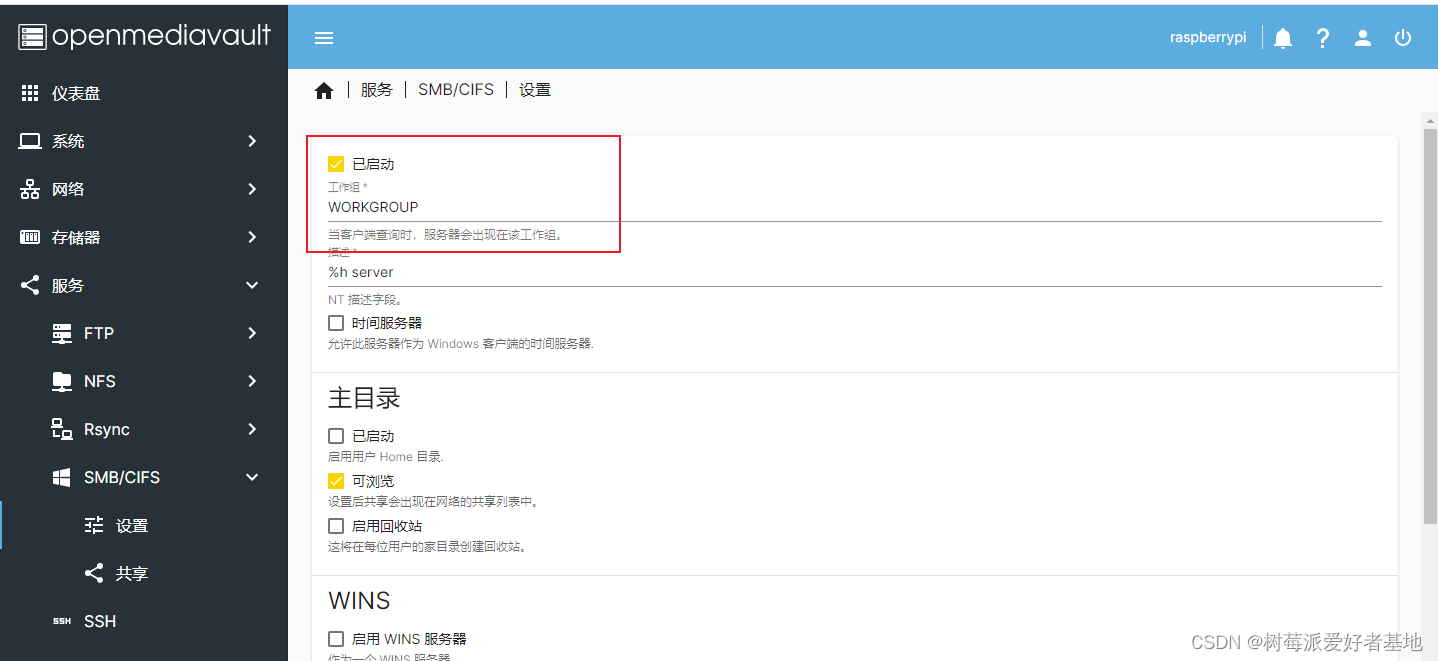
配置SMB服务

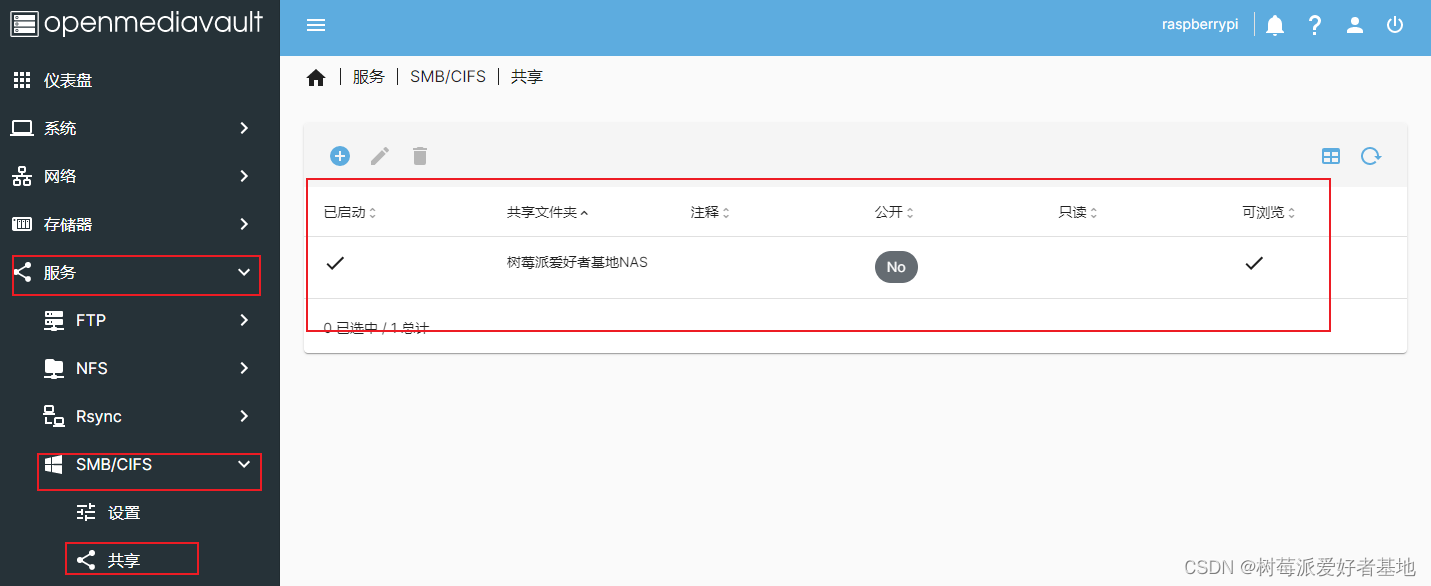
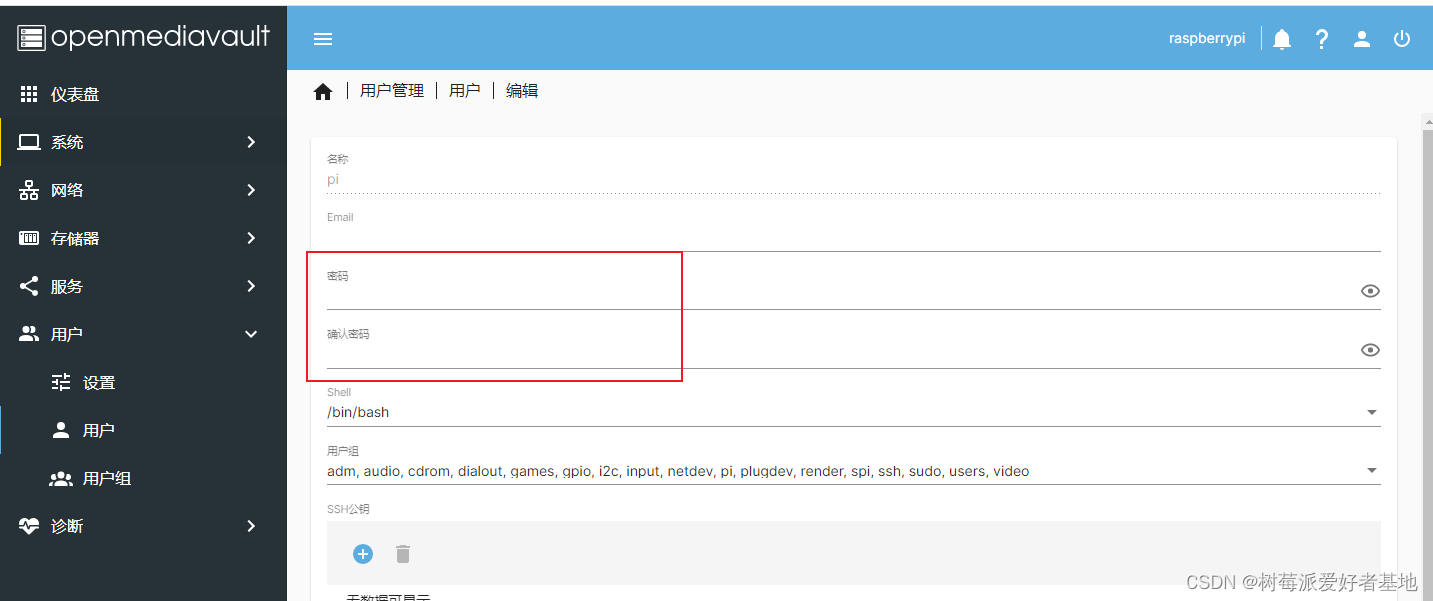
配置一下一般登陆的用户pi

6、开始使用
WINDOWS上直接添加一个映射

然后就能用了

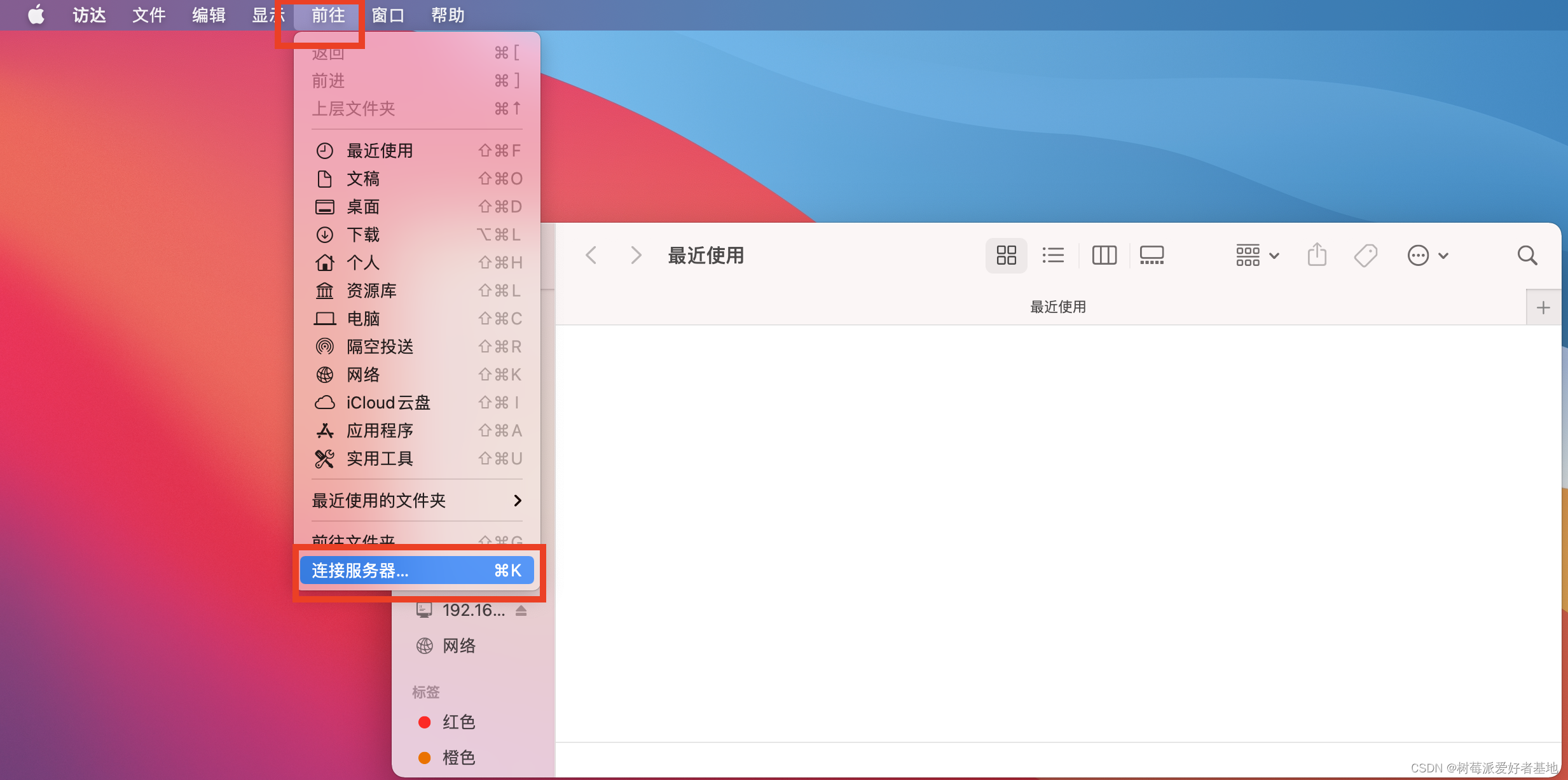
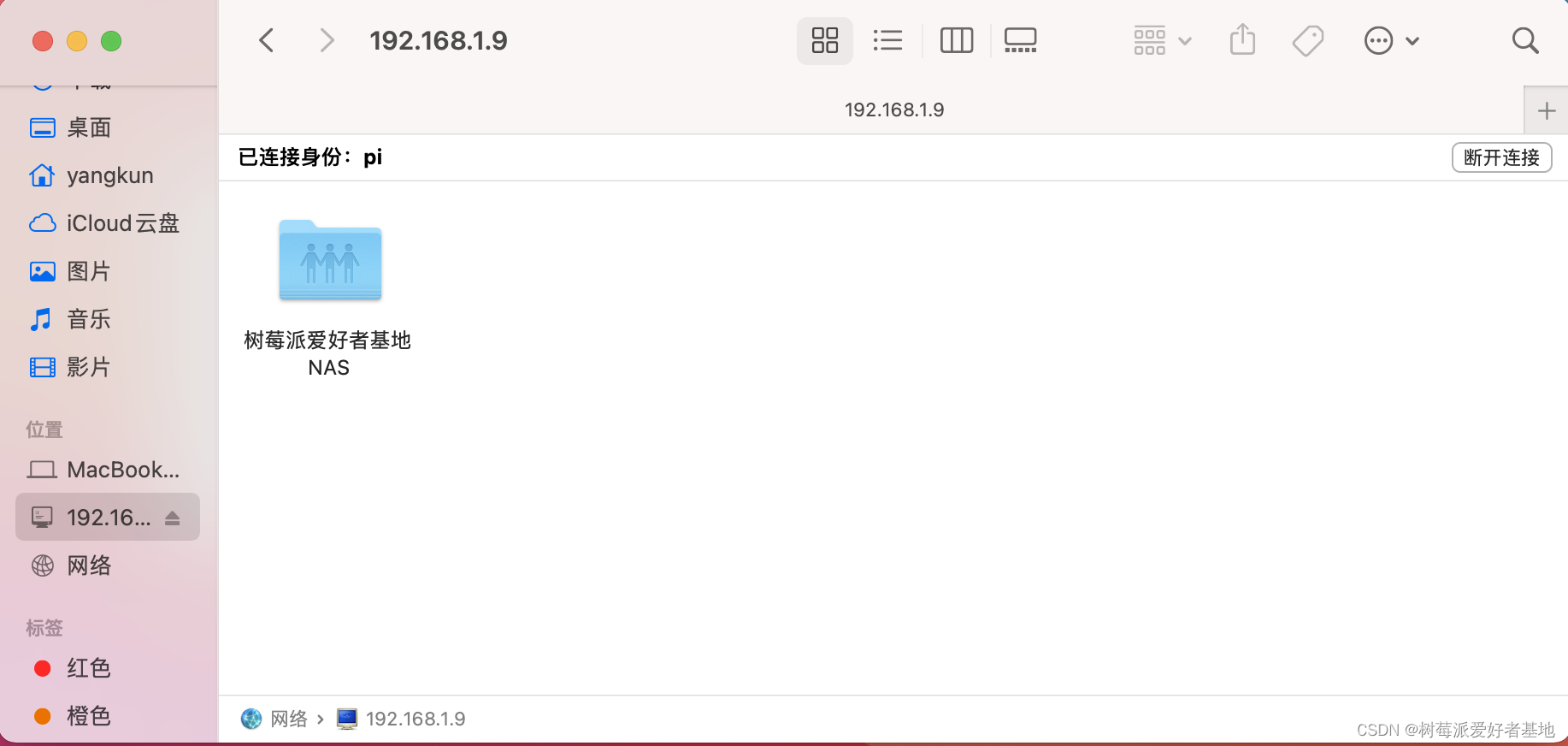
MAC上打开点前往,然后连接服务器就好了

7、给NAS安个小显示屏
启动树莓派的I2C功能
sudo apt-get install -y python3-smbus
sudo apt-get install -y i2c-tools
sudo raspi-config
按照下面的步骤设置开启i2c功能

重启树莓派
sudo reboot
安装Adafruit-SSD1306库
Adafruit-SSD1306库是基于Python的OLED库,可以用于128*64,128*32像素SSD1306芯片控制的屏幕
sudo apt-get remove python3-pip
sudo apt-get install python3-pip
sudo python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel
安装PIL库,有一些图片处理的程序会用到这个。
sudo apt-get install python3-pil
使用pip安装Adafruit-SSD1306库
sudo pip install Adafruit-SSD1306
再下载一份包含代码示例的库后面用
cd ~
sudo apt install git
git clone https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_Python_SSD1306.git
cd ~/Adafruit_Python_SSD1306/examples/
对于屏幕的接线,一定不要接错,树莓派引脚(所有树莓派40针引脚都是这样排列,不需要因为不同版本而改动)如下图所示:
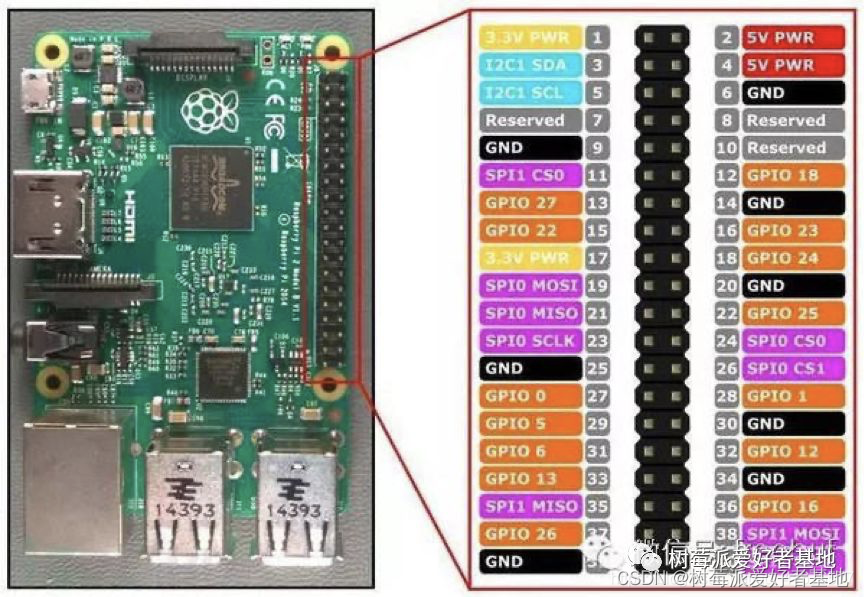
根据屏幕 PCB 上引脚的功能标注接到树莓派上对应的 GPIO 上即可。
屏幕 GND 接树莓派 GND
屏幕 VCC 接树莓派 3V3
屏幕 SDA 接树莓派 SDA
屏幕 SCL 接树莓派 SCL
注意一定不要接反 VCC 和 GND,否则会烧坏屏幕!!!
接上之后通过命令检测是否识别到i2c设备
sudo i2cdetect -y 1
修改一下程序
cd ~
sudo cp ~/Adafruit_Python_SSD1306/examples/stats.py ~/
sudo nano stats.py
把文件里面的内容全替换成下面的内容
import time
import Adafruit_GPIO.SPI as SPI
import Adafruit_SSD1306
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageFont
import subprocess
# Raspberry Pi pin configuration:
RST = None # on the PiOLED this pin isnt used
# Note the following are only used with SPI:
DC = 23
SPI_PORT = 0
SPI_DEVICE = 0
# Beaglebone Black pin configuration:
# RST = 'P9_12'
# Note the following are only used with SPI:
# DC = 'P9_15'
# SPI_PORT = 1
# SPI_DEVICE = 0
# 128x32 display with hardware I2C:
#disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_32(rst=RST)
# 128x64 display with hardware I2C:
disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_64(rst=RST)
# Note you can change the I2C address by passing an i2c_address parameter like:
disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_64(rst=RST, i2c_address=0x3C)
# Alternatively you can specify an explicit I2C bus number, for example
# with the 128x32 display you would use:
# disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_32(rst=RST, i2c_bus=2)
# 128x32 display with hardware SPI:
# disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_32(rst=RST, dc=DC, spi=SPI.SpiDev(SPI_PORT, SPI_DEVICE, max_speed_hz=8000000))
# 128x64 display with hardware SPI:
# disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_64(rst=RST, dc=DC, spi=SPI.SpiDev(SPI_PORT, SPI_DEVICE, max_speed_hz=8000000))
# Alternatively you can specify a software SPI implementation by providing
# digital GPIO pin numbers for all the required display pins. For example
# on a Raspberry Pi with the 128x32 display you might use:
# disp = Adafruit_SSD1306.SSD1306_128_32(rst=RST, dc=DC, sclk=18, din=25, cs=22)
# Initialize library.
disp.begin()
# Clear display.
disp.clear()
disp.display()
# Create blank image for drawing.
# Make sure to create image with mode '1' for 1-bit color.
width = disp.width
height = disp.height
image = Image.new('1', (width, height))
# Get drawing object to draw on image.
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# Draw a black filled box to clear the image.
draw.rectangle((0,0,width,height), outline=0, fill=0)
# Draw some shapes.
# First define some constants to allow easy resizing of shapes.
padding = -2
top = padding
bottom = height-padding
# Move left to right keeping track of the current x position for drawing shapes.
x = 0
# Load default font.
font = ImageFont.load_default()
# Alternatively load a TTF font. Make sure the .ttf font file is in the same directory as the python script!
# Some other nice fonts to try: http://www.dafont.com/bitmap.php
# font = ImageFont.truetype('Minecraftia.ttf', 8)
def get_cpu_temp():
tempfile=open("/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp")
cpu_temp=tempfile.read()
tempfile.close()
return float(cpu_temp)/1000
while True:
# Draw a black filled box to clear the image.
draw.rectangle((0,0,width,height), outline=0, fill=0)
# Shell scripts for system monitoring from here : https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/119126/command-to-display-memory-usage-disk-usage-and-cpu-load
cmd = "hostname -I | cut -d' ' -f1"
IP = subprocess.check_output(cmd, shell = True ).decode("utf-8")
cmd = "top -bn1 | grep load | awk '{printf \"CPU Load: %.2f\", $(NF-2)}'"
CPU = subprocess.check_output(cmd, shell = True ).decode("utf-8")
cmd = "free -m | awk 'NR==2{printf \"Mem: %s/%sMB %.2f%% \", $3,$2,$3*100/$2 }'"
MemUsage = subprocess.check_output(cmd, shell = True ).decode("utf-8")
cmd = "df -h | awk '$NF==\"/\"{printf \"Disk: %d/%dGB %s\", $3,$2,$5}'"
Disk = subprocess.check_output(cmd, shell = True ).decode("utf-8")
# Write two lines of text.
draw.text((x, top), "IP: " + str(IP), font=font, fill=255)
draw.text((x, top+8), str(CPU), font=font, fill=255)
draw.text((x, top+16), str(MemUsage), font=font, fill=255)
draw.text((x, top+25), str(Disk), font=font, fill=255)
draw.text((x, top+35), "Temp: "+str(get_cpu_temp()), font=font, fill=255)
# Display image.
disp.image(image)
disp.display()
time.sleep(.1)
为了让stats.py能够开机自动运行,我们可以做下面的配置,这样我们就可以不用通过工具或路由器去查找树莓派的IP地址等信息!!!
修改/etc/rc.local文件
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
在exit 0前面增加一行:
sudo python /home/pi/stats.py &
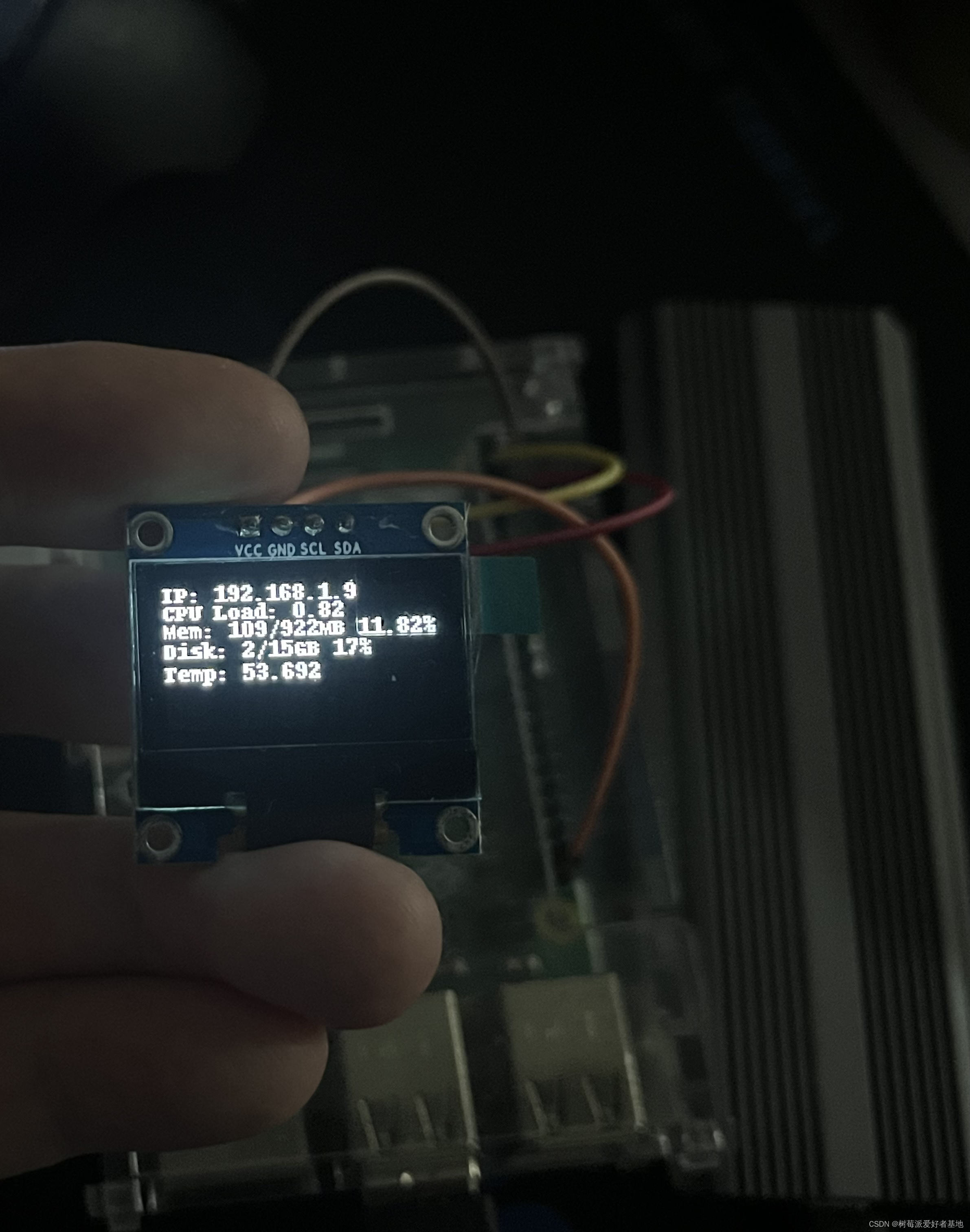
三、看看效果
sudo python stats.py


![[python库] base64库的基本使用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8ce7516a098a4a70bf46a890e67dcef1.png#pic_center)