目录
一.希尔排序
二.划分
三.快速排序
1. 快速排序的算法
2.选择枢纽
一.希尔排序
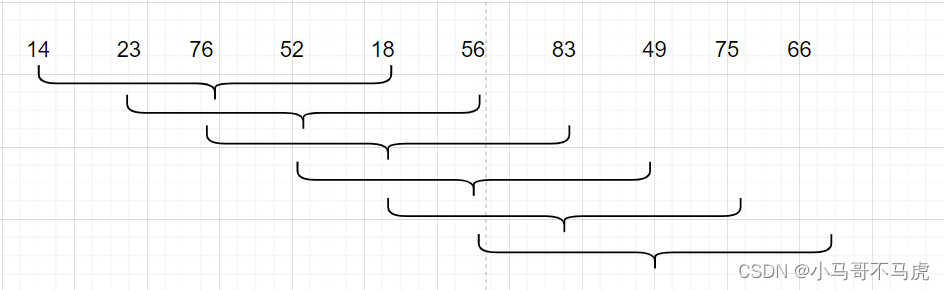
希尔排序是基于插入排序的算法来实现的,不同的是希尔排序是采用n-增量来实现排序,如下是希尔排序的图解:

希尔排序会先以n个增量对元素进行划分,并排序,然后再向后移动一个,在排序,然后缩小间隔n,循环如此直到元素有序
实现代码:
class ArraySh{
private long[] theArray;
private int nElems;
//初始化
public ArraySh(int max){
theArray=new long[max];
nElems=0;
}
//插入操作
public void insert(long value){
theArray[nElems]=value;
nElems++;
}
//显示操作
public void display(){
System.out.print("A=");
for (int i=0;i<nElems;i++)
System.out.print(theArray[i]+" ");
System.out.println(" ");
}
//排序操作
public void ShellSort(){
int innter,outer;
long temp;
int h=1;
while (h<=nElems/3)//间隔大于数组大小结束循环
h=h*3+1; //whlie循环直到生成最大的间隔h
while (h>0){
for (outer=h;outer<nElems;outer++){
temp=theArray[outer];
innter=outer;
while (innter>h-1&&theArray[innter-h]>=temp){
theArray[innter]=theArray[innter-h];
innter-=h;
}
theArray[innter]=temp;
} //结束for循环
h=(h-1)/3;
}
}
}
二.划分
划分就是将数据按某个特定值分为两组,大于特定值的分为一组,小于特定值的分为一组,但划分后的数据还不是有序的
代码:
class Arraypar{
private long[] theArray;
private int nElems;
public Arraypar(int max){
theArray=new long[max];
nElems=0;
}
//插入操作
public void insert(long value){
theArray[nElems]=value;
nElems++;
}
//元素个数
public int size(){
return nElems;
}
public void display(){
System.out.print("A=");
for(int i=0;i<nElems;i++){
System.out.print(theArray[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
}
//寻找特定值位置
public int partitionIt(int left,int right,long pivot){
int leftPtr=left-1;
int rightPtr=right+1;
while(true){
while (left<right&&theArray[++leftPtr]<pivot);//找到比特定值小的
while (right>left&&theArray[++rightPtr]>pivot);//找到比特定值大的
if(leftPtr>=rightPtr) //查找完成
break;
else
swap(leftPtr,rightPtr);
}
return leftPtr;
}
//swap方法
public void swap(int dex1,int dex2){
long temp;
temp=theArray[dex1];
theArray[dex1]=theArray[dex2];
theArray[dex2]=temp;
}
}
例如:
A=149,192,47,152,159,195,66,61,17,167,118,64,27,80,30,105特定值为90,在第8位,划分后:
A= 30,80,47,27,64,17,81,66,66,159,152,192,149,105
三.快速排序
快速排序将元素按一个枢纽分为两组,一组大于枢纽,一组小于枢纽

1. 快速排序的算法
部分代码:
public void recQuicSort(int left,int right){
if(right-left<=0)
return;
else {
int partition=paritionIt(left,right);
recQuicSort(left,partition-1); //左边子数组排序
recQuicSort(partition+1,right); //右边子数组排序
}
}该算法有三个步骤:
1.按枢纽将元素分为左右两个子数组
2.调用自身对左边排序
3.调用自身对右边排序
4.左右排序后合并,完成元素的排序
2.选择枢纽
在对枢纽的选择时,枢纽可以是任意元素,为了方便,我们让枢纽为最右端的元素,然后对排序的算法加入选择枢纽操作:
代码:
public void recQuicSort(int left,int right){
if(right-left<=0)
return;
else {
long piovt=theArray[right]; //枢纽
int partition=paritionIt(left,right,piovt);
recQuicSort(left,partition-1); //左边子数组排序
recQuicSort(partition+1,right); //右边子数组排序
}
}快速排序代码:
class ArrayIns{
private long[] theArray;
private int nElems;
public ArrayIns(int max){
theArray=new long[max];
nElems=0;
}
//插入操作
public void insert(long vallus){
theArray[nElems]=vallus;
nElems++;
}
//显示
public void display(){
System.out.print("A=");
for(int i=0;i<nElems;i++)
System.out.print(theArray[i]+" ");
System.out.println(" ");
}
//快速排序
public void QuickSort(){
recQuickSort(0,nElems-1);
}
public void recQuickSort(int left,int right){
if (right-left<=0)
return;
else {
long pivot=theArray[right];
int partitionIt=partitionIt(left,right,pivot);
recQuickSort(left,partitionIt-1);
recQuickSort(partitionIt+1,right);
}
}
//枢纽操作
public int partitionIt(int left,int right,long pivot){
int leftptr=left-1;
int rightptr=right;
while (true){
while (theArray[++leftptr]<pivot);
while (theArray[--rightptr]>pivot&&rightptr>0);
if (leftptr>rightptr)
break;
else
swap(leftptr,rightptr);
}
swap(leftptr, Math.toIntExact(pivot)); //枢纽与第一组子数组最右边交换
return leftptr;
}
//交换操作
public void swap(int dex1,int dex2){
long temp=theArray[dex1];
theArray[dex1]=theArray[dex2];
theArray[dex2]=temp;
}
}