9 状态编程
9.1 概述
9.1.1 状态
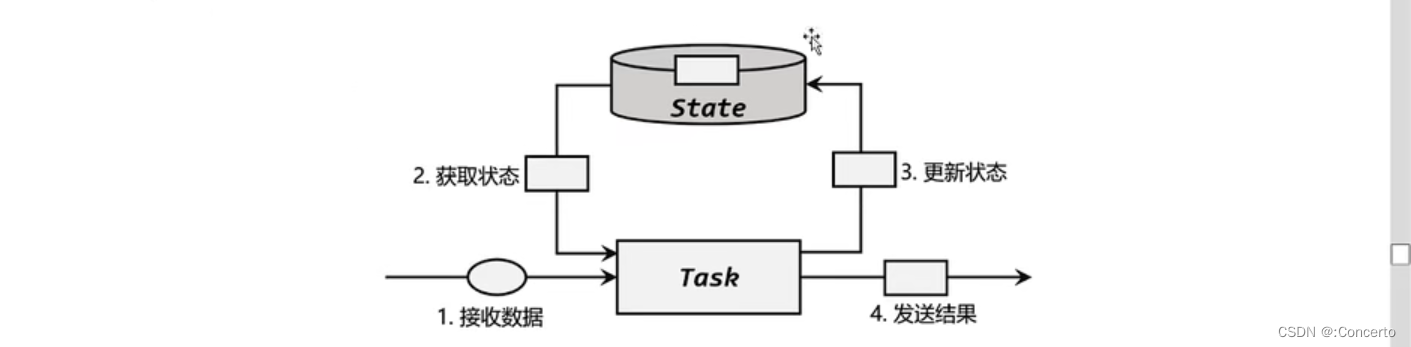
所谓的状态,最常见的就是之前到达的数据,或者由之前数据计算出的某个结果
继承富函数类的函数类就可以获取运行时上下文,也就可以自定义状态,例如process中的ProcessFunction,CoProcessFunction

9.1.2 状态的管理
额外的状态数据存储在数据库中因频繁读写降低性能,因此Flink是把状态保存在内存中来保证性能
状态的具体内容涵盖了:值状态,列表状态,映射状态,聚合状态
9.1.3 状态的分类
- 托管状态:在配置容错机制后,状态会自动持久化保存,并在发生故障时自动恢复
- 算子状态
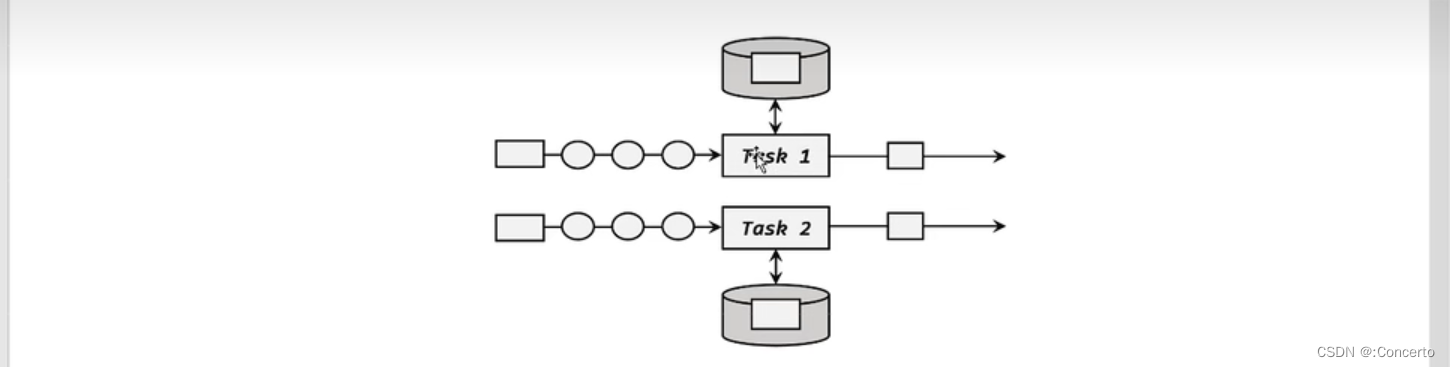
跟本地变量一样了,即每个并行子任务维护着对应的状态,算子的子任务之间状态不共享,还需要持久化保存,即进一步实现CheckpointedFunction接口
- 按键分区状态
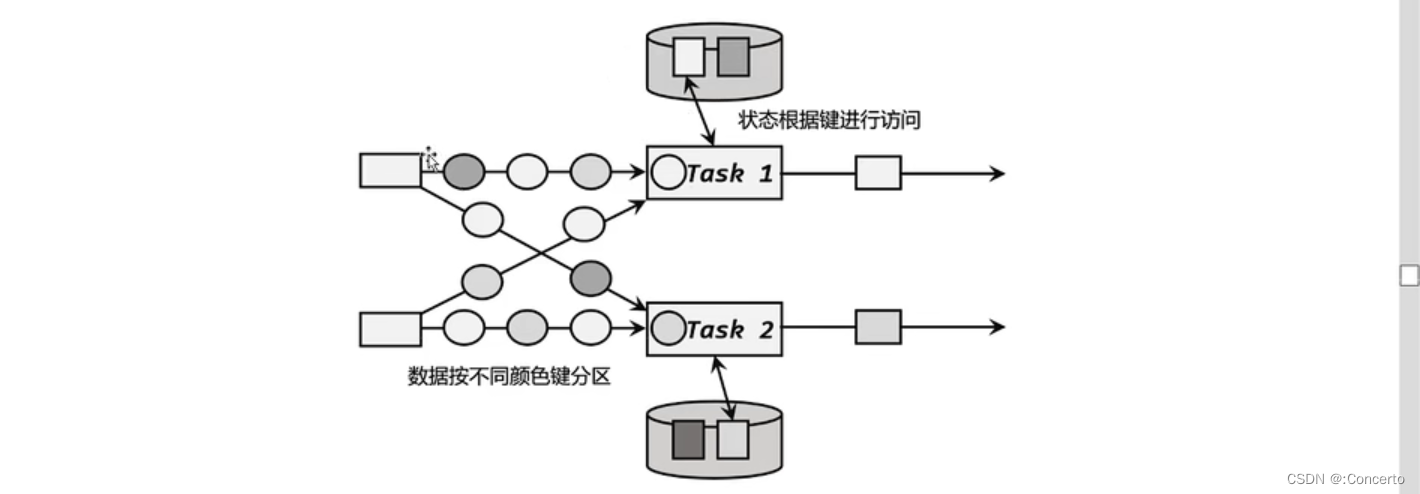
keyby后使用,具有相同键的所有数据,都会分配到同一个并行子任务中,以Keyed State形式保存(底层是键值对存储),以及继承富函数类接口的算子,也可以使用Keyed State
那如果是map、filter这样无状态的基本转换算子,也可以通过富函数类追加Keyed State,或者实现CheckpointedFunction接口来定义Operator State
- 原始状态:全部需要自定义
9.2 按键分区状态
9.2.1 基本概念和特点
keyby后使用,具有相同键的所有数据,都会分配到同一个并行子任务中,以Keyed State形式保存(底层是键值对存储),当新的数据到来,就会根据哈希code去找到key,然后读取对应的value状态值
键组是由不同key的Keyed State形成的,每一组都有一个并行子任务,并行度发生了变化,Keyed State就会按照当前并行度重新分配了
9.2.2 支持的数据结构
- 值状态(ValueState)

接口ValueState的T表示泛型,表示状态的数据内容可以是任何具体的数据类型,接口中的value()方法就是获取当前状态的值,update就是更改当前状态值的方法
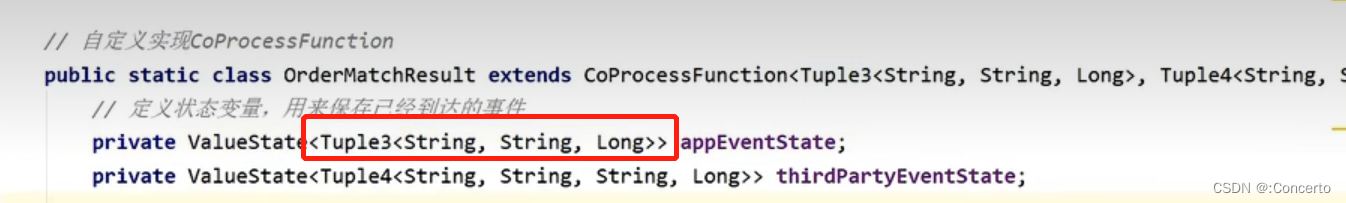
自定义的话,可是可以自由定义类型的

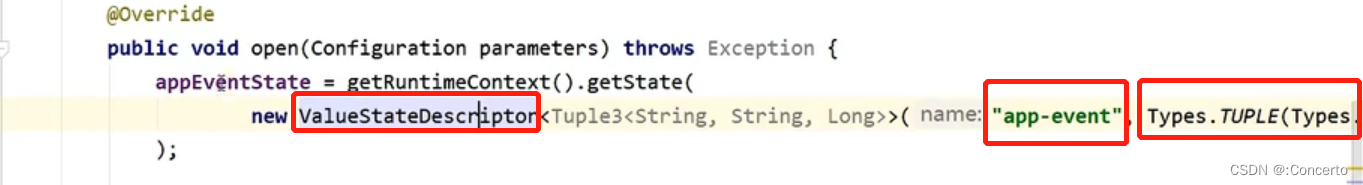
为了让上下文清楚到底哪个是状态,还需要创建一个"状态描述器",ValueStateDescriptor状态描述器中需要传入当前状态名称name以及当前状态的类型typeClass
- 列表状态(ListState)
ListStateJ接口中同样也有一个T表示泛型,表示可以是任何具体的数据类型
并且也提供了一些系列方法,方法如下

并且状态描述器名为ListStateDescriptor,和值状态很像了
- 映射状态(MapState)
MapState<UK,UV>,两个泛型,表示对应的key和value类型
方法如下

方法跟java自身的map操作比较相似,可以一起记忆
- 归约状态(ReducingState)
ReducintState 保存类似于值状态
调用方法类似ListState

ReducingStateDesciptor描述器中,参数比除了状态名称以及状态类型以外,还需要一个ReduceFunction,就跟reduce聚合算子中传入的哪个ReduceFunction一样,因为要做归约的
- 聚合状态(AggregatingState)
和归约状态(ReducingState)差不多,不同的在于描述器中,需要传入AggregateFunction,这个跟那个窗口那一章,窗口函数一样,里面主要有一个Accumulator来表示状态,聚合状态可以跟输入以及输出类型不一样
AggregatingState接口的方法也有add()方法,传入AggregateFunction进行状态聚合以及更新
- 代码
- 简易版本
public class StateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.keyBy(data->data.user)
.flatMap(new MyFlatMap())
.print();
env.execute();
}
//实现自定义MyFlatMap,用于做Keyed State测试
public static class MyFlatMap extends RichFlatMapFunction<Event, String> {
//声明,方便扩大范围
ValueState<Event> myVlaueState;
//使用运行上下文open()的时候,运行时上下文
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
myVlaueState= getRuntimeContext().getState(
new ValueStateDescriptor<Event>("my-state",Event.class));
}
//定义状态
@Override
public void flatMap(Event value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//访问和更新状态
System.out.println(myVlaueState.value());
//更新状态值,value来了后更新进去
myVlaueState.update(value);
System.out.println("my value: "+myVlaueState.value());
}
}
}
结果
有null是因为,状态是key之间隔离的
null
my value: Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:04.819}
null
my value: Event{user='Mary', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:05.836}
Event{user='Mary', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:05.836}
my value: Event{user='Mary', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:06.849}
Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:04.819}
my value: Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:07.856}
null
my value: Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:08.857}
Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:07.856}
my value: Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 00:41:09.857}
Process finished with exit code 130
- 完整版本
public class StateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.keyBy(data->data.user)
.flatMap(new MyFlatMap())
.print();
env.execute();
}
//实现自定义MyFlatMap,用于做Keyed State测试
public static class MyFlatMap extends RichFlatMapFunction<Event, String> {
//声明,方便扩大范围
ValueState<Event> myVlaueState;
ListState<Event> myListState;
//mapState的直接来一个就加一
MapState<String,Long> myMapState;
ReducingState<Event> myReducingState;
AggregatingState<Event,String> myAggregatingState;
//增加一个本地变量进行对比
Long count = 0L;
//使用运行上下文open()的时候,运行时上下文
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
myVlaueState= getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Event>("my-state",Event.class));
myListState= getRuntimeContext().getListState(new ListStateDescriptor<Event>("my-list",Event.class));
myMapState= getRuntimeContext().getMapState(new MapStateDescriptor<String, Long>("my-map",String.class,Long.class));
myReducingState= getRuntimeContext().getReducingState(new ReducingStateDescriptor<Event>("my-reduce",
new ReduceFunction<Event>(){
@Override
public Event reduce(Event value1, Event value2) throws Exception {
//更新时间戳
return new Event(value1.user,value1.url,value2.timestamp);
}
}
,Event.class));
myAggregatingState= getRuntimeContext().getAggregatingState(new AggregatingStateDescriptor<Event, Long, String>("my-agg",
new AggregateFunction<Event, Long, String>() {
@Override
public Long createAccumulator() {
return 0L;
}
@Override
public Long add(Event value, Long accumulator) {
return accumulator+1;
}
@Override
public String getResult(Long accumulator) {
return "count:"+accumulator;
}
@Override
public Long merge(Long a, Long b) {
return a+b;
}
}
, Long.class));
}
//定义状态
@Override
public void flatMap(Event value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//访问和更新状态
//System.out.println(myVlaueState.value());
//更新状态值,value来了后更新进去
myVlaueState.update(value);
//System.out.println("my value: "+myVlaueState.value());
myListState.add(value);
//避免空指针
myMapState.put(value.user,myMapState.get(value.user)==null?1:myMapState.get(value.user)+1);
System.out.println("my map value: "+value.user+" "+myMapState.get(value.user));
myAggregatingState.add(value);//比map简单,自动加了1,因为定义AggregateFunction已经干了
System.out.println("aggregating state:"+myAggregatingState.get());
myReducingState.add(value);
System.out.println("reducing state:"+myReducingState.get());
//本地变量的
count++;
System.out.println("count:"+count);
}
}
}
结果
my map value: Alice 1
aggregating state:count:1
reducing state:Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:08:48.515}
count:1
my map value: Mary 1
aggregating state:count:1
reducing state:Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:08:49.523}
count:2
my map value: Mary 2
aggregating state:count:2
reducing state:Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:08:50.527}
count:3
my map value: Alice 2
aggregating state:count:2
reducing state:Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:08:51.534}
count:4
my map value: Mary 3
aggregating state:count:3
reducing state:Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:08:52.544}
count:5
9.2.3 运用
- 值状态
为了解决窗口计算中,仅仅计算此窗口,滚动窗口并不会从头计算所需要的数据以及窗口太频繁计算而非展示进度的情况
因此可以不开窗,直接基于所有数据进行统计,使用状态保存数据,并且设定定时器再输出,输出得到自由的控制
- 案例
- 值状态
下面就是使用状态编程来实现周期性计算pv的运用
public class PeriodicPvExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.print("input");
//统计每个用户的pv
stream.keyBy(data->data.user)
.process(new PeriodicPvResult())
.print();
env.execute();
}
public static class PeriodicPvResult extends KeyedProcessFunction<String,Event,String> {
//定义状态,保存当前pv统计值以及保存定时器
ValueState<Long> countState;
ValueState<Long> timerTsState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
countState = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Long>("count",Long.class));
timerTsState = getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Long>("timer-ts",Long.class));
}
@Override
public void processElement(Event value, KeyedProcessFunction<String, Event, String>.Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//每来一条数据,就更新对应的count值
Long count = countState.value();
countState.update(count==null?1:count+1);
//如果没有注册过定时器,就注册,如果有就不用
if(timerTsState.value()==null){
//基于当前timestamp加上10秒
ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(value.timestamp+10*1000L);
timerTsState.update(value.timestamp+10*1000L);
}
}
//触发定时器,等用户到来才会触发定时器
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, KeyedProcessFunction<String, Event, String>.OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//定时器触发输出一次统计结果
out.collect(ctx.getCurrentKey()+"'s pv:"+countState.value());
//清空状态, 定时器清空后就立即注册
timerTsState.clear();
//countState.clear();这个不清空,清空就跟窗口一样了
ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(timestamp+10*1000L);
timerTsState.update(timestamp+10*1000L);
}
}
}
结果
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:02.587}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:03.593}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:04.609}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:05.611}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:06.614}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:07.615}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:08.629}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:09.641}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:10.656}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:11.672}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:12.685}
Alice's pv:5
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:13.698}
Mary's pv:2
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 21:48:14.701}
Bob's pv:5
- 列表状态
- 场景
使用列表状态实现全外连接
- 代码
public class TwoStreamJoinExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String,String,Long>> stream1 = env.fromElements(
Tuple3.of("a","stream-1",1000L),
Tuple3.of("b","stream-1",2000L),
Tuple3.of("a","stream-1",3000L)
).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Tuple3<String,String,Long>>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple3<String,String,Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3<String, String, Long> element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.f2;
}
}));
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String,String,Long>> stream2 = env.fromElements(
Tuple3.of("a","stream-2",3000L),
Tuple3.of("b","stream-2",4000L),
Tuple3.of("a","stream-2",6000L)
).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Tuple3<String,String,Long>>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Tuple3<String,String,Long>>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple3<String, String, Long> element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.f2;
}
}));
//实现full join,需要保留数据
//自定义列表状态,实现全外联结
stream1.keyBy(data->data.f0)
.connect(stream2.keyBy(data->data.f0))
.process(new CoProcessFunction<Tuple3<String, String, Long>, Tuple3<String, String, Long>, String>() {
//定义列表状态,用户保存两条流中已经到达的所有数据
private ListState<Tuple2<String, Long>> stream1ListState;
private ListState<Tuple2<String, Long>> stream2ListState;
//上下文
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
stream1ListState= getRuntimeContext().getListState(
new ListStateDescriptor<Tuple2<String, Long>>(
"stream1-list", Types.TUPLE(Types.STRING,Types.LONG)));
stream2ListState= getRuntimeContext().getListState(
new ListStateDescriptor<Tuple2<String,Long>>(
"stream1-list", Types.TUPLE(Types.STRING,Types.STRING,Types.LONG)));
}
@Override
public void processElement1(Tuple3<String, String, Long> left, CoProcessFunction<Tuple3<String, String, Long>, Tuple3<String, String, Long>, String>.Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//获取另一条流中所有数据,配对输出
for(Tuple2<String, Long> right:stream2ListState.get()){
out.collect(left.f0+" "+left.f2+"=>"+right);
}
stream1ListState.add(Tuple2.of(left.f0,left.f2));
}
@Override
public void processElement2(Tuple3<String, String, Long> right, CoProcessFunction<Tuple3<String, String, Long>, Tuple3<String, String, Long>, String>.Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//获取另一条流中所有数据,配对输出
for(Tuple2<String, Long> left:stream1ListState.get()){
out.collect(left+"=>"+right.f0+" "+right.f2);
}
stream2ListState.add(Tuple2.of(right.f0,right.f2));
}
})
.print();
env.execute();
}
}
- 结果
(a,1000)=>a 3000
(b,2000)=>b 4000
a 3000=>(a,1000)
a 3000=>(a,3000)
(a,1000)=>a 6000
(a,3000)=>a 6000
(a,3000)=>a 6000
- 映射状态
- 场景
模拟窗口:10秒钟之内的所有数据按照url做一个划分,统计url页面点击次数
思路:需要窗口起始时间,需要一个定时器,需要使用hashmap存储数据,key是窗口起始时间,value是保存的数据,第四个还需要关闭窗口:清空对应窗口状态
- 代码
public class FakeWindowExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.print("input");
stream.keyBy(data->data.url)
.process(new FakeWindowResult(10000L))
.print();
env.execute();
}
public static class FakeWindowResult extends KeyedProcessFunction<String,Event,String> {
private Long windowSize;//窗口大小
//构造方法
public FakeWindowResult(Long windowSize) {
this.windowSize = windowSize;
}
//定义一个MapState,用来保存每个窗口中统计的count值
MapState<Long,Long> windowUrlCountMapState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
windowUrlCountMapState = getRuntimeContext().getMapState(new MapStateDescriptor<Long, Long>(
"window-count",Long.class,Long.class
));
}
@Override
public void processElement(Event value, KeyedProcessFunction<String, Event, String>.Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//每来一个数据,根据时间戳判断属于哪个窗口(窗口分配器)
Long windowStart = value.timestamp/windowSize*windowSize;//去掉余数,取整数
Long windowEnd = windowStart+windowSize;
// 注册end-1的定时器,即窗口最大的时间戳,是windowEnd-1
ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(windowEnd-1);
//更新状态,进行增量聚合
if(windowUrlCountMapState.contains(windowStart)){
//如果包含,就直接获取值了
Long count = windowUrlCountMapState.get(windowStart);
//更新状态值
windowUrlCountMapState.put(windowStart,count+1);
}else{
//如果没有,给个初始值
windowUrlCountMapState.put(windowStart,1L);
}
}
//定时器触发时输出计算结果
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, KeyedProcessFunction<String, Event, String>.OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
Long windowEnd = timestamp+1;//当前timestamp就是windowEnd-1
Long windowStart =windowEnd-windowSize;
//获取值
Long count = windowUrlCountMapState.get(windowStart);
//输出
out.collect("窗口"+new Timestamp(windowStart)+" ~ "+new Timestamp(windowEnd)
+"url:"+ctx.getCurrentKey()
+ "count:"+count
);
//模拟窗口的关闭,清除map的状态即key,value
windowUrlCountMapState.remove(windowStart);
}
}
}
- 结果
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:12.528}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:13.54}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:14.549}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:15.554}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:16.559}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:17.563}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:18.573}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:19.578}
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:10.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:20.0url:./prod?id=100 count:4
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:10.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:20.0url:./fav count:1
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:10.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:20.0url:./home count:2
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:10.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:20.0url:./cart count:1
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:20.578}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:21.584}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:22.591}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:23.591}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:24.596}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:25.602}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:26.604}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:27.61}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:28.616}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:29.629}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-29 22:49:30.64}
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:20.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:30.0url:./cart count:4
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:20.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:30.0url:./fav count:3
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:20.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:30.0url:./prod?id=100 count:1
窗口2022-11-29 22:49:20.0 ~ 2022-11-29 22:49:30.0url:./home count:2
Process finished with exit code 130
- 聚合状态
统计当前几次访问数据的平均时间戳,查看疏密程度如何
public class AverageTimestampExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.print("input");
//自定义实现平均时间戳的统计
stream.keyBy(data -> data.user)
//跟个数有关系,跟时间没关系,那就用不到定时器,那就是不用ProcessFunction,所以可以换个算子
//就用flatmap算子,但是这个算子得有状态,所以传入一个富函数类的函数
.flatMap(new AvgTsResult(5L))
.print();
env.execute();
}
//实现自定义的RichFlatmapFuntion
public static class AvgTsResult extends RichFlatMapFunction<Event, String> {
public Long count;
public AvgTsResult(Long count) {
this.count = count;
}
//定义一个聚合的状态,用来保存平均时间戳
AggregatingState<Event,Long> avgTsAggState;
//定义一个值状态,保存用户访问的次数
ValueState<Long> countState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
avgTsAggState=getRuntimeContext().getAggregatingState(
new AggregatingStateDescriptor<Event, Tuple2<Long,Long>, Long>(
"avg-ts",
new AggregateFunction<Event,Tuple2<Long, Long>, Long>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<Long, Long> createAccumulator() {
return Tuple2.of(0L,0L);
}
@Override
public Tuple2<Long, Long> add(Event value, Tuple2<Long, Long> accumulator) {
//第一个是时间戳累加,第二个是个数
return Tuple2.of(accumulator.f0+value.timestamp,accumulator.f1+1);
}
@Override
public Long getResult(Tuple2<Long, Long> accumulator) {
//求平均值
return accumulator.f0/accumulator.f1;
}
@Override
public Tuple2<Long, Long> merge(Tuple2<Long, Long> a, Tuple2<Long, Long> b) {
return null;
}
}
,
//聚合的类型
Types.TUPLE(Types.LONG, Types.LONG)
));
countState=getRuntimeContext().getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Long>(
"count",Long.class));
}
//在flatmap中处理核心逻辑
@Override
public void flatMap(Event value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//每来一条数据,curr count加1
Long currCount = countState.value();
if(currCount==null){
currCount=1L;
}else {
currCount++;
}
//更新状态
countState.update(currCount);
avgTsAggState.add(value);//AggregatingStateDescriptor聚合过了
//如果达到count次数就输出结果
if(currCount.equals(count)){
//if(currCount.equals(count)){//count是传进来,用来做判断的
out.collect(value.user+"过去"+count+"次访问平均时间戳为:"+avgTsAggState.get());
//清零状态
countState.clear();
avgTsAggState.clear();//如果没有,就是历史状态的平均值
}
}
}
}
- 结果
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:36.464}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:37.47}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:38.478}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:39.478}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:40.492}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./home', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:41.495}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:42.512}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:43.52}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:44.525}
Mary过去5次访问平均时间戳为:1669743220290
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:45.54}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:46.544}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-11-30 01:33:47.553}
Alice过去5次访问平均时间戳为:1669743224125
9.2.4 状态生存空间
- 概述
由于flink状态是存放在内存中的,一般采用.clear()清除状态的方式手动清除回收,以防内存溢出。
第二种是设置一个TTL,即生存时间,当超出这个值的时候,就将它清除
状态失效时间,失效时间=当前时间+TTL
- 代码
public class StateTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.keyBy(data->data.user)
.flatMap(new MyFlatMap())
.print();
env.execute();
}
//实现自定义MyFlatMap,用于做Keyed State测试
public static class MyFlatMap extends RichFlatMapFunction<Event, String> {
//声明,方便扩大范围
ValueState<Event> myVlaueState;
//增加一个本地变量进行对比
Long count = 0L;
//使用运行上下文open()的时候,运行时上下文
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
ValueStateDescriptor<Event> eventValueStateDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>("my-state", Event.class);
myVlaueState= getRuntimeContext().getState(eventValueStateDescriptor);
//配置状态的TTL,表示一小时失效
StateTtlConfig ttlConfig = StateTtlConfig.newBuilder(Time.hours(1))//ttl时间是处理时间
.setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnReadAndWrite)//更新状态失效时间 //UpdateType是一个枚举类型
.setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.ReturnExpiredIfNotCleanedUp)//到达失效时间,能否返回
.build();
//调用enableTimeToLive方法传入ttl
eventValueStateDescriptor.enableTimeToLive(ttlConfig);
}
//定义状态
@Override
public void flatMap(Event value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
//访问和更新状态
//System.out.println(myVlaueState.value());
//更新状态值,value来了后更新进去
myVlaueState.update(value);
//System.out.println("my value: "+myVlaueState.value());
//本地变量的
count++;
System.out.println("count:"+count);
}
}
}
9.3 算子状态
9.3.1 基本概念和特点
- 特点
跟key无关
- 运用
例如:kafka的Source算子设置了并行度后,kafka的消费者的每一个并行实例,都会为对应的主题分区维护一个偏移量,作为算子状态保存起来
- 分类
- 列表状态(ListState)
- 联合列表状态(UnionListState)
- 广播状态(BroadcastState)
9.3.2 状态类型
- 列表状态(ListState)
与按键分区状态中的列表状态的区别,没有key,如果因并行度进行缩放调整而需要重新分配,所有元素会被收集成一个大列表,再根据并行度均衡分配给所有并行任务。策略就是均衡分配,即轮询
- 联合列表状态(UnionListState)
并行度调整的时候,联合列表状态的算子则会直接广播状态的完整列表,即分别每个并行任务都会有之前的状态列表,并由分区子任务自行选择丢弃哪一些状态项目
- 广播状态(BroadcastState)
广播状态在每个并行子任务的实例都一样,在并行度调整之后,只需要复制一份到新的并行任务就可以实现扩展
广播状态是由键值对形式进行保存的
- 分析

拿到CheckpointedFuntion接口,接口中有initializeState()方法传入FunctionSnapshotContext上下文和snapshotState()方法传入FunctionSnapshotContext快照上下文

context.getOperatorStateStore().getListState(descriptor),其中descriptor是ListStateDescriptor描述器的传入名称和类型的实例
- 代码
public class BufferingSinkExcample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Event> stream = env.addSource(new ClickSource())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<Event>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ZERO)
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<Event>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Event element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.timestamp;
}
})
);
stream.print("input");
//批量缓存输出
stream.addSink(new BufferingSink(10));
env.execute();
}
//除了SinkFunction的接口,持久化还需要CheckpointedFunction
public static class BufferingSink implements SinkFunction<Event> , CheckpointedFunction {
//定义当前类的属性,批量
private final int threshold;
//用来保证缓存的一个List
private List<Event> bufferedElements;
public BufferingSink(int threshold) {
this.threshold = threshold;
this.bufferedElements = new ArrayList<>();
}
//需要定义一个算子状态
private ListState<Event> checkpointedState;
@Override
public void invoke(Event value, Context context) throws Exception {
bufferedElements.add(value);//添加并缓存到列表中
//判断如果达到阈值,就批量写入
if(bufferedElements.size()==threshold){
//用打印到控制台模拟写入外部系统,这边就是打印出来了
for (Event elements:bufferedElements){
System.out.println(elements);
}
System.out.println("===============输出完毕!================");
bufferedElements.clear();//清空列表
}
}
//把本地的保存的list和checkpointedState关联起来
@Override
public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception {
//清空状态
checkpointedState.clear();
//对状态进行持久化,复制缓存的列表到列表状态
for(Event element:bufferedElements){
checkpointedState.add(element);//写入的就不需要再记录进来了
}
}
@Override
public void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception {
//定义算子状态
ListStateDescriptor<Event> descriptor = new ListStateDescriptor<>("buffered-elements", Event.class);
checkpointedState = context.getOperatorStateStore().getListState(descriptor);
//考虑故障恢复的情况,如果故障恢复,需要将ListState元素中复制到本地列表中
if (context.isRestored()){
for (Event element:checkpointedState.get()){
bufferedElements.add(element);
}
}
}
}
}
结果
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:38.014}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:39.031}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:40.037}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:41.042}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:42.046}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:43.051}
input> Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:44.052}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:45.058}
input> Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:46.059}
input> Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:47.07}
Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:38.014}
Event{user='Mary', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:39.031}
Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:40.037}
Event{user='Alice', url='./fav', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:41.042}
Event{user='Bob', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:42.046}
Event{user='Alice', url='./home', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:43.051}
Event{user='Mary', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:44.052}
Event{user='Bob', url='./cart', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:45.058}
Event{user='Bob', url='./home', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:46.059}
Event{user='Alice', url='./prod?id=100', timestamp=2022-12-01 20:37:47.07}
===============输出完毕!================
9.4 广播状态
9.4.1 概述
- 相关概念
概念:所有并行子任务状态都是相同的
运用:动态配置或者动态规则
存储:广播状态底层也是键值对形式存储的,是一个映射状态(MapState)
- 分析
在8.2.4有介绍,截图放这边
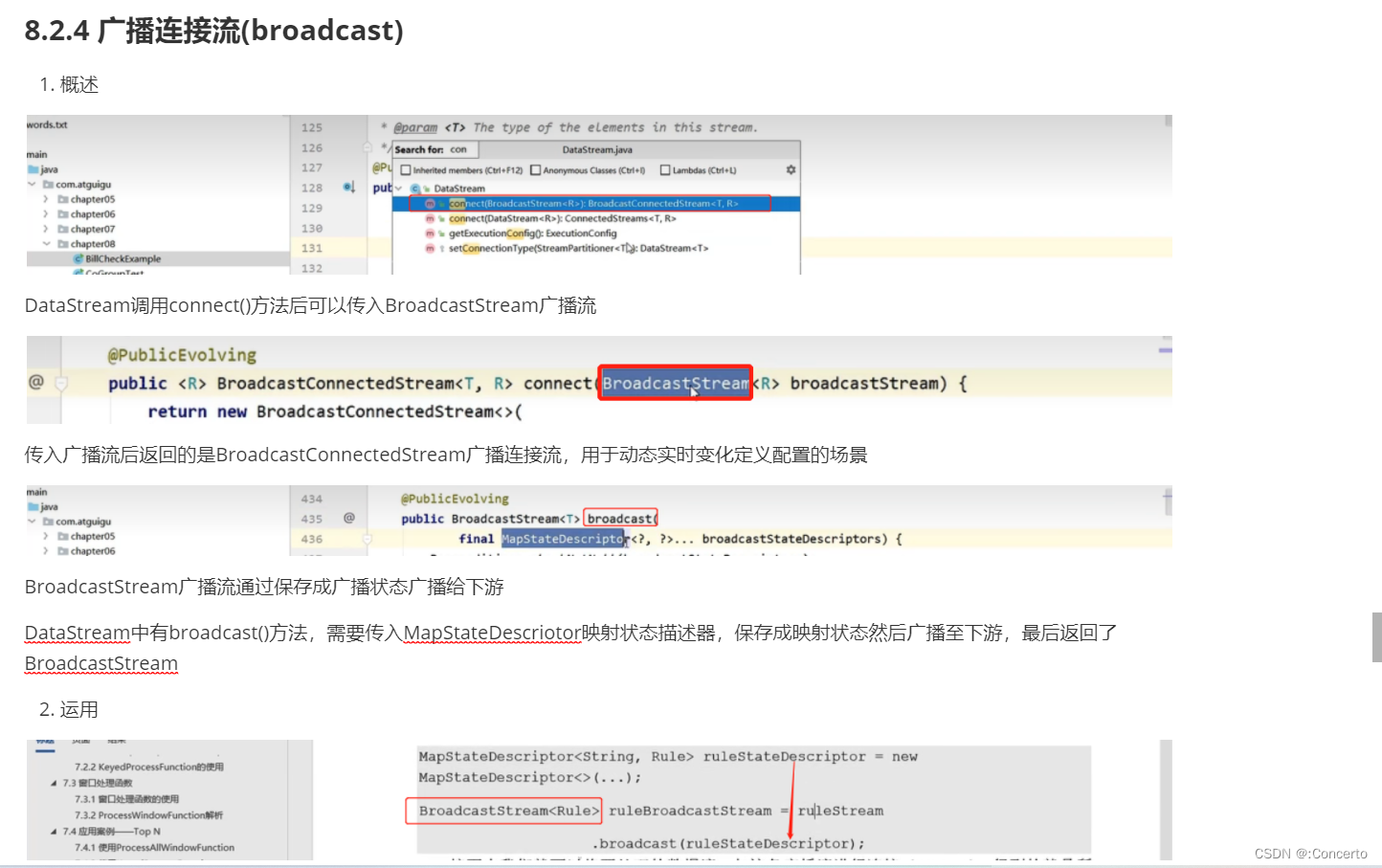
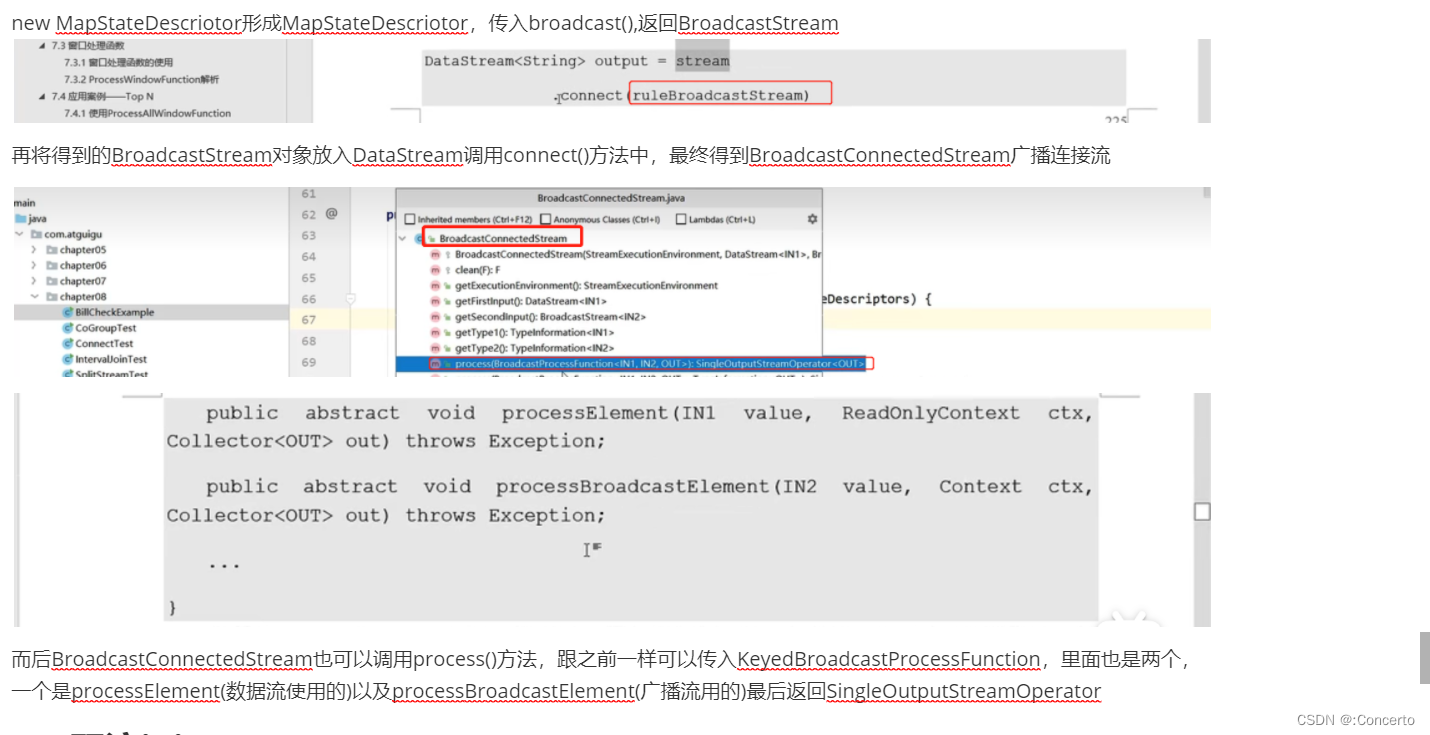
9.4.2 代码实例
- 场景
电商中,往往需要判断用户的先后发生的行为的“组合模式”,比如“登录-下单”后者“登录-支付”,检测出这些连续的行为进行统计,以便了解平台的运用状况以及用户的行为习惯
- 代码
public class BehaviorPatternDetetctExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
//用户行为数据流
DataStreamSource<Action> actionStream = env.fromElements(
new Action("Alice", "login"),
new Action("Alice", "pay"),
new Action("Bob", "login"),
new Action("Bob", "order")
);
//行为模式流,基于这个流构建广播流
DataStreamSource<Pattern> patternStream = env.fromElements(
new Pattern("login", "pay"),
new Pattern("login", "order")
);
//定义广播状态描述器
MapStateDescriptor<Void, Pattern> descriptor = new MapStateDescriptor<>(
"pattern", Types.VOID, Types.POJO(Pattern.class));
BroadcastStream<Pattern> broadcastStream = patternStream.broadcast(descriptor);
//连接两条流进行处理
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String,Pattern>> matches = actionStream.keyBy(data -> data.userId)
.connect(broadcastStream)
.process(new PatternDetector());
matches.print();
env.execute();
}
//实现自定义的KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction
//四个泛型,key类型,第一条流类型,第二条流类型,输出类型
public static class PatternDetector extends KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction<String,Action,Pattern,Tuple2<String,Pattern>> {
//定义一个KeyedState保存当前用户的上一次行为
ValueState<String> prevActionState;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
prevActionState=getRuntimeContext().getState(
new ValueStateDescriptor<String>("last-action",Types.STRING));
}
@Override
public void processBroadcastElement(Pattern value, KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction<String, Action, Pattern, Tuple2<String, Pattern>>.Context ctx, Collector<Tuple2<String, Pattern>> out) throws Exception {
//从上下文中获取广播状态,并用当前数据更新状态
BroadcastState<Void, Pattern> patternState = ctx.getBroadcastState(new MapStateDescriptor<>(
"pattern", Types.VOID, Types.POJO(Pattern.class)));
//更新广播状态
patternState.put(null,value);
}
@Override
public void processElement(Action value, KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction<String, Action, Pattern, Tuple2<String, Pattern>>.ReadOnlyContext ctx, Collector<Tuple2<String, Pattern>> out) throws Exception {
//从广播状态中获取规则以及匹配模式,只能读获取广播状态,不能更新广播状态
ReadOnlyBroadcastState<Void, Pattern> patternState = ctx.getBroadcastState(new MapStateDescriptor<>(
"pattern", Types.VOID, Types.POJO(Pattern.class)));
//得到广播状态的匹配模式
Pattern pattern =patternState.get(null);
//获取用户上一次的行为(在自定义状态的ValueState中)
String prevAction = prevActionState.value();
//判断是否匹配广播的规则
if(pattern!=null&& prevAction!=null) {
if (pattern.action1.equals(prevAction) && pattern.action2.equals(value.action)) {
//如果上一次行为和这一次行为符合规则,那么就符合并输出
//ctx.getCurrentKey()是拿到用户名字
out.collect(new Tuple2<>(ctx.getCurrentKey(), pattern));
}
}
//更新状态
prevActionState.update(value.action);
}
}
//定义用户行为事件和模式的POJO类
public static class Action{
public String userId;
public String action;
public Action() {
}
public Action(String userId, String action) {
this.userId = userId;
this.action = action;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Action{" +
"userId='" + userId + '\'' +
", action='" + action + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public static class Pattern{
public String action1;
public String action2;
public Pattern() {
}
public Pattern(String action1, String action2) {
this.action1 = action1;
this.action2 = action2;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pattern{" +
"action1='" + action1 + '\'' +
", action2='" + action2 + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
}
结果
(Alice,Pattern{action1='login', action2='pay'})
(Bob,Pattern{action1='login', action2='order'})
9.5 状态持久化和状态后端
9.5.1 检查点
- 概念
所有任务的状态在某个时间点的一个快照(一份拷贝),也就是存盘。
如果发生故障,Flink就会最近一次成功保存检查点来恢复应用的状态。
需要数据源具有"数据重放"的能力,例如kafka通过重置数据的偏移量,Source算子保存当前偏移量offset,当作状态保存下来,即存到checkpoint里面
- 代码
默认情况下检查点是关闭的,打开需要这么设置

9.5.2 状态后端
- 过程
首先会由JobManager向所有TaskManager发出检查点的命令,TaskManager收到之后,将当前任务的所有状态进行快照,持久化到存储介质中,一般是分布式文件系统,一般是hdfs
完成之后,多个TaskManager向JobManager返回确认信息,表示检查点保存完成,体现分布式的概念
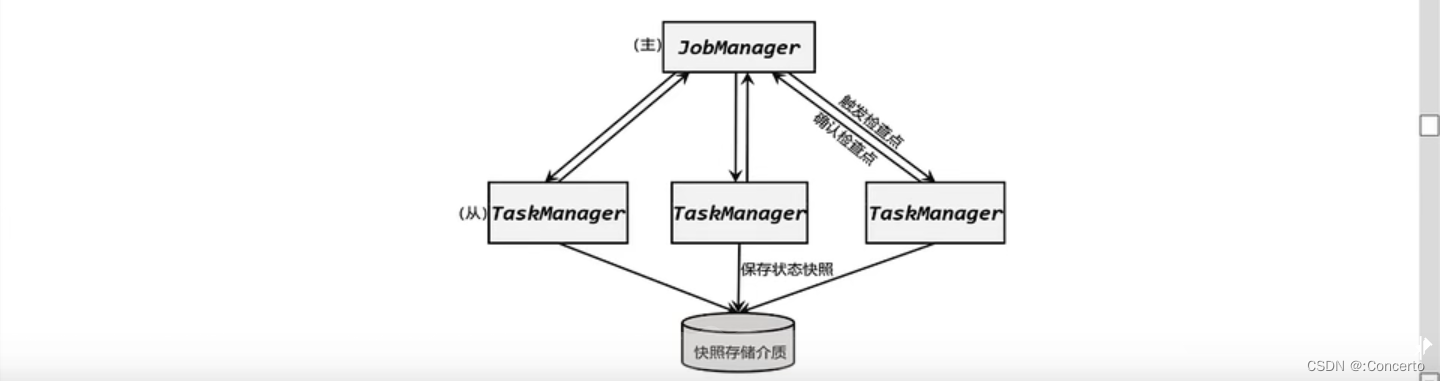
在Flink中,状态的存储、访问以及维护,都是由一个可插拔的组件决定的。这个组件就叫做状态后端
主要负责两件事情,一是本地的状态管理,二是检查点写入远程的持久化存储
- 分类
- 哈希表状态后端(HashMapStateBacked)
把状态放在内存里,保存在TaskManager的JVM堆上,并以键值对形式进行存储,底层是一个哈希表。状态于内存计算性能快,代价是内存的占用
对于检查点的保存,是放在了持久化的分布式文件系统,常用hdfs,或者单独配置一个“检查点存储”来另外指定
- 内嵌RockDB状态后端(EmbeddedRocksDBStateBacked)
将状态数据以key-value存储介质持久化到RocksDB数据库(是一个本地硬盘化的嵌入式数据库)之中,默认存储在TaskManager的本地数据目录中。
采用异步快照并采用增量式保存检查点机制
- 配置
- 在flink-conf.yaml中

- 为每一个作业配置状态后端

但是要引入依赖