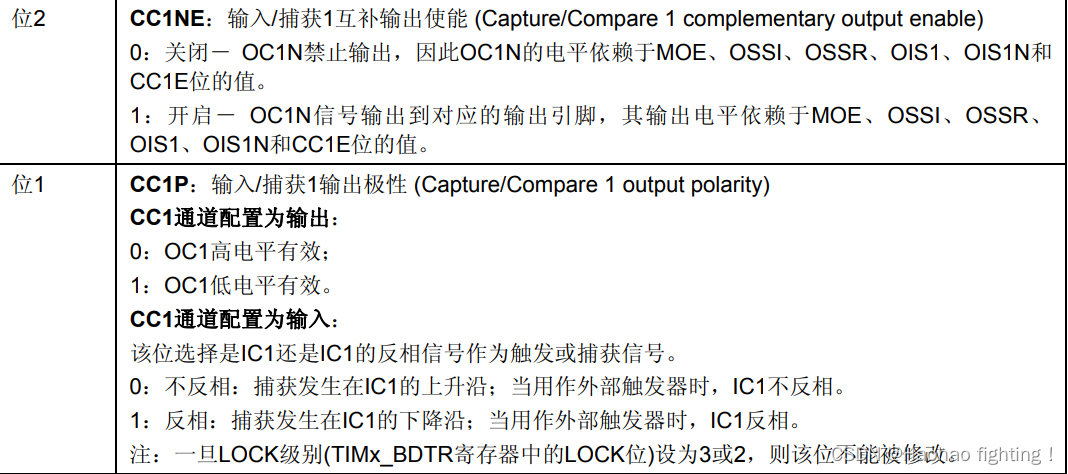
优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN
一、题目
给你链表的头节点head,每k个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是k的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例2:
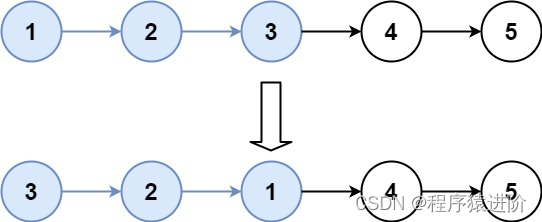
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
二、代码
【1】先实现链表的反转功能
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head) {
// 1、第一个考查点:反转链表
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
// 用户暂时保存next的值;
ListNode nxt = null;
// 遍历链表进行翻转
while(cur != null) {
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// 在原链表上看,pre指向tail节点,cur指向pre下一个节点
return pre;
}
}
【2】实现指定长度数据的反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
// 主要作用:保留开始反转节点的上一个节点
ListNode headPre = new ListNode(0, head);
// 后面会不断更新,直至需要反转
ListNode p0 = headPre;
// 先遍历不反转的部分
for (int i = 1; i < left; i++) {
p0 = p0.next;
}
// 1、第一个考查点:反转链表
ListNode pre = null;
// 这里不再指向头节点,指向开始反转的节点
ListNode cur = p0.next;
// 用户暂时保存next的值;
ListNode nxt = null;
// 遍历链表进行翻转
for (int i = 0; i < right - left + 1; i++) {
if ( cur != null ) {
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
}
// 在原链表上看,pre指向tail节点,cur指向pre下一个节点
// 将 pre节点放入 p0的next节点
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
return headPre;
}
}
【3】实现k位反转,不足k位不反转
```java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 1、计算中记录数
ListNode countList = head;
int count = 0;
while(countList != null) {
count++;
countList = countList.next;
}
// 主要作用:保留开始反转节点的上一个节点
ListNode dummp = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode p0 = dummp;
// 2、第一个考查点:反转链表
while (k <= count) {
// 循环推出条件
count -= k;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = p0.next;
// 遍历链表进行翻转
for(int i = 0; i<k; i++) {
// 用户暂时保存next的值;
ListNode nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// 3、倒序后重新串联
ListNode p0Next = p0.next;
p0.next.next = cur;
p0.next = pre;
p0 = p0Next;
}
// 在原链表上看,pre指向tail节点,cur指向pre下一个节点
return dummp.next;
}
}
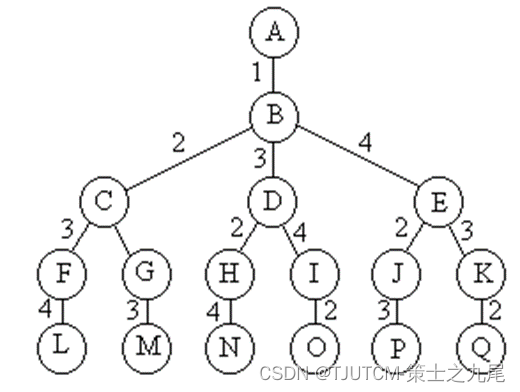
说明:自己尝试画图理解,否则不容易理解,附视频讲解