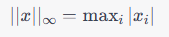栈(Stack)和队列(Queue)都是常见的数据结构,用于存储和操作一组元素。
栈是一种后进先出(Last-In-First-Out,LIFO)的数据结构,类似于把元素堆在一起形成的一堆物体,最后添加的元素首先被取出,而最早添加的元素则最后被取出。类比于现实生活中的例子,可以想象成堆放在一起的盘子,只能从最上面取走或者放置。栈提供了两个基本的操作:
- 入栈(Push):将一个元素添加到栈的顶部。
- 出栈(Pop):从栈的顶部移除一个元素,并返回被移除的元素。
队列是一种先进先出(First-In-First-Out,FIFO)的数据结构,类似于排队等候的人群,最早添加的元素首先被取出,而最后添加的元素则最后被取出。类比于现实生活中的例子,可以想象成加入队列的人们,只有排在前面的人才能先离开队列。队列提供了两个基本的操作:
- 入队(Enqueue):将一个元素添加到队列的末尾。
- 出队(Dequeue):从队列的头部移除一个元素,并返回被移除的元素。
需要注意的是,栈和队列都是线性的数据结构,都可以使用数组或链表来实现。它们在不同场景下有着不同的应用,根据具体的需求选择合适的数据结构可以提高算法的效率。

当我们进一步详细介绍栈和队列时,可以从以下几个方面展开:
-
栈的特点和应用:
- 栈的主要特点是后进先出(LIFO),这意味着最后添加的元素首先被访问。
- 常见的栈的应用包括函数调用栈、表达式求值、逆波兰表达式求值、撤销操作等。
- 栈的实现可以使用数组或链表。使用数组实现的栈称为顺序栈,使用链表实现的栈称为链式栈。
-
队列的特点和应用:
- 队列的主要特点是先进先出(FIFO),这意味着最早添加的元素首先被访问。
- 常见的队列的应用包括任务调度、消息传递、缓冲区管理等。
- 队列的实现同样可以使用数组或链表。使用数组实现的队列称为顺序队列,使用链表实现的队列称为链式队列。
-
栈和队列的基本操作:
- 入栈(Push):将一个元素添加到栈的顶部。
- 出栈(Pop):从栈的顶部移除一个元素,并返回被移除的元素。
- 入队(Enqueue):将一个元素添加到队列的末尾。
- 出队(Dequeue):从队列的头部移除一个元素,并返回被移除的元素。
-
栈和队列的扩展操作:
- 获取栈顶元素(Peek):返回栈顶的元素,但不对栈进行修改。
- 判断栈是否为空(isEmpty):检查栈是否为空,即栈中是否还有元素。
- 判断队列是否为空(isEmpty):检查队列是否为空,即队列中是否还有元素。
- 获取队列的头部元素(Front):返回队列的头部元素,但不对队列进行修改。
通过运用栈和队列,我们可以解决很多实际问题,优化算法的效率以及简化代码的编写。需要根据具体的场景和需求选择适合的数据结构,以充分发挥它们的优势。
当进一步详细介绍栈和队列时,我们可以讨论它们的实现方式、时间复杂度以及一些常见的应用场景。
-
栈的实现方式:
- 数组实现(顺序栈):使用数组来保存栈中的元素。通过一个指针指向栈顶元素,在入栈操作时,将元素添加到指针指向的位置,并将指针上移;在出栈操作时,将指针指向的元素移除,并将指针下移。
- 链表实现(链式栈):使用链表来保存栈中的元素。通过头节点表示栈顶,在入栈操作时,在链表头部插入一个新节点;在出栈操作时,删除链表头节点。
-
队列的实现方式:
- 数组实现(顺序队列):使用数组来保存队列中的元素。使用两个指针分别指向队列的头部和尾部,在入队操作时,将元素添加到尾部,并将尾指针后移;在出队操作时,取出头部元素,并将头指针后移。
- 链表实现(链式队列):使用链表来保存队列中的元素。使用两个指针分别指向队列的头部和尾部,在入队操作时,在链表尾部插入一个新节点;在出队操作时,删除链表头节点。
-
时间复杂度:
- 栈和队列的入栈、出栈、入队和出队操作的时间复杂度均为O(1),即常数时间复杂度。这是因为它们只需要对栈顶或队列头进行操作,不需要遍历整个数据结构。
- 但当需要访问栈或队列中的所有元素时,例如遍历或搜索,时间复杂度将变为O(n),其中n是栈或队列中的元素数量。
-
常见应用场景:
- 栈的应用:函数调用栈(跟踪函数调用和返回)、浏览器的前进后退功能(使用两个栈实现)、括号匹配、逆波兰表达式求值等。
- 队列的应用:任务调度(如操作系统中的进程调度)、消息传递(如消息队列)、缓冲区管理、广度优先搜索(BFS)等。
栈和队列是基础且重要的数据结构,在算法和软件开发中有广泛的应用。了解它们的特点、实现方式和应用场景,可以帮助我们更好地理解和应用它们。
以下是使用C语言实现栈和队列的样例代码:
- C语言中的栈实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int items[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
} Stack;
void initialize(Stack* stack) {
stack->top = -1;
}
void push(Stack* stack, int item) {
if (stack->top == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("Stack Overflow\n");
return;
}
stack->items[++(stack->top)] = item;
}
int pop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == -1) {
printf("Stack Underflow\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return stack->items[(stack->top)--];
}
int is_empty(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == -1;
}
int peek(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == -1) {
printf("Stack is empty\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return stack->items[stack->top];
}
int size(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top + 1;
}
- C语言中的队列实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int items[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
} Queue;
void initialize(Queue* queue) {
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
}
void enqueue(Queue* queue, int item) {
if (queue->rear == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
printf("Queue is full\n");
return;
}
if (queue->front == -1) {
queue->front = 0;
}
queue->items[++(queue->rear)] = item;
}
int dequeue(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->front == -1 || queue->front > queue->rear) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return queue->items[(queue->front)++];
}
int is_empty(Queue* queue) {
return queue->front == -1 || queue->front > queue->rear;
}
int peek(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->front == -1 || queue->front > queue->rear) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return queue->items[queue->front];
}
int size(Queue* queue) {
return queue->rear - queue->front + 1;
}
使用上述C语言代码,可以创建栈和队列对象,并进行相应的操作,如入栈、出栈、入队、出队等。
请注意,在C语言中,我们需要手动处理溢出和下溢的情况,并使用初始化函数来初始化栈和队列。此外,由于数组的特性,使用数组下标来实现栈和队列的操作。
这是使用C语言实现栈和队列的另一种方法:
- C语言中的栈实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int* items;
int top;
int size;
} Stack;
Stack* create_stack(int size) {
Stack* stack = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
stack->items = (int*)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
stack->top = -1;
stack->size = size;
return stack;
}
void push(Stack* stack, int item) {
if (stack->top == stack->size - 1) {
printf("Stack Overflow\n");
return;
}
stack->items[++(stack->top)] = item;
}
int pop(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == -1) {
printf("Stack Underflow\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return stack->items[(stack->top)--];
}
int is_empty(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top == -1;
}
int peek(Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == -1) {
printf("Stack is empty\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return stack->items[stack->top];
}
int size(Stack* stack) {
return stack->top + 1;
}
- C语言中的队列实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int* items;
int front;
int rear;
int size;
} Queue;
Queue* create_queue(int size) {
Queue* queue = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
queue->items = (int*)malloc(size * sizeof(int));
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
queue->size = size;
return queue;
}
void enqueue(Queue* queue, int item) {
if (queue->rear == queue->size - 1) {
printf("Queue is full\n");
return;
}
if (queue->front == -1) {
queue->front = 0;
}
queue->items[++(queue->rear)] = item;
}
int dequeue(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->front == -1 || queue->front > queue->rear) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return queue->items[(queue->front)++];
}
int is_empty(Queue* queue) {
return queue->front == -1 || queue->front > queue->rear;
}
int peek(Queue* queue) {
if (queue->front == -1 || queue->front > queue->rear) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return queue->items[queue->front];
}
int size(Queue* queue) {
return queue->rear - queue->front + 1;
}
这种实现方式通过动态分配内存来创建栈和队列的数组,允许在运行时指定大小,并且能够避免固定大小的限制。
其他用途
栈和队列是一种常用的数据结构,在计算机科学和编程中有广泛的应用。以下是一些使用栈和队列的常见场景和用途:
栈的应用:
- 函数调用:栈可以用于函数调用过程中的参数传递、返回地址保存等。
- 表达式求值:栈可以用于中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式,并进行表达式求值。
- 浏览器历史记录:栈可以用于浏览器的前进、后退功能的实现。
- 括号匹配:栈可以用于检查表达式中的括号是否匹配。
- 撤销操作:栈可以用于记忆用户的操作序列,以便撤销之前的操作。
队列的应用:
- 任务调度:队列可以用于任务调度,按照先来先服务的原则处理任务。
- 缓冲区管理:队列可以用于管理缓冲区,实现生产者-消费者模型。
- 广度优先搜索:队列可以用于广度优先搜索算法,用于解决图和树的遍历问题。
- 打印队列:队列可以用于管理打印任务的顺序,按照先到先服务的原则进行打印。
- 消息传递:队列可以用于消息传递和事件驱动编程中,实现消息队列和事件队列的功能。
除了上述应用,栈和队列还在其他许多领域和算法中得到应用,例如图算法、字符串处理、编译器设计等。它们是解决问题和优化算法的重要工具之一。
当然,我很乐意为您继续提供关于栈和队列的其他应用。以下是更多使用栈和队列的示例:
栈的应用:
- 撤销/恢复功能:栈可用于实现编辑器、图形界面应用程序等中的撤销和恢复功能,保存操作历史并逆向执行操作。
- 网页浏览器中的前进和后退功能:通过使用两个栈,一个用于保存已访问的网页,另一个用于保存后退访问的网页,可以实现前进和后退浏览功能。
- 符号表达式求解:在编译器和解释器中,栈用于解析并计算符号表达式,例如逆波兰表达式。
- 历史记录:栈可用于实现文本编辑器、命令行终端等应用程序中的历史记录功能。
队列的应用:
- 消息传递和任务处理:队列可用于实现多线程/多进程环境下的任务调度和消息传递机制,确保任务按照顺序执行。
- 模拟系统:队列可用于模拟和建模真实世界中的系统,如银行排队、交通流量等。
- 并发请求处理:在网络服务器中,队列可用于处理并发请求,避免资源竞争和请求丢失。
- 图像处理:队列可用于图像处理中的滤波器、卷积等操作的处理和管理。
下面是栈和队列的简单示例代码:
栈的实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int stack[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
} Stack;
void initStack(Stack* s) {
s->top = -1;
}
int isEmpty(Stack* s) {
return s->top == -1;
}
int isFull(Stack* s) {
return s->top == MAX_SIZE - 1;
}
void push(Stack* s, int item) {
if (isFull(s)) {
printf("Stack is full. Cannot push %d.\n", item);
return;
}
s->stack[++(s->top)] = item;
}
int pop(Stack* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) {
printf("Stack is empty. Cannot pop.\n");
return -1;
}
return s->stack[(s->top)--];
}
int peek(Stack* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) {
printf("Stack is empty. No element to peek.\n");
return -1;
}
return s->stack[s->top];
}
队列的实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int queue[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
} Queue;
void initQueue(Queue* q) {
q->front = -1;
q->rear = -1;
}
int isEmpty(Queue* q) {
return q->front == -1 && q->rear == -1;
}
int isFull(Queue* q) {
return (q->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == q->front;
}
void enqueue(Queue* q, int item) {
if (isFull(q)) {
printf("Queue is full. Cannot enqueue %d.\n", item);
return;
}
if (isEmpty(q)) {
q->front = q->rear = 0;
} else {
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
q->queue[q->rear] = item;
}
int dequeue(Queue* q) {
if (isEmpty(q)) {
printf("Queue is empty. Cannot dequeue.\n");
return -1;
}
int item = q->queue[q->front];
if (q->front == q->rear) {
q->front = q->rear = -1;
} else {
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
return item;
}
int front(Queue* q) {
if (isEmpty(q)) {
printf("Queue is empty. No front element.\n");
return -1;
}
return q->queue[q->front];
}
这些示例代码使用了C语言的数组来实现栈和队列。栈的实现使用了一个top指针来表示栈顶,队列的实现使用了front和rear两个指针来表示队首和队尾。
您可以使用以下代码来测试栈和队列的功能:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// 测试栈
Stack stack;
initStack(&stack);
push(&stack, 1);
push(&stack, 2);
push(&stack, 3);
printf("%d\n", pop(&stack)); // 输出:3
printf("%d\n", peek(&stack)); // 输出:2
// 测试队列
Queue queue;
initQueue(&queue);
enqueue(&queue, 1);
enqueue(&queue, 2);
enqueue(&queue, 3);
printf("%d\n", dequeue(&queue)); // 输出:1
printf("%d\n", front(&queue)); // 输出:2
return 0;
}
栈和队列是计算机科学中常用的数据结构,它们在实际应用中有很多用途。以下是一些常见的实际应用场景:
栈的实际应用:
- 函数调用:栈常用于函数调用过程中的内存管理。当一个函数被调用时,函数的局部变量和参数会被压入栈中,在函数执行完毕后再从栈中弹出。
- 表达式求值:在编译器或计算器等应用中,栈可以用来求解表达式的值。常见的算术表达式求值算法就是基于栈来实现的,例如逆波兰表达式求值。
- 括号匹配:栈可以用于检测括号是否匹配。通过遍历字符串并将左括号入栈,当遇到右括号时,弹出栈顶元素并检查是否匹配。
- 浏览器的前进和后退:浏览器中的前进和后退功能可以使用两个栈来实现,一个栈保存前进的页面,另一个栈保存后退的页面。
队列的实际应用:
- 任务调度:操作系统中的任务调度通常使用队列来实现。任务按照先进先出的顺序排队,调度器从队列中选择下一个要执行的任务。
- 网络数据传输:在计算机网络中,队列用于缓存发送和接收的数据包。数据包按照顺序进入队列,并按照先进先出的原则进行传输。
- 多线程同步:在多线程编程中,队列可以用于线程间的同步和通信。一个线程将数据放入队列,另一个线程从队列中取出数据。
- 打印队列:打印机常常需要处理大量的打印请求,这些请求可以使用队列来进行排队,保证打印的顺序。
除了以上提到的实际应用,栈和队列还被广泛应用于图算法、深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索以及其他许多算法和数据结构的实现中。
以下是C++语言实现栈和队列的代码示例:
栈的实现:
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
using namespace std;
class Stack {
private:
int stack[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
public:
Stack() {
top = -1;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return top == MAX_SIZE - 1;
}
void push(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Stack is full. Cannot push " << item << endl;
return;
}
stack[++top] = item;
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty. Cannot pop." << endl;
return -1;
}
return stack[top--];
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty. No element to peek." << endl;
return -1;
}
return stack[top];
}
};
int main() {
// 测试栈
Stack stack;
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
cout << stack.pop() << endl; // 输出:3
cout << stack.peek() << endl; // 输出:2
return 0;
}
队列的实现:
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
using namespace std;
class Queue {
private:
int queue[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
public:
Queue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return front == -1 && rear == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == front;
}
void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is full. Cannot enqueue " << item << endl;
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
front = rear = 0;
} else {
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
queue[rear] = item;
}
int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty. Cannot dequeue." << endl;
return -1;
}
int item = queue[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = -1;
} else {
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
return item;
}
int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty. No front element." << endl;
return -1;
}
return queue[front];
}
};
int main() {
// 测试队列
Queue queue;
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(3);
cout << queue.dequeue() << endl; // 输出:1
cout << queue.getFront() << endl; // 输出:2
return 0;
}
这些示例代码使用了C++语言的类来实现栈和队列。它们包括一些常见的操作,例如入栈、出栈、获取栈顶元素、入队、出队、获取队首元素等。
您可以使用以下代码来测试栈和队列的功能:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 测试栈
Stack stack;
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
cout << stack.pop() << endl; // 输出:3
cout << stack.peek() << endl; // 输出:2
// 测试队列
Queue queue;
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(3);
cout << queue.dequeue() << endl; // 输出:1
cout << queue.getFront() << endl; // 输出:2
return 0;
}
首先是栈的代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
using namespace std;
class Stack {
private:
int stack[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
public:
Stack() {
top = -1;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return top == MAX_SIZE - 1;
}
void push(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Stack is full. Cannot push " << item << endl;
return;
}
stack[++top] = item;
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty. Cannot pop." << endl;
return -1;
}
return stack[top--];
}
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty. No element to peek." << endl;
return -1;
}
return stack[top];
}
};
int main() {
Stack stack;
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
cout << stack.pop() << endl; // 输出:3
cout << stack.peek() << endl; // 输出:2
return 0;
}
上述代码实现了一个基本的栈,通过push函数将元素压入栈中,pop函数将栈顶元素弹出并返回,peek函数返回栈顶元素的值,isEmpty函数检查栈是否为空,isFull函数检查栈是否已满。
在main函数中,我们创建了一个Stack对象,并依次将元素1、2、3压入栈中。然后我们使用pop函数弹出栈顶元素,并用peek函数获取新的栈顶元素。
接下来是队列的代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
using namespace std;
class Queue {
private:
int queue[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
public:
Queue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return front == -1 && rear == -1;
}
bool isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == front;
}
void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is full. Cannot enqueue " << item << endl;
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
front = rear = 0;
} else {
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
queue[rear] = item;
}
int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty. Cannot dequeue." << endl;
return -1;
}
int item = queue[front];
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = -1;
} else {
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
return item;
}
int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is empty. No front element." << endl;
return -1;
}
return queue[front];
}
};
int main() {
Queue queue;
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(2);
queue.enqueue(3);
cout << queue.dequeue() << endl; // 输出:1
cout << queue.getFront() << endl; // 输出:2
return 0;
}
上述代码实现了一个基本的队列,通过enqueue函数将元素入队列,dequeue函数从队列中取出并返回元素,getFront函数返回队首元素的值,isEmpty函数检查队列是否为空,isFull函数检查队列是否已满。
在main函数中,我们创建了一个Queue对象,并依次将元素1、2、3入队列。然后我们使用dequeue函数出队列一个元素,并用getFront函数获取新的队首元素。