文章目录
- 0 前言
- 1 技术背景
- 2 技术介绍
- 3 重识别技术实现
- 3.1 数据集
- 3.2 Person REID
- 3.2.1 算法原理
- 3.2.2 算法流程图
- 4 实现效果
- 5 部分代码
- 6 最后
0 前言
🔥 优质竞赛项目系列,今天要分享的是
基于深度学习的行人重识别
该项目较为新颖,适合作为竞赛课题方向,学长非常推荐!
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
1 技术背景
行人重识别技术,是智能视频监控系统的关键技术之一,其研宄是针对特定目标行人的视频检索识别问题。行人再识别是一种自动的目标判定识别技术,它综合地运用了计算机视觉技术、机器学习、视频处理、图像分析、模式识别等多种相关技术于监控系统中,其主要描述的是在多个无重叠视域的摄像头监控环境之下,通过相关算法判断在某个镜头下出现过的感兴趣的目标人物是否在其他摄像头下再次出现。
2 技术介绍
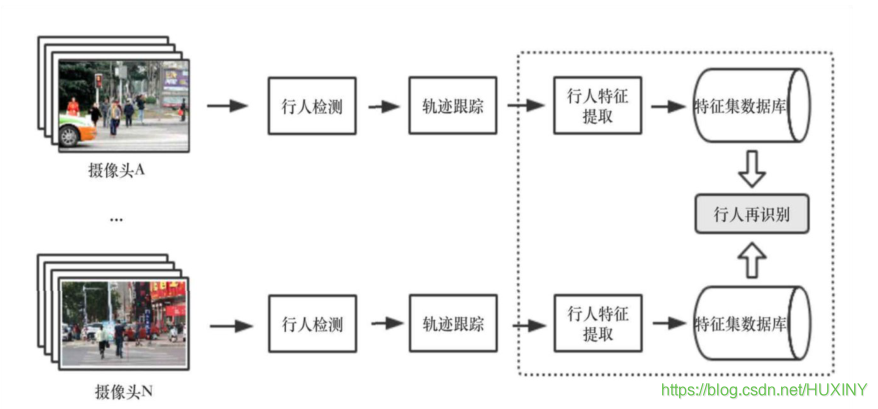
在视频监控系统中,行人再识别任务的整体框架如下图所示:
—个监控系统由多个视域不相交的监控摄像头组成,摄像机的位置可以随时更改,同时也可以随时增加或减少摄像机。不两监控摄像头所摄取的画面、视角等各不相同。在这样的监控系统中,对行人的动向监测是,至关重要的。
对行人的监控主要基于以下三个基本的模块:
-
行人检测:
行人检测的目标是在图片中定位到行人的具体位置。这一步骤仅涉及到对于静止的单张图片的处理,而没有动态的处理,没有时间序列上的相关分析。 -
行人轨迹跟踪:
行人轨迹跟踪的主要任务是在一段时间内提供目标任务的位置移动信息。与行人检测不同,轨迹跟踪与时间序列紧密相关。行人轨迹跟踪是在行人检测的基础上进行的。 -
行人再识别:
行人再识别任务的目标是在没有相重合视域的摄像头或摄像机网络内的不同背景下的许多行人中中识别某个特定行人。行人再识别的分析基于行人检测和轨迹跟踪的结果。其主要步骤首先是检测和跟踪视频序列中的行人,从而提取行人的特征,建立构建模型所需的行人特征集数据库。
在此基础上,用训练出的模型进行学习从而判断得出某个摄像头下的行人与另一摄像头下的目标人物为同一个人。在智能视频监控系统中的行人再识别任务具有非常广阔的应用前景。行人再识别的应用与行人检测、目标跟踪、行人行为分析、敏感事件检测等等都有着紧密的联系,这些分析处理技术对于公安部门的刑侦工作和城市安防建设工作有着重要的意义。
3 重识别技术实现
3.1 数据集
目前行人再识别的研究需要大量的行人数据集。行人再识别的数据集主要是通过在不同区域假设无重叠视域的多个摄像头来采集拍摄有行人图像的视频,然后对视频提取帧,对于视频帧图像采用人工标注或算法识别的方式进行人体检测及标注来完成的。行人再识别数据集中包含了跨背景、跨时间、不同拍摄角度下、各种不同姿势的行人图片,如下图所示。

3.2 Person REID
3.2.1 算法原理
给定N个不同的行人从不同的拍摄视角的无重叠视域摄像机捕获的图像集合,行人再识别的任务是学习一个模型,该模型可以尽可能减小行人姿势和背景、光照等因素带来的影响,从而更好地对行人进行整体上的描述,更准确地对不同行人图像之间的相似度进行衡量。
我这里使用注意力相关的特征的卷积神经网络。该基础卷积神经网络架构可以由任何卷积神经网络模型代替,例如,VGG-19,ResNet-101。
该算法的核心模块在于注意力学习模型。
3.2.2 算法流程图

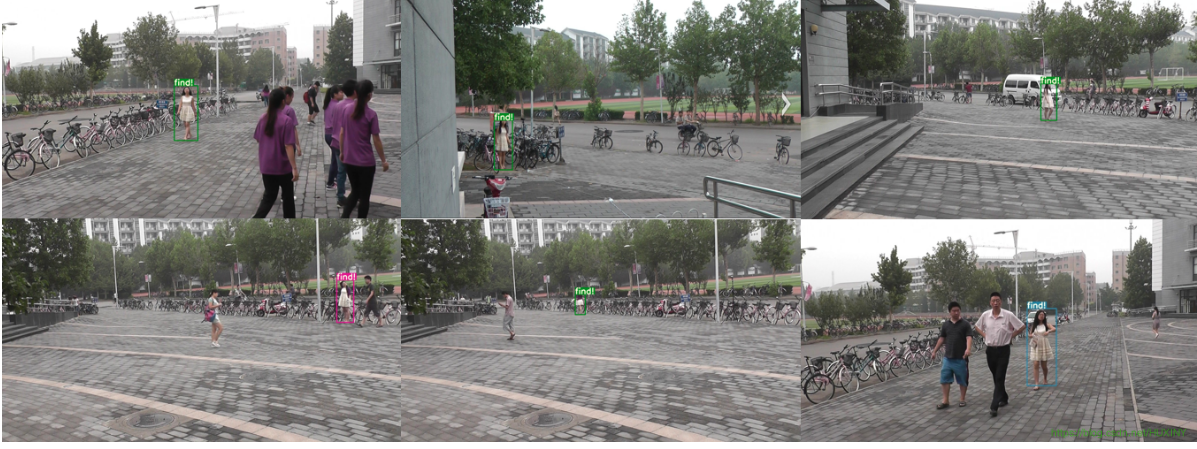
4 实现效果
在多行人场景下,对特定行人进行寻找

5 部分代码
import argparse
import time
from sys import platform
from models import *
from utils.datasets import *
from utils.utils import *
from reid.data import make_data_loader
from reid.data.transforms import build_transforms
from reid.modeling import build_model
from reid.config import cfg as reidCfg
def detect(cfg,
data,
weights,
images='data/samples', # input folder
output='output', # output folder
fourcc='mp4v', # video codec
img_size=416,
conf_thres=0.5,
nms_thres=0.5,
dist_thres=1.0,
save_txt=False,
save_images=True):
# Initialize
device = torch_utils.select_device(force_cpu=False)
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False # set False for reproducible results
if os.path.exists(output):
shutil.rmtree(output) # delete output folder
os.makedirs(output) # make new output folder
############# 行人重识别模型初始化 #############
query_loader, num_query = make_data_loader(reidCfg)
reidModel = build_model(reidCfg, num_classes=10126)
reidModel.load_param(reidCfg.TEST.WEIGHT)
reidModel.to(device).eval()
query_feats = []
query_pids = []
for i, batch in enumerate(query_loader):
with torch.no_grad():
img, pid, camid = batch
img = img.to(device)
feat = reidModel(img) # 一共2张待查询图片,每张图片特征向量2048 torch.Size([2, 2048])
query_feats.append(feat)
query_pids.extend(np.asarray(pid)) # extend() 函数用于在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表)。
query_feats = torch.cat(query_feats, dim=0) # torch.Size([2, 2048])
print("The query feature is normalized")
query_feats = torch.nn.functional.normalize(query_feats, dim=1, p=2) # 计算出查询图片的特征向量
############# 行人检测模型初始化 #############
model = Darknet(cfg, img_size)
# Load weights
if weights.endswith('.pt'): # pytorch format
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights, map_location=device)['model'])
else: # darknet format
_ = load_darknet_weights(model, weights)
# Eval mode
model.to(device).eval()
# Half precision
opt.half = opt.half and device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA
if opt.half:
model.half()
# Set Dataloader
vid_path, vid_writer = None, None
if opt.webcam:
save_images = False
dataloader = LoadWebcam(img_size=img_size, half=opt.half)
else:
dataloader = LoadImages(images, img_size=img_size, half=opt.half)
# Get classes and colors
# parse_data_cfg(data)['names']:得到类别名称文件路径 names=data/coco.names
classes = load_classes(parse_data_cfg(data)['names']) # 得到类别名列表: ['person', 'bicycle'...]
colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(len(classes))] # 对于每种类别随机使用一种颜色画框
# Run inference
t0 = time.time()
for i, (path, img, im0, vid_cap) in enumerate(dataloader):
t = time.time()
# if i < 500 or i % 5 == 0:
# continue
save_path = str(Path(output) / Path(path).name) # 保存的路径
# Get detections shape: (3, 416, 320)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).unsqueeze(0).to(device) # torch.Size([1, 3, 416, 320])
pred, _ = model(img) # 经过处理的网络预测,和原始的
det = non_max_suppression(pred.float(), conf_thres, nms_thres)[0] # torch.Size([5, 7])
if det is not None and len(det) > 0:
# Rescale boxes from 416 to true image size 映射到原图
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results to screen image 1/3 data\samples\000493.jpg: 288x416 5 persons, Done. (0.869s)
print('%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:], end='') # print image size '288x416'
for c in det[:, -1].unique(): # 对图片的所有类进行遍历循环
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # 得到了当前类别的个数,也可以用来统计数目
if classes[int(c)] == 'person':
print('%g %ss' % (n, classes[int(c)]), end=', ') # 打印个数和类别'5 persons'
# Draw bounding boxes and labels of detections
# (x1y1x2y2, obj_conf, class_conf, class_pred)
count = 0
gallery_img = []
gallery_loc = []
for *xyxy, conf, cls_conf, cls in det: # 对于最后的预测框进行遍历
# *xyxy: 对于原图来说的左上角右下角坐标: [tensor(349.), tensor(26.), tensor(468.), tensor(341.)]
if save_txt: # Write to file
with open(save_path + '.txt', 'a') as file:
file.write(('%g ' * 6 + '\n') % (*xyxy, cls, conf))
# Add bbox to the image
label = '%s %.2f' % (classes[int(cls)], conf) # 'person 1.00'
if classes[int(cls)] == 'person':
#plot_one_bo x(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)])
xmin = int(xyxy[0])
ymin = int(xyxy[1])
xmax = int(xyxy[2])
ymax = int(xyxy[3])
w = xmax - xmin # 233
h = ymax - ymin # 602
# 如果检测到的行人太小了,感觉意义也不大
# 这里需要根据实际情况稍微设置下
if w*h > 500:
gallery_loc.append((xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax))
crop_img = im0[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax] # HWC (602, 233, 3)
crop_img = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(crop_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) # PIL: (233, 602)
crop_img = build_transforms(reidCfg)(crop_img).unsqueeze(0) # torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 128])
gallery_img.append(crop_img)
if gallery_img:
gallery_img = torch.cat(gallery_img, dim=0) # torch.Size([7, 3, 256, 128])
gallery_img = gallery_img.to(device)
gallery_feats = reidModel(gallery_img) # torch.Size([7, 2048])
print("The gallery feature is normalized")
gallery_feats = torch.nn.functional.normalize(gallery_feats, dim=1, p=2) # 计算出查询图片的特征向量
# m: 2
# n: 7
m, n = query_feats.shape[0], gallery_feats.shape[0]
distmat = torch.pow(query_feats, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(m, n) + \
torch.pow(gallery_feats, 2).sum(dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(n, m).t()
# out=(beta∗M)+(alpha∗mat1@mat2)
# qf^2 + gf^2 - 2 * qf@gf.t()
# distmat - 2 * qf@gf.t()
# distmat: qf^2 + gf^2
# qf: torch.Size([2, 2048])
# gf: torch.Size([7, 2048])
distmat.addmm_(1, -2, query_feats, gallery_feats.t())
# distmat = (qf - gf)^2
# distmat = np.array([[1.79536, 2.00926, 0.52790, 1.98851, 2.15138, 1.75929, 1.99410],
# [1.78843, 1.96036, 0.53674, 1.98929, 1.99490, 1.84878, 1.98575]])
distmat = distmat.cpu().numpy() # : (3, 12)
distmat = distmat.sum(axis=0) / len(query_feats) # 平均一下query中同一行人的多个结果
index = distmat.argmin()
if distmat[index] < dist_thres:
print('距离:%s'%distmat[index])
plot_one_box(gallery_loc[index], im0, label='find!', color=colors[int(cls)])
# cv2.imshow('person search', im0)
# cv2.waitKey()
print('Done. (%.3fs)' % (time.time() - t))
if opt.webcam: # Show live webcam
cv2.imshow(weights, im0)
if save_images: # Save image with detections
if dataloader.mode == 'images':
cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)
else:
if vid_path != save_path: # new video
vid_path = save_path
if isinstance(vid_writer, cv2.VideoWriter):
vid_writer.release() # release previous video writer
fps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
width = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
height = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*fourcc), fps, (width, height))
vid_writer.write(im0)
if save_images:
print('Results saved to %s' % os.getcwd() + os.sep + output)
if platform == 'darwin': # macos
os.system('open ' + output + ' ' + save_path)
print('Done. (%.3fs)' % (time.time() - t0))
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='cfg/yolov3.cfg', help="模型配置文件路径")
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/coco.data', help="数据集配置文件所在路径")
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='weights/yolov3.weights', help='模型权重文件路径')
parser.add_argument('--images', type=str, default='data/samples', help='需要进行检测的图片文件夹')
parser.add_argument('-q', '--query', default=r'query', help='查询图片的读取路径.')
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=416, help='输入分辨率大小')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.1, help='物体置信度阈值')
parser.add_argument('--nms-thres', type=float, default=0.4, help='NMS阈值')
parser.add_argument('--dist_thres', type=float, default=1.0, help='行人图片距离阈值,小于这个距离,就认为是该行人')
parser.add_argument('--fourcc', type=str, default='mp4v', help='fourcc output video codec (verify ffmpeg support)')
parser.add_argument('--output', type=str, default='output', help='检测后的图片或视频保存的路径')
parser.add_argument('--half', default=False, help='是否采用半精度FP16进行推理')
parser.add_argument('--webcam', default=False, help='是否使用摄像头进行检测')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
with torch.no_grad():
detect(opt.cfg,
opt.data,
opt.weights,
images=opt.images,
img_size=opt.img_size,
conf_thres=opt.conf_thres,
nms_thres=opt.nms_thres,
dist_thres=opt.dist_thres,
fourcc=opt.fourcc,
output=opt.output)
6 最后
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate