Mybatis学习笔记3 在Web中应用Mybatis_biubiubiu0706的博客-CSDN博客
上篇最后在DAO实现类中,代码固定,没有业务逻辑,这篇笔记中对该实现类进行封装,就是说,以后不用写DAO实现类了


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--javassist依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.29.1-GA</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>下面是几个javassist基本使用的demo
import javassist.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLClassLoader;
/**
* @author hrui
* @date 2023/9/17 18:05
*/
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test03() throws Exception {
// 获取类池,这个类池就是用来生成class的
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 制造类(需要告诉javassist,类名是啥)
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.example.javassist.Test");//在内存中
//制造方法
String methodCode="public void insert(){System.out.println(\"Hello World\");}";
CtMethod ctMethod=CtMethod.make(methodCode,ctClass);
// 给类添加⽅法
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
//写入磁盘
ctClass.writeFile("src/main/java/");
//还可以这样 下面是可以加载到的,加载不到原因可能是我当时没有放到测试目录
// Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.example.javassist.Test");//这样加载不到类
//用自定义类加载器
ClassLoader customClassLoader = new URLClassLoader(new URL[]{new File("src/main/java/").toURI().toURL()});
Class<?> aClass = customClassLoader.loadClass("com.example.javassist.Test");
Object instance = aClass.newInstance();
// 调用生成的方法
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("insert");
method.invoke(instance);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void test02() throws Exception {
// 获取类池,这个类池就是用来生成class的
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 制造类(需要告诉javassist,类名是啥)
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.example.javassist.Test");//在内存中
//制造方法
String methodCode="public void insert(){System.out.println(123);}";
CtMethod ctMethod=CtMethod.make(methodCode,ctClass);
// 给类添加⽅法
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
// 用反射调⽤⽅法 这样是内存中直接调用
Class<?> aClass = ctClass.toClass();
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("insert");
method.invoke(o);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void test01() throws Exception {
// 获取类池,这个类池就是用来生成class的
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 制造类(需要告诉javassist,类名是啥)
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.example.javassist.Test");//在内存中
// 制造⽅法
// 1.返回值类型 2.⽅法名 3.形式参数列表 4.所属类
CtMethod ctMethod = new CtMethod(CtClass.voidType, "insert", new
CtClass[]{}, ctClass);
// 设置⽅法的修饰符列表
ctMethod.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC);
// 设置⽅法体
ctMethod.setBody("{System.out.println(\"hello world\");}");
// 给类添加⽅法
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
// 用反射调⽤⽅法 这样是内存中直接调用
Class<?> aClass = ctClass.toClass();
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("insert");
method.invoke(o);
}
}因本机安装的是JDK8,没有报错,将高版本报错情况记录下来,以便以后用高版本JDK遇到类似问题,方便解决


解决办法



设想一个问题 既然这样的话,能不能用javassist动态设计一个类,然后实现DAO接口呢

@org.junit.Test
public void testGenerateImpl() throws Exception {
//获取类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
//制造类
CtClass ctClassImpl = pool.makeClass("com.example.javassist.TestImpl");//在内存中
//制造接口
CtClass ctClassInterface = pool.makeInterface("com.example.javassist.Test1");//在内存中
//类去实现接口 又可以说是类去添加接口
ctClassImpl.addInterface(ctClassInterface);//TestImpl implements Test1
//去实现接口中的方法 这个相对比较复杂,这里我们假设接口里就一个方法
//先制造方法
CtMethod ctMethod=CtMethod.make("public void delete(){System.out.println(\"删除成功!\");}",ctClassImpl);
//将方法添加到类中
ctClassImpl.addMethod(ctMethod);
//在内存中生成类(这一步JVM已经将类加载到内存中)
Class<?> aClass = ctClassImpl.toClass();
Test1 test=(Test1)aClass.newInstance();
test.delete();
}
上面方法示例可见,我们是有办法动态生成接口实现类的
上面方法演示过于简单
比如说

下面使用javassist动态生成实现类并实现接口中所有方法

@org.junit.Test
public void testGenerateImpl2(){
//获取类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
//制造类
CtClass ctClassImpl = pool.makeClass("com.example.javassist.TestImpl2");//在内存中
//制造接口
CtClass ctClassInterface = pool.makeInterface("com.example.javassist.Test1");//在内存中
//类去实现接口 又可以说是类去添加接口
ctClassImpl.addInterface(ctClassInterface);//TestImpl2 implements Test1
//实现接口中所有方法
//先获取接口中的所有方法
Method[] declaredMethods = Test1.class.getDeclaredMethods();
//System.out.println(declaredMethods.length);
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(declaredMethods));
Arrays.stream(declaredMethods).forEach(method -> {
//method是接口中的抽象方法,我们需要把抽象方法实现了
try {
//methodCode public void delete(){}
//methodCode public int update(String actno,double balance)
StringBuilder methodCode=new StringBuilder();
methodCode.append("public ");
methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName()+" ");//返回值类型
methodCode.append(method.getName());//追加方法名
methodCode.append("(");
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();//参数有可能1个也可能有多个
for(int i=0;i<parameterTypes.length;i++){
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];//第一个参数的类型
methodCode.append(parameterType.getName());//参数类型
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append("arg"+i);//参数名
if(i!=(parameterTypes.length-1)) {
methodCode.append(",");//如果不是最后一个参数
}
}
methodCode.append("){System.out.println(\"Hello World\");}");
System.out.println(methodCode);
//CtMethod ctMethod=CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(),ctClassImpl);
//将方法添加到类中
//ctClassImpl.addMethod(ctMethod);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}程序写到这部 先执行一下
public int update(java.lang.String arg0,double arg1){System.out.println("Hello World");}
public void delete(){System.out.println("Hello World");}
public int insert(java.lang.String arg0){System.out.println("Hello World");}
public java.lang.String selectByActno(java.lang.String arg0){System.out.println("Hello World");}
接下来就是关于返回值的问题
@org.junit.Test
public void testGenerateImpl2() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, CannotCompileException {
//获取类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
//制造类
CtClass ctClassImpl = pool.makeClass("com.example.javassist.TestImpl2");//在内存中
//制造接口
CtClass ctClassInterface = pool.makeInterface("com.example.javassist.Test1");//在内存中
//类去实现接口 又可以说是类去添加接口
ctClassImpl.addInterface(ctClassInterface);//TestImpl2 implements Test1
//实现接口中所有方法
//先获取接口中的所有方法
Method[] declaredMethods = Test1.class.getDeclaredMethods();
//System.out.println(declaredMethods.length);
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(declaredMethods));
Arrays.stream(declaredMethods).forEach(method -> {
//method是接口中的抽象方法,我们需要把抽象方法实现了
try {
//methodCode public void delete(){}
//methodCode public int update(String actno,double balance)
StringBuilder methodCode=new StringBuilder();
methodCode.append("public ");
methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName()+" ");//返回值类型
methodCode.append(method.getName());//追加方法名
methodCode.append("(");
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();//参数有可能1个也可能有多个
for(int i=0;i<parameterTypes.length;i++){
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];//第一个参数的类型
methodCode.append(parameterType.getName());//参数类型
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append("arg"+i);//参数名
if(i!=(parameterTypes.length-1)) {
methodCode.append(",");//如果不是最后一个参数
}
}
methodCode.append("){System.out.println(\"Hello World\");");
//动态添加renturn语句
String simpleName = method.getReturnType().getSimpleName();//比如 int void String
if("void".equals(simpleName)){
//如果是void啥都不写
}else if("int".equals(simpleName)){
methodCode.append("return 1;");
}else if("String".equals(simpleName)){
methodCode.append("return \"1\";");
}
//System.out.println(simpleName);
methodCode.append("}");
System.out.println(methodCode);
CtMethod ctMethod=CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(),ctClassImpl);
//将方法添加到类中
ctClassImpl.addMethod(ctMethod);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
//在内存中生成类(这一步JVM已经将类加载到内存中)
Class<?> aClass = ctClassImpl.toClass();
Test1 test=(Test1)aClass.newInstance();
test.delete();
int count = test.insert("sad");
test.update("sad",1.1);
}上面方式虽然实现的比较low,主要为说明Mybatis底层javassist的使用
下面对
Mybatis学习笔记3 在Web中应用Mybatis_biubiubiu0706的博客-CSDN博客
中的项目进行修改,就是说AccountDaoImpl不写了
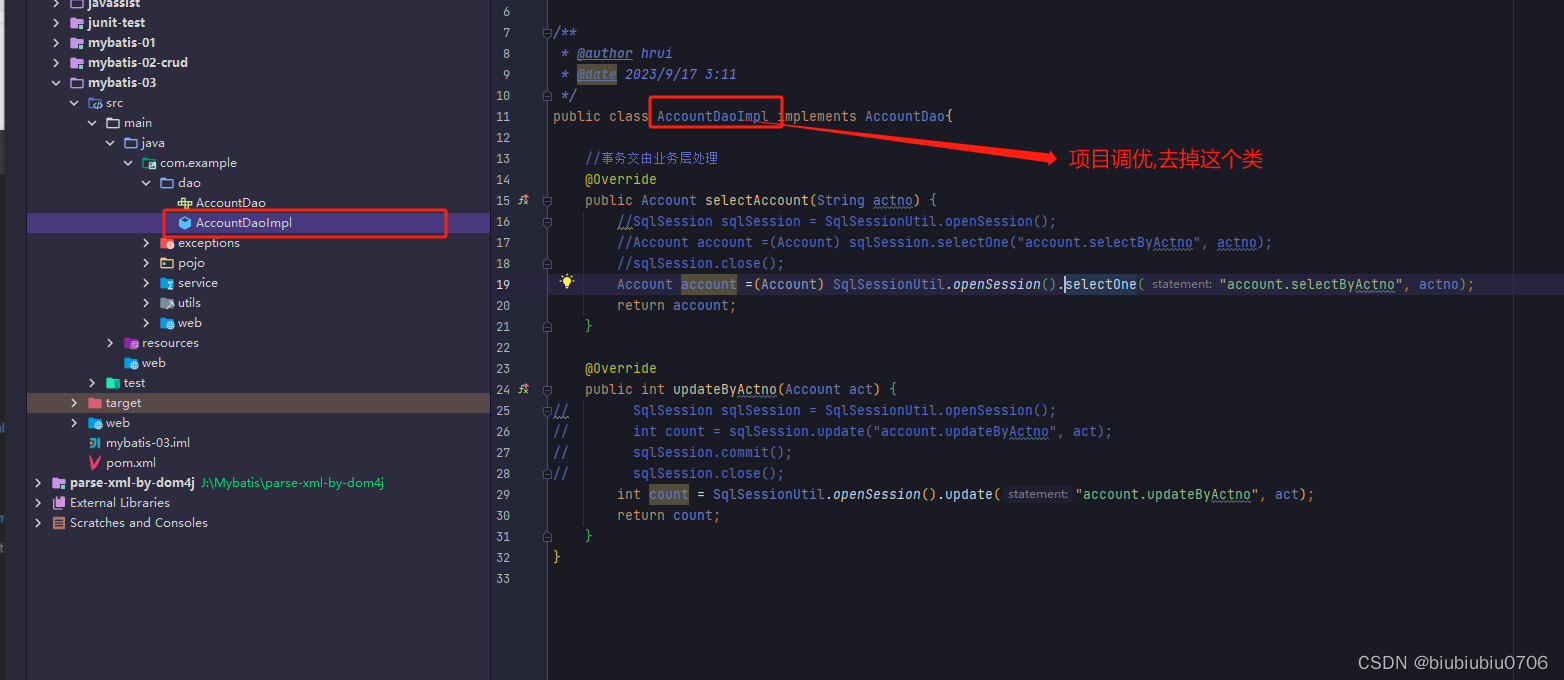
mybatis-03中只引入了mybatis依赖,但是可以直接使用ClassPool,而这个类是javassist的,原因是mybatis对javassist进行了封装
下面这段代码就是大概性的介绍Mybatis内部的一种封装
package com.example.utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.ClassPool;
import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.ibatis.javassist.CtMethod;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 工具类:可以动态的生成DAO的实现类。(或者说可以动态生成DAO的代理类)
* 注意注意注意注意注意!!!!!!:
* 凡是使用GenerateDaoProxy的,SQLMapper.xml映射文件中namespace必须是dao接口的全名,id必须是dao接口中的方法名。
*/
public class GenerateDaoProxy { // GenerateDaoProxy是mybatis框架的开发者写的。
/**
* 生成dao接口实现类,并且将实现类的对象创建出来并返回。
* @param daoInterface dao接口
* @return dao接口实现类的实例化对象。
*/
public static Object generate(SqlSession sqlSession, Class daoInterface){
// 类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 制造类(com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDao --> com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDaoProxy)
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass(daoInterface.getName() + "Proxy"); // 实际本质上就是在内存中动态生成一个代理类。
// 制造接口
CtClass ctInterface = pool.makeInterface(daoInterface.getName());
// 实现接口
ctClass.addInterface(ctInterface);
// 实现接口中所有的方法
Method[] methods = daoInterface.getDeclaredMethods();
Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(method -> {
// method是接口中的抽象方法
// 将method这个抽象方法进行实现
try {
// Account selectByActno(String actno);
// public Account selectByActno(String actno){ 代码; }
StringBuilder methodCode = new StringBuilder();
methodCode.append("public ");
methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName());
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append(method.getName());
methodCode.append("(");
// 需要方法的形式参数列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
methodCode.append(parameterType.getName());
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append("arg" + i);
if(i != parameterTypes.length - 1){
methodCode.append(",");
}
}
methodCode.append(")");
methodCode.append("{");
// 需要方法体当中的代码
methodCode.append("org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession sqlSession = com.example.utils.SqlSessionUtil.openSession();");
// 需要知道是什么类型的sql语句
// sql语句的id是框架使用者提供的,具有多变性。对于我框架的开发人员来说。我不知道。
// 既然我框架开发者不知道sqlId,怎么办呢?mybatis框架的开发者于是就出台了一个规定:凡是使用GenerateDaoProxy机制的。
// sqlId都不能随便写。namespace必须是dao接口的全限定名称。id必须是dao接口中方法名。
String sqlId = daoInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(sqlId).getSqlCommandType();
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.INSERT) {
}
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.DELETE) {
}
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.UPDATE) {
methodCode.append("return sqlSession.update(\""+sqlId+"\", arg0);");
}
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT) {
String returnType = method.getReturnType().getName();
methodCode.append("return ("+returnType+")sqlSession.selectOne(\""+sqlId+"\", arg0);");
}
methodCode.append("}");
CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(), ctClass);
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 创建对象
Object obj = null;
try {
Class<?> clazz = ctClass.toClass();
obj = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}
那么业务层就可以这么写


上面这步,出了点错,写完时候还没查出来
其实这个封装Mybatis已经做好了
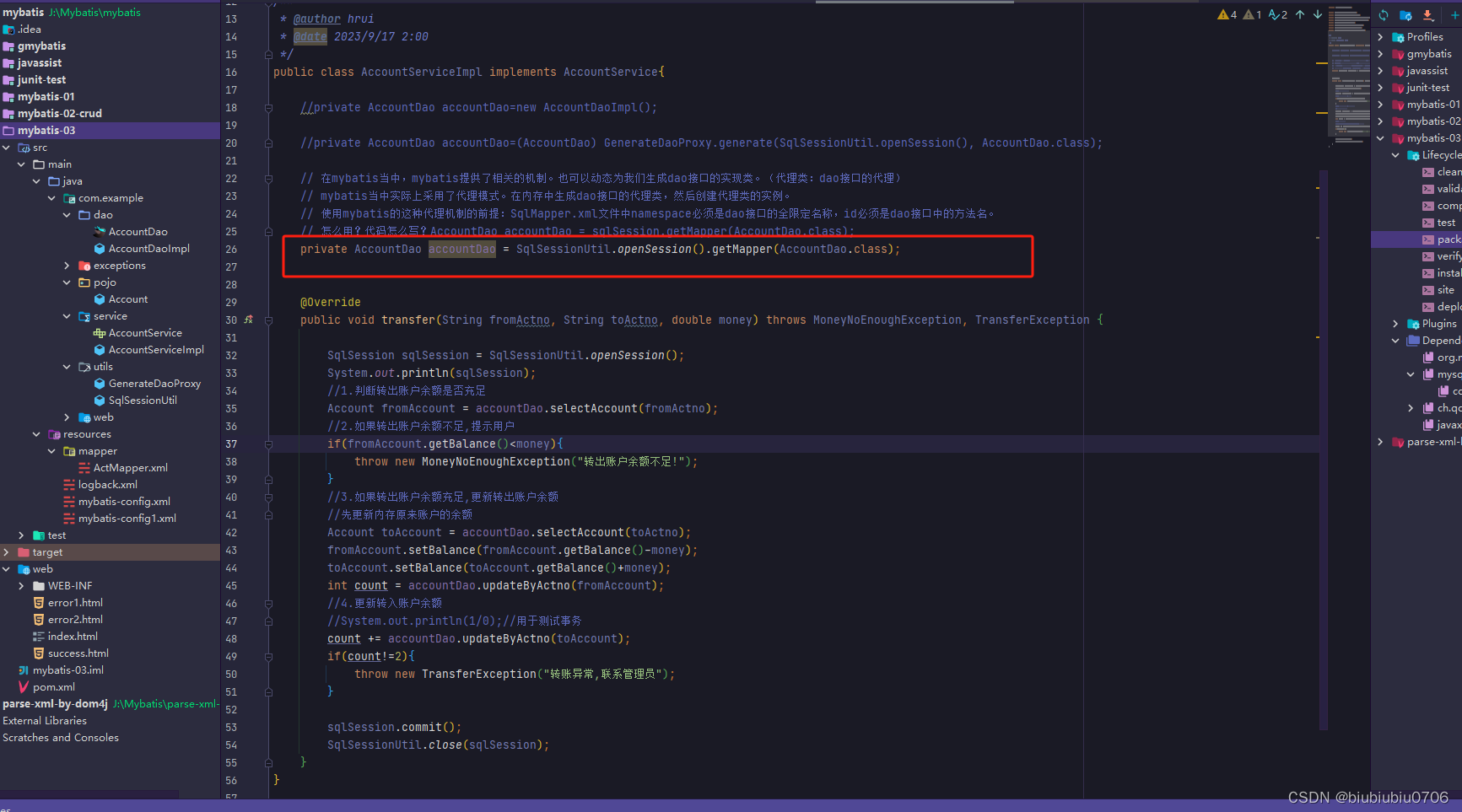
这样,面向接口的CRUD就产生了,以后无需再写持久层的实现类
完整的SqlSessionUtil类
package com.example.utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author hrui
* @date 2023/9/8 14:55
*/
public class SqlSessionUtil {
//工具类的构造方法一般都是私有化
//方法都是静态的
//为了防止new对象,构造方法私有化
private SqlSessionUtil(){
}
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
//类加载时候执行
//SqlSessionUtil工具类在被加载的时候,解析mybatis-config1.xml.创建sqlSessionFactory对象
static{
try {
//SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//下面这么写的原因是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder就是为了创建sqlSessionFactory而来的,使用完后,就不需要,都不需要创建个局部变量
//一个sqlSessionFactory对应一个数据库
sqlSessionFactory= new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config1.xml"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//全局的 服务器级别的,一个服务器当中定义一个即可
private static ThreadLocal<SqlSession> local=new ThreadLocal<>();
//获取会话对象 返回会话对象
public static SqlSession openSession(){
SqlSession sqlSession=local.get();
if(sqlSession==null){
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
local.set(sqlSession);
}
return sqlSession;
}
//提供一个关闭的方法
public static void close(SqlSession sqlSession){
if(sqlSession!=null){
//因为核心配置文件中配置POOLED 这里关闭是交还给连接池
sqlSession.close();
//注意移除SqlSession对象和当前线程的绑定关系
//因为Tomcat服务器支持线程池 比如说t1线程用完了,close交还给连接池了,这个sqlSession属于不可用的状态,你没有remove出去 如果t2线程拿到了,那么这个sqlSession不可用
local.remove();
}
}
}







![[论文笔记]P-tuning v2](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/dd505fa8137f31ec18647f439d986672.png)