目录:
一:dlib的shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks模型
二、眨眼检测
三、张口检测
四、眨眼检测+张口检测
五、人脸识别
六、人脸识别+活体检测
七、人脸识别破解方法
八、参考资料及下载
一:dlib的shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks模型
该模型能够检测人脸的68个特征点(facial landmarks),定位图像中的眼睛,眉毛,鼻子,嘴巴,下颌线(ROI,Region of Interest)
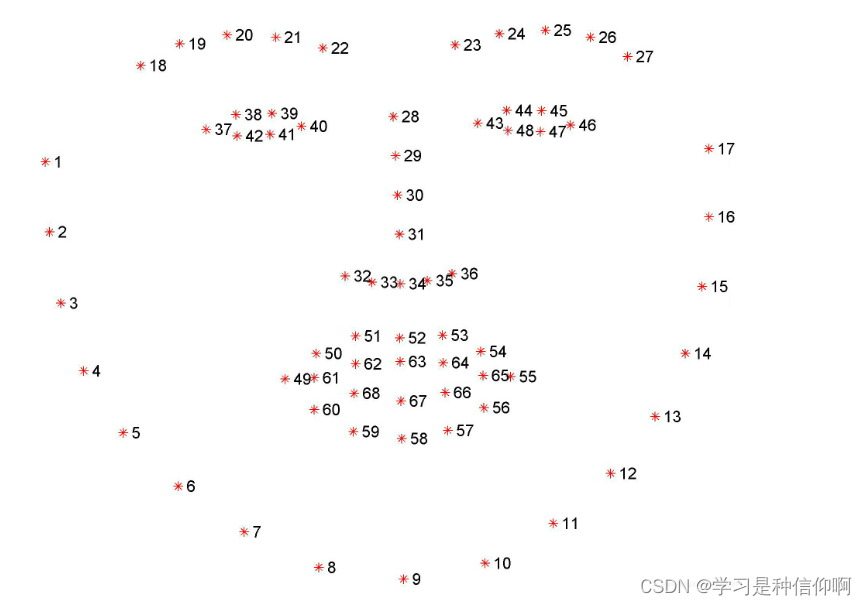
下颌线[1,17]
左眼眉毛[18,22]
右眼眉毛[23,27]
鼻梁[28,31]
鼻子[32,36]
左眼[37,42]
右眼[43,48]
上嘴唇外边缘[49,55]
上嘴唇内边缘[66,68]
下嘴唇外边缘[56,60]
下嘴唇内边缘[61,65]
在使用的过程中对应的下标要减1,像数组的下标是从0开始。
模型链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/Lee_01/article/details/89140668
https://blog.csdn.net/Lee_01/article/details/89145740
二、眨眼检测
基本原理:计算眼睛长宽比 Eye Aspect Ratio,EAR.当人眼睁开时,EAR在某个值上下波动,当人眼闭合时,EAR迅速下降,理论上会接近于零,当时人脸检测模型还没有这么精确。所以我们认为当EAR低于某个阈值时,眼睛处于闭合状态。为检测眨眼次数,需要设置同一次眨眼的连续帧数。眨眼速度比较快,一般1~3帧就完成了眨眼动作。两个阈值都要根据实际情况设置。
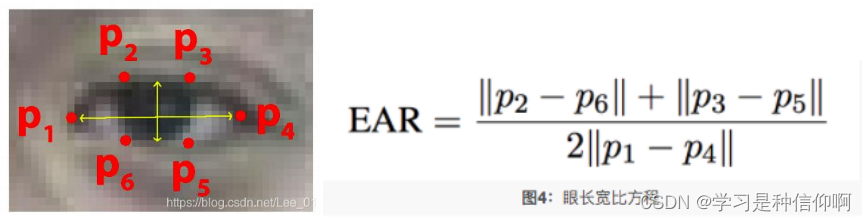
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Lee_01/article/details/89151044
from imutils.video import FileVideoStream
from imutils.video import VideoStream
from imutils import face_utils
import numpy as np
import imutils
import dlib
import cv2
import sys
def _help():
print("Usage:")
print(" python blink_detect.py")
print(" python blink_detect.py <path of a video>")
print("For example:")
print(" python blink_detect.py video/lee.mp4")
print("If the path of a video is not provided, the camera will be used as the input.Press q to quit.")
def eye_aspect_ratio(eye):
A = np.linalg.norm(eye[1] - eye[5])
B = np.linalg.norm(eye[2] - eye[4])
C = np.linalg.norm(eye[0] - eye[3])
ear = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
return ear
def blink_detection(vs, file_stream):
# define three constants, one for the eye aspect ratio to indicate
# blink and then the other constants for the min/max number of consecutive
# frames the eye must be below the threshold
EAR_THRESH = 0.2
EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN = 1
EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX = 2
# initialize the frame counters and the total number of blinks
blink_counter = [0, 0] # left eye and right eye
blink_total = [0, 0] # left eye and right eye
print("[INFO] loading facial landmark predictor...")
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
# grab the indexes of the facial landmarks for the left and
# right eye, respectively
(lStart, lEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["left_eye"]
(rStart, rEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["right_eye"]
print("[INFO] starting video stream thread...")
while True:
# if this is a file video stream, then we need to check if
# there any more frames left in the buffer to process
if file_stream and not vs.more():
break
frame = vs.read()
if frame is not None:
frame = imutils.resize(frame)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(gray, 0)
if len(rects) == 1:
rect = rects[0]
shape = predictor(gray, rect)
shape = face_utils.shape_to_np(shape)
left_eye = shape[lStart:lEnd]
right_eye = shape[rStart:rEnd]
left_ear = eye_aspect_ratio(left_eye)
right_ear = eye_aspect_ratio(right_eye)
# compute the convex hull for the left and right eye, then
# visualize each of the eyes
left_eye_hull = cv2.convexHull(left_eye)
right_eye_hull = cv2.convexHull(right_eye)
cv2.drawContours(frame, [left_eye_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.drawContours(frame, [right_eye_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# check to see if the eye aspect ratio is below the blink
# threshold, and if so, increment the blink frame counter
if left_ear < EAR_THRESH:
blink_counter[0] += 1
# otherwise, the eye aspect ratio is not below the blink
# threshold
else:
# if the eyes were closed for a sufficient number of
# then increment the total number of blinks
if EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN <= blink_counter[0] and blink_counter[0] <= EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX:
blink_total[0] += 1
blink_counter[0] = 0
# draw the total number of blinks on the frame along with
# the computed eye aspect ratio for the frame
cv2.putText(frame, "LBlinks: {}".format(blink_total[0]), (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "LEAR: {:.2f}".format(left_ear), (10, 60),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# check to see if the eye aspect ratio is below the blink
# threshold, and if so, increment the blink frame counter
if right_ear < EAR_THRESH:
blink_counter[1] += 1
# otherwise, the eye aspect ratio is not below the blink
# threshold
else:
# if the eyes were closed for a sufficient number of
# then increment the total number of blinks
if EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN <= blink_counter[1] and blink_counter[1] <= EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX:
blink_total[1] += 1
blink_counter[1] = 0
# draw the total number of blinks on the frame along with
# the computed eye aspect ratio for the frame
cv2.putText(frame, "RBlinks: {}".format(blink_total[1]), (200, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "REAR: {:.2f}".format(right_ear), (200, 60),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
elif len(rects) == 0:
cv2.putText(frame, "No face!", (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
else:
cv2.putText(frame, "More than one face!", (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.namedWindow("Frame", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
# if the `q` key was pressed, break from the loop
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.stop()
if len(sys.argv) > 2 or "-h" in sys.argv or "--help" in sys.argv:
_help()
elif len(sys.argv) == 2:
vs = FileVideoStream(sys.argv[1]).start()
file_stream = True
blink_detection(vs, file_stream)
else:
vs = VideoStream(src=0).start()
file_stream = False
blink_detection(vs, file_stream)
dlib模型官网下载地址:http://dlib.net/files/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat.bz2
三、张口检测
检测原理:类似眨眼检测,计算Mouth Aspect Ratio,MAR.当MAR大于设定的阈值时,认为张开了嘴巴。
from imutils.video import FileVideoStream
from imutils.video import VideoStream
from imutils import face_utils
import numpy as np
import imutils
import dlib
import cv2
import sys
def _help():
print("Usage:")
print(" python mouth_open_detect.py")
print(" python mouth_open_detect.py <path of a video>")
print("For example:")
print(" python mouth_open_detect.py video/lee.mp4")
print("If the path of a video is not provided, the camera will be used as the input.Press q to quit.")
def mouth_aspect_ratio(mouth):
A = np.linalg.norm(mouth[2] - mouth[9]) # 51, 59
B = np.linalg.norm(mouth[4] - mouth[7]) # 53, 57
C = np.linalg.norm(mouth[0] - mouth[6]) # 49, 55
mar = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
return mar
def mouth_open_detection(vs, file_stream):
MAR_THRESH = 0.5
print("[INFO] loading facial landmark predictor...")
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
(mStart, mEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["mouth"]
print("[INFO] starting video stream thread...")
while True:
if file_stream and not vs.more():
break
frame = vs.read()
if frame is not None:
frame = imutils.resize(frame, width=450)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(gray, 0)
for rect in rects:
shape = predictor(gray, rect)
shape = face_utils.shape_to_np(shape)
mouth = shape[mStart:mEnd]
mar = mouth_aspect_ratio(mouth)
mouth_hull = cv2.convexHull(mouth)
cv2.drawContours(frame, [mouth_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
if mar > MAR_THRESH:
cv2.putText(frame, "Mouth is open!", (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "MAR: {:.2f}".format(mar), (300, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if key == ord("q"):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.stop()
if len(sys.argv) > 2 or "-h" in sys.argv or "--help" in sys.argv:
_help()
elif len(sys.argv) == 2:
vs = FileVideoStream(sys.argv[1]).start()
file_stream = True
mouth_open_detection(vs, file_stream)
else:
vs = VideoStream(src=0).start()
file_stream = False
mouth_open_detection(vs, file_stream)
四、眨眼检测+张口检测
from imutils.video import FileVideoStream
from imutils.video import VideoStream
from imutils import face_utils
import numpy as np
import dlib
import cv2
import sys
def _help():
print("Usage:")
print(" python liveness_detect.py")
print(" python liveness_detect.py <path of a video>")
print("For example:")
print(" python liveness_detect.py video/lee.mp4")
print("If the path of a video is not provided, the camera will be used as the input.Press q to quit.")
def eye_aspect_ratio(eye):
# (|e1-e5|+|e2-e4|) / (2|e0-e3|)
A = np.linalg.norm(eye[1] - eye[5])
B = np.linalg.norm(eye[2] - eye[4])
C = np.linalg.norm(eye[0] - eye[3])
ear = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
return ear
def mouth_aspect_ratio(mouth):
# (|m2-m9|+|m4-m7|)/(2|m0-m6|)
A = np.linalg.norm(mouth[2] - mouth[9]) # 51, 59
B = np.linalg.norm(mouth[4] - mouth[7]) # 53, 57
C = np.linalg.norm(mouth[0] - mouth[6]) # 49, 55
mar = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
return mar
def liveness_detection(vs, file_stream):
EAR_THRESH = 0.15
EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN = 1
EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX = 2
MAR_THRESH = 0.5
# 初始化眨眼的连续帧数以及总的眨眼次数
blink_counter = 0
blink_total = 0
print("[INFO] loading facial landmark predictor...")
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("model/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
(lStart, lEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["left_eye"]
(rStart, rEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["right_eye"]
(mStart, mEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["mouth"]
print("[INFO] starting video stream thread...")
while True:
# if this is a file video stream, then we need to check if
# there any more frames left in the buffer to process
if file_stream and not vs.more():
break
frame = vs.read()
if frame is not None:
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
rects = detector(gray, 0)
# 只能处理一张人脸
if len(rects) == 1:
shape = predictor(gray, rects[0]) # 保存68个特征点坐标的<class 'dlib.dlib.full_object_detection'>对象
shape = face_utils.shape_to_np(shape) # 将shape转换为numpy数组,数组中每个元素为特征点坐标
left_eye = shape[lStart:lEnd]
right_eye = shape[rStart:rEnd]
left_ear = eye_aspect_ratio(left_eye)
right_ear = eye_aspect_ratio(right_eye)
ear = (left_ear + right_ear) / 2.0
mouth = shape[mStart:mEnd]
mar = mouth_aspect_ratio(mouth)
left_eye_hull = cv2.convexHull(left_eye)
right_eye_hull = cv2.convexHull(right_eye)
mouth_hull = cv2.convexHull(mouth)
cv2.drawContours(frame, [left_eye_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.drawContours(frame, [right_eye_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
cv2.drawContours(frame, [mouth_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
# EAR低于阈值,有可能发生眨眼,眨眼连续帧数加一次
if ear < EAR_THRESH:
blink_counter += 1
# EAR高于阈值,判断前面连续闭眼帧数,如果在合理范围内,说明发生眨眼
else:
# if the eyes were closed for a sufficient number of
# then increment the total number of blinks
if EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN <= blink_counter and blink_counter <= EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX:
blink_total += 1
blink_counter = 0
cv2.putText(frame, "Blinks: {}".format(blink_total), (0, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "Mouth: {}".format("open" if mar > MAR_THRESH else "closed"),
(130, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "EAR: {:.2f}".format(ear), (300, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "MAR: {:.2f}".format(mar), (450, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
elif len(rects) == 0:
cv2.putText(frame, "No face!", (0, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
else:
cv2.putText(frame, "More than one face!", (0, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.namedWindow("Frame", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
# 按下q键退出循环(鼠标要点击一下图片使图片获得焦点)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
vs.stop()
if len(sys.argv) > 2 or "-h" in sys.argv or "--help" in sys.argv:
_help()
elif len(sys.argv) == 2:
video_stream = FileVideoStream(sys.argv[1]).start()
file_stream = True
liveness_detection(video_stream, file_stream)
else:
video_stream = VideoStream(src=0).start()
file_stream = False
liveness_detection(video_stream, file_stream)
五、人脸识别
# -*-coding:GBK -*-
import face_recognition
import os
import cv2
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
import numpy as np
import datetime
import threading
class Recorder:
pass
record_dic = {}
unknown_pic = []
flag_over = 0 # 定义一个是否进行来访记录的标记
# 定时去保存对比图像信息,并且将位置人员的图像保存下来
def save_recorder(name, frame):
global record_dic
global flag_over
global unknown_pic
if flag_over == 1: return
try:
record = record_dic[name]
seconds_diff = (datetime.datetime.now() - record.times[-1]).total_seconds()
if seconds_diff < 60 * 10:
return
record.times.append(datetime.datetime.now())
print('更新记录', record_dic, record.times)
except KeyError:
newRec = Recorder()
newRec.times = [datetime.datetime.now()]
record_dic[name] = newRec
print('添加记录', record_dic, newRec.times)
if name == '未知头像':
s = str(record_dic[name].times[-1])
# print(s)
# 未知人员的图片名称
filename = s[:10]+s[-6:] + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(filename, frame)
unknown_pic.append(filename)
# 解析已有人员的所有照片并得到照片名和人物面部编码信息
def load_img(path):
print('正在加载已知人员的图片...')
for dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk(path):
print(filenames)
facelib = []
for filename in filenames:
filepath = os.sep.join([dirpath, filename])
# 把对应每张图片加载进来
face_image = face_recognition.load_image_file(filepath)
face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(face_image)[0]
facelib.append(face_encoding)
return facelib,filenames
facelib, facenames = load_img('facelib')
# print(facenames)
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
# 通过缩小图片(缩小为1/4),提高对比效率
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0,0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25)
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:,:,::-1] # 将opencv的BGR格式转换为RGB格式
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = []
# 循环多张人脸
for face_encoding in face_encodings:
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(facelib, face_encoding, tolerance=0.39)
name = '未知头像'
if True in matches:
# 如果摄像头里面的头像匹配了已知人物头像,则取出第一个True的位置
first_match_index = matches.index(True)
name = facenames[first_match_index][:-4] # 取出文件上对应的人名
face_names.append(name)
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
# 还原原图片大小
top *= 4
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0,0,255), thickness=2) # 标注人脸信息
img_PIL = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
font = ImageFont.truetype('simhei.ttf', 40)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_PIL)
draw.text((left+6, bottom-6), name, font=font, fill=(255,255,255))
frame = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img_PIL),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
save_recorder(name, frame)
cv2.imshow('capture', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
video_capture.release()
六、人脸识别+活体检测
import face_recognition
from imutils import face_utils
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw,ImageFont
import numpy as np
import threading #导入threading模块
import yagmail
import dlib
import datetime
import time
import cv2
import os
import sys
# 初始化眨眼次数
blink_total = 0
# 初始化张嘴次数
mouth_total = 0
# 设置图片存储路径
# pic_path = './dataset'
# 图片数量
pic_total = 0
# 初始化眨眼的连续帧数以及总的眨眼次数
blink_counter = 0
# 初始化张嘴状态为闭嘴
mouth_status_open = 0
# 眼长宽比例值
EAR_THRESH = 0.15
EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN = 1
EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX = 5 # 当EAR小于阈值时,接连多少帧一定发生眨眼动作
# 嘴长宽比例值
MAR_THRESH = 0.15
# 人脸检测器
detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
# 特征点检测器
predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("modles/shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat")
# 获取左眼的特征点
(lStart, lEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["left_eye"]
# 获取右眼的特征点
(rStart, rEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["right_eye"]
# 获取嘴巴特征点
(mStart, mEnd) = face_utils.FACIAL_LANDMARKS_IDXS["inner_mouth"]
class Recorder:
pass
red_dict = {}
unknownjpg = []
def sendemail(title,contents,fileslist):#将照片和访问记录上传云端
# yag = yagmail.SMTP("发件人邮箱",'密码' ,'smtp.qq.com', 465)
# yag.send(['收件人邮箱1','收件人邮箱2'],title,contents,fileslist)
yag=yagmail.SMTP("xxx@qq.com",'mbiwgdukvqaadfei','smtp.qq.com',465)#发件人邮箱
yag.send(['xxx@163.com','xxx@163.com'],title,contents,fileslist)#收件人邮箱(注意和上面邮箱不同)
def dicttostr():#生成来访记录列表
strlist = []
listkey =list(sorted(red_dict.keys()))#取字典的key
for item in listkey:#通过循环,合成每一条来访记录
strlist.extend([item + ','+str(onetime) for onetime in red_dict[item].times])
return strlist
flagover = 0#全局标志,用来控制是否保持来访记录
def saveRecorder(name, frame):#保存和添加来访记录
global red_dict
global flagover
global unknownjpg
if flagover == 1:#响应全局标志,如果为1时,关闭来访记录
return
try:
red = red_dict[name]#如果多次识别,比较时间
secondsDiff = (datetime.datetime.now() - red.times[-1]).total_seconds()
if secondsDiff < 5*60: # 如果两次识别在5分钟内,将被过滤掉
return
red.times.append(datetime.datetime.now())
print('更新记录', red_dict, red.times)
except (KeyError):
newRed = Recorder()
newRed.times = [datetime.datetime.now()]
red_dict[name] = newRed
print('添加记录', red_dict, newRed.times)
if name == 'Unknown':
s = str(red_dict[name].times[-1])
print('写入', s[:10] + s[-6:])
filename = s[:10] + s[-6:] + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(filename, frame)
unknownjpg.append(filename)
def loop_timer_headle(): # 定时器循环触发函数
print('————————Timer headle!————————', str(datetime.datetime.now()))
global timer2
global flagover
global red_dict
global unknownjpg
flagover = 1
timer2 = threading.Timer(60 * 5, loop_timer_headle) # 创建定时器 5分钟
timer2.start()
# 发送邮件
sendemail("来访统计记录", '\n'.join(dicttostr()), unknownjpg)
red_dict.clear()
unknownjpg.clear()
print("清空")
time.sleep(10)
print("重新开始")
flagover = 0
timer2 = threading.Timer(2, loop_timer_headle)
timer2.start()
def load_img(sample_dir):#导入数据库照片
print('loading sample face..')
for (dirpath, dirnames, filenames) in os.walk(sample_dir): # 一级一级的文件夹递归
print(dirpath, dirnames, filenames)
facelib = []
for filename in filenames:
filename_path = os.sep.join([dirpath, filename])
print(filename_path)
faceimage = face_recognition.load_image_file(filename_path)
# 由于我们每个图像只有一个脸,我只关心每个图像中的第一个编码,所以我取索引0
face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(faceimage)[0]
facelib.append(face_encoding)
return facelib, filenames
# def getFaceEncoding(src):#获取人脸编码
# image = face_recognition.load_image_file(src) # 加载人脸图片
# # 获取图片人脸定位[(top,right,bottom,left )]
# face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(image)
# img_ = image[face_locations[0][0]:face_locations[0][2], face_locations[0][3]:face_locations[0][1]]
# img_ = cv2.cvtColor(img_, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# # display(img_)
# face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(image, face_locations)[0] # 默认人脸数为1,对人脸图片进行编码
# return face_encoding
#对比两张照片距离
# def simcos(a, b):
# a = np.array(a)
# b = np.array(b)
# dist = np.linalg.norm(a - b) # 二范数
# sim = 1.0 / (1.0 + dist) #
# return sim
# 提供对外比对的接口 返回比对的相似度
# def comparison(face_src1, face_src2):
# xl1 = getFaceEncoding(face_src1)
# xl2 = getFaceEncoding(face_src2)
# value = simcos(xl1, xl2)
# print(value)
# 眼长宽比例
def eye_aspect_ratio(eye):
# (|e1-e5|+|e2-e4|) / (2|e0-e3|)
A = np.linalg.norm(eye[1] - eye[5])
B = np.linalg.norm(eye[2] - eye[4])
C = np.linalg.norm(eye[0] - eye[3])
ear = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
return ear
# 嘴长宽比例
def mouth_aspect_ratio(mouth):
A = np.linalg.norm(mouth[1] - mouth[7]) # 61, 67
B = np.linalg.norm(mouth[3] - mouth[5]) # 63, 65
C = np.linalg.norm(mouth[0] - mouth[4]) # 60, 64
mar = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
return mar
def main():
global blink_total # 使用global声明blink_total,在函数中就可以修改全局变量的值
global mouth_total
global pic_total
global blink_counter
global mouth_status_open
# video_path, src = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
facelib, facename = load_img('dataset')
vs = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
face_locations = [] # 定义列表存放人脸位置
face_encodings = [] # 定义列表存放人脸特征编码
process_this_frame = True # 定义信号量
while True:
ret, frame = vs.read() # 捕获一帧图片
small_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=0.25, fy=0.25) # 将图片缩小1/4,为人脸识别提速
rgb_small_frame = small_frame[:, :, ::-1] # 将opencv的BGR格式转为RGB格式
if process_this_frame: # 使用信号量对当前的处理进行保护
# 找到人脸位置,并生成特征码
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(rgb_small_frame)
face_encodings = face_recognition.face_encodings(rgb_small_frame, face_locations)
face_names = [] # 定义列表,放置识别结果
for face_encoding in face_encodings: # 循环多张人脸
matches = face_recognition.compare_faces(facelib, face_encoding) # 人脸识别
name = "Unknown" # 定义默认的识别结果为Unknown
if True in matches: # 如果识别出来,就将名称取出
first_match_index = matches.index(True)
name = facename[first_match_index][:-4]
face_names.append(name) # 保存识别结果
process_this_frame = not process_this_frame # 信号量保护结束
# 显示结果
for (top, right, bottom, left), name in zip(face_locations, face_names):
top *= 4 # 还原人脸的原始尺寸
right *= 4
bottom *= 4
left *= 4
cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), 2) # 标注人脸
img_PIL = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)) # 转换图片格式
font = ImageFont.truetype('simhei.ttf', 40) # 加载字体
position = (left + 6, bottom - 6) # 指定文字输出位置
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img_PIL) # 绘制照片
draw.text(position, name, font=font, fill=(255, 255, 255)) # 绘制文字
frame = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(img_PIL), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) # 将图片转回OpenCV格式
saveRecorder(name, frame) # 过滤并保存记录
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
rects = detector(gray, 0) # 人脸检测
# 只能处理一张人脸
if len(rects) == 1:
shape = predictor(gray, rects[0]) # 保存68个特征点坐标的<class 'dlib.dlib.full_object_detection'>对象
shape = face_utils.shape_to_np(shape) # 将shape转换为numpy数组,数组中每个元素为特征点坐标
left_eye = shape[lStart:lEnd] # 取出左眼对应的特征点
right_eye = shape[rStart:rEnd] # 取出右眼对应的特征点
left_ear = eye_aspect_ratio(left_eye) # 计算左眼EAR
right_ear = eye_aspect_ratio(right_eye) # 计算右眼EAR
ear = (left_ear + right_ear) / 2.0 # 求左右眼EAR的均值
inner_mouth = shape[mStart:mEnd] # 取出嘴巴对应的特征点
mar = mouth_aspect_ratio(inner_mouth) # 求嘴巴mar的均值
# left_eye_hull = cv2.convexHull(left_eye) # 寻找左眼轮廓
# right_eye_hull = cv2.convexHull(right_eye) # 寻找右眼轮廓
# mouth_hull = cv2.convexHull(inner_mouth) # 寻找内嘴巴轮廓
# cv2.drawContours(frame, [left_eye_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1) # 绘制左眼轮廓
# cv2.drawContours(frame, [right_eye_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1) # 绘制右眼轮廓
# cv2.drawContours(frame, [mouth_hull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1) # 绘制嘴巴轮廓
# EAR低于阈值,有可能发生眨眼,眨眼连续帧数加一次
if ear < EAR_THRESH:
blink_counter += 1
# EAR高于阈值,判断前面连续闭眼帧数,如果在合理范围内,说明发生眨眼
else:
# if the eyes were closed for a sufficient number of
# then increment the total number of blinks
if EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MIN <= blink_counter <= EAR_CONSEC_FRAMES_MAX:
blink_total += 1
blink_counter = 0
# 通过张、闭来判断一次张嘴动作
if mar > MAR_THRESH:
mouth_status_open = 1
else:
if mouth_status_open:
mouth_total += 1
mouth_status_open = 0
cv2.putText(frame, "Blinks: {}".format(blink_total), (0, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "Mouth: {}".format(mouth_total),
(130, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "EAR: {:.2f}".format(ear), (300, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(frame, "MAR: {:.2f}".format(mar), (450, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
elif len(rects) == 0:
cv2.putText(frame, "No face!", (0, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
else:
cv2.putText(frame, "More than one face!", (0, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# cv2.namedWindow("Frame", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# cv2.imshow('Frame', frame) # 将图片显示出来
# liveness_detection(vs)
if blink_total >= 1 and mouth_total >= 1:
cv2.putText(frame, "True", (200, 200),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
blink_total = 0
mouth_total = 0
cv2.namedWindow("Frame", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow('Frame', frame) # 将图片显示出来
k = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF # 按键判断
if k == ord(' '):
break;
# comparison(pic_path, src)
vs.release()
time.sleep(2) # 休眠2秒
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
七、人脸识别破解方法
注入应用攻击:在程序中设置断点,通过不断演示人脸识别流程来触发该断点,然后分析并修改程序存储的值,最终使得静态照片也能通过活体检测
照片攻击:利用合法用户的照片进行验证
视频攻击:利用视频合成软件将合法用户的照片合成为视频
3D建模攻击:制作合法用户的脸部3D模型
脸部模具攻击
利用接口防护不当和设计缺陷
防攻击方式:
多重验证
识别伪造痕迹
提高验证速度
八、参考资料及下载
CSDN下载:后续补上
参考:人脸活体检测人脸识别:眨眼+张口
参考:使用dlib人脸检测模型进行人脸活体检测:眨眼+张口
参考:Python开发系统实战项目:人脸识别门禁监控系统








![[附源码]计算机毕业设计Python第三方游戏零售平台(程序+源码+LW文档)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ddc3e6ce45714a0998add4c465841949.png)