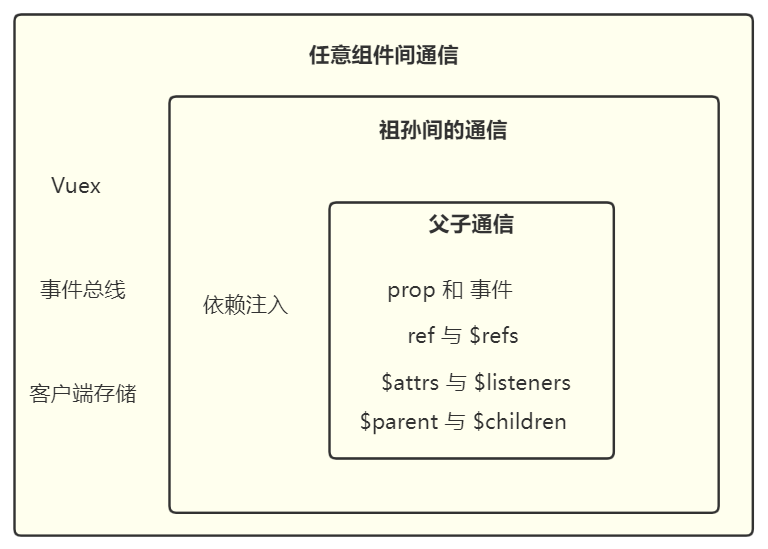
引言
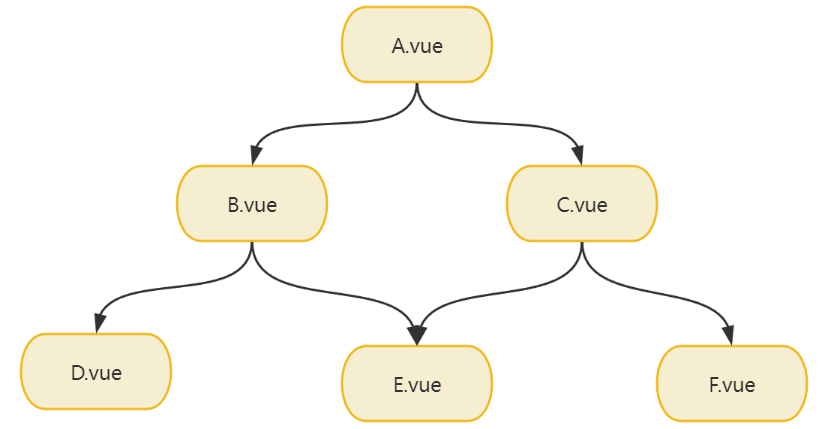
组件间的关系有父子关系、兄弟关系、祖孙关系和远亲关系。
不同的关系间,组件的通信有不同的方式。
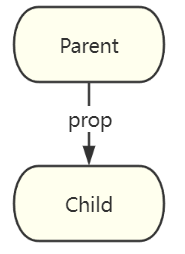
一、prop 和 $emit
prop向下传递,emit向上传递。
父组件使用 prop 向子组件传递信息。
ParentComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<ChildComponent
msg="Hello,this is the message passed from the parent component.">
</ChildComponent>
<ChildComponent
:msg="parentMsg">
</ChildComponent>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
data() {
return {
parentMsg: 'Hello,this is the message passed from the parent component.'
}
},
components: {
ChildComponent
}
}
</script>
ChildComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
msg: String
}
}
</script>
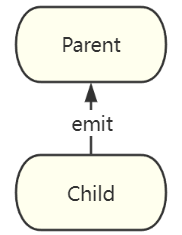
子组件通过实例的事件方法 $emit 向父组件通信
$emit 触发一个自定义事件,并接受一个参数作为抛出值。父组件通过 $event 或回调函数获取传递值。
ParentComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<!-- <ChildComponent @custom-event="handleCustomEvent"></ChildComponent> -->
<!-- 或者 -->
<ChildComponent @custom-event="msg=$event"></ChildComponent>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue';
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: '现在为空'
}
},
components: {
ChildComponent
},
methods: {
handleCustomEvent(msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
},
}
</script>
ChildComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="sendMsgToParent">发送消息到父组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello,this is the message passed from child component.'
}
},
methods: {
sendMsgToParent() {
this.$emit('custom-event', this.msg);
}
}
}
</script>
优先使用 prop 和 事件进行父子组件间的通信。
二、$parent 和 $children
子实例可以用 this.$parent 访问父实例,同时子实例被推入父实例的 $children 数组中。
ParentComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>父组件</h3>
<p>来自子组件 1 的消息:{{ msg1 }}</p>
<p>来自子组件 2 的消息:{{ msg2 }}</p>
<button @click="receiveMsgFromChildren">接收子组件的消息</button>
<br><br>
<button @click="msg1= '现在为空';msg2='现在为空'">清空</button>
<ChildComponent1 />
<ChildComponent2 />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildComponent1 from './ChildComponent1.vue';
import ChildComponent2 from './ChildComponent2.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {
msg1: '现在为空',
msg2: '现在为空'
}
},
components: {
ChildComponent1,
ChildComponent2
},
methods: {
receiveMsgFromChildren() {
this.msg1 = this.$children[0].msg;
this.msg2 = this.$children[1].msg;
}
},
}
</script>
ChildComponent1.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件1</h3>
<button @click="sendMsgToParent">发送消息给父组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello,this is the message passed from child component1.'
}
},
methods: {
sendMsgToParent() {
this.$parent.msg1 = this.msg;
}
}
}
</script>
ChildComponent2.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>子组件2</h3>
<button @click="sendMsgToParent">发送消息给父组件</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello,this is the message passed from child component2.'
}
},
methods: {
sendMsgToParent() {
this.$parent.msg2 = this.msg;
}
}
}
</script>


三、依赖注入
依赖注入设置两个选项:provide 和 inject
provide 选项允许我们提供一系列数据或方法。然后在设置了 provide 选项的组件的所有后代组件里都可以通过 inject 选项获取这些数据或方法。
provide 选项应该是一个对象或返回一个对象的函数。
provide: {
foo: 'bar'
}
provide: {
return {
foo: 'bar'
}
}
inject 选项可以为以下值:
- 一个字符串数组,其元素值为
provide属性的 key。 - 一个对象,对象的 key 是绑定在本地的,可以与
provide不同,如果要设置为不同名的属性,那么就要给该属性设置from属性来说明它来自哪个provide提供的属性,同时你可以为它提供默认值default。
inject: ['foo']
inject: {
foo: {
from: 'bar'
default: 'foo'
}
}
四、ref 和 $refs
ref 属性为普通 DOM 元素或子组件指定引用,该引用会被注册到父组件的 $refs 对象上。
<div ref="div"></div>
<child-component ref="child" />
使用
vm.$refs.div
vm.$refs.child
如果你尝试在 created 或 mounted 钩子中访问 ref,通常会得到 undefined。因为 ref 本身是作为渲染结果被创建的,在初始渲染(beforeUpdate之前)的时候你不能访问它们。
五、事件总线
使用事件总线进行组件间通信的步骤:
1.创建事件总线
// EventBus.js
import Vue from 'vue';
export const EventBus = new Vue();
2.引入事件总线
import { EventBus } from './EventBus.js';
3.在发送组件中触发事件
EventBus.$emit('custom-event',eventData);
4.在接收组件中监听事件
EventBus.$on('custom-event',(data)=>{
//处理 data
});
5.移除监听事件
EventBus.$off('custom-event')
六、$attrs 与 $listeners
$attrs包含了父组件传递给子组件的所有没有在子组件 props 中声明的属性(除了class和style)。当子组件没有声明任何props时,$attrs中会包含所有父组件传递的属性(除了class和style),这在创建高级别的通用组件时非常有用,因为你无需知道父组件会传递哪些属性。
下面是一个示例来说明$attrs的用法:
假设我们有一个名为MyButton的子组件,它可以接收label属性,但同时也希望允许父组件传递任意额外的HTML属性给按钮元素。我们可以使用$attrs来实现这一点:
<template>
<button v-bind="$attrs">
{{ label }}
</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
label: String,
},
};
</script>
在这个示例中,MyButton组件只声明了一个名为label的prop,但它使用v-bind="$attrs"将所有父组件传递的属性绑定到按钮元素上。这意味着,父组件可以像这样使用MyButton:
<MyButton label="Click me" class="btn btn-primary" id="my-button" @click.native="handleClick" />
在这里,class和id属性会被传递到<button>元素,而label会被解析为"Click me",同时@click事件也会正常工作。

$listeners 包含了父作用域中的 (不含 .native 修饰器的) v-on 事件监听器。它可以通过 v-on="$listeners" 传入内部组件——在创建更高层次的组件时非常有用。
ParentComponent.vue
<template>
<div>
<MyButton label="Click me" class="btn btn-primary" id="my-button" @click="handleClick" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyButton from './MyButton.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyButton
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
console.log('点击了1次')
}
}
};
</script>
MyButton.vue
<template>
<button v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners">
{{ label }}
</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
label: String,
},
};
</script>
七、Vuex
以后专门学习,在此不做介绍先。
八、浏览器客户端存储
MDN-客户端存储