★ 样本查询
给Spring Data传入一个样本数据,Spring Data就能从数据库中查询出和样本相同的数据。
被查询的数据并不需要和样本是完全相同的,可能只需要和样本有几个属性是相同的。
总结:
样本查询–就是把参数作为样本去查询数据库的数据,根据自定义的匹配规则,如果对应上就能把数据查出来
样本查询也可以定义其中查询的一些匹配规则
▲ 样本查询的API(QueryByExampleExecutor):
JpaRepository继承了QueryByExampleExecutor接口,该接口提供了如下“样本查询”方法:
- <S extends T> Optional<S> findOne(Example<S> example);
- <S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example);
- <S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort);
- <S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable);
- <S extends T> long count(Example<S> example);
- <S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example);
只要让DAO接口继承该QueryByExampleExecutor接口,DAO组件就可调用上面的样本查询方法。
——方法实现不要你操心,Spring Data会负责搞定它们。
▲ 创建Example
Example查询的关键在于Example参数,它提供了如下两个of()类方法来创建Example对象:
- of(T probe):以probe对象创建最简单的Example对象,使用默认的匹配规则。
要求被查询对象与样本对象所有属性都严格相等。
- of(T probe, ExampleMatcher matcher):以probe创建Example对象,并使用matcher指定匹配规则。
▲ ExampleMatcher提供了如下静态方法来创建实例:
- static ExampleMatcher matching():创建一个需要所有属性都匹配的匹配器。 (and运算符)
- static ExampleMatcher matchingAll():完全等同于matching()方法
- static ExampleMatcher matchingAny():创建一个只要任意一个属性匹配的匹配器。(or运算符)
▲ ExampleMatcher还可通过如下方法来指定对特定属性的匹配规则:
- withIgnoreCase():指定属性匹配时默认不区分大小写。
- withIgnoreCase(String... propertyPaths):指定propertyPaths参数列出的属性在匹配时不区分大小写。
- withIgnoreNullValues():指定不比较Example对象中属性值为null的属性。
- withIgnorePaths(String... ignoredPaths):指定忽略ignoredPaths参数列出的属性,也就是这些属性不参与匹配。
- withIncludeNullValues():强行指定要比较Example对象中属性值为null的属性。
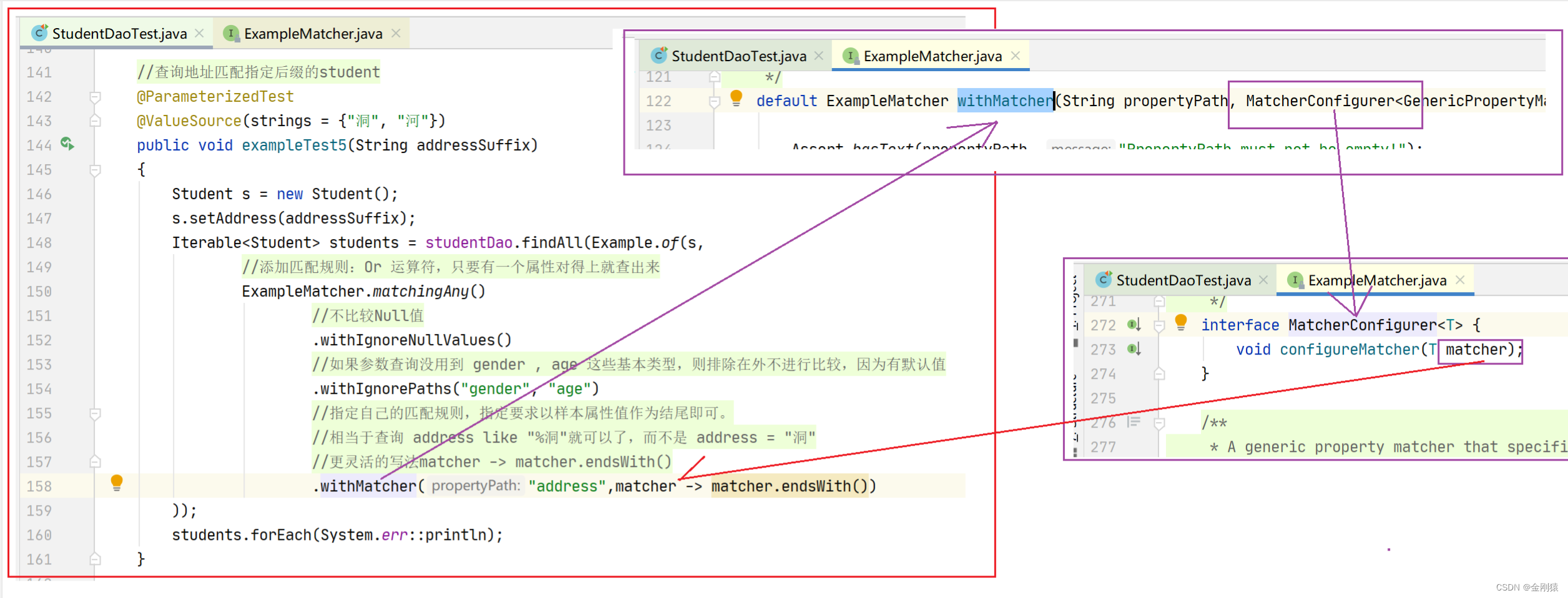
- withMatcher(String propertyPath, 比较器):对propertyPath参数指定的属性使用专门的匹配规则。
▲ 样本查询的步骤:
(1) 让DAO接口要么继承JpaRepository(是QueryByExampleExecutor的子接口),
或者增加继承QueryByExampleExecutor
(2) DAO组件可调用QueryByExampleExecutor的样本查询方法
代码演示:
需求:根据一个对象中的某些属性作为样本,去数据库查询数据
要实现样本查询,
Dao接口需要继承 JpaRepository 接口,
或者增加继承 QueryByExampleExecutor 接口
接口可以继承接口,并且可以继承不只一个接口,但是不能实现接口。
因为接口的成员方法都具有抽象属性,不具有方法体,无法实现继承的接口
1、这样实现样本查询的接口继承

2、不需要在StudentDao组件写方法,或者写sql语句,直接在测试类进行查询方法的调用,因为DAO组件会调用QueryByExampleExecutor的样本查询方法,不用我们写。
DAO组件调用QueryByExampleExecutor的样本查询方法时,
查询的默认的匹配规则,要求被查询对象与样本对象所有属性都严格相等。
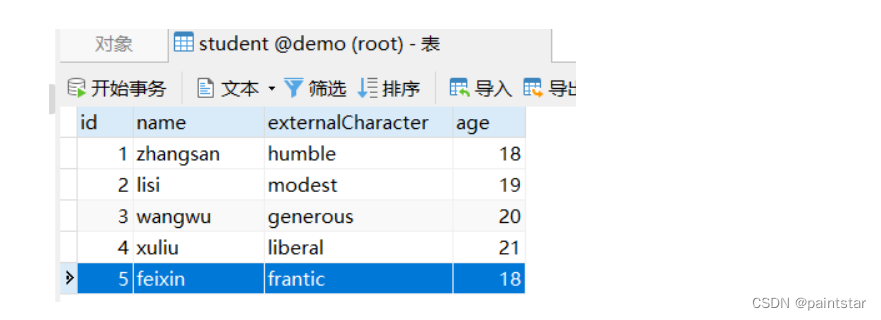
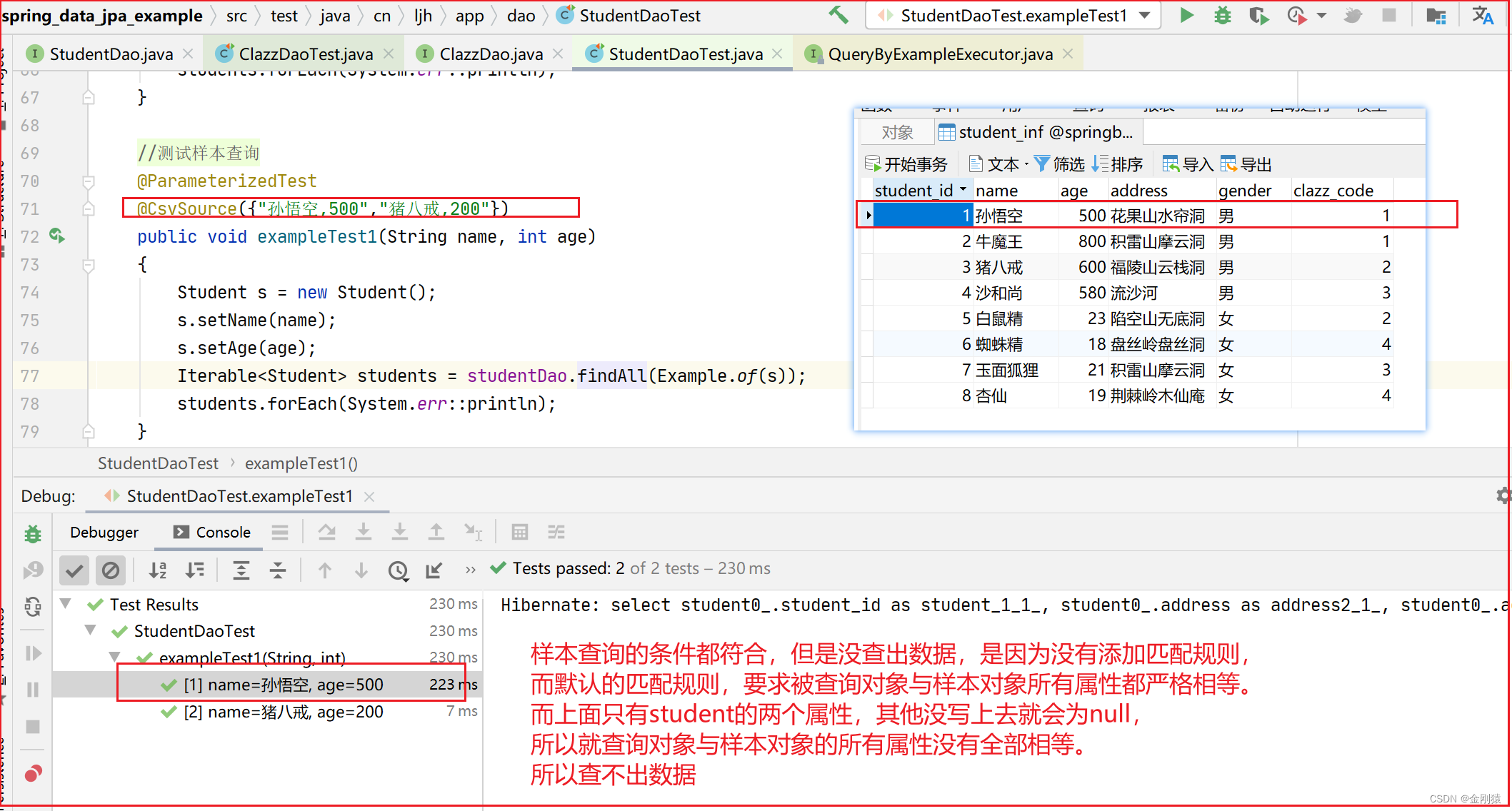
如图:
样本查询的条件都符合,但是没查出数据,是因为没有添加匹配规则,
而默认的匹配规则,要求被查询对象与样本对象所有属性都严格相等。
而上面只有student的两个属性,其他没写上去就会为null,
所以就查询对象与样本对象的所有属性没有全部相等。
所以查不出数据
没有指定匹配规则,所以要求样本对象(s) 和 查询对象(Student) 的所有属性都相等才行
测试1:没有添加匹配规则的测试
默认匹配规则:要求被查询对象与样本对象所有属性都严格相等
测试2:添加匹配规则的测试
添加匹配规则:不比较 Null 值
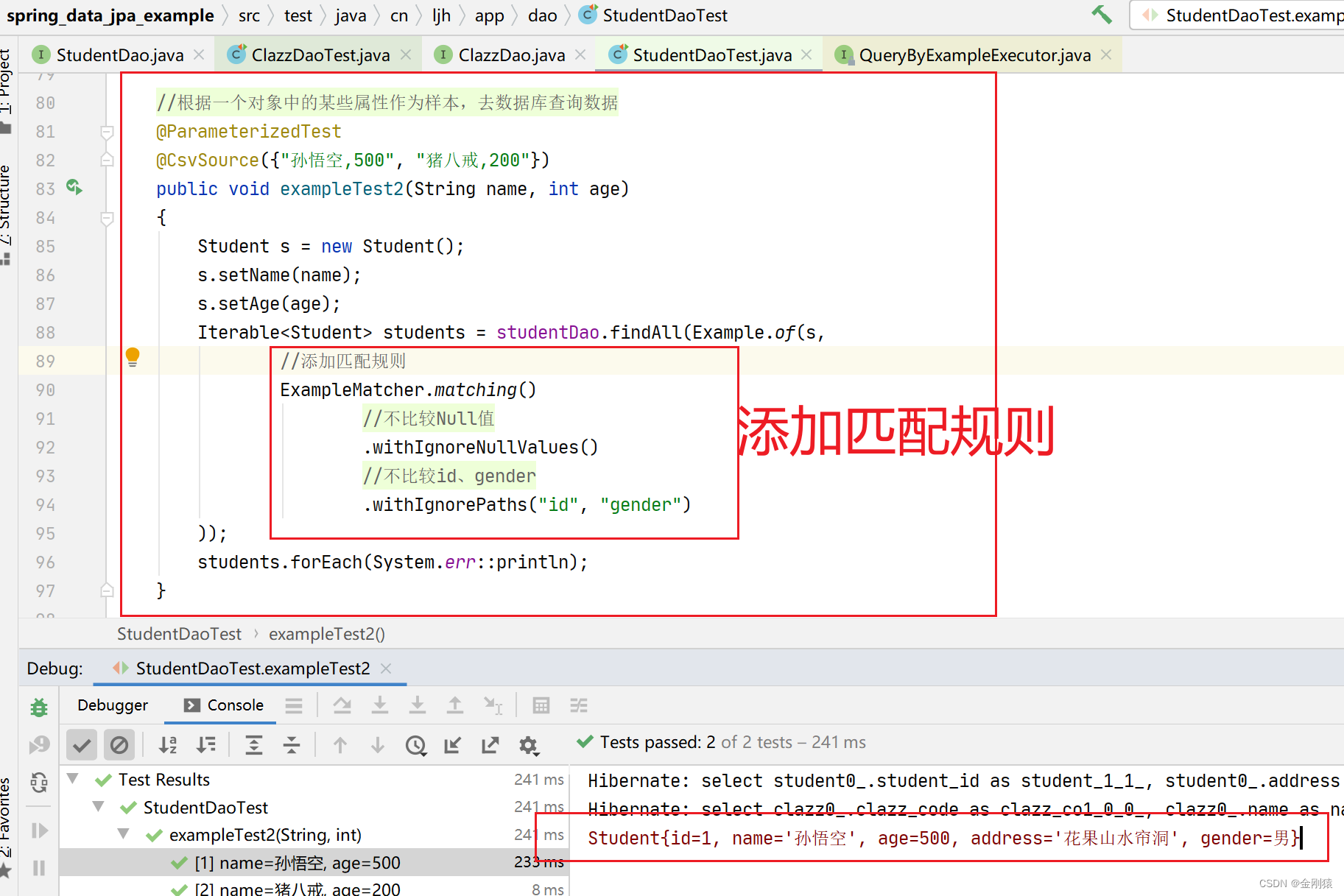
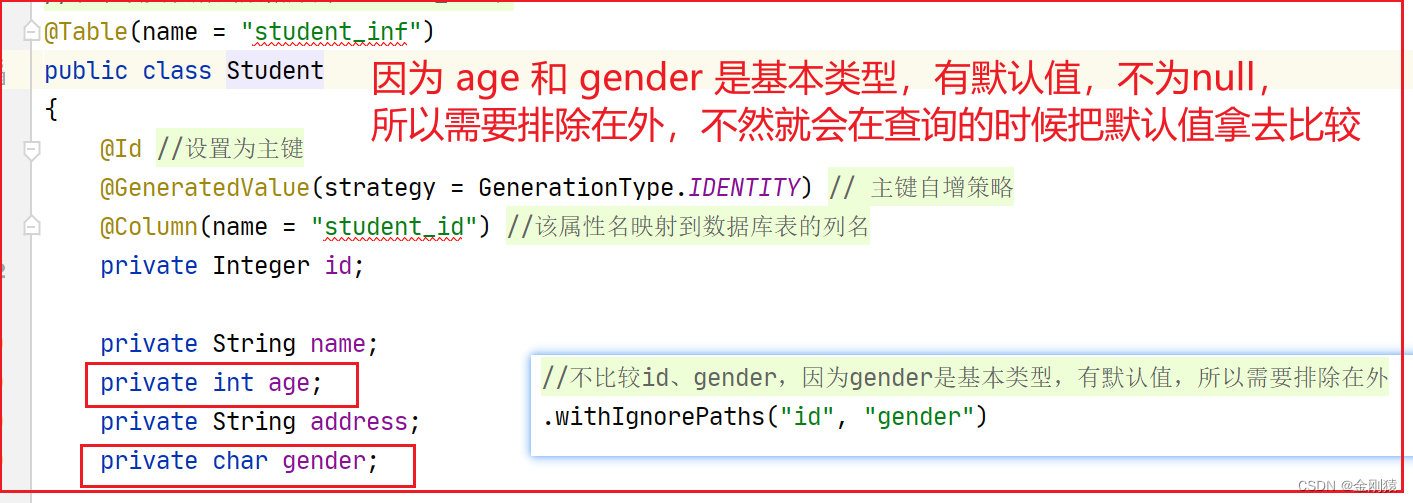
解释:.withIgnorePaths (“id”, “gender”)
id 是 Integer 类型,默认值是null , 所以也可以不排除
基本类型的属性,如果不作为参数去查询,就需要排除出去
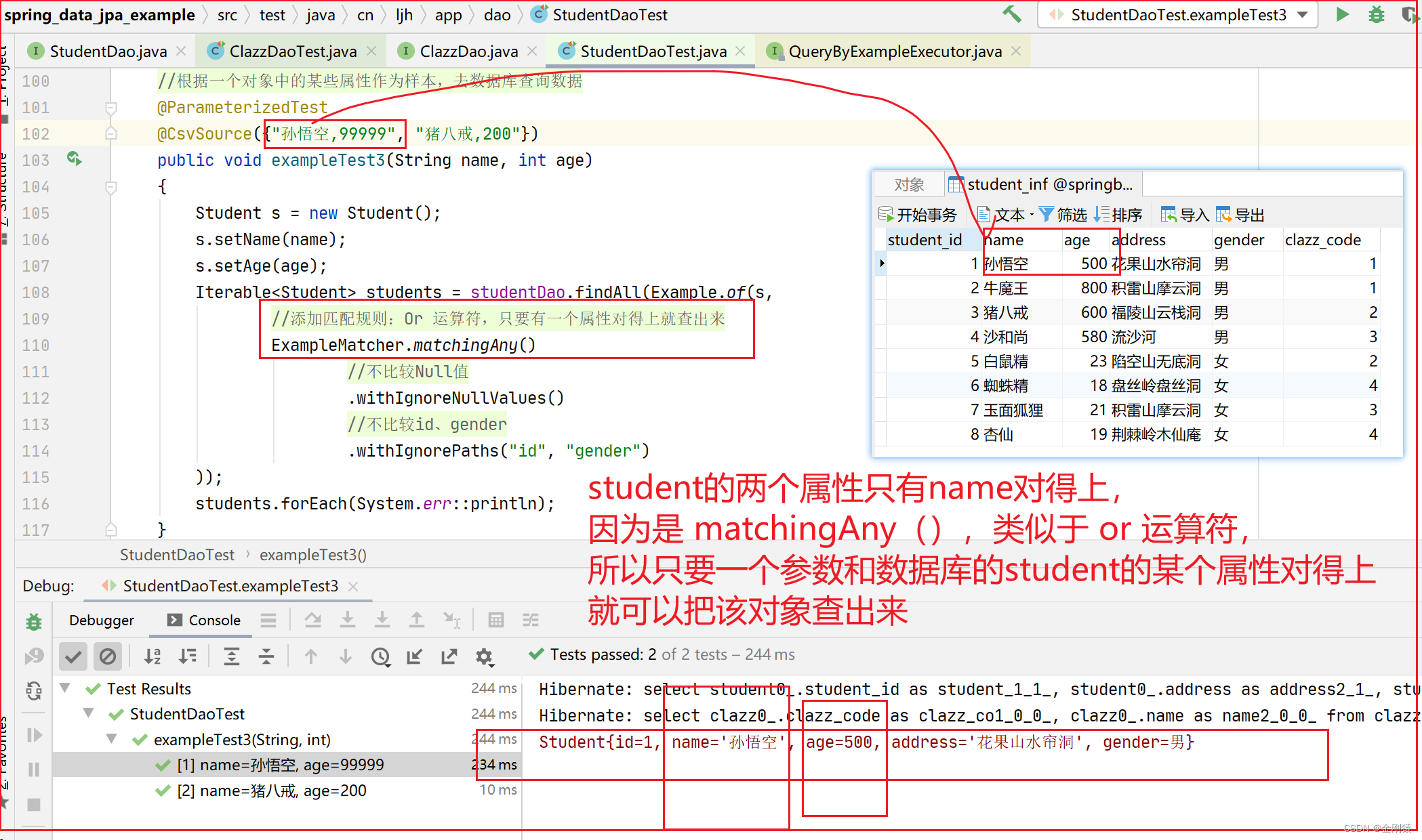
测试3:添加匹配规则的测试
添加匹配规则:调用 matchingAny() ,相当于 OR 运算符,只要有一个参数和查询的student对象对应得上,就能将该对象查出来
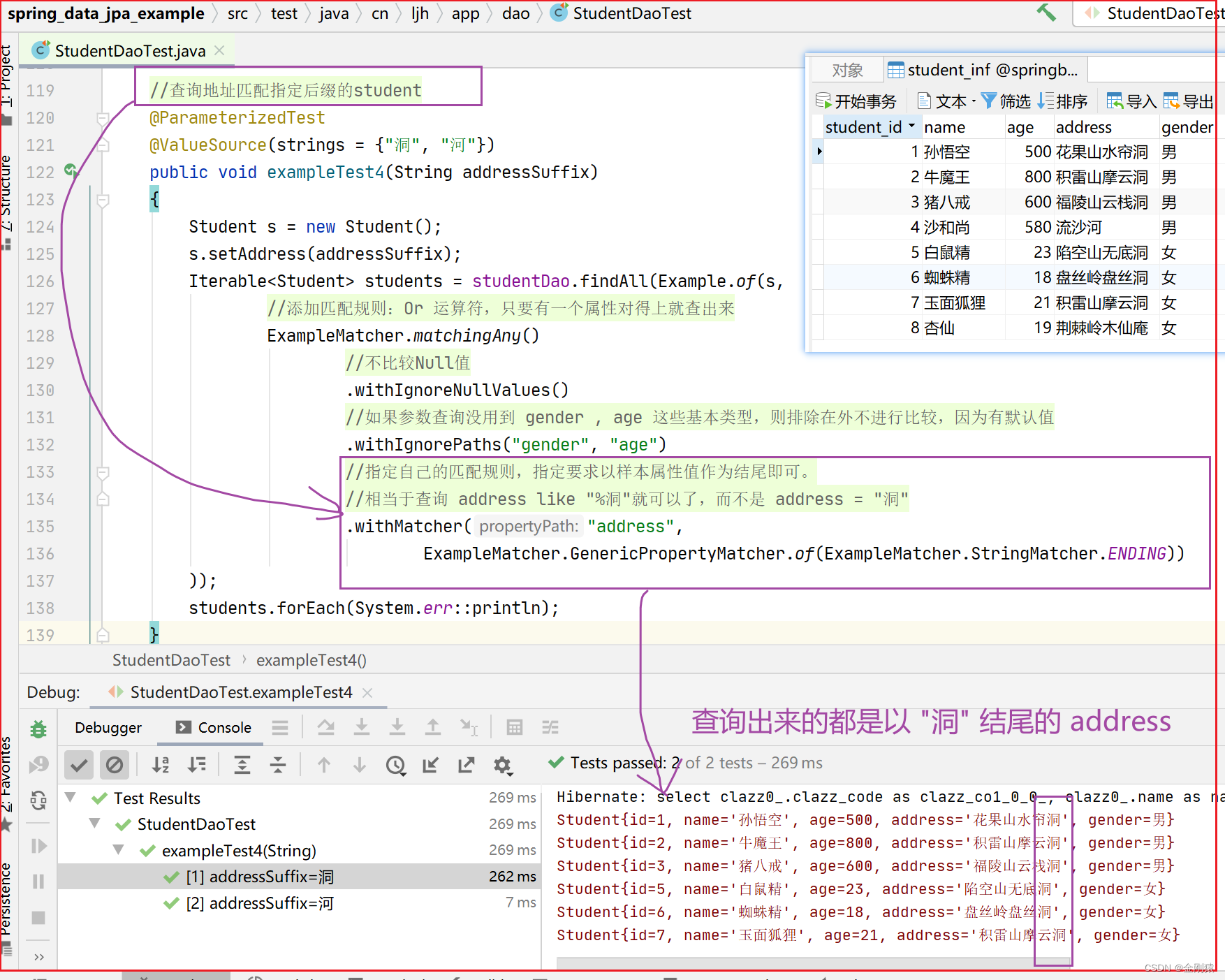
测试4:添加匹配规则的测试
添加的匹配规则:.withMatcher()
作用:
指定自己的匹配规则,指定要求以样本属性值作为结尾即可。
相当于查询 address like "%洞"就可以了,而不是 address = “洞”
需求:查询地址匹配指定后缀的student
匹配规则方法: .withMatcher() ,还能这样写,更灵活
.withMatcher(“address”,matcher -> matcher.endsWith())
也是以该样本属性作为后缀进行查询
完整代码
StudentDao
这个接口只需要再继承 QueryByExampleExecutor 这个接口就可以了,
或者直接继承 JpaRepository 接口也可以
不需要在StudentDao组件写方法,或者写sql语句,直接在测试类进行查询方法的调用,因为DAO组件会调用QueryByExampleExecutor的样本查询方法,不用我们写。
package cn.ljh.app.dao;
import cn.ljh.app.domain.Student;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.QueryByExampleExecutor;
import java.util.List;
//CrudRepository 的第一个泛型参数是被操作的实体类型,第二个参数是实体的主键类型
//public interface StudentDao extends CrudRepository<Student,Integer>
//如果要做样本查询,Dao接口需要继承 JpaRepository 接口,
//public interface StudentDao extends JpaRepository<Student,Integer>
//或者增加继承 QueryByExampleExecutor 接口
public interface StudentDao extends CrudRepository<Student,Integer> , QueryByExampleExecutor<Student>
{
//查询年龄大于指定参数的学生
List<Student> findByAgeGreaterThan(int startAge);
//根据年龄和班级名称查询学生
//Age 和 ClazzName 用 And 连接起来,表示两个查询条件,
//ClazzName这两个单词中间没有And连接起来,表示是一个路径写法,表示是Clazz类的name属性
List<Student> findByAgeAndClazzName(int age , String clazzName);
//根据地址后缀进行分页查询,查询 address 带有 "洞" 的学生并进行分页
Page<Student> findByAddressEndingWith(String addrSuffix, Pageable pageable);
}
StudentDaoTest
package cn.ljh.app.dao;
import cn.ljh.app.domain.Student;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.CsvSource;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ValueSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.*;
import java.util.List;
//SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE : 表示不需要web环境
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.NONE)
public class StudentDaoTest
{
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
/**
* @ValueSource: 每次只能传一个参数
* @CsvSource:每次可以传多个参数
*/
//需求:查询年龄大于指定参数的记录
//参数化测试
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(ints = {20, 200})
public void testFindByAgeGreaterThan(int startAge)
{
List<Student> students = studentDao.findByAgeGreaterThan(startAge);
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//根据年龄和班级名称查询学生
//Age 和 ClazzName 用 And 连接起来,表示两个查询条件,
//ClazzName这两个单词中间没有And连接起来,表示是一个路径写法,表示是Clazz类的name属性
@ParameterizedTest
//参数一个是int,一个是String,这个注解在传参的时候会自动进行类型转换
@CsvSource(value = {"20,超级A营", "18,超级D班"})
public void testFindByAgeAndClazzName(int age, String clazzName)
{
List<Student> students = studentDao.findByAgeAndClazzName(age, clazzName);
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//pageNo: 要查询哪一页的页数 , pageSize: 每页显示的条数
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({"洞,2,3", "洞,1,4", "洞,3,2"})
public void testFindByAddressEndingWith(String addrSuffix, int pageNo, int pageSize)
{
//分页对象,此处的pageNo是从0开始的,0代表第一页,所以这里的 pageNo 要 -1
Pageable pageable1 = PageRequest.of(pageNo - 1, pageSize);
Page<Student> students = studentDao.findByAddressEndingWith(addrSuffix, pageable1);
int number = students.getNumber() + 1;
System.err.println("总页数:" + students.getTotalPages());
System.err.println("总条数:" + students.getTotalElements());
System.err.println("当前第:" + number + " 页");
System.err.println("当前页有:" + students.getNumberOfElements() + " 条数据");
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//==============测试样本查询从这里开始=====================================================
//根据一个对象中的某些属性作为样本,去数据库查询数据
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({"孙悟空,500", "猪八戒,200"})
public void exampleTest1(String name, int age)
{
Student s = new Student();
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
//没有指定匹配规则,所以要求样本对象(s) 和 查询对象(Student) 的所有属性都相等才行
Iterable<Student> students = studentDao.findAll(Example.of(s));
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//根据一个对象中的某些属性作为样本,去数据库查询数据
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({"孙悟空,500", "猪八戒,200"})
public void exampleTest2(String name, int age)
{
Student s = new Student();
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
Iterable<Student> students = studentDao.findAll(Example.of(s,
//添加匹配规则
ExampleMatcher.matching()
//不比较Null值
.withIgnoreNullValues()
//不比较id、gender,因为gender是基本类型,有默认值,所以需要排除在外
.withIgnorePaths("gender")
));
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//根据一个对象中的某些属性作为样本,去数据库查询数据
@ParameterizedTest
@CsvSource({"孙悟空,99999", "猪八戒,200"})
public void exampleTest3(String name, int age)
{
Student s = new Student();
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
Iterable<Student> students = studentDao.findAll(Example.of(s,
//添加匹配规则:Or 运算符,只要有一个属性对得上就查出来
ExampleMatcher.matchingAny()
//不比较Null值
.withIgnoreNullValues()
//不比较id、gender
.withIgnorePaths("id", "gender")
));
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//查询地址匹配指定后缀的student
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = {"洞", "河"})
public void exampleTest4(String addressSuffix)
{
Student s = new Student();
s.setAddress(addressSuffix);
Iterable<Student> students = studentDao.findAll(Example.of(s,
//添加匹配规则:Or 运算符,只要有一个属性对得上就查出来
ExampleMatcher.matchingAny()
//不比较Null值
.withIgnoreNullValues()
//如果参数查询没用到 gender , age 这些基本类型,则排除在外不进行比较,因为有默认值
.withIgnorePaths("gender", "age")
//指定自己的匹配规则,指定要求以样本属性值作为结尾即可。
//相当于查询 address like "%洞"就可以了,而不是 address = "洞"
.withMatcher("address",
ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatcher.of(ExampleMatcher.StringMatcher.ENDING))
));
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
//查询地址匹配指定后缀的student
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = {"洞", "河"})
public void exampleTest5(String addressSuffix)
{
Student s = new Student();
s.setAddress(addressSuffix);
Iterable<Student> students = studentDao.findAll(Example.of(s,
//添加匹配规则:Or 运算符,只要有一个属性对得上就查出来
ExampleMatcher.matchingAny()
//不比较Null值
.withIgnoreNullValues()
//如果参数查询没用到 gender , age 这些基本类型,则排除在外不进行比较,因为有默认值
.withIgnorePaths("gender", "age")
//指定自己的匹配规则,指定要求以样本属性值作为结尾即可。
//相当于查询 address like "%洞"就可以了,而不是 address = "洞"
//更灵活的写法matcher -> matcher.endsWith()
.withMatcher("address",matcher -> matcher.endsWith())
));
students.forEach(System.err::println);
}
}