1. 背景说明
实现基本与定长分配一致,不过将定长分配改为动态分配,解除了长度限制,实现更加灵活。
2. 示例代码
1) status.h
/* DataStructure 预定义常量和类型头文件 */
#ifndef STATUS_H
#define STATUS_H
#define CHECK_NULL(pointer) if (!(pointer)) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NULL_PTR); \
return NULL; \
}
#define CHECK_RET(ret) if (ret != RET_OK) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret); \
return ret; \
}
#define CHECK_VALUE(value, ERR_CODE) if (value) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_CODE); \
return ERR_CODE; \
}
#define CHECK_FALSE(value, ERR_CODE) if (!(value)) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_CODE); \
return FALSE; \
}
/* 函数结果状态码 */
#define TRUE 1 /* 返回值为真 */
#define FALSE 0 /* 返回值为假 */
#define RET_OK 0 /* 返回值正确 */
#define INFEASIABLE 2 /* 返回值未知 */
#define ERR_MEMORY 3 /* 访问内存错 */
#define ERR_NULL_PTR 4 /* 空指针错误 */
#define ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE 5 /* 内存分配错 */
#define ERR_NULL_STACK 6 /* 栈元素为空 */
#define ERR_PARA 7 /* 函数参数错 */
#define ERR_OPEN_FILE 8 /* 打开文件错 */
#define ERR_NULL_QUEUE 9 /* 队列为空错 */
#define ERR_FULL_QUEUE 10 /* 队列为满错 */
#define ERR_NOT_FOUND 11 /* 表项不存在 */
typedef int Status; /* Status 是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如 RET_OK 等 */
typedef int Bollean; /* Boolean 是布尔类型,其值是 TRUE 或 FALSE */
#endif // !STATUS_H2) hString.h
/* 串的堆分配存储实现头文件 */
#ifndef HSTRING_H
#define HSTRING_H
#include "status.h"
typedef struct {
char *ch;
int length;
} HString;
/* 初始化(产生空串)字符串 T */
void InitString(HString *T);
/* 生成一个其值等于串常量 chars 的串 T */
Status StrAssign(const char *chars, HString *T);
/* 初始条件: 串 S 存在
操作结果: 由串 S 复制得串 T */
Status StrCopy(const HString *S, HString *T);
/* 初始条件: 串 S 存在
操作结果: 若 S 为空串,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE */
Bollean StrEmpty(const HString *S);
/* 若 S > T,则返回值 > 0;若 S = T,则返回值 = 0;若 S < T,则返回值 < 0 */
int StrCompare(const HString *S, const HString *T);
/* 返回 S 的元素个数,称为串的长度 */
int StrLength(const HString *S);
/* 将 S 清为空串 */
Status ClearString(HString *S);
/* 用 T 返回由 S1 和 S2 联接而成的新串 */
Status Concat(const HString *S1, const HString *S2, HString *T);
/* 用 Sub 返回串 S 的第 pos 个字符起长度为 len 的子串
其中,1 ≤ pos ≤ StrLength(S) 且 0 ≤ len ≤ StrLength(S) - pos + 1 */
Status SubString(const HString *S, int pos, int len, HString *Sub);
/* 算法 4.1,T 为非空串。若主串 S 中第 pos 个字符之后存在与 T 相等的子串
则返回第一个这样的子串在 S 中的位置,否则返回 0 */
int Index(const HString *S, const HString *T, int pos);
/* 算法 4.4, 在串 S 的第 pos 个字符之前插入串 T, 1 ≤ pos ≤ StrLength(S) + 1 */
Status StrInsert(const HString *T, int pos, HString *S);
/* 从串 S 中删除第 pos 个字符起长度为 len 的子串 */
Status StrDelete(int pos, int len, HString *S);
/* 初始条件: 串 S, T 和 V 存在, T 是非空串(此函数与串的存储结构无关)
操作结果: 用 V 替换主串 S 中出现的所有与 T 相等的不重叠的子串 */
Status Replace(const HString *T, const HString *V, HString *S);
/* 堆分配类型的字符串无法销毁(结构体)*/
void DestroyString(void);
/* 输出 T 字符串 */
void StrPrint(const HString *T);
#endif // !HSTRING_H3) hString.c
/* 串的堆分配存储实现源文件 */
#include "hString.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* 初始化(产生空串)字符串 T */
void InitString(HString *T)
{
T->length = 0;
T->ch = NULL;
}
/* 生成一个其值等于串常量 chars 的串 T */
Status StrAssign(const char *chars, HString *T)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!chars, ERR_NULL_PTR);
if (T->ch) {
free(T->ch);
}
int length = (int)strlen(chars);
if (length == 0) {
T->ch = NULL;
T->length = 0;
return RET_OK;
}
T->ch = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * length);
CHECK_VALUE(!(T->ch), ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
T->length = length;
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
T->ch[i] = chars[i];
}
return RET_OK;
}
/* 初始条件: 串 S 存在
操作结果: 由串 S 复制得串 T */
Status StrCopy(const HString *S, HString *T)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!S || !T, ERR_NULL_PTR);
if (T->ch) {
free(T->ch);
}
T->ch = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * (S->length));
CHECK_VALUE(!(T->ch), ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
T->length = S->length;
for (int i = 0; i < S->length; ++i) {
T->ch[i] = S->ch[i];
}
return RET_OK;
}
/* 初始条件: 串 S 存在
操作结果: 若 S 为空串,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE */
Bollean StrEmpty(const HString *S)
{
return ((S->length == 0) && (S->ch == NULL)) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
/* 若 S > T,则返回值 > 0;若 S = T,则返回值 = 0;若 S < T,则返回值 < 0 */
int StrCompare(const HString *S, const HString *T)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!S || !T, ERR_NULL_PTR);
for (int i = 0; i < S->length && i < T->length; ++i) {
if (S->ch[i] != T->ch[i]) {
return S->ch[i] - T->ch[i];
}
}
return S->length - T->length;
}
/* 返回 S 的元素个数,称为串的长度 */
int StrLength(const HString *S)
{
return S->length;
}
/* 将 S 清为空串 */
Status ClearString(HString *S)
{
if (S->ch) {
free(S->ch);
S->ch = NULL;
}
S->length = 0;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 用 T 返回由 S1 和 S2 联接而成的新串 */
Status Concat(const HString *S1, const HString *S2, HString *T)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!S1 || !S2 || !T, ERR_NULL_PTR);
if (T->ch) {
free(T->ch);
}
int length = S1->length + S2->length;
T->ch = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * length);
CHECK_VALUE(!(T->ch), ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
for (int i = 0; i < S1->length; ++i) {
T->ch[i] = S1->ch[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < S2->length; ++i) {
T->ch[S1->length + i] = S2->ch[i];
}
T->length = length;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 用 Sub 返回串 S 的第 pos 个字符起长度为 len 的子串
其中,1 ≤ pos ≤ StrLength(S) 且 0 ≤ len ≤ StrLength(S) - pos + 1 */
Status SubString(const HString *S, int pos, int len, HString *Sub)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!S || !Sub, ERR_NULL_PTR);
CHECK_VALUE((pos < 1) || (pos > S->length) || (len < 0) || (len > S->length - pos + 1), ERR_PARA);
if (Sub->ch) {
free(Sub->ch);
}
if (len == 0) {
Sub->ch = NULL;
Sub->length = 0;
} else {
Sub->ch = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * len);
CHECK_VALUE(!(Sub->ch), ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
Sub->ch[i] = S->ch[pos - 1 + i];
}
Sub->length = len;
}
return RET_OK;
}
/* 算法 4.1,T 为非空串。若主串 S 中第 pos 个字符之后存在与 T 相等的子串
则返回第一个这样的子串在 S 中的位置,否则返回 0 */
int Index(const HString *S, const HString *T, int pos)
{
int maxRange = StrLength(S) - StrLength(T) + 1;
CHECK_VALUE((pos < 1) || (pos > maxRange), 0);
HString sub;
InitString(&sub);
while (pos <= maxRange) {
SubString(S, pos, StrLength(T), &sub);
if (StrCompare(&sub, T) != 0) {
++pos;
} else {
return pos;
}
}
return 0;
}
/* 算法 4.4, 在串 S 的第 pos 个字符之前插入串 T, 1 ≤ pos ≤ StrLength(S) + 1 */
Status StrInsert(const HString *T, int pos, HString *S)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!T || !S, ERR_NULL_PTR);
CHECK_VALUE((pos < 1) || (pos > S->length + 1), ERR_PARA);
if (T->length == 0) {
return RET_OK;
}
S->ch = (char *)realloc(S->ch, sizeof(char) * (unsigned int)(S->length + T->length));
CHECK_VALUE(!(S->ch), ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
for (int i = S->length - 1; i >= pos - 1; --i) {
S->ch[i + T->length] = S->ch[i];
}
S->length += T->length;
for (int i = 0; i < T->length; ++i) {
S->ch[pos - 1 + i] = T->ch[i];
}
return RET_OK;
}
/* 从串 S 中删除第 pos 个字符起长度为 len 的子串 */
Status StrDelete(int pos, int len, HString *S)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!S, ERR_NULL_PTR);
CHECK_VALUE(pos - 1 + len > S->length, ERR_PARA);
for (int i = pos - 1; i < S->length - len; ++i) {
S->ch[i] = S->ch[i + len];
}
S->length -= len;
S->ch = (char *)realloc(S->ch, sizeof(char) * S->length);
return RET_OK;
}
/* 初始条件: 串 S, T 和 V 存在, T 是非空串(此函数与串的存储结构无关)
操作结果: 用 V 替换主串 S 中出现的所有与 T 相等的不重叠的子串 */
Status Replace(const HString *T, const HString *V, HString *S)
{
CHECK_VALUE(!T || !V || !S, ERR_NULL_PTR);
int pos = 1;
do {
pos = Index(S, T, pos);
if (pos) {
StrDelete(pos, StrLength(T), S);
StrInsert(V, pos, S);
pos += StrLength(V);
}
} while (pos);
return RET_OK;
}
/* 堆分配类型的字符串无法销毁(结构体)*/
void DestroyString(void)
{
printf("Do not need to destroy!\n");
}
/* 输出 T 字符串 */
void StrPrint(const HString *T)
{
for (int i = 0; i < T->length; ++i) {
putchar(T->ch[i]);
}
}4) main.c
/* 入口程序源文件 */
#include "hString.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
HString t, s, r;
InitString(&t);
InitString(&s);
InitString(&r);
char *p = "Good bye!", *q = "Good luck!";
StrAssign(p, &t);
printf("The length of t is %d, and t is %s, and t is: ", StrLength(&t),
(StrEmpty(&t) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty");
StrPrint(&t);
putchar('\n');
StrAssign(q, &s);
printf("The length of s is %d, and s is %s, and s is: ", StrLength(&s),
(StrEmpty(&s) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty");
StrPrint(&s);
putchar('\n');
Status ret = StrCompare(&s, &t);
char ch = (ret == 0) ? '=' : ((ret < 0) ? '<' : '>');
printf("s %c t\n", ch);
Concat(&s, &t, &r);
printf("The conncection of s and t is: ");
StrPrint(&r);
putchar('\n');
printf("Now s is: ");
StrAssign("oo", &s);
StrPrint(&s);
putchar('\n');
printf("Now t is: ");
StrAssign("o", &t);
StrPrint(&t);
putchar('\n');
Replace(&t, &s, &r);
printf("After use s replace t, r is: ");
StrPrint(&r);
putchar('\n');
ClearString(&s);
printf("After clear s, the length of s is %d, and s is %s, and s is: ", StrLength(&s),
(StrEmpty(&s) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty");
StrPrint(&s);
putchar('\n');
SubString(&r, 6, 4, &s);
printf("s is the string of r from 6th and length is %d\n", s.length);
StrPrint(&s);
putchar('\n');
StrCopy(&r, &t);
printf("After copy string r into string t, t is: ");
StrPrint(&t);
putchar('\n');
StrInsert(&s, 6, &t);
printf("After insert s into the 6th character of t, t is: ");
StrPrint(&t);
putchar('\n');
StrDelete(1, 5, &t);
printf("After delete 5 characters of t from 1th character, t is: ");
StrPrint(&t);
putchar('\n');
printf("The position of the 1th same string with s from 1th character of t is %d\n",
Index(&t, &s, 1));
printf("The position of the 1th same string with s from 2th character of t is %d\n",
Index(&t, &s, 2));
ClearString(&s);
ClearString(&t);
ClearString(&r);
DestroyString();
return 0;
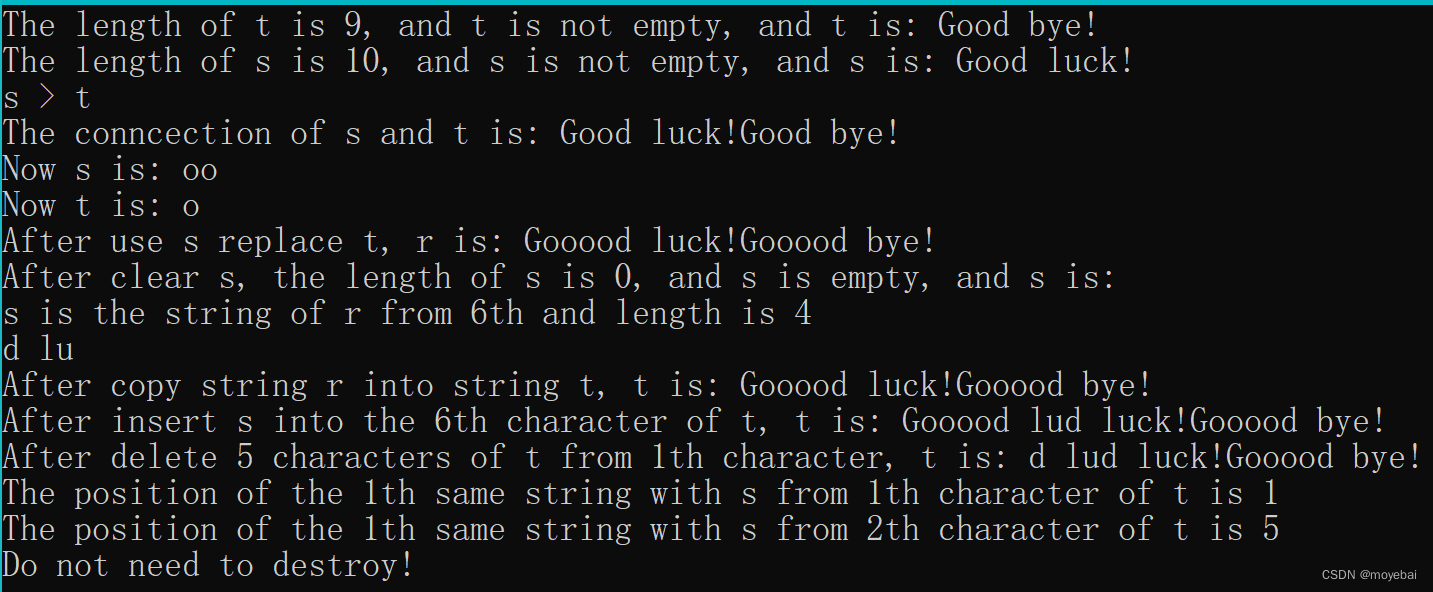
}3. 输出示例
![[JAVAee]spring-Bean对象的执行流程与生命周期](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b0f5481691db4660ba22ffcace54a445.png)