一、ref 引用
1.1、什么是 ref 引用
ref 用来辅助开发者在不依赖于jQuery的情况下,获取 DOM 元素或组件的引用。
每个vue的组件实例上,都包含一个$refs对象,里面存储着对应的 DOM 元素或组件的引用。默认情况下,组件的$refs指向一个空对象。
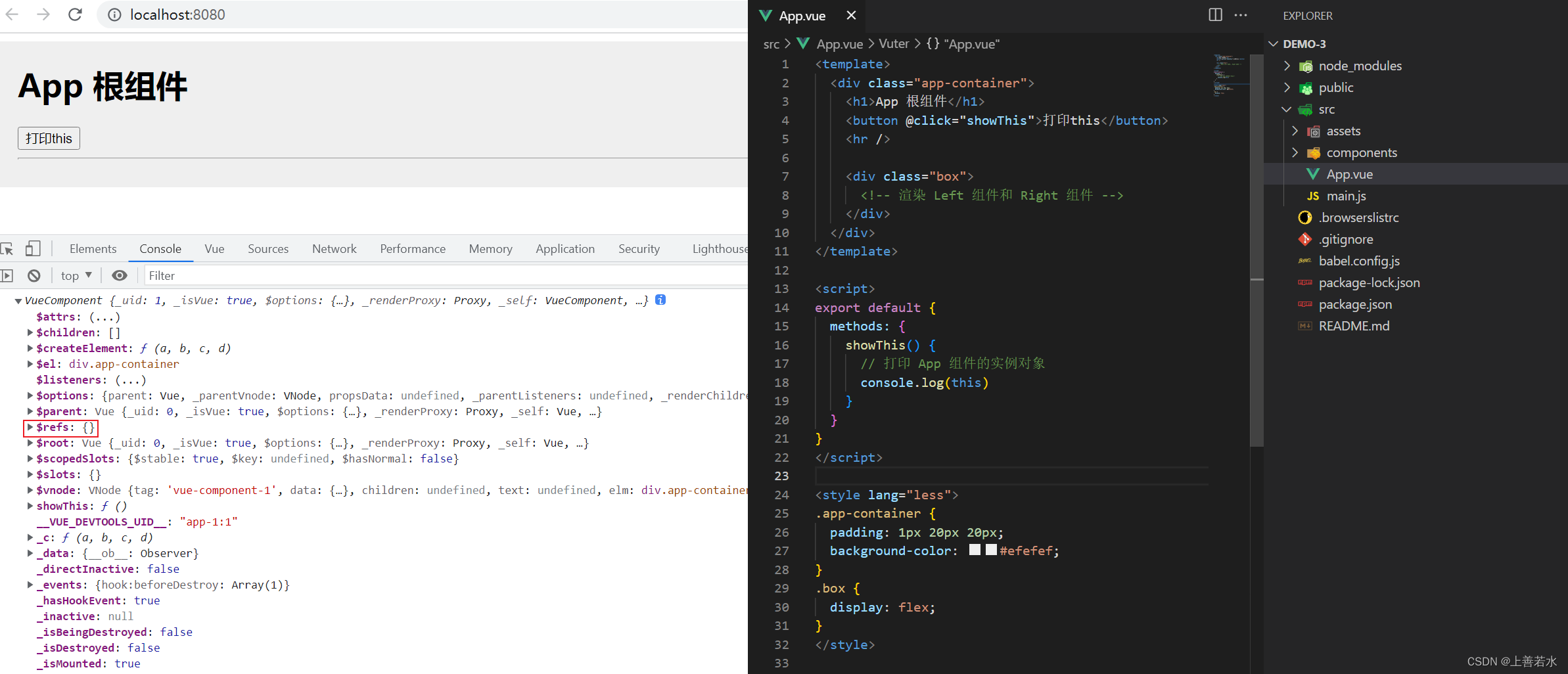
1.2、使用ref引用 DOM 元素
如果想要使用 ref 引用页面上的 DOM 元素,则可以按照如下的方式进行操作:
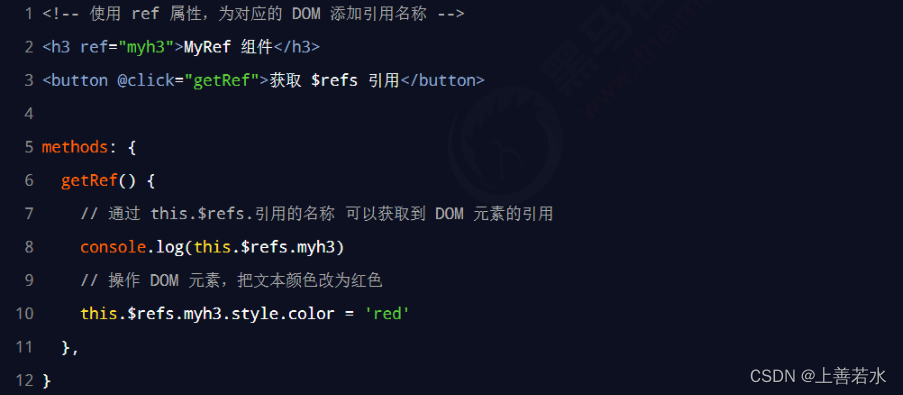
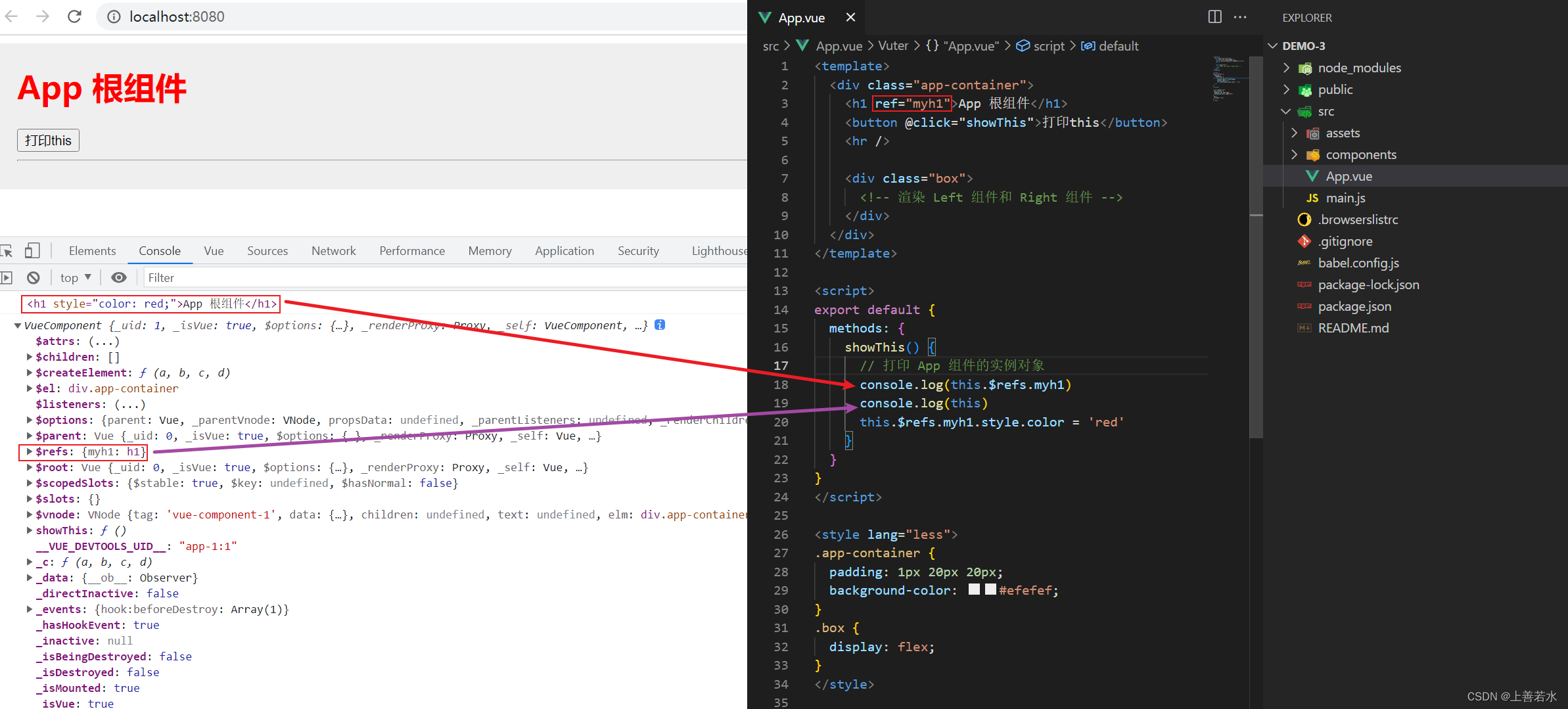
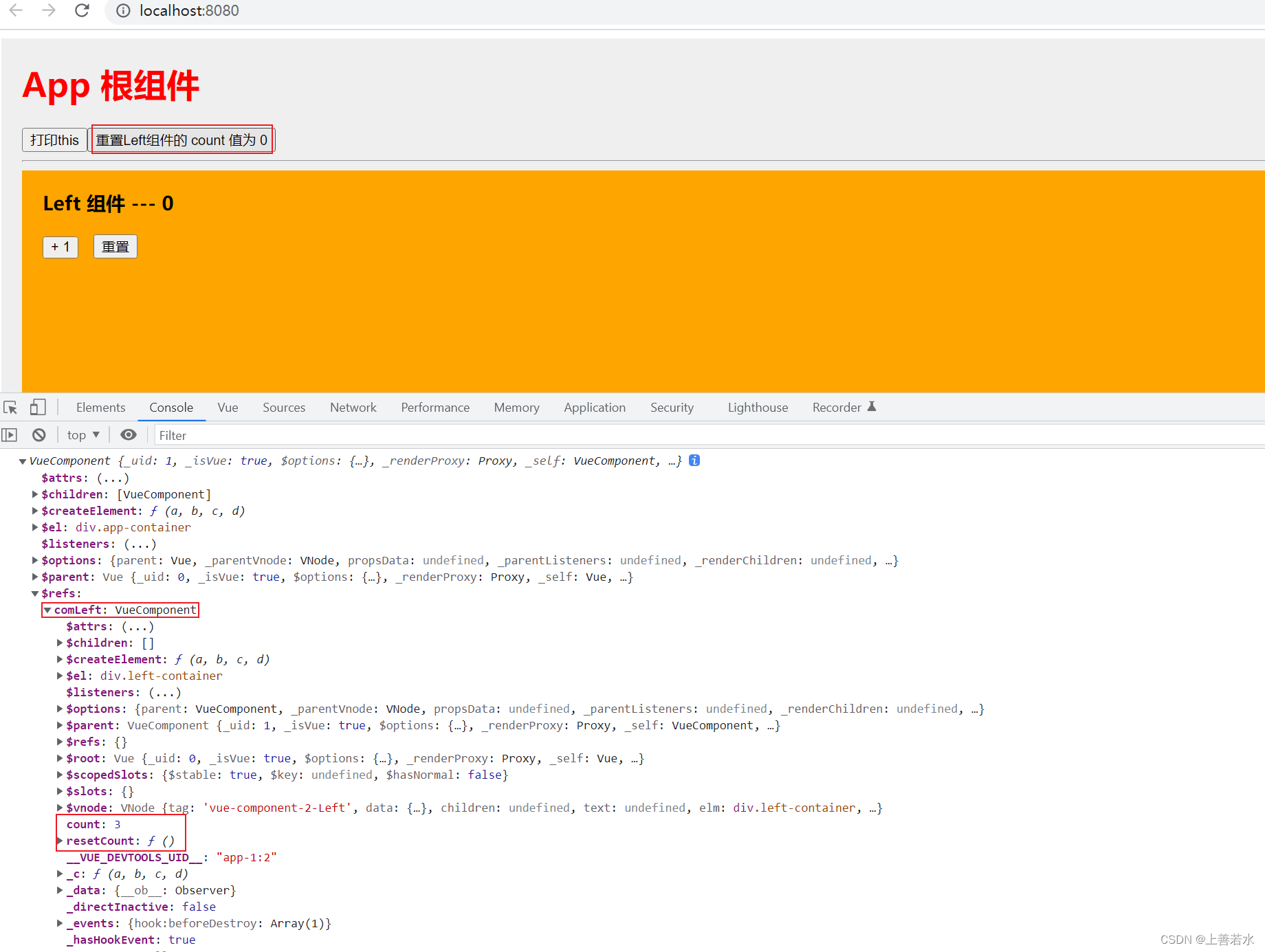
1.3、使用ref引用组件实例
如果想要使用ref引用页面上的组件实例,则可以按照如下的方式进行操作:
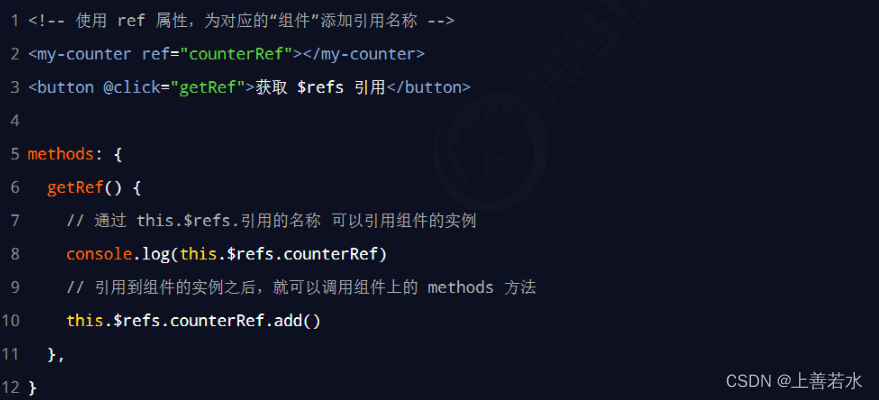
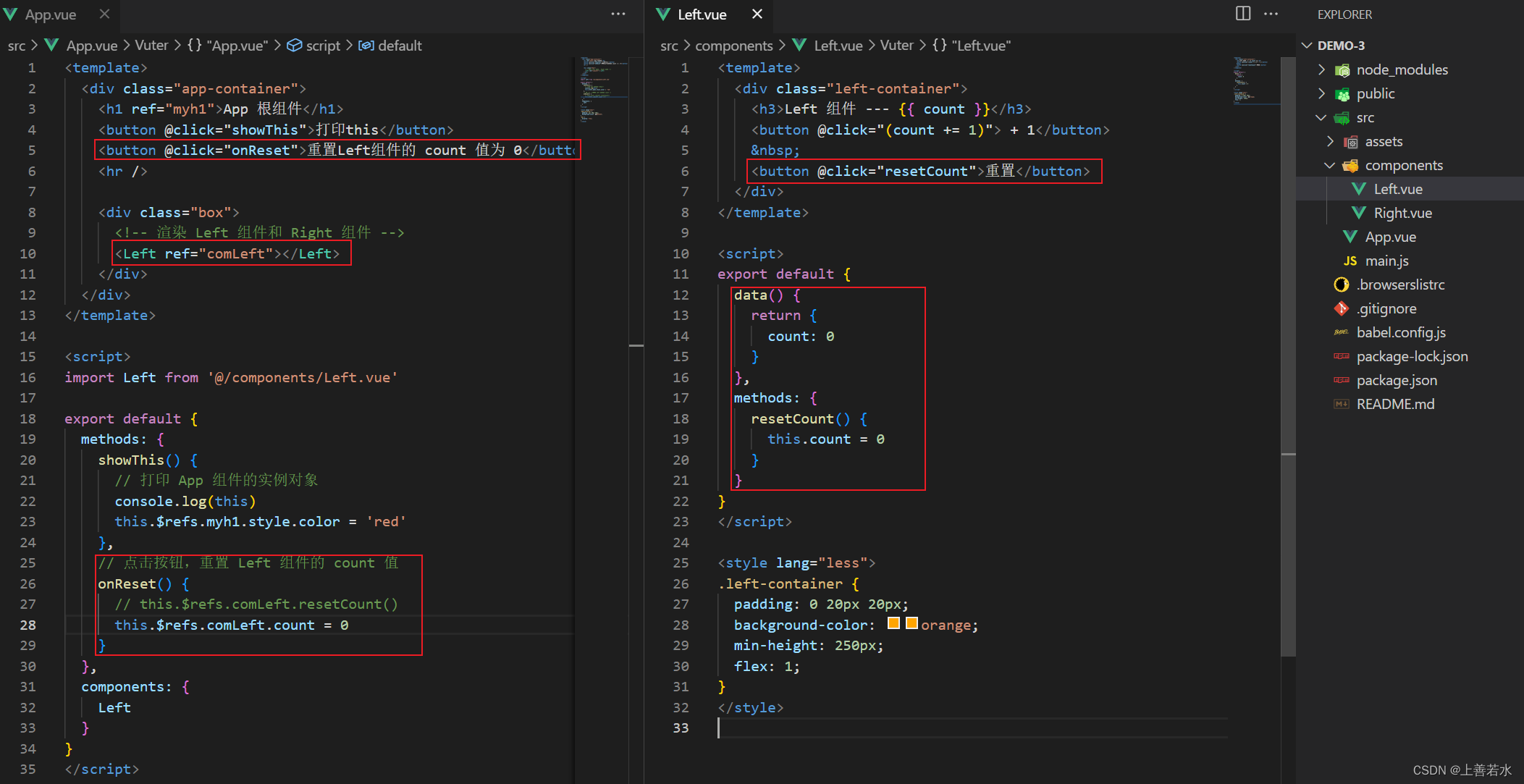
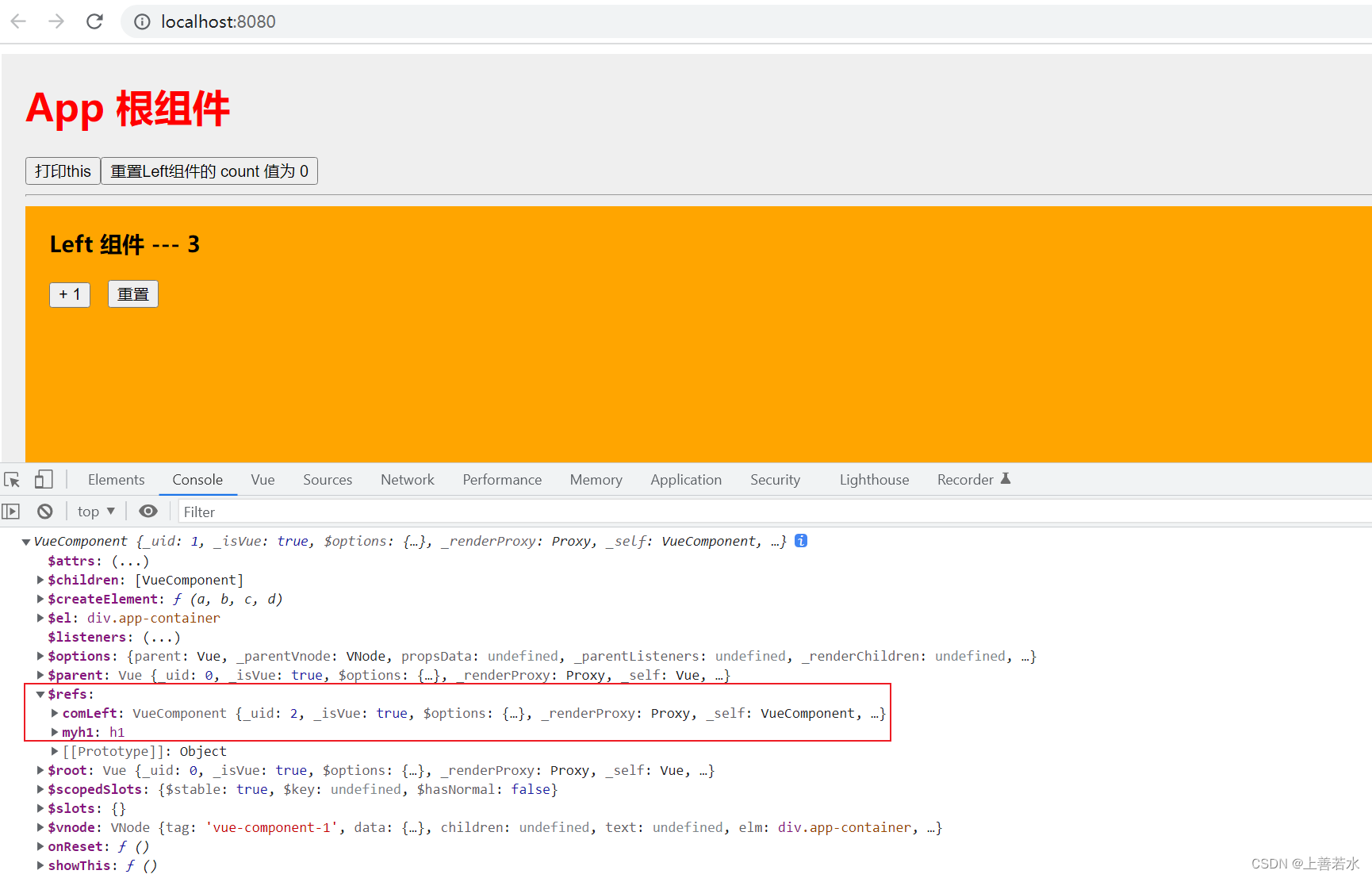
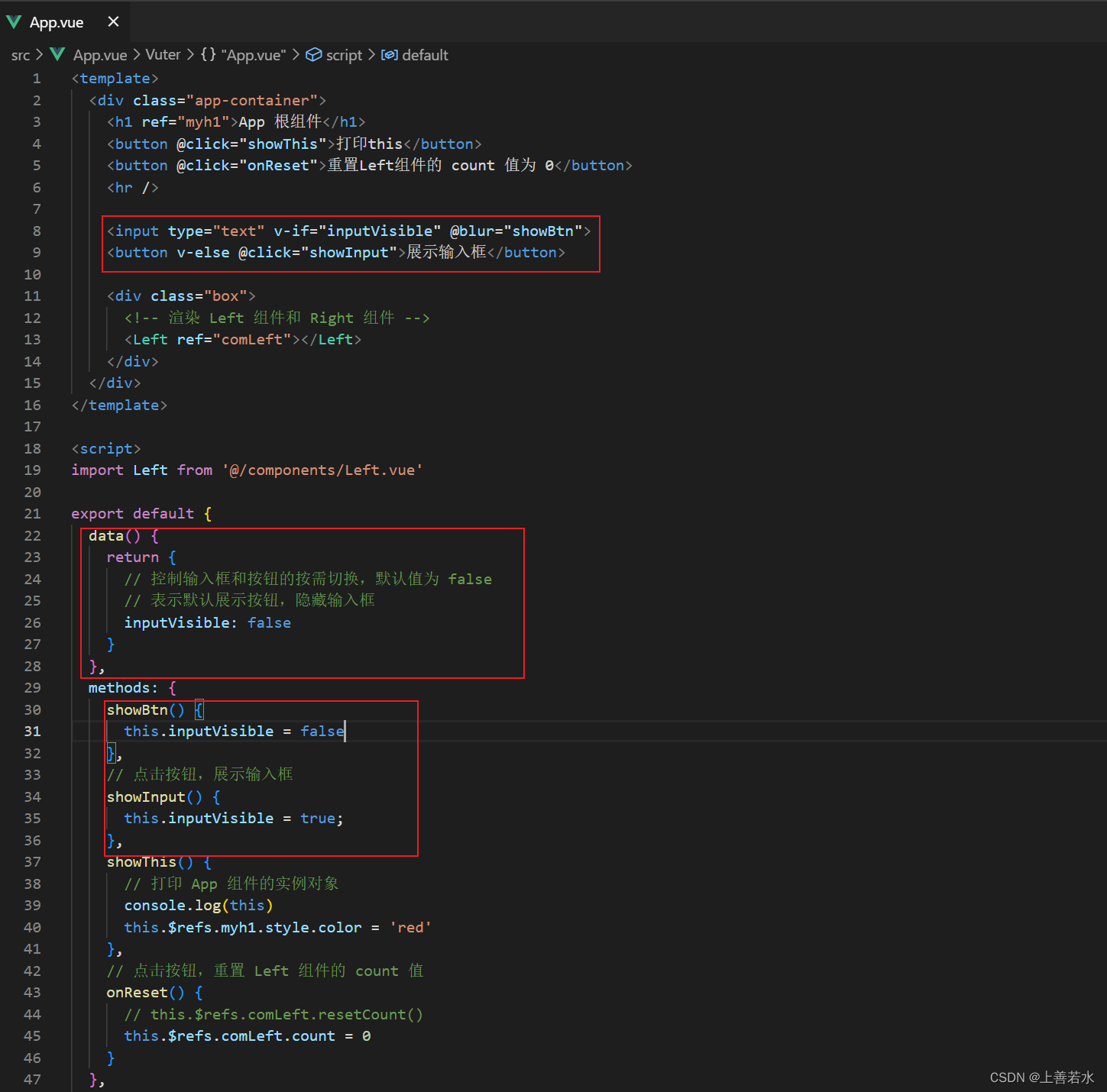
1.4、控制文本框和按钮的按需切换
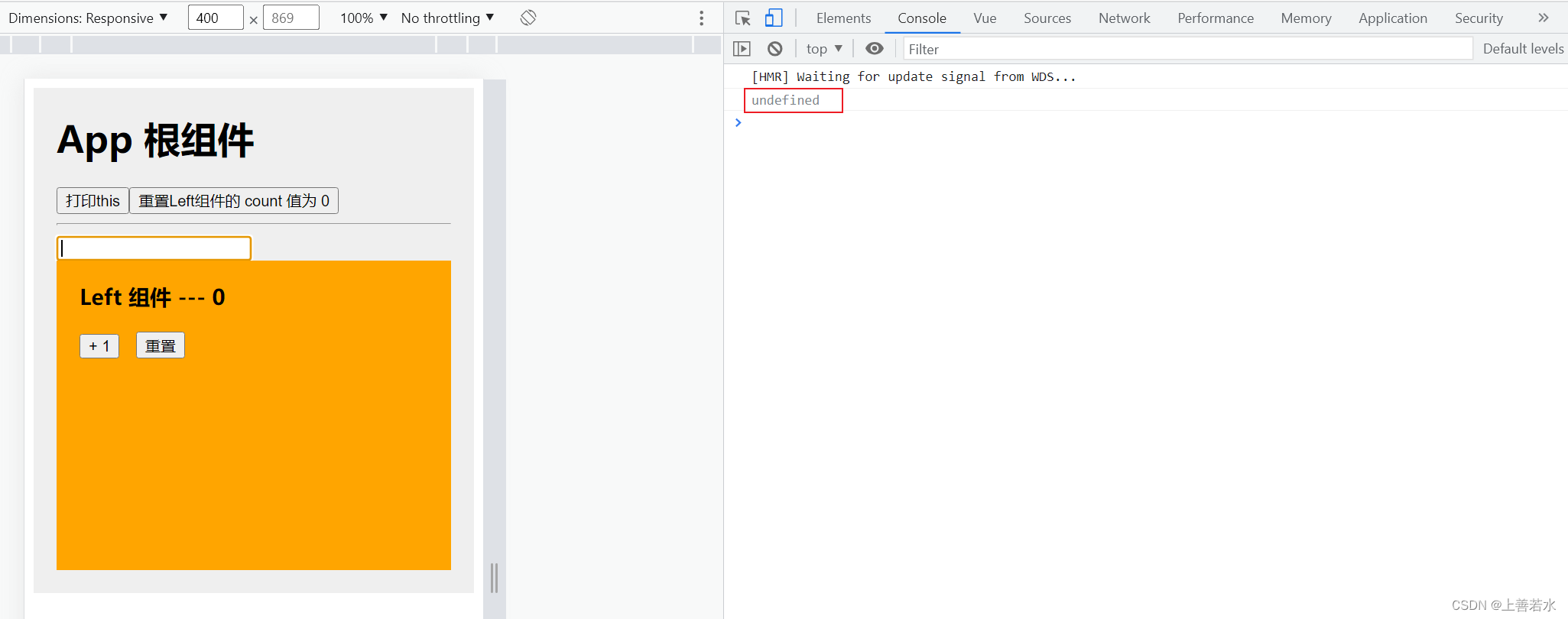
通过布尔值inputVisible来控制组件中的文本框与按钮的按需切换。示例代码如下:

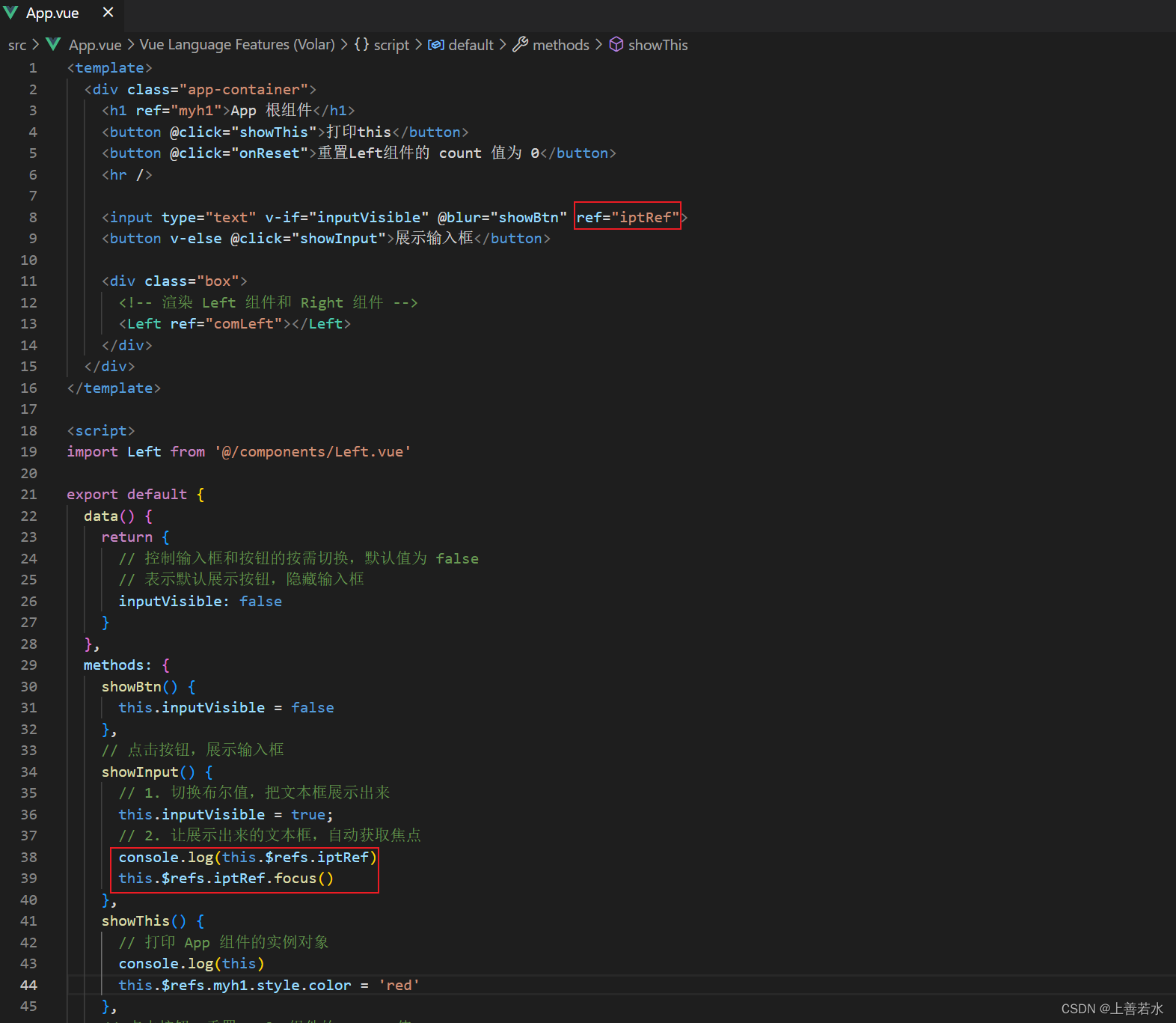
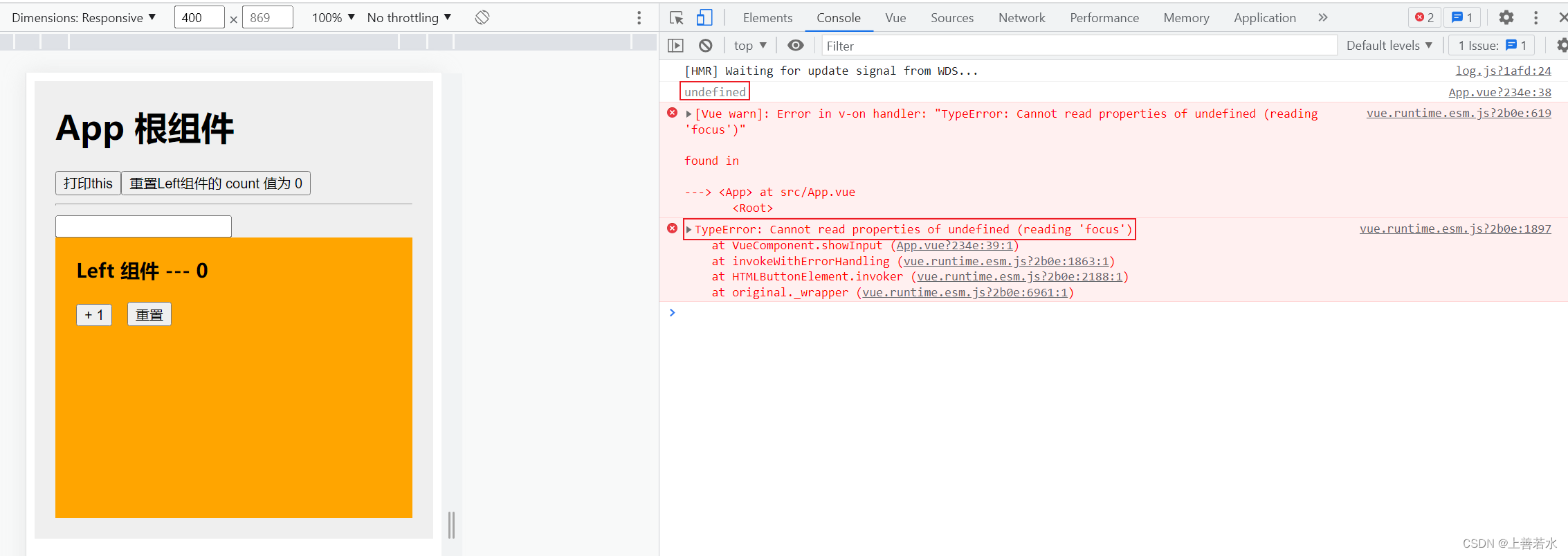
1.5、让文本框自动获取焦点
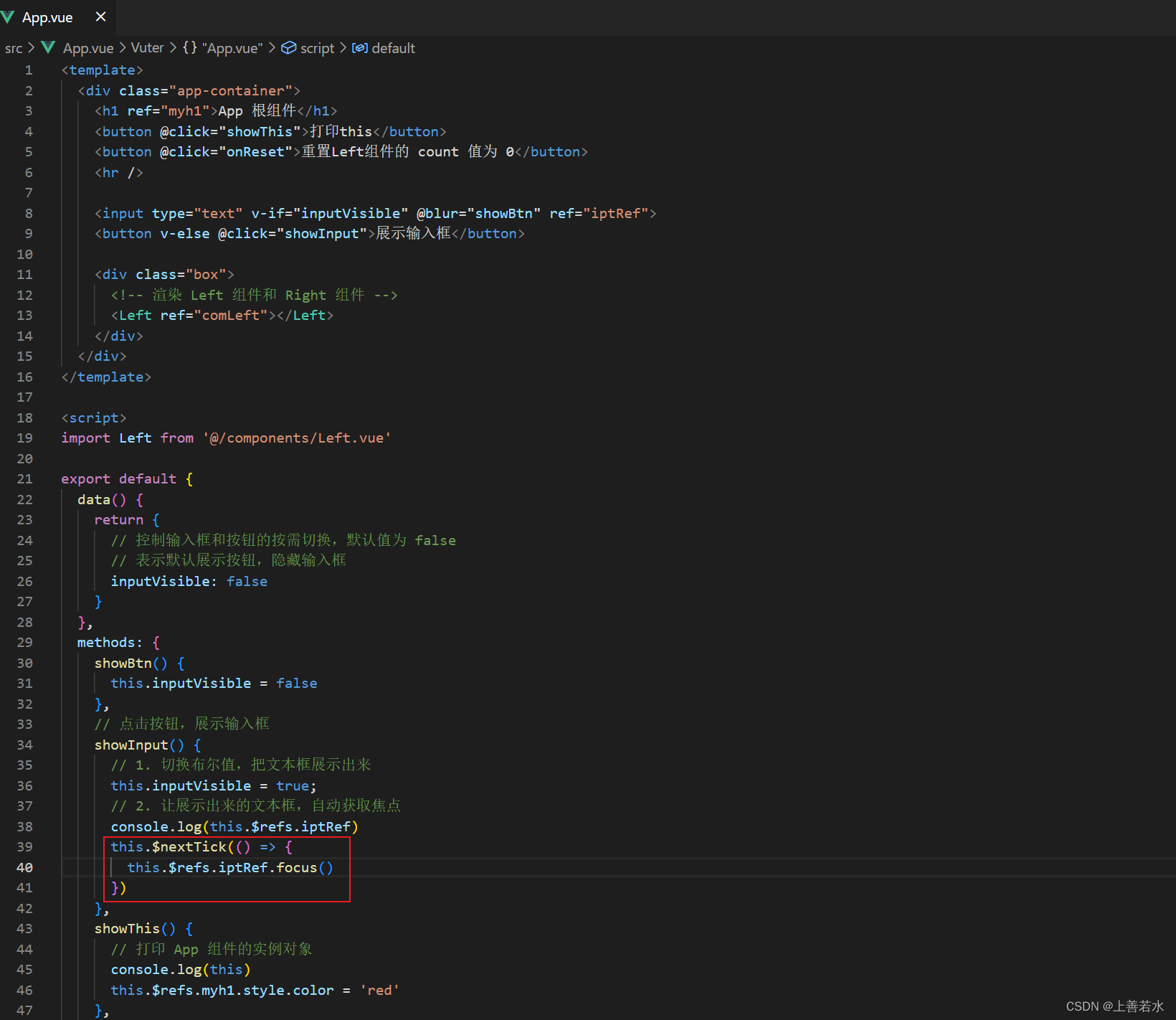
当文本框展示出来之后,如果希望它立即获得焦点,则可以为其添加ref引用,并调用原生 DOM 对象的 .focus()方法即可。示例代码如下:
1.6、this.$nextTick(cb)方法
组件的$nextTick(cb)方法,会把 cb 回调 推迟到下一个 DOM 更新周期之后执行。通俗的理解是:等组件的 DOM 更新完成之后,再执行 cb 回调函数。从而能保证 cb 回调函数可以操作到最新的 DOM 元素。
二、数组的常用方法
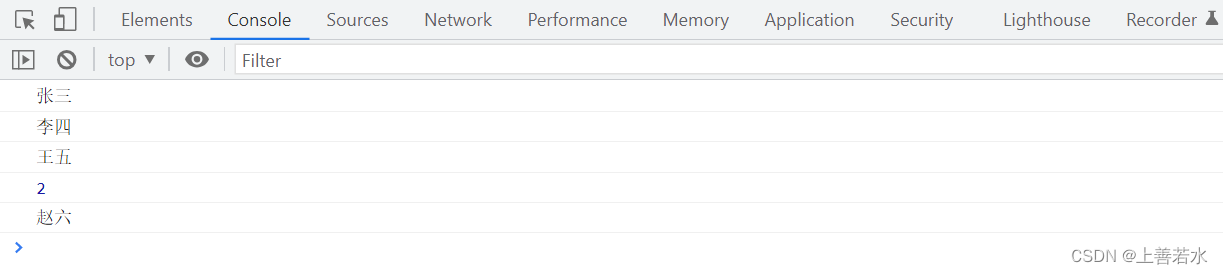
2.1、forEach()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr = ['张三','李四','王五','赵六']
// forEach 循环一旦开始,无法在中间被停止
arr.forEach((item, index) => {
console.log(item)
if(item === '王五') {
console.log(index)
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
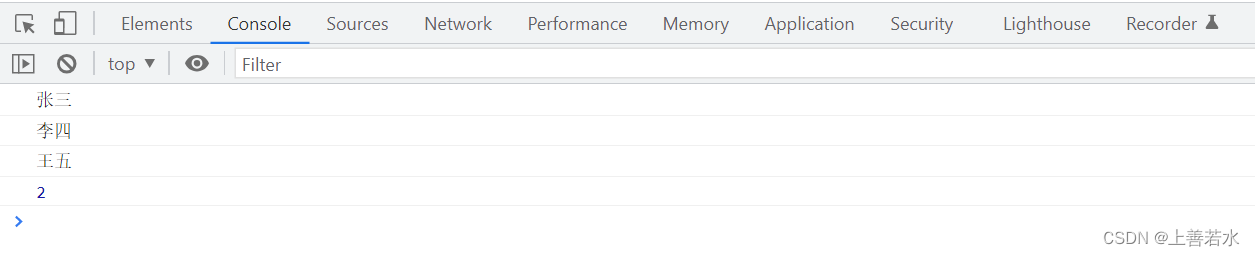
2.2、some()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr = ['张三','李四','王五','赵六']
arr.some((item, index) => {
console.log(item)
if(item === '王五') {
console.log(index)
// 在找到对应的项之后,可以通过 return true 固定的语法,来终止 some 循环
return true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.3、every()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr = [
{ id: 1, name: '西瓜', state: true },
{ id: 2, name: '榴莲', state: false },
{ id: 3, name: '草莓', state: true },
]
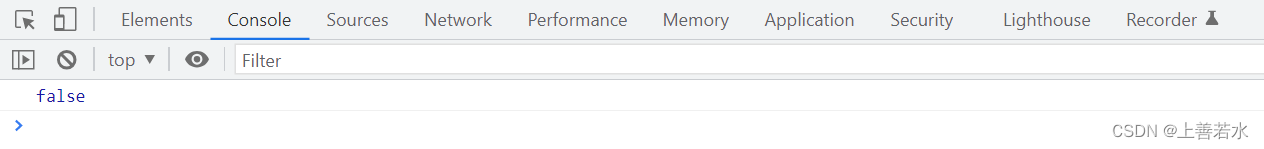
// 需求:判断数组中,水果是否被全选了!
const result = arr.every(item => item.state)
console.log(result)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4、filter()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr = [
{ id: 1, name: '西瓜', state: true, price: 10, count: 1 },
{ id: 2, name: '榴莲', state: false, price: 80, count: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '草莓', state: true, price: 20, count: 3 },
]
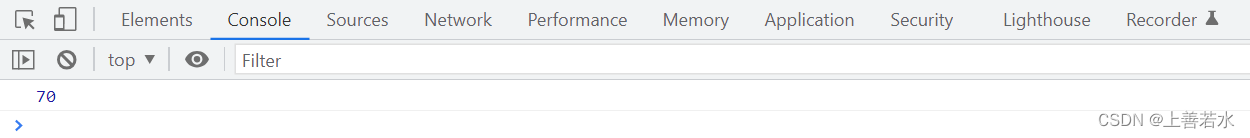
// 需求:把购物车数组中,已勾选的水果,总价累加起来!
let amt = 0 // 总价
arr.filter(item => item.state).forEach(item => {
amt += item.price * item.count
})
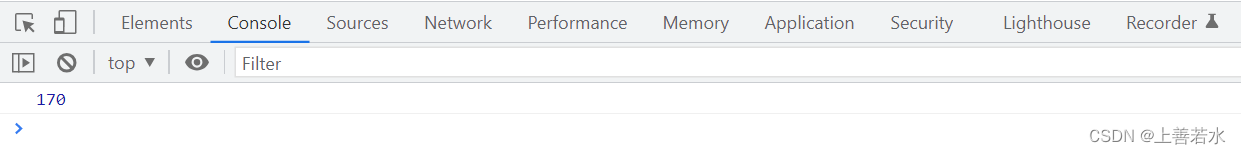
console.log(amt)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.5、reduce()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const arr = [
{ id: 1, name: '西瓜', state: true, price: 10, count: 1 },
{ id: 2, name: '榴莲', state: true, price: 80, count: 2 },
{ id: 3, name: '草莓', state: false, price: 20, count: 3 },
]
// arr.filter(item => item.state).reduce((累加的结果, 当前循环项) => { }, 初始值)
const result = arr.filter(item => item.state).reduce((amt, item) => amt += item.price * item.count, 0)
console.log(result)
</script>
</body>
</html>