目录
错排问题
有理数运算
错排问题
年会抽奖__牛客网
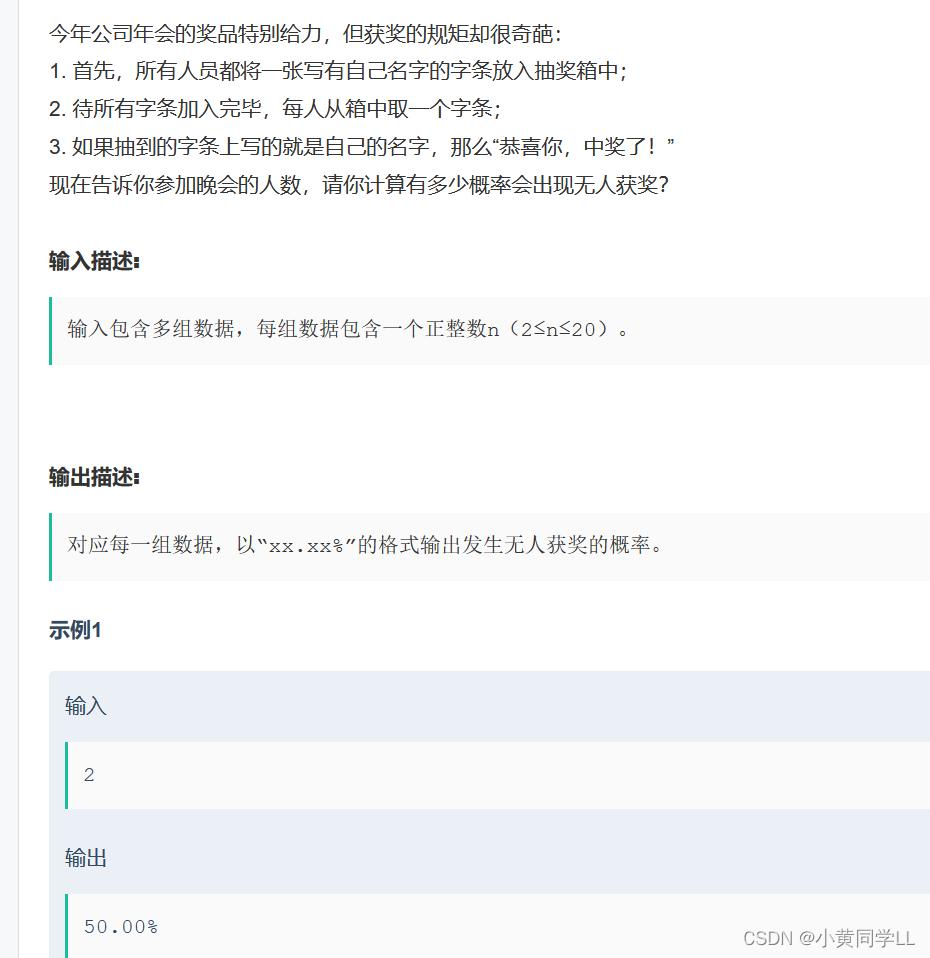

全部都不获奖的概率必定是由n个人都拿错的情况种数除n个人拿出的所有排列情况数。n个人拿出的所有排列情况数显然是n的阶乘。
假设
a的名字没有被a拿到,其他n - 1个人都有可能拿到,即有n - 1种情况。假设b拿到了a的名字,那么对于b的名字有两种情况:
- 第一种是
b的名字被a拿到了,也就是a、b互相拿到了对方的名字,那么对于其他n - 2个人互相拿错又是一个子问题f(n - 2).- 第二种是
b的名字没有被a拿到,则剩下的问题是子问题f(n - 1).因此可得递推公式
f(n) = (n - 1) * (f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)).最终得出公式n人都不获奖的概率
h(n) = (n - 1) * (f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)) / (n!)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
int main()
{
long long d[21] = { 0, 0, 1 }; // 错排数量,预留第一项为0,配合下文中输入的n
long long f[21] = { 1, 1, 2 }; // 阶乘
for (int i = 3; i <= 20; i++)
{
d[i] = (i - 1) * (d[i - 1] + d[i - 2]); //错排的递推公式
f[i] = i * f[i - 1]; //阶乘的递推公式
}
int n;
while (std::cin >> n)
{
printf("%.2f%%\n", 100.0 * d[n] / f[n]); //用100.0来把结果处理成double,保留两位小数
}
return 0;
}有理数运算
Rational Arithmetic (20)__牛客网
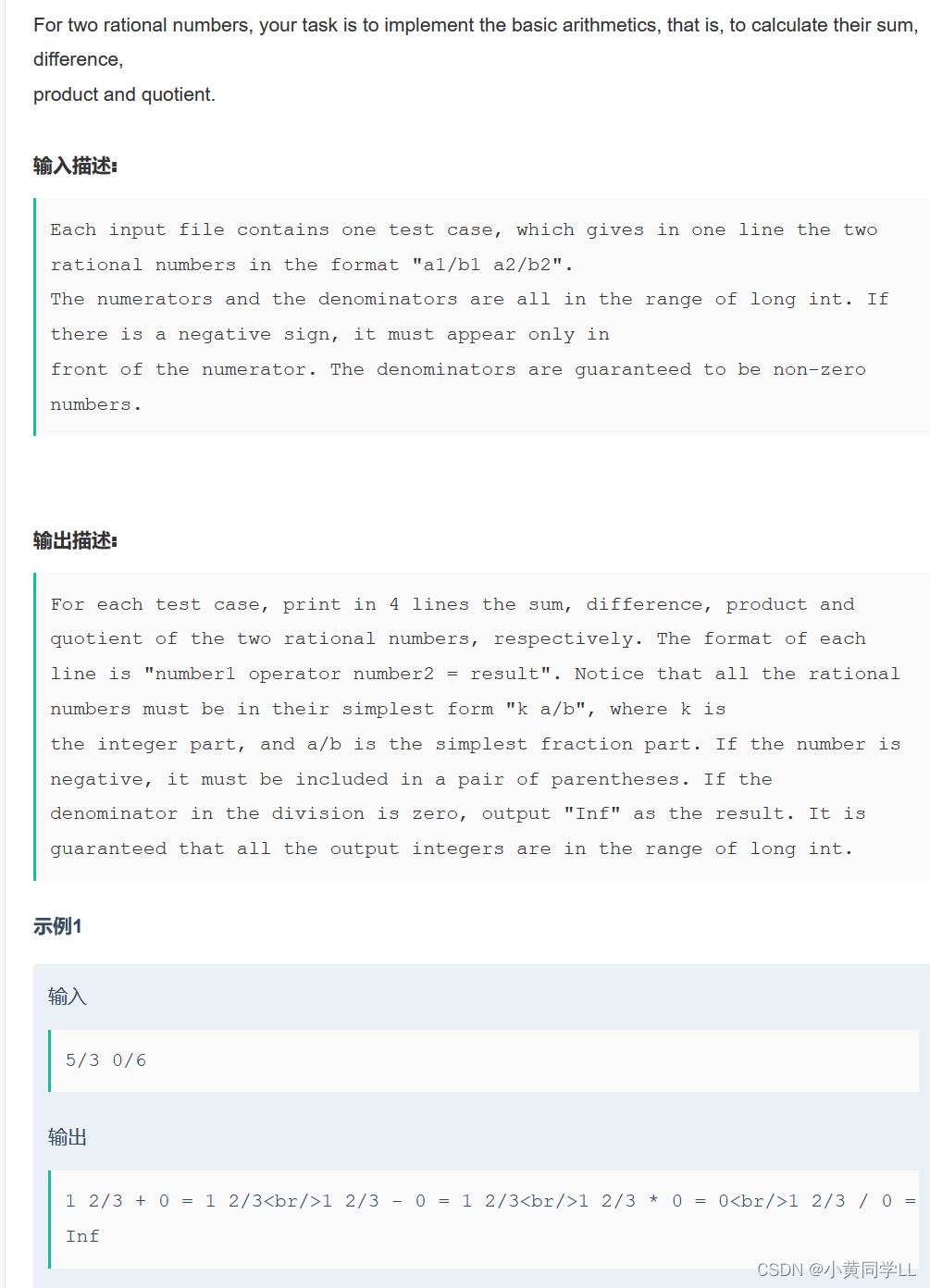
实现对两个有理数的基本运算,包括加、减、乘、除。
输入描述:
每个输入文件只包含一个测试用例,测试用例会给出一行数据,格式为
“a1/b1 a2/b2”分子分母的范围都在长整型的范围内,如果数字为负,则符号只会出现在分子的前面。分母一定是非零数。
输出描述:
针对每个测试用例,都输出四行,分别是这两个有理数的和、差、积和商,格式为
“
数
1
操作符 数
2 =
结果
”
。注意,所有的有理数都将遵循一个简单形式
“k a/b”
,其中
k
是整数部分,
a/b
是最简分数形式,如果该数为负数,则必
须用括号包起来。如果除法中的除数为
0
,则输出
“Inf”
。结果中所有的整数都在
long int
的范围内。
C++标准类写法:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int64;
class Rational
{
public:
Rational(int64 n, int64 d)
{
negetive = false;
isZero = false;
// 在输入时分母永远不可能为0,但是经过运算之后分母可能为0
if (0 == d)
{
isZero = true;
return;
}
// 分子小于0,表示为负数
if (n < 0)
{
negetive = !negetive;
}
// 在输入时分母一定不会小于0, 但是经过计算之后分母也可能会小于0
if (d < 0)
{
negetive = !negetive;
}
// 如果分数是假分数,必须要将其化简为真分数 比如:5 / 3----> 1 2/3
integer = n / d;
numerator = n - integer * d;
denominator = abs(d);
// 如果不是最简的分数,还需要将其化简为最简的分数: 10 / 15 ----> 2 / 3
// 只需给分子和分母分别除分子和分母最大公约数
if (numerator < -1 || numerator > 1)
{
int gcd = CalcGCD(abs(numerator), denominator);
if (gcd)
{
numerator /= gcd;
denominator /= gcd;
}
}
totalnumerator = integer * denominator + numerator;
}
Rational operator+(const Rational& r)const
{
int64 n = totalnumerator * r.denominator + r.totalnumerator * denominator;
int64 d = denominator * r.denominator;
return Rational(n, d);
}
Rational operator-(const Rational& r)const
{
int64 n = totalnumerator * r.denominator - r.totalnumerator * denominator;
int64 d = denominator * r.denominator;
return Rational(n, d);
}
Rational operator*(const Rational& r)const
{
int64 n = totalnumerator * r.totalnumerator;
int64 d = denominator * r.denominator;
return Rational(n, d);
}
Rational operator/(const Rational& r)const
{
int64 n = totalnumerator * r.denominator;
int64 d = denominator * r.totalnumerator;
return Rational(n, d);
}
private:
// 求最大公约数:辗转相除
int64 CalcGCD(int64 a, int64 b)
{
if (0 == b)
return a;
return CalcGCD(b, a % b);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Rational& r)
{
if (r.isZero)
{
_cout << "Inf";
return _cout;
}
if (0 == r.integer && 0 == r.numerator)
{
_cout << "0";
return _cout;
}
// 如果是负数,需要用()括起来
if (r.negetive)
{
_cout << "(-";
}
// 输出有理数:整数 + 分数
// 整数: 可能存在也可能不存在
if (r.integer)
{
_cout << abs(r.integer);
// 如果分数部分存在,整数和分数之间有一个空格
if (r.numerator)
{
_cout << " ";
}
}
// 分数: 可能存在也可能不存在
if (r.numerator)
{
_cout << abs(r.numerator) << "/" << r.denominator;
}
if (r.negetive)
{
_cout << ")";
}
return _cout;
}
private:
int64 numerator; // 分子
int64 denominator; // 分母
int64 integer; // 整数部分
bool negetive; // 负数
bool isZero; // 分母是否为0
int64 totalnumerator; // 参与运算的分子:原分子 + 整数部分
};
int main()
{
int64 n1, d1, n2, d2;
while (scanf("%lld/%lld %lld/%lld", &n1, &d1, &n2, &d2) != EOF)
{
Rational r1(n1, d1);
Rational r2(n2, d2);
cout << r1 << " + " << r2 << " = " << r1 + r2 << endl;
cout << r1 << " - " << r2 << " = " << r1 - r2 << endl;
cout << r1 << " * " << r2 << " = " << r1 * r2 << endl;
cout << r1 << " / " << r2 << " = " << r1 / r2 << endl;
}
return 0;
}C语言强行模拟:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a,ll b)
{
if(b==0) return a;
return gcd(b,a%b);
}
void totout(ll n,ll d)
{
if(d==0){
cout<<"Inf"<<endl;
return;
}
ll mod=gcd(n,d);
n/=mod;
d/=mod;
ll zheng=n/d;
ll fz=n-zheng*d;
ll fm=d;
if(fz<0||fm<0||zheng<0) cout<<"(";
if(n==0) cout<<0;
else if(zheng&&fz==0) printf("%lld",zheng);
else if (zheng) printf("%lld %lld/%lld",zheng,fz,abs(fm));
else if(fm<0) printf("-%lld/%lld",fz,abs(fm));
else printf("%lld/%lld",fz,fm);
if(fz<0||fm<0||zheng<0) cout<<")";
}
void add(ll n1,ll d1,ll n2,ll d2)
{
ll n=n1*d2+n2*d1;
ll d=d1*d2;
totout(n,d);
}
void sub(ll n1,ll d1,ll n2,ll d2)
{
ll n=n1*d2-n2*d1;
ll d=d1*d2;
totout(n,d);
}
void mul(ll n1,ll d1,ll n2,ll d2)
{
ll n=n1*n2;
ll d=d1*d2;
totout(n,d);
}
void div(ll n1,ll d1,ll n2,ll d2)
{
ll n=n1*d2;
ll d=d1*n2;
totout(n,d);
}
int main()
{
ll n1,d1,n2,d2;
scanf("%lld/%lld %lld/%lld",&n1,&d1,&n2,&d2);
totout(n1,d1);cout<<" + ";totout(n2,d2);cout<<" = ";add(n1,d1,n2,d2);
cout<<endl;
totout(n1,d1);cout<<" - ";totout(n2,d2);cout<<" = ";sub(n1,d1,n2,d2);
cout<<endl;
totout(n1,d1);cout<<" * ";totout(n2,d2);cout<<" = ";mul(n1,d1,n2,d2);
cout<<endl;
totout(n1,d1);cout<<" / ";totout(n2,d2);cout<<" = ";div(n1,d1,n2,d2);
return 0;
}