目录
一、配置MySQL数据库驱动包
二、JDBC常规操作
1、创建数据源
2、建立连接
3、操作数据库,执行sql语句
4、关闭资源
三、JDBC实现图书管理系统
1、建表
2、连接数据库
3、创建实体类
a、Book类
b、BookShelf类
c、User类
d、Administrator类
e、RegularUser类
4、实现操作类
a、Operate接口
b、 添加图书方法
c、删除图书
d、显示图书
e、查找图书
f、借阅图书
g、归还图书
h、退出系统
5、Main
6、效果演示
一、配置MySQL数据库驱动包
进入maven的中央仓库https://mvnrepository.com/在搜索框中输入mysql,找到与自己电脑上MySQL版本相关的jar包进行下载,如MySQL为5.x版本,那jar包也选择5.x版本:

点击对应版本后,点击jar进行下载:
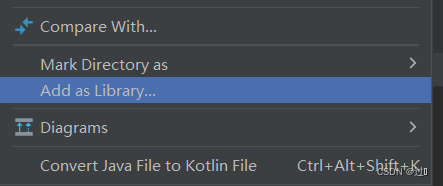
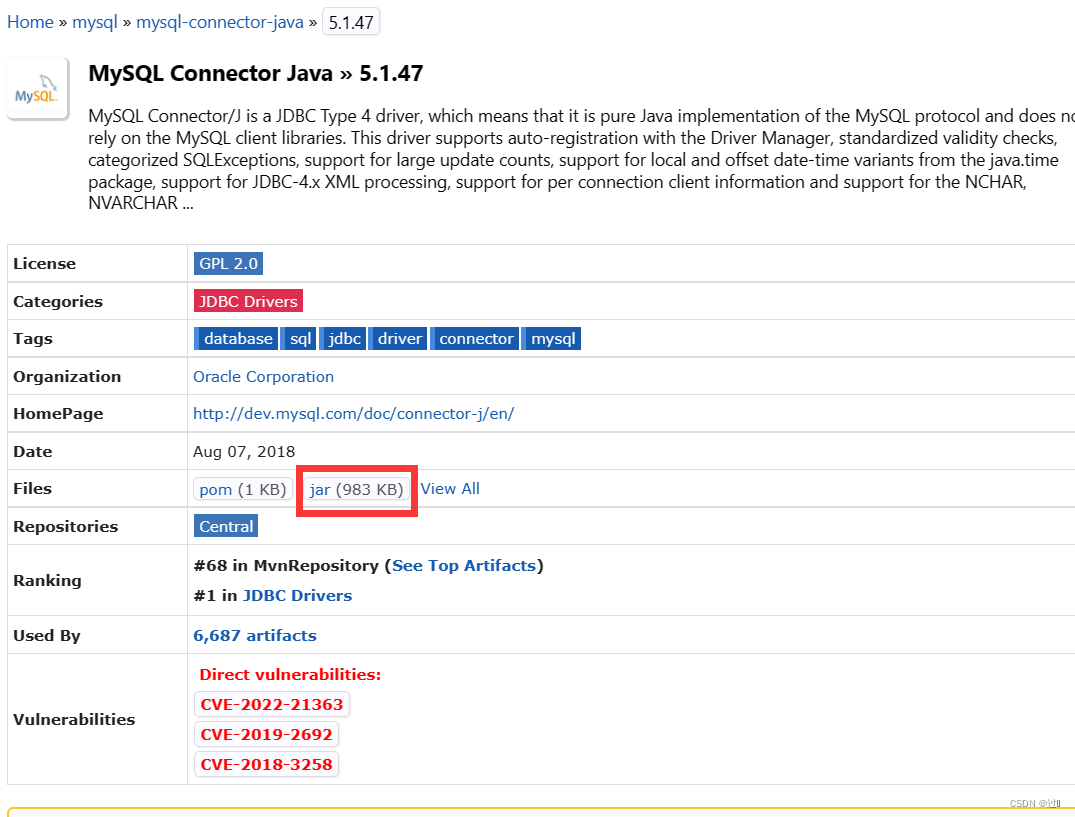 在idea中创建一个项目,并创建一个lib文件夹,将下载好的jar包放到文件夹lib下,然后双击lib选择Add as...完成配置。
在idea中创建一个项目,并创建一个lib文件夹,将下载好的jar包放到文件夹lib下,然后双击lib选择Add as...完成配置。
二、JDBC常规操作
1、创建数据源
DataSource dataSource=new MysqlDataSource();
//设置数据库所在地址
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
//设置数据库用户名
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root");
//设置数据库的登录密码
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("1789");url的格式为:jdbc:mysql://服务器地址:端口/数据库名?参数名=参数值
2、建立连接
Connection connection = (Connection) dataSource.getConnection();3、操作数据库,执行sql语句
以删除数据为例:
String sql="delete from book where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
statement.executeUpdate()在sql语句中有些数据是不确定的需要用户输入,就暂时用?替代,然后再使用statement.setxx()进行替换,最后对语句进行执行,对于插入、修改、删除操作利用 executeUpdate()执行,返回值为一个整数表示多少行受影响,而对于查询操作使用executeQuery()执行,返回的是一张表,需要使用ResultSet结果集接收,并利用其next()方法对得到的结果集进行遍历,例如:对于book表查找得到的内容进行输出:
String sql="select * from book";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while(resultSet.next()){
int id=resultSet.getInt("id");
String name=resultSet.getString("name");
String author=resultSet.getString("author");
Double price=resultSet.getDouble("price");
String theme=resultSet.getString("theme");
boolean isBorrowed=resultSet.getBoolean("statue");
Date borrowTime=resultSet.getDate("borrow_time");
Date returnTime=resultSet.getDate("return_time");
System.out.println("Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", theme='" + theme + '\'' +
", isBorrowed=" + isBorrowed +
", borrowTime=" + borrowTime +
", returnTime=" + returnTime +
'}');
}4、关闭资源
对于JDBC中资源使用完毕后要进行关闭,对于先使用的资源后关闭,对于后使用的资源先关闭,以上述的查找操作为例:
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();三、JDBC实现图书管理系统
之前在JavaSE实现了图书管理系统,但是每次运行结束后数据也随之丢失,也不符合实际应用,那么使用JDBC连接MySQL数据库就可以实现。
1、建表
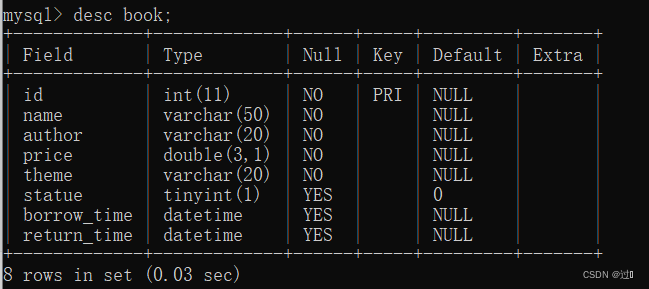
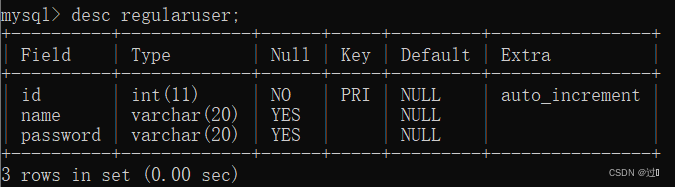
针对图书管理的需求,需要建立存放书的表、管理员表和普通用户表。
create table book(id int primary key,name varchar(50) not null,
price double(3,1) not null,theme varchar(20) not null,
statue boolean default false,borrow_time datetime,return_time datetime);create table administrator(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),password varchar(20));create table regularuser(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(20),password varchar(20));三个表的结构分别为:

2、连接数据库
创建DBUtil类,其中定义了一个静态方法返回数据库的连接,在之后的操作数据库时进行使用。
import com.mysql.jdbc.Connection;
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
//1.创建数据源
DataSource dataSource =new MysqlDataSource();
//设置数据库所在地址
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/library?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false");
//设置数据库用户名
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root");
//设置数据库的登录密码
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("gsy20021014");
//2.建立连接
Connection connection = (Connection) dataSource.getConnection();
return connection;
}
}3、创建实体类
实体可以分为两类:书和用户,书包含书类和书架类,用户包含管理员类和普通用户类
为什么还要定义类?直接操作表不就行
当时这个问题也是困惑了我很久,但是在写代码时就会发现整个项目之间没有联系,没有封装性,比如在后面登录时选择身份时如果没有类就很难完成,有了类使整个项目联系密切,逻辑性强。
a、Book类
表示书类,相对于se版本的图书系统,增加了借书时间和还书时间两个属性,并且书类和创建的book表的内容几乎一致。 定义了两个构造方法,一个包含所有的属性,另一个没有包含是否借出、借书时间和还书时间。
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Book {
private int id;//图书编号
private String name;//图书名称
private String author;//图书作者
private double price;//图书价格
private String theme;//图书主题
private boolean isBorrowed;//图书是否被借出
private Date borrowTime;//借阅时间
private Date returnTime;//归还时间
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Date getBorrowTime() {
return borrowTime;
}
public void setBorrowTime(Date borrowTime) {
this.borrowTime = borrowTime;
}
public Date getReturnTime() {
return returnTime;
}
public void setReturnTime(Date returnTime) {
this.returnTime = returnTime;
}
public Book(int id,String name, String author, double price, String theme) {
this.id=id;
this.name = name;
this.price=price;
this.author = author;
this.theme = theme;
this.isBorrowed = false;//默认未借出
}
public Book(int id, String name, String author, double price, String theme, boolean isBorrowed, Date borrowTime, Date returnTime) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.theme = theme;
this.isBorrowed = isBorrowed;
this.borrowTime = borrowTime;
this.returnTime = returnTime;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getTheme() {
return theme;
}
public void setTheme(String theme) {
this.theme = theme;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", theme='" + theme + '\'' +
", isBorrowed=" + isBorrowed +
", borrowTime=" + borrowTime +
", returnTime=" + returnTime +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Book book = (Book) o;
return isBorrowed == book.isBorrowed && Objects.equals(name, book.name) && Objects.equals(author, book.author) && Objects.equals(theme, book.theme);
}b、BookShelf类
仍然需要书架类,便于之后对book表的各种操作,但是构造方法发生了改变,之前的currentSize书架当前存放书本书目是固定的,并且默认是书架中存放了几本书,而现在需要统计Book表中存放了多少条数据,在此使用了全列查询,对得到的结果集遍历,将书存放到书架上,并且得到currentSize的大小。
import util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Date;
public class Bookshelf {
private Book[] books ;//书架类
private int size;//书架当前存放图书的数目
private int currentSize=0;
public Bookshelf(int size) {
books = new Book[size];
this.size=size;
}
public Bookshelf() throws SQLException {
books = new Book[10000];//默认能存放10000本书
this.size=10000;
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from book";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
int count=0;
while(resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
String author = resultSet.getString("author");
Double price = resultSet.getDouble("price");
String theme = resultSet.getString("theme");
boolean isBorrowed = resultSet.getBoolean("statue");
Date borrowTime = resultSet.getTime("borrow_time");
Date returnTime = resultSet.getTime("return_time");
books[count++] = new Book(id, name, author, price, theme, isBorrowed, borrowTime, returnTime);
}
this.currentSize=count;
}
public int getCurrentSize() {
return this.currentSize;
}
public void setCurrentSize(int currentSize) {
this.currentSize = currentSize;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
/**
* 获取指定位置的图书
* @param pos
* @return
*/
public Book getBook(int pos){
if(pos>=size){
System.out.println("已超出书架当前容量");
}else{
return books[pos];
}
return null;
}
public void addBook(Book book){
books[currentSize]=book;
}
/**
* 修改指定位置的图书
* @param pos
* @param book
* @return
*/
public void modify(int pos,Book book){
if(pos>=size){
System.out.println("已超出书架当前容量");
return ;
}else{
books[pos]=book;
}
}
}c、User类
User类是管理员和普通用户的父类,因为在登录时登录时选择不同身份来对数据库进行操作,除了表中属性,还需要定义一个接口数组用于存放各种对书架的相关操作方法,需要一个展示菜单的方法并返回选项,然后再定义一个doWork()方法是依据选项来操作数据库。还需要定义一个身份验证的方法。
import book.Bookshelf;
import operate.Operate;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public abstract class User {
public int id;//用户编号
public String name;//用户姓名
public String password;//用户密码
public Operate[] operates;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public User( String name, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
public User() {
}
public abstract int menu();
public void doWork(int option, Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
this.operates[option].work(books);
}
public abstract boolean authentication(String name, String pwd)throws SQLException;
}d、Administrator类
管理员的主要功能是对图书进行增加、删除、查看以及查找,管理员类继承User类,需要对父类定义的接口数组完善将自己特有的方法进行填充。对于重写身份验证方法,使用select name,password from administrator ,遍历结果集得到姓名和密码,若有对应的密码和密码则登录成功,否则登录失败。
import operate.*;
import util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Administrator extends User{
public Administrator(){
}
public Administrator(String name, String password) {
super(name,password);
this.operates=new Operate[]{
new ExitOpe(),
new AddBook(),
new DelBook(),
new DisplayBook(),
new FindBook()
};
}
@Override
public int menu() {
System.out.println("*******************************************");
System.out.println(" 1.添加图书 2.删除图书 ");
System.out.println(" 3.显示图书 4.查找图书 ");
System.out.println(" 0.退出系统 ");
System.out.println("*******************************************");
System.out.println("请输入您的操作:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = sc.nextInt();
return option;
}
@Override
public boolean authentication(String name,String pwd) throws SQLException {
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select name,password from administrator where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
ResultSet resultSet=statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
String na=resultSet.getString("name");
String pw=resultSet.getString("password");
if(pw.equals(pwd)&&na.equals(name)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}e、RegularUser类
普通用户类同样继承User类,内部实现与管理员类相似。
import operate.*;
import util.DBUtil;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RegularUser extends User{
public RegularUser(){
}
public RegularUser(String name, String password) {
super(name,password);
this.operates=new Operate[]{
new ExitOpe(),
new BorrowBook(),
new ReturnBook(),
new DisplayBook(),
new FindBook(),
};
}
@Override
public int menu() {
System.out.println("*******************************************");
System.out.println(" 1.借阅图书 2.归还图书 ");
System.out.println(" 3.显示图书 4.查找图书 ");
System.out.println(" 0.退出系统 ");
System.out.println("*******************************************");
System.out.println("请输入您的操作:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = sc.nextInt();
return option;
}
@Override
public boolean authentication(String name, String pwd) throws SQLException {
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select name,password from regularuser where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
ResultSet resultSet=statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
String na=resultSet.getString("name");
String pw=resultSet.getString("password");
if(pw.equals(pwd)&&na.equals(name)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
4、实现操作类
a、Operate接口
创建一个接口,内部定义一个抽象的work方法,然后操作类都实现这个接口,并重写work方法。
import book.Bookshelf;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public interface Operate {
void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException;
}b、 添加图书方法
由于书架当时的初始容量为10000,但还是进行了判断,如果容量已满则无法添加,再进一步输入要添加图书的信息,利用图书类中的equals()方法对添加的图书与已经存放的图书,若有重复则无法添加,否则使用insert插入语句进行添加,完成对数据库的更新,并且要将该图书添加到书架类的数组中。
public class AddBook implements Operate{
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
if(books.getCurrentSize()>= books.getSize()){
System.out.println("书架已满,无法继续添加");
}else{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入图书信息:");
System.out.println("图书编号:");
int id=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("图书名称:");
String name=sc.next();
System.out.println("图书作者:");
String author = sc.next();
System.out.println("图书价格:");
int price = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("图书主题:");
sc.nextLine();
String theme= sc.nextLine();
Book book = new Book(id,name, author, price, theme);
for (int i = 0; i < books.getCurrentSize(); i++) {
if(book.equals(books.getBook(i))){
System.out.println("该图书已经存在,无法继续添加!");
return;
}
}
String sql="insert into book(id,name,author,price,theme) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
statement.setString(2,name);
statement.setString(3,author);
statement.setDouble(4,price);
statement.setString(5,theme);
books.addBook(book);
books.setCurrentSize(books.getCurrentSize()+1);
int ret=statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret>0){
System.out.println("添加成功!");
}
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
}c、删除图书
输入要删除的图书名称,利用书架类的数组遍历,此处不使用select语句进行查找是后面对书架进行删除时需要得到图书在书架的位置,找到后使用delete语句删除图书,然后再使用循环覆盖删除书架中的该图书。
public class DelBook implements Operate{
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("请输入要删除的图书名称");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=sc.nextLine();
int pos=-1;
for (int i = 0; i < books.getCurrentSize(); i++) {
if(name.equals(books.getBook(i).getName())){
pos=i;
break;
}
}
if(pos==-1){
System.out.println("未找到您要删除的图书");
}else{
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="delete from book where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
int ret=statement.executeUpdate();
if(ret>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
for(int i= pos+1;i<books.getCurrentSize();i++){
Book book=books.getBook(i);
books.modify(i-1,book);
}
books.modify(books.getCurrentSize(),null);
books.setCurrentSize(books.getCurrentSize()-1);
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
}
d、显示图书
显示所有的图书信息,此处使用select语句对book表进行全列查询,此处也可以遍历书架得到所有图书的信息。
public class DisplayBook implements Operate{
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from book";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
System.out.println("====================================================================================================================");
while(resultSet.next()){
int id=resultSet.getInt("id");
String name=resultSet.getString("name");
String author=resultSet.getString("author");
Double price=resultSet.getDouble("price");
String theme=resultSet.getString("theme");
boolean isBorrowed=resultSet.getBoolean("statue");
Date borrowTime=resultSet.getDate("borrow_time");
Date returnTime=resultSet.getDate("return_time");
System.out.println("Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", theme='" + theme + '\'' +
", isBorrowed=" + (isBorrowed?"已借出":"未借出") +
", borrowTime=" + borrowTime +
", returnTime=" + returnTime +
'}');
}
System.out.println("====================================================================================================================");
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
e、查找图书
此处使用的是select语句对图书名称进行精确查询,也使用循环遍历书架更为方便。
public class FindBook implements Operate{
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("请输入要查找的图书名称");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
int pos=-1;
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql="select * from book where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,str);
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet==null){
System.out.println("未找到您要找的书籍");
return;
}
System.out.println("====================================================================================================================");
while(resultSet.next()){
int id=resultSet.getInt("id");
String name=resultSet.getString("name");
String author=resultSet.getString("author");
Double price=resultSet.getDouble("price");
String theme=resultSet.getString("theme");
boolean isBorrowed=resultSet.getBoolean("statue");
Date borrowTime=resultSet.getTime("borrow_time");
Date returnTime=resultSet.getTime("return_time");
System.out.println("Book{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", theme='" + theme + '\'' +
", isBorrowed=" + (isBorrowed?"已借出":"未借出") +
", borrowTime=" + borrowTime +
", returnTime=" + returnTime +
'}');
}
System.out.println("====================================================================================================================");
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
f、借阅图书
在借阅图书时,首先对输入的图书进行查找,若有才能进行借阅,使用update语句对图书的是否借出还有借阅时间进行修改,在创建图书类的日期是使用的是util包的Date类,但是在book表中的datetime是sql包的Date类,需要进行转换,对数据库中的book表完成更新后,同时也要修改书架上的图书信息。
public class BorrowBook implements Operate{
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("请输入要借阅的图书名称");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=sc.nextLine();
int pos=-1;
for (int i = 0; i < books.getCurrentSize(); i++) {
if(name.equals(books.getBook(i).getName())){
pos=i;
break;
}
}
if(pos==-1){
System.out.println("未找到您需要的图书");
}else{
if(books.getBook(pos).isBorrowed()==true){
System.out.println("该图书已经借出");
return;
}
Date date=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
java.sql.Date sd=new java.sql.Date(date.getTime());
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql1="update book set borrow_time=? where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement1=connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
statement1.setDate(1,sd);
statement1.setString(2,name);
String sql2="update book set statue=? where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement2=connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
Boolean flag=true;
statement2.setBoolean(1,flag);
statement2.setString(2,name);
statement1.executeUpdate();
statement1.close();
statement2.executeUpdate();
statement2.close();
connection.close();
books.getBook(pos).setBorrowed(true);
books.getBook(pos).setBorrowTime(date);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
}
}
}
g、归还图书
在归还图书时,也要对图书的借阅状态和归还时间进行修改,操作与借阅图书类似。
public class ReturnBook implements Operate {
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("请输入要归还的图书名称");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=sc.nextLine();
int pos=-1;
for (int i = 0; i < books.getCurrentSize(); i++) {
if(name.equals(books.getBook(i).getName())){
pos=i;
break;
}
}
if(pos==-1){
System.out.println("未找到您需要的图书");
}else{
Date date=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
java.sql.Date sd=new java.sql.Date(date.getTime());
Connection connection= DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql1="update book set return_time=? where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement1=connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
statement1.setDate(1,sd);
statement1.setString(2,name);
String sql2="update book set statue=? where name=?";
PreparedStatement statement2=connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
Boolean flag=false;
statement2.setBoolean(1,flag);
statement2.setString(2,name);
statement1.executeUpdate();
statement1.close();
statement2.executeUpdate();
statement2.close();
connection.close();
books.getBook(pos).setBorrowed(false);
books.getBook(pos).setReturnTime(date);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
}
}
}
h、退出系统
使用System.exit(0)方法退出系统,虽然该方法没有任何异常,但因为重写了Operate中的work方法,work方法抛出了sql异常,那么该方法也需要抛出异常。
public class ExitOpe implements Operate{
@Override
public void work(Bookshelf books) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("退出成功,欢迎下次使用!");
System.exit(0);
}
}5、Main
在测试类中需要实现登录函数,由于在登录时才知道用户身份,所以使用User类为返回值进行向上转型,在登录函数中首先选择身份,然后对身份进行验证,验证成功后,即登录成功。
public class Main {
public static User login() throws SQLException {
System.out.println("请选择登录身份:1)管理员 2)普通用户");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int option=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入姓名:");
String name=sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String pwd=sc.next();
if(option==1){
boolean flag=new Administrator().authentication(name,pwd);
if(flag){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
return new Administrator(name,pwd);
}else{
System.out.println("姓名或密码输入有误");
}
}else if(option==2){
boolean flag=new RegularUser().authentication(name,pwd);
if(flag){
System.out.println("登陆成功!");
return new RegularUser(name,pwd);
}else{
System.out.println("姓名或密码输入有误");
}
}else{
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Bookshelf books=new Bookshelf();
User user=login();
while(true){
int ret=user.menu();
user.doWork(ret,books);
}
}
}
6、效果演示
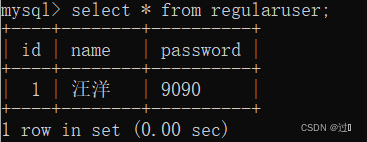
管理员和普通用户表如下所示:

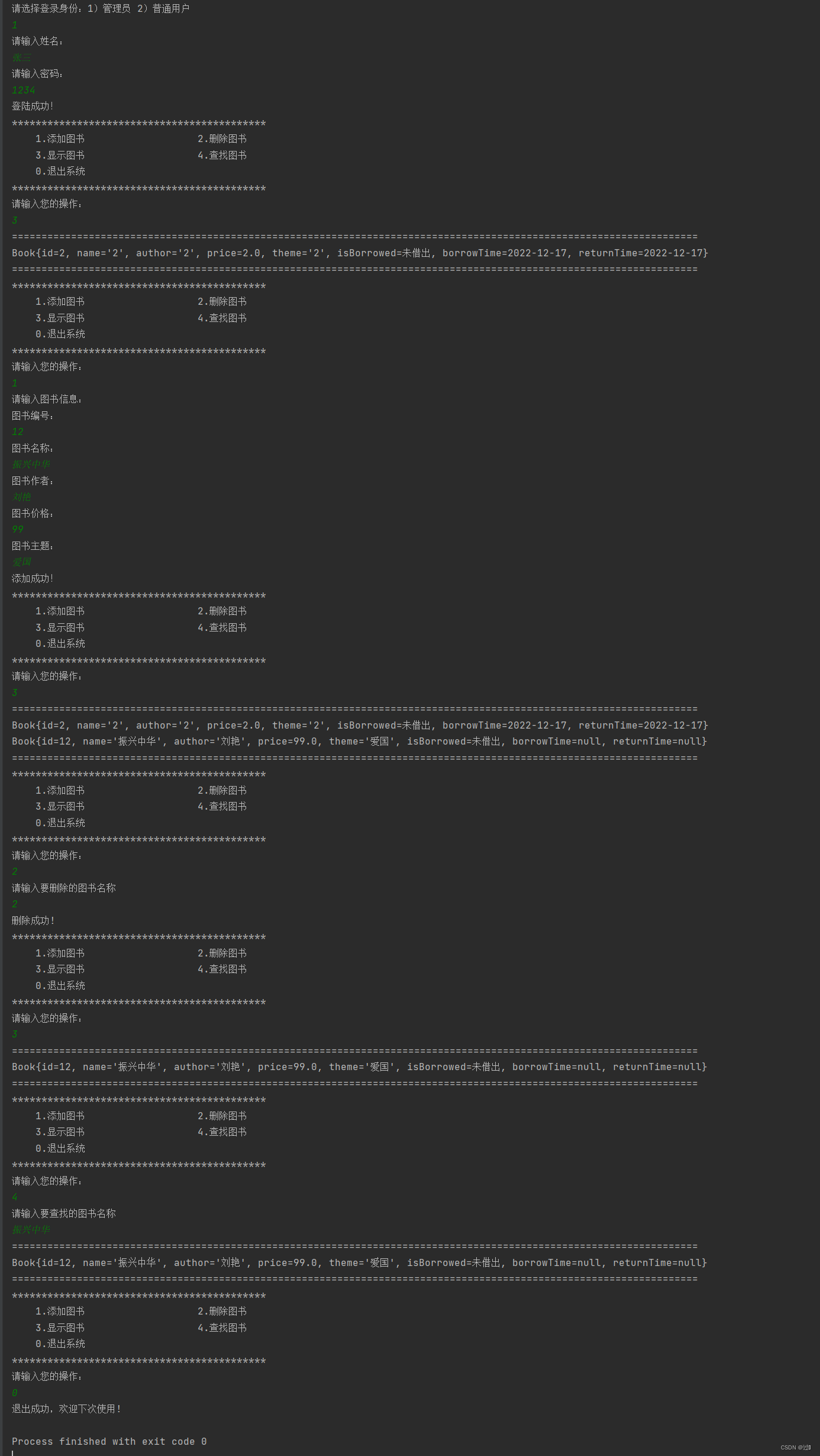
运行效果演示:
管理员:
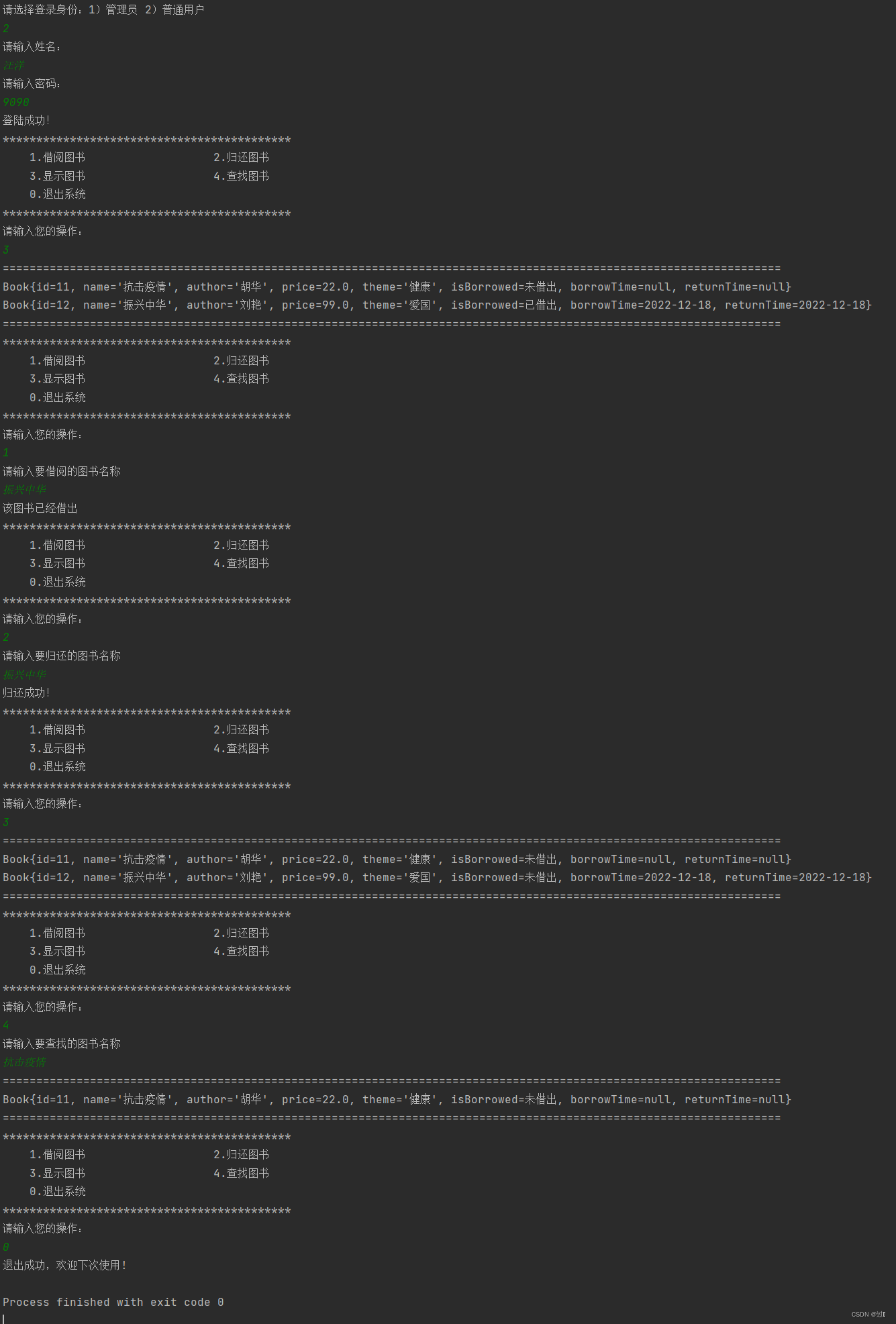
 普通用户:
普通用户:










![[激光原理与应用-61]:激光器 - 种子源 - 1064nm皮秒种子源参数解读](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/cd06f23bc955a04d3c7c8565f8cd5931.jpeg)
