文章目录
- 【 1. 数据类型分类 】
- 1.1 字符型
- 1.2 整型
- 1.3 浮点型
- 1.4 布尔型
- 1.5 无类型
- 1.6 枚举类型
- 1.7 其他类型
- 1.8 类型占用大小输出
- 【 2. typedef 类型声明 】
- 使用编程语言进行编程时,我们需要用到各种变量来存储各种信息。变量保留的是它所存储的值的内存位置,这意味着,当创建一个变量时,就会在内存中保留一些空间。
- 我们可能需要存储各种数据类型(比如字符型、宽字符型、整型、浮点型、双浮点型、布尔型等)的信息,操作系统会根据变量的数据类型,来分配内存和决定在保留内存中存储什么。
【 1. 数据类型分类 】
- 变量的大小会根据编译器和所使用的电脑而有所不同。
- C++ 允许在 char、int 和 double 数据类型前放置 大小修饰符。修饰符用于改变基本类型的含义,所以它更能满足各种情境的需求。修饰符 signed、unsigned、long 和 short 可应用于整型,signed 和 unsigned 可应用于字符型,long 可应用于双精度型。
- 修饰符 signed 和 unsigned 也可以作为 long 或 short 修饰符的前缀。例如:unsigned long int。
- C++默认是 有符号的 。例如 signed int a; 和 int a; 是一样的。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
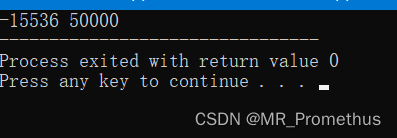
short int i;
short unsigned int j;
j = 50000;
i = j;
cout << i << " " << j;
return 0;
}
1.1 字符型
- 字符类型,用于存储 ASCII 字符。
- wchar_t 的来源:typedef short int wchar_t;故wchar_t 实际上的空间是和 short int 一样。
| 名称 | 关键字 | 位 | 范围 |
|---|
| 字符型 | char | 1 个字节 | -128 ~ 127 或者 0 ~ 255 |
| 无符号字符型 | unsigned char | 1 个字节 | 0 ~ 255 |
| 有符号字符型 | signed char | int | -128 ~ 127 |
| 宽字符型 | wchar_t | 2 或 4 个字节 | 1 个宽字符 |
1.2 整型
| 名称 | 关键字 | 位 | 范围 |
|---|
| 整型 | int | 4 个字节 | -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 |
| 有符号整型 | signed int | 4 个字节 | -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 |
| 无符号整型 | unsigned int | 4 个字节 | 0 ~ 4294967295 |
| 短整型 | short int | 2 个字节 | -32768 ~ 32767 |
| 有符号短整型 | signed short int | 2 个字节 | -32768 ~ 32767 |
| 无符号短整型 | unsigned short int | 2 个字节 | 0 ~ 65,535 |
| 长整型 | long int | 8 个字节 | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| 有符号长整型 | signed long int | 8 个字节 | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| 无符号长整型 | unsigned long int | 8 个字节 | 0 ~ 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
1.3 浮点型
- 单精度浮点型:用于存储单精度浮点数。单精度是这样的格式,1 位符号,8 位指数,23 位小数,通常占用4个字节。
- 双精度浮点型:用于存储双精度浮点数。双精度是 1 位符号,11 位指数,52 位小数,通常占用 8 个字节。
| 名称 | 关键字 | 位 | 范围 |
|---|
| 单精度浮点型 | float | 4 个字节 | +/- 3.4e +/- 38 (~7 个数字) |
| 双精度浮点型 | double | 8 个字节 | +/- 1.7e +/- 308 (~15 个数字) |
| 多精度浮点型 | long double | 16 个字节 | +/- 1.7e +/- 308 (~15 个数字) |
1.4 布尔型
| 名称 | 关键字 | 位 | 范围 |
|---|
| 布尔型 | bool | 1个字节 | 存储值 true 或 false,即 1或 0 |
1.5 无类型
1.6 枚举类型
- 枚举类型(enumeration)是C++中的一种派生数据类型,它是由用户定义的若干枚举常量的集合。
- 如果一个变量只有几种可能的值,可以定义为枚举(enumeration)类型。所谓"枚举"是指将变量的值一 一列举出来,变量的值只能在列举出来的值的范围内。
- 创建枚举,需要使用关键字 enum。枚举类型的一般形式为:
enum 枚举名
{
标识符[=整型常数],
标识符[=整型常数],
...
标识符[=整型常数]
} 枚举变量;
- 如果枚举没有初始化, 即省掉"=整型常数"时, 则从第一个标识符开始。
enum color { red, green, blue } c;
c = blue;
- 默认情况下,第一个名称的值为 0,第二个名称的值为 1,第三个名称的值为 2,以此类推。但是,也可以给名称赋予一个特殊的值,只需要添加一个初始值即可。例如,在下面的枚举中,green 的值为 5,blue 的值为 6,因为 默认情况下,每个名称都会比它前面一个名称大 1,但 red 的值依然为 0。
enum color { red, green=5, blue };
1.7 其他类型
1.8 类型占用大小输出
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl;
cout << "bool: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(bool);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::max)();
cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<bool>::min)() << endl;
cout << "char: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(char);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::max)();
cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<char>::min)() << endl;
cout << "signed char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(signed char);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::max)();
cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<signed char>::min)() << endl;
cout << "unsigned char: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned char);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max)();
cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min)() << endl;
cout << "wchar_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(wchar_t);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::max)();
cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<wchar_t>::min)() << endl;
cout << "short: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(short);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::max)();
cout << "\t\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<short>::min)() << endl;
cout << "int: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(int);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<int>::min)() << endl;
cout << "unsigned: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned>::min)() << endl;
cout << "long: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long>::min)() << endl;
cout << "unsigned long: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(unsigned long);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<unsigned long>::min)() << endl;
cout << "double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(double);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<double>::min)() << endl;
cout << "long double: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(long double);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<long double>::min)() << endl;
cout << "float: \t\t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(float);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<float>::min)() << endl;
cout << "size_t: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(size_t);
cout << "\t最大值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::max)();
cout << "\t最小值:" << (numeric_limits<size_t>::min)() << endl;
cout << "string: \t" << "所占字节数:" << sizeof(string) << endl;
cout << "type: \t\t" << "************size**************"<< endl;
return 0;
}
【 2. typedef 类型声明 】
- 可以使用 typedef 为一个已有的类型取一个新的名字。
typedef int feet;
feet distance;