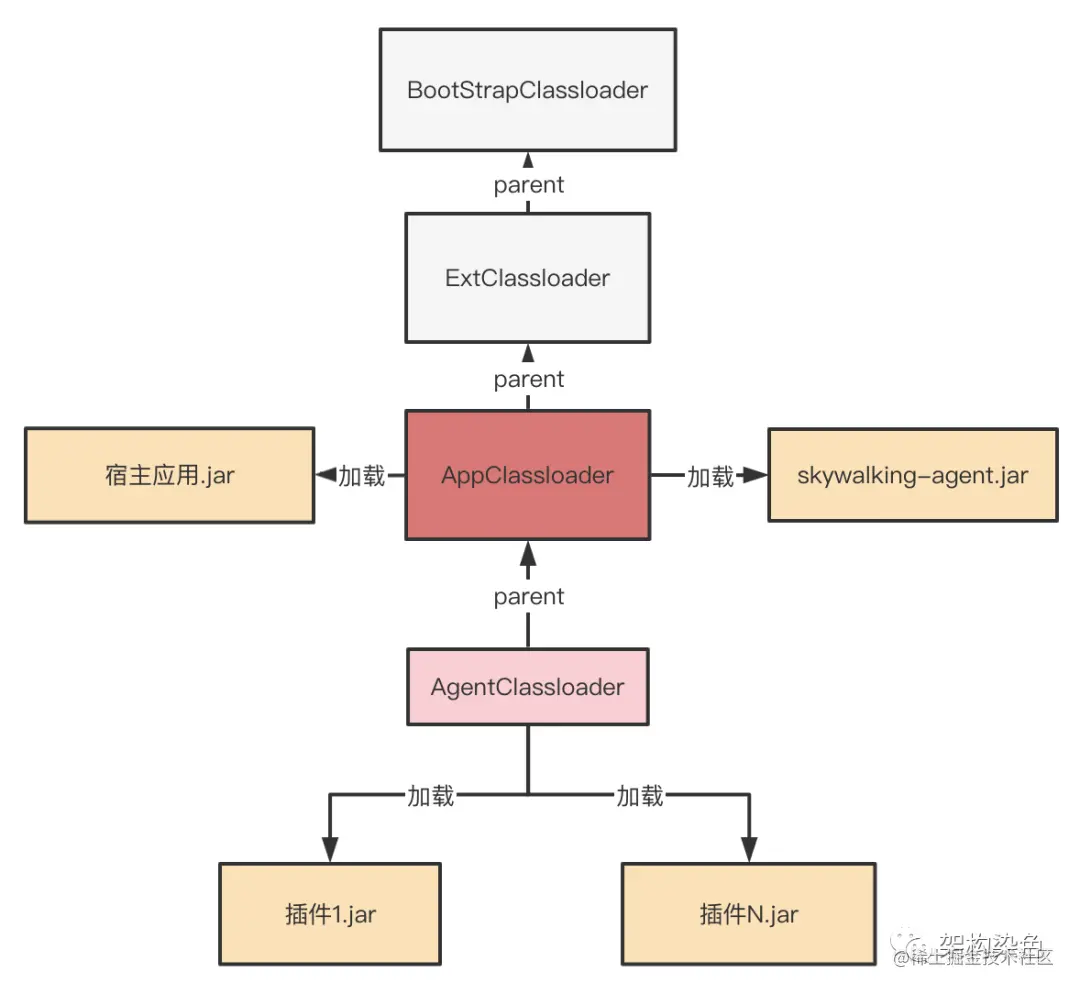
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:haystack = "sadbutsad", needle = "sad"
输出:0
解释:"sad" 在下标 0 和 6 处匹配。
第一个匹配项的下标是 0 ,所以返回 0 。
示例 2:
输入:haystack = "leetcode", needle = "leeto"
输出:-1
解释:"leeto" 没有在 "leetcode" 中出现,所以返回 -1 。
提示:
1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
haystack 和 needle 仅由小写英文字符组
方法一:暴力匹配
思路及算法
我们可以让字符串 与字符串
的所有长度为 mm 的子串均匹配一次。
为了减少不必要的匹配,我们每次匹配失败即立刻停止当前子串的匹配,对下一个子串继续匹配。如果当前子串匹配成功,我们返回当前子串的开始位置即可。如果所有子串都匹配失败,则返回 -1−1。
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
for (int i = 0; i + m <= n; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (haystack.charAt(i + j) != needle.charAt(j)) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度:,其中 nn 是字符串
的长度,
是字符串
的长度。最坏情况下我们需要将字符串
与字符串
的所有长度为
的子串均匹配一次。
空间复杂度:。我们只需要常数的空间保存若干变量。
方法二:算法
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
if (m == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] pi = new int[m];
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < m; i++) {
while (j > 0 && needle.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j)) {
j = pi[j - 1];
}
if (needle.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
pi[i] = j;
}
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (j > 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j)) {
j = pi[j - 1];
}
if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
if (j == m) {
return i - m + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度:,其中 nn 是字符串
的长度,mm 是字符串
的长度。我们至多需要遍历两字符串一次。
空间复杂度:,其中
是字符串
的长度。我们只需要保存字符串
的前缀函数。





![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django汽配管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/70fb56155b7d42febb9f80bfb0e2c510.png)