1.AVL树介绍
我们知道一般情况下二叉搜索树的查找效率是很高的,但是遇到极端情况下时间复杂度就会来到O(N)
那么为了消除这种极端情况的影响,我们就需要调节这个二叉树通过一些操作转成一颗二叉平衡树,调节完毕就会得到一颗AVL树。
2.AVL树模拟实现
(0)结点结构
static class Node{
public int val;//结点值
public Node left;//左孩子
public Node right;//右孩子
public Node parent;//父亲结点
public int bf;//平衡因子
}这里和一般的二叉树最大的差别就是多一个平衡因子bf,这个是方便我们调节二叉树高度的,因为作为一颗平衡树要保证所有结点的左右子树的高度差的绝对值要小于等于1。
那么接下来我们来一步一步构建一颗AVL树,那么一般情况下和二叉搜素树的构建没有区别,只不过当出现有的结点不满足红色字体的条件时,就需要进行旋转调节高度。
(1)右单旋
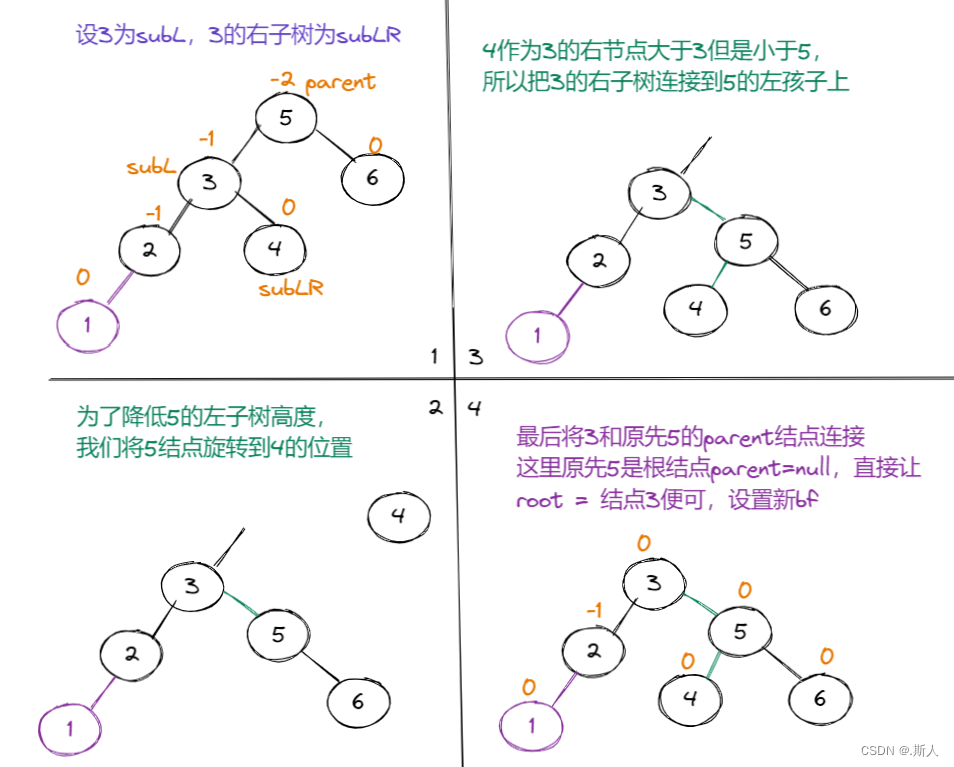
当我们按照5 6 3 4 2 1的顺序构建AVL树时,当插入1结点时,就会出现5结点的bf==-2,此时就要进行右单旋,以拔高5结点右树的高度。
这里可以发现,最后平衡因子发生改变的只有3和5结点,且平衡因子均变成了0。
上图转换为代码语言为:
当出现上图这种情况,即parent.bf == -2 且parent的左子树 parent.left.bf == -1时,我们进行右单旋
public static void rotateRight(Node parent){ //图1 Node subL=parent.left; Node subLR=subL.right;//这个值可能为null Node tmp=parent.parent;//记录parent的父亲结点-也可能为空 if parent == root 时 if(parent==root){ root=subL;//更新root } //图2 连接3 5结点 subL.right=parent; parent.parent=subL; //图3--连接4 5结点 parent.left=subLR; if(subLR!=null){ subLR.parent=parent; } //parent可能为某个结点的子节点,需要进行连接 subL.parent=tmp; if(tmp!=null){ if(tmp.left==parent){ tmp.left=subL; }else{ tmp.right=subL; } } //图4--更新bf subL.bf=0; parent.bf=0; }
(2)左单旋
左单旋和右单旋十分甚至九分相似
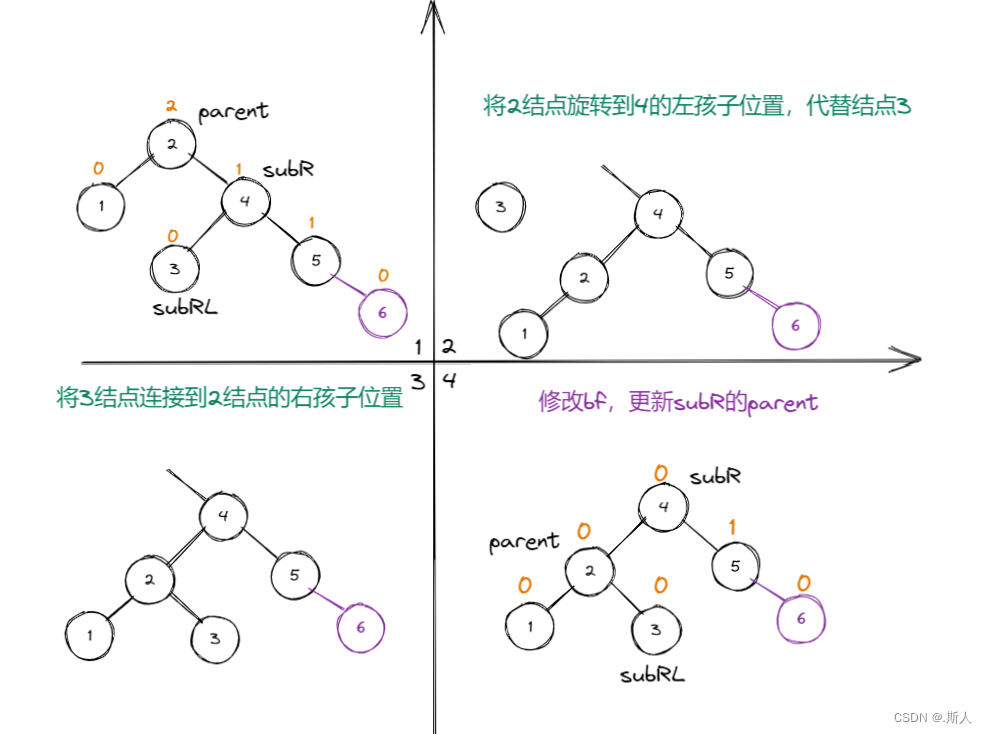
当我们按 2 1 4 3 5 6 的顺序插入时,当插入到6结点时,会出现2结点的平衡因子 == 2
这时候就要进行左单旋:
这里可以发现,最后平衡因子发生改变的只有2和4结点,且平衡因子也均变成了0。
上图转换为代码语言为:
当出现上图这种情况,即parent.bf == 2 且parent的左子树 parent.left.bf == 1时,我们进行左单旋:
public static void rotateLeft(Node parent){ //图1 Node subR=parent.right; Node subRL=subR.left;//这个值可能为null Node tmp=parent.parent;//记录parent的父亲结点-也可能为空 if parent == root 时 if(parent==root){ root=subR;//更新root } //图2 连接2 4结点 subR.left=parent; parent.parent=subR; //图3--连接2 3结点 parent.right=subRL; if(subRL!=null){ subRL.parent=parent; } //parent可能为某个结点的子节点,需要进行连接 subR.parent=tmp; if(tmp!=null){ if(tmp.left==parent){ tmp.left=subR; }else{ tmp.right=subR; } } //图4--更新bf subR.bf=0; parent.bf=0; }
(3)右左双旋
有的时候,当插入出现问题是不是一次简单的左/右单旋就能解决问题,这时候就涉及到双旋。
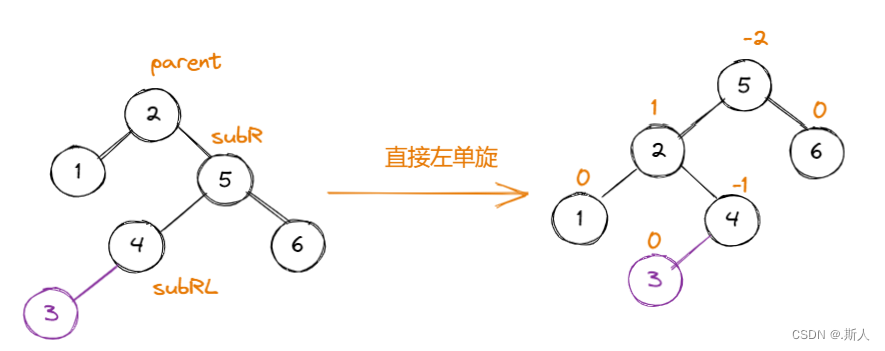
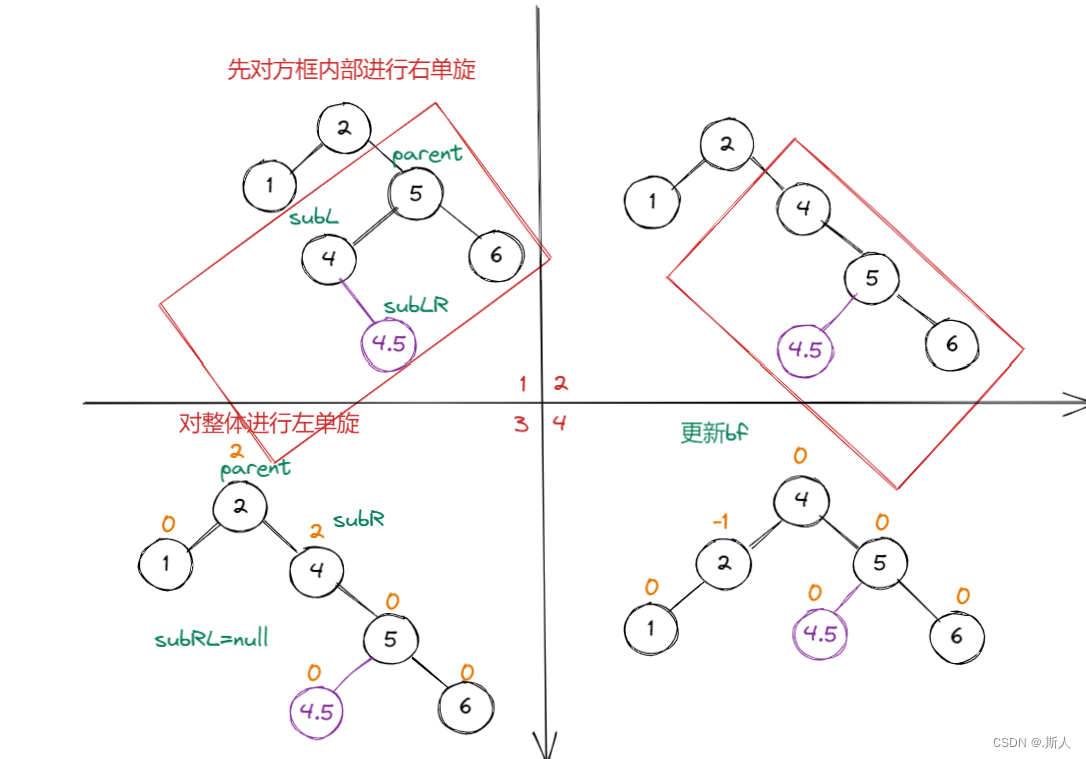
例如:按 2 1 5 4 6 3进行插入时,当插入3结点时,我们会得到这样的图
此时我们直接左单旋会得到:
可以发现这样调节是没有用的,所以需要采用右左双旋的办法,先对subR这颗子树进行右单旋,再对整体进行左单旋
那么这里平衡因子的更新并不是固定的,是需要分情况的:
现在插入的是3,bf的更新为 parent.bf=0,subR.bf=0
如果插入的是4.5 bf的更新为 parent.bf=-1,subR.bf=0
由此我们可以发现parent.bf值的决定性因素为:新插入结点的父节点的平衡因子大小
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
下图中:
如果subRL.bf == -1,则 旋转完后,subRL.bf=0;subR.bf=1;parent.bf=0;
如果subRL.bf == 1,则 旋转完后,subRL.bf=0;subR.bf=0;parent.bf=-1;
当出现上图这种情况,即parent.bf == 2 且parent的左子树 parent.left.bf == -1时,我们进行右左单旋。
右左双旋代码实现:
public static void rotateRL(Node parent){ Node subR = parent.right; Node subRL = subR.left; int bf= subR.bf; //先对右子树进行右单旋 rotateRight(parent.right); //再对整体进行左单选 rotateLeft(parent); //更新bf if(bf==1){ parent.bf=-1; subR.bf=0; }else if(bf==-1){ parent.bf=0; subR.bf=1; } subRL.bf=0; }
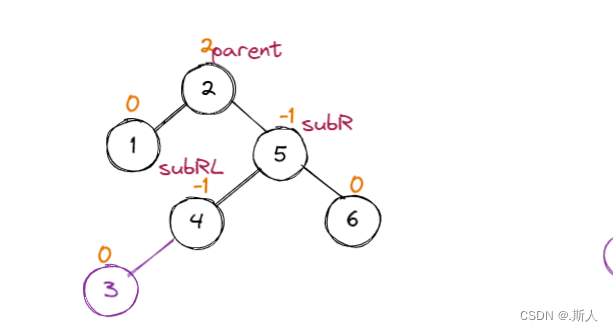
(4)左右双旋
做法与右左双旋一致,但也要分情况更新平衡因子
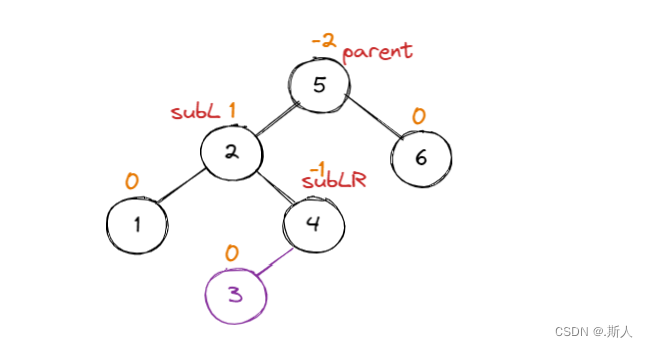
按5 6 2 1 4 3的顺序,插入3结点的时候,不能直接整体右旋,需要先局部左旋再整体右旋。
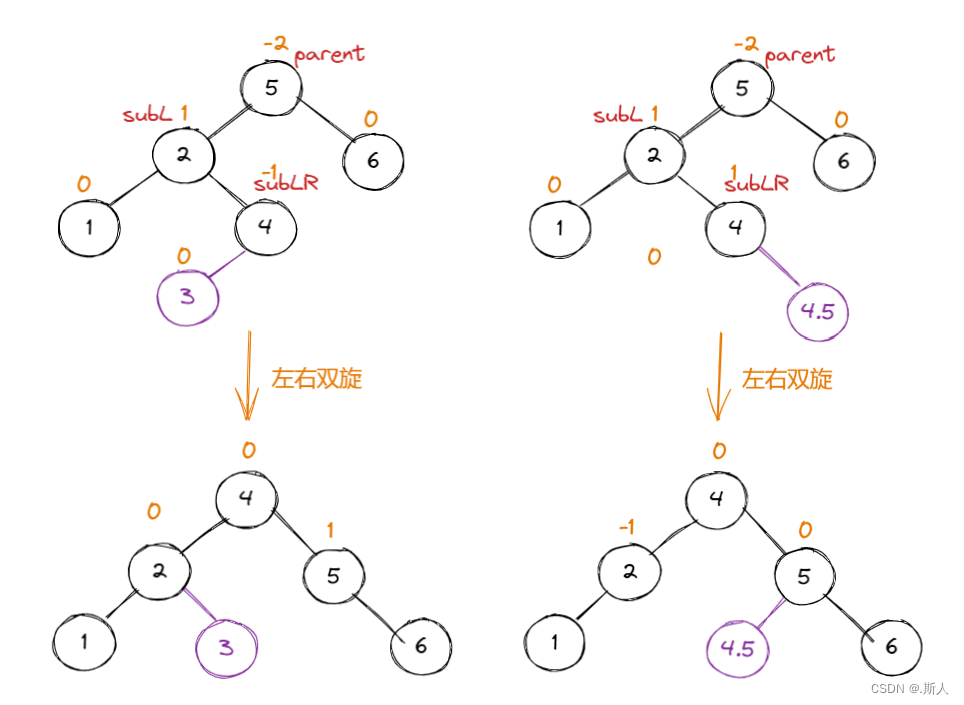
根据subLR的bf不同,我们最后的bf调节也需要分情况讨论。
在这里我直接给出结论:
subLR.bf == -1;旋转后,subL.bf = 0;subLR.bf=0;parent.bf=1;
subLR.bf == 1;旋转后,subL.bf = -1;subLR.bf=0;parent.bf=0;
代码如下:
public static void rotateLR(Node parent){ Node subL=parent.left; Node subLR=subL.right; int bf= subLR.bf; //先对左子树进行左单旋 rotateLeft(parent.right); //再对整体进行右单旋 rotateRight(parent); //更新bf if(bf==1){ parent.bf=0; subL.bf=-1; }else if(bf==-1){ parent.bf=1; subL.bf=0; } subLR.bf=0; }
插入函数
public static void insertNode(int val){ Node node=new Node(val);//创建新结点 if(root==null){ root=node; }else{ //先按照二叉搜索树的方式插入 Node cur=root; Node prv=cur.parent; while(cur!=null){ prv=cur; if(cur.val>node.val){ cur=cur.left; if(cur==null){ prv.left=node; } }else if(cur.val< node.val){ cur=cur.right; if(cur==null){ prv.right=node; } }else{ return;//相等不插入树中 } } //设置新结点的父节点 node.parent=prv; //更新所有的父节点bf平衡因子 Node parent=node.parent; cur = node; while(parent!=null){ if(cur==parent.left){ parent.bf-=1; }else{ parent.bf+=1; } //检查调节完的bf是否正确 if(parent.bf==2){ if(cur.bf==1){ rotateLeft(parent); }else if(cur.bf==-1){ rotateRL(parent); } break;//旋转完成之后,以parent为根的树已经和插入之前的高度相同, //不会再对上层树的平衡性造成影响,毕竟parent.bf是0 }else if(parent.bf==-2){ if(cur.bf==-1){ rotateRight(parent); }else{ rotateLR(parent); } break;//旋转完成之后,以parent为根的树已经和插入之前的高度相同, //不会再对上层树的平衡性造成影响 }else if(parent.bf==0){ //bf==0 代表平衡了,不用向上调节了 break; }else{ cur=parent; parent=parent.parent; } } } }
测试建立的AVL树是否正确(两个方面)
1.检查是否是二叉搜索树
通过中序遍历的方式来判断--判断得到的数组是不是有序的
代码如下:
//判断是不是二叉搜索树 private static List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(); private static void isSearch(Node root){ //中序遍历判断是否有序 inorder(root); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i)+" "); } System.out.println(); } private static void inorder(Node root){ if(root==null)return; inorder(root.left); list.add(root.val); inorder(root.right); }
2.检查是否是二叉平衡树
通过判断所有结点的左右子树高度之差来判断
代码如下:
//判断是不是二叉平衡树 public static int height(Node root){ if(root==null)return 0; int leftLen=height(root.left); int rightLen=height(root.right); return leftLen>rightLen?leftLen+1:rightLen+1; } private static boolean isBalance(Node root){ if(root==null)return true; int leftLen=height(root.left); int rightLen=height(root.right); //同时判断平衡因子是否正确 if(rightLen-leftLen!=root.bf){ System.out.println("这个结点"+root.val+"平衡因子异常"); return false; } return Math.abs(leftLen-rightLen)<=1&& isBalance(root.left)&&isBalance(root.right); }
检测
结果:
public static boolean isAVL(Node root){ isSearch(root); return isBalance(root); }测试用例:
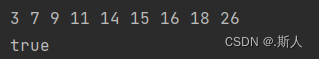
1:- 常规场景1
{16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15}
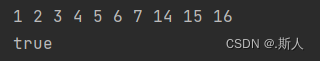
2.- 特殊场景2
{4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14}
AVL树的适用场景
不难发现,需要构造一个AVL树如果输入极端的话,需要进行大量的旋转操作,这无疑是很消耗时间的,由此可以看出AVL树不适合大量插入和删除,适合的是场景应该满足插入少删除少。