《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》线性表-数组描述
5表示在 数据结构算法与应用C++语言描述 书中所在章节。
本文包含了《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》第五章主要练习题答案,给出了线性表数组描述完整测试代码。
5.1 数据对象
5.1.1 定义
数据对象(data object)是一组实例或值。
digit={0, 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8, 9}
如digit是数据对象,0,1,…,9是digit的实例。
5.1.2 特点
- 数据对象的一个实例,要么是一个不可再分的“原子”,要么是由另一个数据对象的实例作为成员复合而成。
letter={A,B,C,...,Z, a, b,c,...z}
string={a,b,...,aa,ab,ac,...}
如数据对象string是由所有可能的串实例组成的集合。每个实例都由字符组成。例如,good,a trip to Hawaii,going down hill 和 abcabcdabcde 都是串实例。第一个串由4个元素g、o、o和d顺序组成,每个元素都是数据对象letter的实例。
- 数据对象的实例以及构成实例的元素通常都有某种相关性。
在串good中,g是第一字母,o是第二和第三个字母,而d是最后一个字母。
- 任何一个数据对象通常都有一组相关的操作或函数。
这些函数可以把对象的某个实例转化成该对象的另外一个实例,或转化成另一个数据对象的实例,或者同时进行上述两种转化。函数也可以不用转化而创建一个新的实例。例如,把两个自然数相加的函数创建了一个新的自然数,而两个加数并没有发生转化。
5.1.3 数据结构
数据结构(data structure)是一个数据对象,同时这个对象的实例以及构成实例的元素都存在着联系,而且这些联系由相关的函数来规定。
研究数据结构,关心的是数据对象(实际上是实例)的描述以及相关函数的具体实现。
数据对象描述得好,函数的实现就会高效。
最常用的数据对象以及操作都已经在C++中作为基本数据类型而实现,如整数对象(int)、布尔对象(bool)等。其他数据对象均可以用基本数据类型以及由C++的类、数组和指针所提供的组合功能来描述。本书研究线性表、栈、队列和优先级队列。
5.2 线性表数据结构
5.2.1 定义
线性表(linear list)也称有序表(ordered list),它的每一个实例都是元素的一个有序集合。每一个实例的形式为( e 0 e_0 e0, e 1 e_1 e1,…, e n − 1 e_{n-1} en−1),其中n是有穷自然数, e i e_i ei是线性表的元素,i是元素 e i e_i ei的索引,n是线性表的长度或大小。元素可以被看做原子,它们本身的结构与线性表的结构无关。当n=0时,线性表为空;当n>0时, e 0 e_0 e0是线性表的第0个元素或首元素, e n − 1 e_{n-1} en−1是线性表的最后一个元素。可以认为 e 0 e_{0} e0先于 e 1 e_{1} e1, e 1 e_{1} e1先于 e 2 e_{2} e2,等等。除了这种先后关系之外,线性表不再有其他关系。
5.2.2 举例
- 1)一个班级的学生按姓名的字母顺序排列的列表;
- 2)按非递减次序排列的考试分数表;
- 3)按字母顺序排列的会议列表;
- 4)奥林匹克男子篮球比赛的金牌获得者按年代次序排列的列表。
5.2.3 线性表的抽象数据类型
抽象数据类型(abstract data type,ADT),既能说明数据结构的实例,也说明对它的操作。抽象数据类型的说明独立于任何程序语言的描述。所有对抽象数据类型的语言描述必须满足抽象数据类型的说明,抽象数据类型的说明保证了程序语言描述的有效性。另外,所有满足抽象数据类型说明的语言描述,都可以在应用中替换使用。
抽象数据类型linearList
{
实例
有限个元素的有序集合
操作
empty():若表空,则返回true,否则返回false
size():返回线性表的大小(表的元素个数)
get(index):返回线性表中索引为index的元素
indexOf(x):返回线性表中第一次出现的x的索引。若x不存在,则返回-1
erase(index):删除索引为index的元素,索引大于index的元素其索引减1
insert(index,x):把x插人线性表中索引为index的位置上,索引大于等于index的元素其索引加1
output():从左到右输出表元素
}
5.2.4 抽象类linearList
抽象类
一个抽象类包含着没有实现代码的成员函数。这样的成员函数称为纯虚函数(pure virtual function)。纯虚函数用数字0作为初始值来说明,形式如下:
virtual int myPurevirtualFunction(int x)=0;
抽象数据类型不依赖程序语言,C++抽象类依赖程序语言。可以建立抽象类的对象指针。
抽象类的派生类,只有实现了基类的所有纯虚函数才是具体类,否则依然是抽象类而不能实例化。
具体类
具体类是没有纯虚函数的类。只有具体类才可以实例化。也就是说,我们只能对具体类建立实例或对象。
linearList抽象类定义
将抽象类的析构函数定义为虚函数,目的是,当一个线性表的实例离开作用域时需要调用的缺省析构函数时引用对象中数据类型的析构函数。
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 线性表虚类
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef __LINEARLIST_H_
#define __LINEARLIST_H_
#include<iostream>
using std::ostream;
template <class T>
class linearList
{
public:
virtual ~linearList() {};
virtual bool empty() const = 0;//返回true 当且仅当线性表为空
virtual int size() const = 0;//返回线性表的元素个数
virtual T& get(int theIndex) const = 0;//返回索引为theIndex的元素
virtual int indexOf(const T& theElement) const = 0;//返回元素theElement第一次出现时的索引
virtual void erase(int theIndex) = 0;//删除索引为theIndex的元素
virtual void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) = 0;//把元素theElement插入线性表中索引为theIndex的位置上
virtual void output(ostream& out) const = 0;//把线性表插入输入流out
};
#endif
5.3 数组描述
5.3.1 描述
在数组描述(array representation)中,用数组来存储线性表的元素。
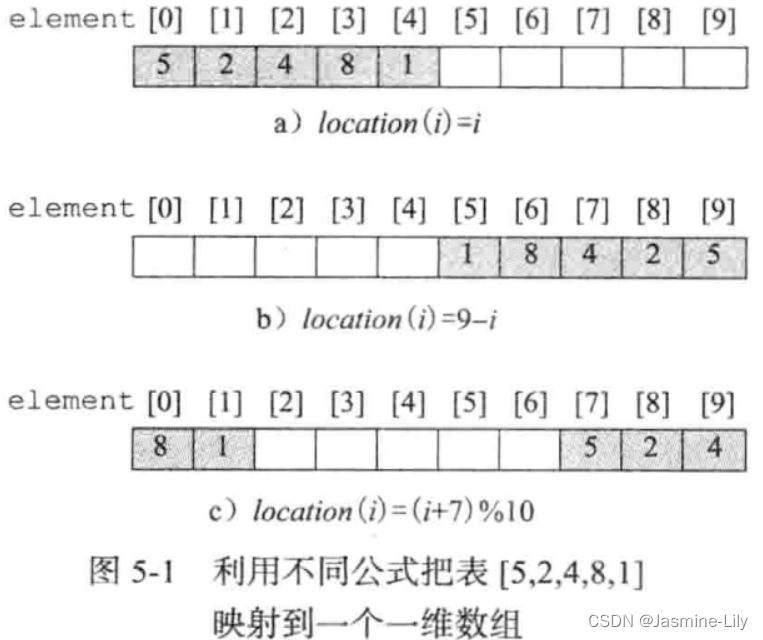
假定使用一个一维数组element来存储线性表的元素。数组element的位置有element[0]…element[arrayLength-1],其中 arrayLength是数组长度或容量。数组的每一个位置都可以存储线性表的一个元素。我们需要一个映射,使线性表的一个元素对应数组的一个位置。映射方式可以有很多种,以下三种是比较经典的。
l
o
c
a
t
i
o
n
(
i
)
=
i
location(i) = i
location(i)=i
l o c a t i o n ( i ) = a r r a y L e n g t h − i − 1 location(i) = arrayLength - i - 1 location(i)=arrayLength−i−1
l o c a t i o n ( i ) = ( l o c a t i o n ( 0 ) + i ) % a r r a y L e n g t h location(i) = (location(0) + i) \% arrayLength location(i)=(location(0)+i)%arrayLength
对应的图为:
5.3.2 变长一维数组
对于一个数组,要增加或减少这个数组的长度,首先要建立一个具有新长度的数组,然后把数组a的元素复制到这个新数组,最后改变数组指针a的值,使它能够引用新数组。
本程序的时间复杂度为O(n)。
/*
作用:将数组的长度加倍
输入:指针a指向需要改变长度的数组,oldLength表示数组原来的长度,newLength表示需要改变的新长度
结果:将数组扩容/缩容 为newLength
*/
template<class T>
void changeLength(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{
if (newLength < 0)
throw illegalParameterValue("new length must be >= 0");
T* temp = new T[newLength];
int number = min(oldLength, newLength);
copy(a, a + number, temp);
delete[] a;
a = temp;
}
5.3.3 线性表数组描述声明
template<class T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{
public:
/*构造函数*/
arrayList(int initialCapacity = 1);
/*复制构造函数*/
arrayList(const arrayList<T>&);
/*使用链表构造数组*/
arrayList(const chain<T>& theChain);
/*析构函数*/
~arrayList() { delete[] element; }
/*其他成员函数*/
bool empty() const { return arraySize == 0; }
int size() const { return arraySize; }
T& get(int theIndex) const;
int indexOf(const T& theElement) const;
void erase(int theIndex);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement,int size);
void output(ostream& out) const;
/*练习题5 时间复杂度为O(1)*/
void trimToSize();
int capacity() const { return arrayLength; }
/*练习题11*/
void push_back(const T& theElement);//将元素theElement插入数组的最右端
/*练习题12*/
T pop_back();//删除数组最右端元素,并返回该元素
/*练习题13*/
void swap(arrayList<T>& theList);
/*练习题14*/
void reserve(int theCapacity);
/*练习题15*/
void set(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
/*练习题16*/
void clear();
/*练习题17*/
void removeRange(int theIndex1, int theIndex2);
/*练习题18*/
int lastIndexOf(T theElement);
/*练习题22*/
void reverse();
/*练习题23*/
void leftShift(int num);
/*练习题24*/
void circularShift(int i);
/*练习题25*/
void half();
/*练习题28*/
void meld(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b);
/*练习题29*/
void merge(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b);
/*练习题30*/
void split(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b);
void reSet(int capacity);
/*迭代器相关*/
//问题:扩展迭代器,使之成为随机访问迭代器,这个暂时不太会。
class iterator
{
public:
//用C++的typedef语句实现双向迭代器
//这一小段typedef暂时不太懂
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;//双向迭代器
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;//是一个与机器相关的数据类型,通常用来保存两个指针减法操作的结果。
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T& reference;
//构造函数
iterator(T* thePosition = 0) { position = thePosition; }
//解引用操作符
T& operator*() const { return *position; }
//指针操作符->
T* operator->() const { return &*position; }
//迭代器的值增加
iterator& operator++()//前加
{
++position;
return *this;
}
iterator operator++(int)//后加
{
iterator old = *this;
++position;
return old;
}
//迭代器的值减少
iterator& operator--()//前减
{
--position;
return *this;
}
iterator operator--(int)//后减
{
iterator old = *this;
--position;
return old;
}
//测试是否相等
bool operator!=(const iterator right) const
{
return position != right.position;
}
bool operator==(const iterator right) const
{
return position == right.position;
}
protected:
T* position;
};
iterator begin() { return iterator(element); }
iterator end() { return iterator(element + arraySize); }//返回的是最后一个元素后面的一个位置
/*重载操作符*/
/*练习题7*/
T& operator[](int i);
const T& operator[](int i) const;
/*练习题8*/
bool operator==(arrayList<T> right) const;
/*练习题9*/
bool operator!=(arrayList<T> right) const;
/*练习题10*/
bool operator<(arrayList<T> right) const;
/*排序*/
void bubbleSort();
void rankSort();
int indexOfMax();
void selectionSort();
void insertSort();
/*友元函数*/
//这个函数用于一次性输入很多元素到线性表
friend istream& operator>> <T>(istream& in, arrayList<T>& m);//已测
protected:
void checkIndex(int theIndex) const;//若索引theIndex无效,则抛出异常
/*setLength()函数没有重新分配内存*/
/*setLength(),setSize(),setElement()函数只应用于swap()函数*/
void setLength(int Length) { arrayLength = Length; }
void setSize(int Size) { arraySize = Size; }
void setElement(T* theElement) { element = theElement; }
T* address() const { return element; }
T* element;//存储线性表元素的一维数组
int arrayLength;//一维数组的容量
int arraySize;//线性表的元素个数
};
5.4 练习题
所有练习题答案见完整测试代码,注释中说明了题目的对应关系。
-
5.编写一个方法arrayList::trimToSize,它使数组的长度等于max(listSize,1)。这个方法的复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
7.重载操作符[],使得表达式x[i]返回对线性表第i个元素的引用。若线性表没有第i个元素,则抛出异常illegallndex。语句x[i]=y和y=x[i]按以往预期的方式执行。测试你的代码。
-
8.重载操作符==,使得表达式x==y返回true,当且仅当两个用数组描述的线性表x和y相等(即对所有的i,两个线性表的第i个元素相等)。测试你的代码。
-
9.重载操作符!=,使得表达式x!=y返回true,当且仅当两个用数组描述的线性表x和y不等(见练习8)。测试你的代码。
-
10.重载操作符<,使得表达式x<y返回true,当且仅当用数组描述的线性表x按字典顺序小于用数组描述的线性表y(见练习8)。测试你的代码。
-
11.编写方法arrayList::push_back,它把元素theElement插到线性表的右端。不要利用insert方法。方法的时间复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
12.编写方法arrayList::pop_back,它把线性表右端的元素删除。不要利用erase方法。方法的时间复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
13.编写方法arrayList::swap(theList),它交换线性表的元素*this和theList。方法的时间复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
14.编写方法arrayList::reserve(theCapacity),它把数组的容量改变为当前容量和theCapacity的较大者。测试你的代码。
-
15.编写方法arrayList::set(thelndex,theElement),它用元素theElement替换索引为thelndex的元素。若索引theIndex超出范围,则抛出异常。返回原来索引为thelndex的元素。测试你的代码。
-
16.编写方法arrayList::clear,它使线性表为空。方法的复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
17.编写方法arrayList::removeRange,它删除指定索引范围内的所有元素。方法的复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
18.编写方法arrayList::lastInexOf,它的返回值是指定元素最后出现时的索引。如果这样的元素不存在,则返回-1。方法的复杂度是多少?测试你的代码。
-
22.1)编写方法arrayList::reverse,它原地颠倒线性表元素的顺序(即在数组element中完成操作,不创建新的数组)。颠倒顺序之前,线性表的第k个元素是element[k],颠倒之后,线性表的第k个元素是element[listSize-k-1]。不要利用STL函数reverse。
2)方法应具有listSize的线性复杂度。证明这个性能。
3)设计测试数据,测试方法的正确性。 -
23.1)编写方法arrayList::leftShift(i),它将线性表的元素向左移动i个位置。如果x=[0,1,2,3,4],那么 x.leftShift(2)的结果是x=[2,3,4]。
2)计算方法的复杂度。
3)测试你的代码。
24.在一个循环移动的操作中,线性表的元素根据给定的值,按顺时针方向移动。例如,x=[0,1,2,3,4],循环移动2的结果是x=[2,3,4,0,1]。
1)描述一下如何利用3次逆转操作完成循环移动。每一次逆转操作都可以将线性表的一部分或全部逆转。
2)编写方法arrayList::circularShift(i),它将线性表的元素循环移动i个位置。方法应具有线性表长度的线性复杂度。
3)测试你的代码。 -
25.调用语句x.half(),可以将x的元素隔一个删除一个。如果x.size()是7,x.element[]=[2,13,4,5,17,8,29],那么x.half()的结果是x.size()是4,x.element[]=[2,4,17,29]。如果x.size()是4,x.element[]=[2,13,4,5],那么x.half()的结果是x.size()是2,x.element[]=[2,4]。如果x为空,那么x.half()的结果也是x为空。
1)编写方法arrayList::half()。不能利用类arrayList的其他方法。复杂度应该为O(listSize)。
2)证明方法的复杂度为O(listSize)。
3)测试你的代码。 -
28.令a和b是类arrayList的两个对象。
1)编写方法arrayList::meld(a,b),它生成一个新的线性表,从a的第0个元素开始,交替地包含a和b的元素。如果一个表的元素取完了,就把另一个表的剩余元素附加到新表中。调用语句c.meld(a,b)使c成为合并后的表。方法应具有两个输人线性表大小的线性复杂度。
2)证明方法具有a和b大小之和的线性复杂度。
3)测试你的代码。 -
29.令a和b是类arrayList的两个对象。假设它们的元素从左到右非递减有序。
1)编写方法arrayList::merge(a,b),它生成一个新的有序线性表,包含a和b的所有元素。归并后的线性表是调用对象*this。不要利用STL函数merge。
2)计算方法的复杂度。
3)测试你的代码。 -
30.1)编写方法arrayList::split(a,b),它生成两个线性表a和b。a包含*this中索引为偶数的元素,b包含其余的元素。2)计算方法的复杂度3)测试你的代码。
5.5 完整测试代码
_4linearList.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 线性表虚类
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef __LINEARLIST_H_
#define __LINEARLIST_H_
#include<iostream>
using std::ostream;
template <class T>
class linearList
{
public:
virtual ~linearList() {};
virtual bool empty() const = 0;//返回true 当且仅当线性表为空
virtual int size() const = 0;//返回线性表的元素个数
virtual T& get(int theIndex) const = 0;//返回索引为theIndex的元素
virtual int indexOf(const T& theElement) const = 0;//返回元素theElement第一次出现时的索引
virtual void erase(int theIndex) = 0;//删除索引为theIndex的元素
virtual void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) = 0;//把元素theElement插入线性表中索引为theIndex的位置上
virtual void output(ostream& out) const = 0;//把线性表插入输入流out
};
#endif
_5arrayList.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 数组线性表头文件---单表
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef __ARRAYLIST_H_
#define __ARRAYLIST_H_
/*事实证明,模板与模板是可以不在同一个头文件下的。但是,模板函数声明和定义要在同一个头文件下。*/
#include <algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstddef>
#include <iterator>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_2myFunctions.h"
#include "_4linearList.h"
using std::ostream;
using std::ostringstream;
using std::find;
using std::cout;
using std::copy;
using std::min;
using std::copy_backward;
using std::ostream_iterator;
using std::bidirectional_iterator_tag;
using std::ptrdiff_t;
//由于不能互相包含头文件,因此给出声明
template<class T>
class chain;
void arrayListTest();//arrayList测试函数,测试arrayList所有函数
template<class T>
class arrayList : public linearList<T>
{
public:
/*构造函数*/
arrayList(int initialCapacity = 1);
/*复制构造函数*/
arrayList(const arrayList<T>&);
/*使用链表构造数组*/
arrayList(const chain<T>& theChain);
/*析构函数*/
~arrayList() { delete[] element; }
/*其他成员函数*/
bool empty() const { return arraySize == 0; }
int size() const { return arraySize; }
T& get(int theIndex) const;
int indexOf(const T& theElement) const;
void erase(int theIndex);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement,int size);
void output(ostream& out) const;
/*练习题5 时间复杂度为O(1)*/
void trimToSize();
int capacity() const { return arrayLength; }
/*练习题11*/
void push_back(const T& theElement);//将元素theElement插入数组的最右端
/*练习题12*/
T pop_back();//删除数组最右端元素,并返回该元素
/*练习题13*/
void swap(arrayList<T>& theList);
/*练习题14*/
void reserve(int theCapacity);
/*练习题15*/
void set(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
/*练习题16*/
void clear();
/*练习题17*/
void removeRange(int theIndex1, int theIndex2);
/*练习题18*/
int lastIndexOf(T theElement);
/*练习题22*/
void reverse();
/*练习题23*/
void leftShift(int num);
/*练习题24*/
void circularShift(int i);
/*练习题25*/
void half();
/*练习题28*/
void meld(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b);
/*练习题29*/
void merge(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b);
/*练习题30*/
void split(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b);
void reSet(int capacity);
/*迭代器相关*/
//问题:扩展迭代器,使之成为随机访问迭代器,这个暂时不太会。
class iterator
{
public:
//用C++的typedef语句实现双向迭代器
//这一小段typedef暂时不太懂
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;//双向迭代器
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;//是一个与机器相关的数据类型,通常用来保存两个指针减法操作的结果。
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T& reference;
//构造函数
iterator(T* thePosition = 0) { position = thePosition; }
//解引用操作符
T& operator*() const { return *position; }
//指针操作符->
T* operator->() const { return &*position; }
//迭代器的值增加
iterator& operator++()//前加
{
++position;
return *this;
}
iterator operator++(int)//后加
{
iterator old = *this;
++position;
return old;
}
//迭代器的值减少
iterator& operator--()//前减
{
--position;
return *this;
}
iterator operator--(int)//后减
{
iterator old = *this;
--position;
return old;
}
//测试是否相等
bool operator!=(const iterator right) const
{
return position != right.position;
}
bool operator==(const iterator right) const
{
return position == right.position;
}
protected:
T* position;
};
iterator begin() { return iterator(element); }
iterator end() { return iterator(element + arraySize); }//返回的是最后一个元素后面的一个位置
/*重载操作符*/
/*练习题7*/
T& operator[](int i);
const T& operator[](int i) const;
/*练习题8*/
bool operator==(arrayList<T> right) const;
/*练习题9*/
bool operator!=(arrayList<T> right) const;
/*练习题10*/
bool operator<(arrayList<T> right) const;
/*排序*/
void bubbleSort();
void rankSort();
int indexOfMax();
void selectionSort();
void insertSort();
/*友元函数*/
//这个函数用于一次性输入很多元素到线性表
friend istream& operator>> <T>(istream& in, arrayList<T>& m);//已测
protected:
void checkIndex(int theIndex) const;//若索引theIndex无效,则抛出异常
/*setLength()函数没有重新分配内存*/
/*setLength(),setSize(),setElement()函数只应用于swap()函数*/
void setLength(int Length) { arrayLength = Length; }
void setSize(int Size) { arraySize = Size; }
void setElement(T* theElement) { element = theElement; }
T* address() const { return element; }
T* element;//存储线性表元素的一维数组
int arrayLength;//一维数组的容量
int arraySize;//线性表的元素个数
};
/*构造函数*/
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(int initialCapacity)
{
//检查初始数组大小是否符合要求
if ( initialCapacity < 1 )
{
ostringstream s("");
s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << "Must be > 0";
throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());
}
//初始化数组私有元素
arrayLength = initialCapacity;
element = new T[arrayLength];
arraySize = 0;
}
/*复制构造函数*/
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const arrayList<T>& theList)
{
arrayLength = theList.arrayLength;
arraySize = theList.arraySize;
//为新数组分配内存
element = new T[arrayLength];
//将旧数组中的元素复制到新数组
copy(theList.element, theList.element + arraySize, element);
}
/*使用chain初始化数组,使用了迭代器*/
template<class T>
arrayList<T>::arrayList(const chain<T>& theChain)
{
arraySize = theChain.size();
arrayLength = arraySize;
element = new T[arraySize];//使得数组的长度和容量相等
//首先定义一个链表迭代器指向链表首地址
/*这里为什么要是有typename?原因是不使用typename将会引发错误:
错误 C7510 “iterator”: 类型 从属名称的使用必须以“typename”为前缀。
只有加上typename才可解决这个问题,具体原因暂时不清楚。
原因:typename是class的同义词;这里使用typename或class都可通过编译。
目的在于告诉编译器chain<T>::iterator是一个类型而非变量,本程序中为了解决
头文件互相引用的问题,只声明了chain是一个类,编译器在此处并不知道chain的
成员iterator是类型还是变量,因此为解决二义性问题必须使用typename或class声
明iterator是类型。
*/
typename chain<T>::iterator pointer = theChain.begin();
int i = 0;
while (pointer != nullptr)
{
*(element + i) = *pointer;
pointer++;
i++;
}
}
/*检查索引是否有效*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{
if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= arraySize)
{
ostringstream s("");
s << "index = " << theIndex << "size = "<<arraySize;
throw illegalIndex(s.str());
}
}
/*返回索引为theIndex的元素;若此元素不存在,则抛出异常*/
template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
return element[theIndex];
}
/*返回元素theElement第一次出现时的索引;若该元素不存在,则返回-1*/
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const//const表示此函数不更改形参的内容
{
int theIndex = (int)(find(element, element + arraySize, theElement) - element);
if (theIndex == arraySize)
return -1;
else
return theIndex;
}
/*如果数组元素数量为0,则将其容量设置为1*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::trimToSize()
{
if (arraySize == 0)
{
//数组中无元素时,将数组容量设置为1
changeLength(element, arrayLength, 1);
arrayLength = 1;
}
}
/*删除索引为theIndex的元素;如果该元素不存在,则抛出illegalIndex异常*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
copy(element + theIndex + 1, element + arraySize, element + theIndex);
element[--arraySize].~T();//调用析构函数,更安全
trimToSize();
//如果数组所存数据太少,使得arraySize<= arrayLength / 4,以下语句将缩小数组大小
while (arraySize < arrayLength / 4)
{
changeLength(element, arrayLength, arrayLength / 2);
arrayLength /= 2;
}
}
/*在索引theIndex的位置上插入一个元素theElement*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{
/*判断是否为有效索引*/
if(theIndex != 0 && theIndex != arraySize)
checkIndex(theIndex);
//有效索引,确定是否数组已满
if (arraySize == arrayLength)
{
//数组空间已满,数组长度倍增
changeLength(element, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);
arrayLength *= 2;
}
copy_backward(element + theIndex, element + arraySize, element + arraySize + 1);
element[theIndex] = theElement;
arraySize += 1;
}
/*在索引theIndex的位置上插入一个元素theElement,如果指定size,当数组空间满时将数组的容量设定为size*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement,int size)
{
/*判断是否为有效索引*/
if(theIndex != 0 && theIndex != arraySize)
checkIndex(theIndex);
//有效索引,确定是否数组已满
if (arraySize == arrayLength)
{
//数组空间已满,数组长度设置为size
changeLength(element, arrayLength, size);
arrayLength = size;
}
copy_backward(element + theIndex, element + arraySize, element + arraySize + 1);
element[theIndex] = theElement;
arraySize += 1;
}
/*数组元素输出*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{
copy(element, element + arraySize, ostream_iterator<T>(cout, " "));
}
/*在数组最右端插入元素theElement*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::push_back(const T& theElement)
{
//有效索引,确定数组已满
if (arraySize == arrayLength)
{
//数组空间已满,数组长度设置为size
changeLength(element, arrayLength, arrayLength*2);
arrayLength = arrayLength * 2;
}
*(element + arraySize) = theElement;
arraySize++;
}
/*删除数组最右端元素并返回该元素*/
template<class T>
T arrayList<T>::pop_back()
{
checkIndex(arraySize-1);
T temp = element[arraySize - 1];
arraySize--;
trimToSize();//如果数组中无元素,则将数组的容量置为1
//如果数组所存数据太少,使得arraySize<= arrayLength / 4,以下语句将缩小数组大小
while (arraySize < arrayLength / 4)
{
changeLength(element, arrayLength, arrayLength / 2);
arrayLength /= 2;
}
return temp;
}
/*交换两数组的元素,传递的参数必须是引用*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::swap(arrayList<T>& theList)
{
T* temp = element;
int thisLength = arrayLength;
int thisSize = arraySize;
element = theList.address();
arraySize = theList.size();
arrayLength = theList.capacity();
theList.setSize(thisSize);
theList.setLength(thisLength);
theList.setElement(temp);
}
/*将数组的容量改编为当前容量和theCapacity的较大者*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::reserve(int theCapacity)
{
if (arrayLength < theCapacity)
{
T* temp = new T[theCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
temp[i] = element[i];
}
delete[] element;
element = temp;
arrayLength = theCapacity;
}
}
/*用元素theElement替换索引为theIndex的元素*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::set(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
element[theIndex] = theElement;
}
/*清空数组*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::clear()
{
arraySize = 0;
trimToSize();
}
/*删除[theIndex1,theIndex2]指定索引范围内的元素*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::removeRange(int theIndex1, int theIndex2)
{
//首先检查索引是否有效
checkIndex(theIndex1);
checkIndex(theIndex2);
for (int i = theIndex1; i < arraySize - (theIndex2 - theIndex1); i++)
{
element[i] = element[i + theIndex2 - theIndex1 + 1];
}
arraySize -= theIndex2 - theIndex1 + 1;
}
/*返回值为指定元素最后出现时的索引;如果元素不存在,则返回-1。*/
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::lastIndexOf(T theElement)
{
for (int i = arraySize - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (element[i] == theElement)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/*原地颠倒线性表元素的顺序*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::reverse()
{
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize / 2; i++)
Swap<T>(element[i], element[arraySize - i - 1]);
}
/*将线性表的元素向左移动i个位置*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::leftShift(int num)
{
//首先检查索引是否有效
checkIndex(num-1);
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize - num + 1; i++)
{
element[i] = element[i + num];
}
arraySize -= num;
}
/*将线性表的元素循环左移i位*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::circularShift(int num)
{
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
push_back(element[i]);
leftShift(num);
}
/*将线性表的元素隔一个删除一个*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::half()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= (arraySize+1) / 2; i++)
element[i] = element[2 * i];
arraySize = (arraySize+1) / 2;
}
/*
创建一个新的线性表,该表包含了a和b中的所有元素,其中a和b的元素轮流出现,表中的首
元素为a中的第一个元素。在轮流排列元素时,如果某个表的元素用完了,则把另一个表的其
余元素依次添加在新表的后部。代码的复杂性应与两个输入表的长度呈线性比例关系。
归并后的线性表是调用对象*this
*/
template <class T>
void arrayList<T>::meld(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b)
{
(*this).clear();
int i = 0;
while (i < a.size() && i < b.size())
{
push_back(a[i]);
push_back(b[i]);
i++;
}
while (i < a.size())
{
push_back(a[i]);
i++;
}
while (i < b.size())
{
push_back(b[i]);
i++;
}
}
/*有序列表a,b,合并生成一个新的有序列表,新列表为(*this)*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::merge(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b)
{
(*this).clear();
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while ((i < a.size()) && (j < b.size()))
{
if (a[i] < b[j])
{
push_back(a[i]);
i++;
}
else if (a[i] == b[j])
{
push_back(a[i]);
push_back(b[j]);
i++;
j++;
}
else
{
push_back(b[j]);
j++;
}
}
while (i < a.size())
{
push_back(a[i]);
i++;
}
while (j < b.size())
{
push_back(b[j]);
j++;
}
}
/*生成两个线性表a和b,a包含*this中索引为奇数的元素,b包含其余的元素*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::split(arrayList<T>& a, arrayList<T>& b)
{
a.clear();
b.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
a.push_back(element[i]);
else
b.push_back(element[i]);
}
}
/*将数组的容量设置为capacity,并将数组的大小设置为capacity,只用于sparseMatrix类*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::reSet(int capacity)
{
if (capacity < 0)
throw illegalParameterValue("capacity must be >= 0");
T* temp = new T[capacity];
delete[] element;
element = temp;
arraySize = capacity;
}
/*友元函数 重载>>操作符*/
template<class T>
istream& operator>>(istream& in, arrayList<T>& m)
{
int numberOfElement = 0;
cout << "Please enter the number of elements:" << endl;
while (!(in >> numberOfElement)) {//如果输入类型不匹配,则执行循环体
in.clear(); // reset input设置标志位为有效
while (in.get() != '\n') //删除没有用的输入
continue; // get rid of bad input
cout << "Please enter the number of elements:" << endl;
}
T inElement = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElement; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the element: " << (i + 1) << endl;
while (!(in >> inElement)) {//如果输入类型不匹配,则执行循环体
in.clear(); // reset input设置标志位为有效
while (in.get() != '\n') //删除没有用的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the element: " << (i + 1) << endl;
}
m.push_back(inElement);
}
return in;
}
/*重载<<操作符*/
template<class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const arrayList<T>& x)
{
x.output(out);
return out;
}
/*重载[]操作符*/
template<class T>
T& arrayList<T>::operator[](int i)
{
return element[i];
}
template<class T>
const T& arrayList<T>::operator[](int i) const
{
return element[i];
}
/*重载==操作符*/
template<class T>
bool arrayList<T>::operator==(arrayList<T> right) const
{
if (arraySize == right.size())
{
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
if ((*this)[i] != right[i])
return false;//遇到不相等直接返回false
}
return true;//都相等时返回true
}
else
return false;
}
/*重载!=操作符*/
template<class T>
bool arrayList<T>::operator!=(arrayList<T> right) const
{
if (arraySize == right.size())
{
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
if ((*this)[i] != right[i])
return true;//遇到不相等直接返回true
}
return false;//都相等时返回false
}
else
return true;//元素数量不相等返回true
}
/*重载<操作符*/
//当left的长度小于右边时,比较left和right的元素;如所有left元素按字典顺序小于对应的right元素,则返回true,反之返回false
//当left的长度大于右边时,返回false
template<class T>
bool arrayList<T>::operator<(arrayList<T> right) const
{
if (arraySize <= right.size())
{
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
if ((*this)[i] >= right[i])
return false;//遇到大于直接返回false
}
return true;//都小于时返回false
}
else
return false;//元素数量不相等返回true
}
/*排序*/
/*功能:及时终止的冒泡排序,时间复杂度为n(n-1)/2*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::bubbleSort()
{
bool is_sorted = true;
for (int i = arraySize; is_sorted && i > 1; i--)
{
is_sorted = false;//先设置为未交换,如果交换了就会被设置为交换。
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++)
{
if (element[j] > element[j + 1])
{
Swap<T>(element[j], element[j + 1]);
is_sorted = true;
}
}
}
}
/*按名次排序*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::rankSort()
{
int* r = new int[arraySize];
//初始化名次
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
r[i] = 0;
//计算名次
for (int i = arraySize - 1; i >= 0; i--) //从右往左拿出每个元素与其他元素比较
{
for (int j = 0; j < i ; j++)
{
if (*(element + i) > *(element + j))
r[i]++;
else
r[j]++;
}
}
//按名次排序
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++)
{
if (i != r[i])
{
Swap<T>(element[i], element[r[i]]);
Swap<T>(r[i], r[r[i]]);
}
}
delete[] r;
}
/*返回整个数组中最大元素的索引*/
template<class T>
int arrayList<T>::indexOfMax()
{
int indexMax = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arraySize; i++)
{
if (element[i] > element[indexMax])
{
indexMax = i;
}
}
return indexMax;
}
/*选择排序*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::selectionSort()
{
bool is_sorted = false;
for (int i = arraySize; i > 1 && !is_sorted; i--)
{
is_sorted = true;
int indexMax = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
if (element[j] > element[indexMax])
indexMax = j;
else
is_sorted = false;
}
Swap<T>(element[i - 1], element[indexMax]);
}
}
/*原地插入排序*/
template<class T>
void arrayList<T>::insertSort()
{
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arraySize; i++)
{
temp = element[i];//存住要插入的元素
//如果它前面的元素都大于该元素的话,就将它前面的元素后移一位
int j = 0;
for (j = i - 1; temp < element[j]; j--)
{
element[j + 1] = element[j];
}
element[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
#endif
_5arrayList.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 测试_5arrayList.h头文件中的所有函数
*/
#include<iostream>
#include "_3sorting.h"
#include "_5arrayList.h"
#include "_6chain.h"
#include <iomanip>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::ios_base;
using std::boolalpha;
void arrayListTest()
{
cout << endl << "********************************arrayListTest()函数开始***************************************" << endl;
cout << endl << "成员函数测试********************************************************************" << endl;
//测试使用chain初始化数组的构造函数
cout << "测试使用chain初始化数组的构造函数***********" << endl;
chain<int> chainData;
chainData.insert(0, 99);
chainData.insert(1, 22);
chainData.insert(2, 8);
cout << "chainData = " << chainData << endl;//chainData = 99 22 8
arrayList<int> arrayData(chainData);
cout << "arrayData = " << arrayData << endl;//arrayData = 99 22 8
arrayList<int> data(10);
cout << "插入元素8***********************************" << endl;
data.insert(0, 8);
cout << "data.capacity() = " << data.capacity() << endl;//data.capacity() = 10
cout << "data.size() = " << data.size() << endl;//data.size() = 1
cout << "获取第一个元素******************************" << endl;
cout << "data.get(0) = " << data.get(0) << endl;//data.get(0) = 8
cout << "移除第一个元素******************************" << endl;
data.erase(0);
cout << "此时无元素**********************************" << endl;
cout << "data.size() = " << data.size() << endl;//data.size() = 0
cout << "data.capacity() = " << data.capacity() << endl;//data.capacity() = 1
cout << "插入6个元素*********************************" << endl;
data.insert(0, 3);
data.insert(0, 4);
data.insert(0, 5);
data.insert(0, 6);
data.insert(0, 8);
data.insert(5, 1);
cout << "data.size() = " << data.size() << endl;//data.size() = 6
cout << "data.capacity() = " << data.capacity() << endl;//data.capacity() = 8
cout << "data.indexOf(1) = " << data.indexOf(1) << endl;//data.indexOf(1) = 5
cout << data << endl;//8 6 5 4 3 1
cout << "插满元素并将数组长度设置为10***************" << endl;
data.insert(2, 99, 10);
data.insert(2, 99, 10);
data.insert(6, 99, 10);
cout << "data.size() = " << data.size() << endl;//data.size() = 9
cout << "data.capacity() = " << data.capacity() << endl;//data.capacity() = 10
cout << data << endl;//8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "入栈元素99*********************************" << endl;
data.push_back(99);
cout << data << endl;//8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1 99
cout << "出栈元素99*********************************" << endl;
int popback = data.pop_back();
cout << "popback = " << popback << endl;//popback = 99
cout << data << endl;//8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "生成新数组data3****************************" << endl;
arrayList<int> data3(2);
data3.push_back(99);
data3.push_back(99);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 99 99
cout << "交换数组data和data3************************" << endl;
data.swap(data3);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 99 99
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "函数reserve()******************************" << endl;
data3.reserve(12);
cout << "data3.size() = " << data3.size() << endl;//data3.size() = 9
cout << "data3.capacity() = " << data3.capacity() << endl;//data3.capacity() = 12
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "函数set()**********************************" << endl;
data3.set(0, 99);
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 99 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "交换数组data和data3************************" << endl;
data.swap(data3);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 199 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 99 99
cout << "清空数组data3******************************" << endl;
data3.clear();
cout << "data3.size() = " << data3.size() << endl;//data3.size() = 0
cout << "data3.capacity() = " << data3.capacity() << endl;//data3.capacity() = 2
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 =
cout << "删除数组data索引为[0,2]的元素**************" << endl;
data.removeRange(0, 2);
cout << "data.size() = " << data.size() << endl;//data.size() = 6
cout << "data.capacity() = " << data.capacity() << endl;//data.capacity() = 12
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 99 5 4 99 3 1
cout << "指定元素最后出现的索引*********************" << endl;
cout << "data.lastIndexOf(99) = " << data.lastIndexOf(99) << endl;//data.lastIndexOf(99) = 3
cout << "data.lastIndexOf(1) = " << data.lastIndexOf(1) << endl;//data.lastIndexOf(1) = 5
cout << "data.lastIndexOf(4) = " << data.lastIndexOf(4) << endl;//data.lastIndexOf(4) = 2
cout << "原地颠倒线性表元素*************************" << endl;
data.reverse();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 1 3 99 4 5 99
cout << "data数组左移2位****************************" << endl;
data.leftShift(2);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 99 4 5 99
cout << "data数组循环左移2位************************" << endl;
data.circularShift(2);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 5 99 99 4
data.insert(0, 5);
data.insert(0, 3);
data.insert(0, 2);
data.insert(0, 8);
data.insert(0, 9);
data.insert(0, 6);
cout << "data数组隔元素删除元素*********************" << endl;
cout << "data原 = " << data << endl;//data原 = 6 9 8 2 3 5 5 99 99 4
data.half();
cout << "data后 = " << data << endl;//data后 = 6 8 3 5 99
cout << "合并两数组的元素***************************" << endl;
data3.insert(0, 5);
data3.insert(0, 3);
data3.insert(0, 2);
data3.insert(0, 8);
data3.insert(0, 9);
data3.insert(0, 6);
data.insert(0, 3);
data.insert(0, 2);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 2 3 6 8 3 5 99
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 6 9 8 2 3 5
arrayList<int> data4(10);
data4.meld(data, data3);
cout << "data4.meld(data,data3) = " << data4 << endl;//data4.meld(data,data3) = 2 6 3 9 6 8 8 2 3 3 5 5 99
cout << "合并两有序数组****************************" << endl;
data4.merge(data, data3);
cout << "data4.merge(data,data3) = " << data4 << endl;//data4.merge(data,data3) = 2 3 6 6 8 3 5 9 8 2 3 5 99
cout << "按奇偶索引拆分数组************************" << endl;
data4.split(data, data3);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 2 6 8 5 8 3 99
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 3 6 3 9 2 5
cout << endl << "迭代器*************************************************************************" << endl;
cout << "it指向data.begin()**************" << endl;
arrayList<int>::iterator it = data.begin();
cout << "*it = " << *it << endl;//*it = 2
cout << "it后++之后**********************" << endl;
it++;
cout << "*it = " << *it << endl;//*it = 6
cout << "it前++之后**********************" << endl;
++it;
cout << "*it = " << *it << endl;//*it = 8
cout << "it后--之后**********************" << endl;
it--;
cout << "*it = " << *it << endl;//*it = 6
cout << "it前--之后**********************" << endl;
--it;
cout << "*it = " << *it << endl;//*it = 2
cout << "it指向data.end()****************" << endl;
it = data.end();
cout << "*it = " << *it << endl;//*it = 99
cout << "it1指向data.end()***************" << endl;
arrayList<int>::iterator it1 = data.begin();
cout.setf(ios_base::boolalpha);//可以显示为true或false
cout << "(it1 == it) = " << (it1 == it) << endl;//(it1 == it) = false
cout << "(it1 != it) = " << (it1 != it) << endl;//(it1 != it) = true
cout << endl << "重载操作符*********************************************************************" << endl;
cout << "测试[]操作符*********************" << endl;
cout << "data[2] = " << data[2] << endl;//data[2] = 8
data[2] = 9;
arrayList<int> data1(data);
//data1.erase(0);
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 2 6 9 5 8 3 99
cout << "data1 = " << data1 << endl;//data1 = 2 6 9 5 8 3 99
cout << "测试==操作符*********************" << endl;
if (data == data1)
cout << "data == data1!" << endl;//data == data1!
cout << "测试!=操作符*********************" << endl;
if (data != data1)
cout << "data != data1!" << endl;
cout << "测试<操作符**********************" << endl;
if (data < data1)
cout << "data < data1!" << endl;//data2 < data!
arrayList<int> data2(2);
data2.insert(0, 1);
data2.insert(0, 1);
if (data2 < data)
cout << "data2 < data!" << endl;
cout << endl << "排序***************************************************************************" << endl;
cout << "冒泡排序**********************************" << endl;
data.bubbleSort();
data3.bubbleSort();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;//data = 2 3 5 6 8 9 99
cout << "data3 = " << data3 << endl;//data3 = 2 3 3 5 6 9
cout << "rankSort()排序****************************" << endl;
data.reverse();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
data.rankSort();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
cout << "indexOfMax()******************************" << endl;
cout << "data.indexOfMax() = " << data.indexOfMax() << endl;
cout << "selectionSort()排序***********************" << endl;
data.reverse();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
data.selectionSort();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
cout << "insertSort()排序**************************" << endl;
data.reverse();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
data.insertSort();
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
cout << endl << "友元函数***********************************************************************" << endl;
cout << "cin>>*************************************" << endl;
arrayList<int> cindata;
cin >> cindata;
cout << "cindata = " << cindata << endl;
cindata.reverse();
cout << "reversedata = " << cindata << endl;
cout << endl << "********************************arrayListTest()函数结束***************************************" << endl;
}
_6chainNode.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日22点06分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 链表的结点
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _CHAINNODE_H_
#define _CHAINNODE_H_
template <class T>
struct chainNode
{
//数据成员
T element;
chainNode<T>* next;
//方法
chainNode() {}
chainNode(const T& element)
{
this->element = element;
this->next = nullptr;
}
chainNode(const T& element, chainNode<T>* next)
{
this->element = element;
this->next = next;
}
};
#endif
_6chain.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 链表线性表头文件---单链表
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _CHAIN_H_
#define _CHAIN_H_
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<cmath>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_2myFunctions.h"
#include "_4linearList.h"
#include "_5arrayList.h"
#include "_6chainNode.h"
using std::ostream;
using std::ostringstream;
using std::find;
using std::cout;
using std::forward_iterator_tag;
using std::ptrdiff_t;
using std::endl;
void chainTest();//测试函数,函数定义在chain.cpp中。
template<class T>
class chain : public linearList<T>
{
public:
//构造函数,复制构造函数和析构函数
chain(int initialCapacity = 10);
chain(const chain<T>&);
chain(const arrayList<T>& arrayTo);//直接使用构造函数--使用数组初始化链表
~chain();
//抽象数据类型ADT方法
bool empty() const { return listSize == 0; }
int size() const { return listSize; }
T& get(int theIndex) const;
int indexOf(const T& theElement) const;
void erase(int theIndex);
void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
void output(ostream& out) const;
void clear();
void push_back(const T& theElement);
void setSize(int theSize);
void set(int theIndex, const T& theElement);
void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
int lastIndexOf(const T& theElement);
void swap(chain<T>& theChain);
void toArray(arrayList<T>& theArray);
void leftShift(int i);
void reverse();
void meld(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b);
void merge(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b);
void split(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b);
void circularShift(int i);
/*迭代器*/
class iterator
{
public:
//向前迭代器所需要的typedef
typedef forward_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T* pointer;
typedef T& reference;
/*构造函数*/
iterator(chainNode<T>* theNode = nullptr) { node = theNode; }
/*解引用操作*/
T& operator*() const { return node->element; }
T* operator->() const { return &node->element; }
/*迭代器加法操作*/
iterator& operator++() //前加
{
node = node->next; return *this;
}
iterator& operator++(int) //后加
{
iterator old = *this;
node = node->next;
return old;
}
/*相等检验*/
bool operator!=(const iterator right) const { return node != right.node; }
bool operator==(const iterator right) const { return node == right.node; }
protected:
chainNode<T>* node;
};
iterator begin() const { return iterator(firstNode); }
iterator end() const { return iterator(nullptr); }
/*重载操作符*/
T& operator[](int i);
const T& operator[](int i) const;
bool operator==(chain<T>& right) const;
bool operator!=(chain<T>& right) const;
bool operator<(chain<T>& right) const;
/*排序*/
void bubbleSort();
void rankSort();
T maxOfList();
void selectionSort();
void insertSort();
void binSort(int range);
void baseBinSort(int range);
/*友元函数*/
friend istream& operator>> <T>(istream& in, chain<T>& m);//已测
protected:
void checkIndex(int theIndex) const;
//如果索引无效,抛出异常
chainNode<T>* firstNode;//指向链表第一个节点的指针
int listSize;//线性表的元素个数
};
/*友元函数 重载>>操作符*/
template<class T>
istream& operator>>(istream& in, chain<T>& m)
{
int numberOfElement = 0;
cout << "Please enter the number of elements:" << endl;
while (!(in >> numberOfElement)) {//如果输入类型不匹配,则执行循环体
in.clear(); // reset input设置标志位为有效
while (in.get() != '\n') //删除没有用的输入
continue; // get rid of bad input
cout << "Please enter the number of elements:" << endl;
}
T inElement = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElement; i++)
{
cout << "Please enter the element: " << (i + 1) << endl;
while (!(in >> inElement)) {//如果输入类型不匹配,则执行循环体
in.clear(); // reset input设置标志位为有效
while (in.get() != '\n') //删除没有用的输入
continue;
cout << "Please enter the element: " << (i + 1) << endl;
}
m.push_back(inElement);
}
return in;
}
/*构造函数:实质上initialCapacity没有意义的,但是为了与类arrayList相容*/
template<class T>
chain<T>::chain(int initialCapacity)
{
//构造函数
if (initialCapacity < 1)
{
ostringstream s("");
s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << "Must be > 0";
throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());
}
firstNode = nullptr;
listSize = 0;
}
/*复制构造函数*/
template<class T>
chain<T>::chain(const chain<T>& theList)
{
listSize = theList.listSize;
if (listSize == 0)
{
firstNode = nullptr;
return;
}
chainNode<T>* sourceNode = theList.firstNode;
firstNode = new chainNode<T>(sourceNode->element);//复制链表theList的首元素
sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
chainNode<T>* targetNode = firstNode;//当前链表*this的最后一个节点
while (sourceNode != nullptr)
{
targetNode->next = new chainNode<T>(sourceNode->element);
targetNode = targetNode->next;
sourceNode = sourceNode->next;
}
}
/*使用arrayList初始化链表的构造函数*/
template<class T>
chain<T>::chain(const arrayList<T>& arrayTo)
{
listSize = arrayTo.size();
if (listSize == 0)
{
firstNode = nullptr;
}
else
{
int data = arrayTo.get(0);
firstNode = new chainNode<T>(data);
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int i = 1; i < listSize; i++)
{
data = arrayTo.get(i);
currentNode->next = new chainNode<T>(data);
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
}
}
/*析构函数*/
template<class T>
chain<T>::~chain()
{
while (firstNode != nullptr)
{
chainNode<T>* nextNode = firstNode->next;
delete firstNode;
firstNode = nextNode;
}
}
/*检查索引是否有效*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const
{
if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex >= listSize)
{
ostringstream s("");
s << "index = " << theIndex << "size = " << listSize;
throw illegalIndex(s.str());
}
}
/*获取索引为theIndex的元素*/
template<class T>
T& chain<T>::get(int theIndex) const
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < theIndex; i++)
currentNode = currentNode->next;
return currentNode->element;
}
/*返回元素theElement首次出现时的索引,若该元素不存在,则返回-1。*/
template<class T>
int chain<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const
{
//搜索链表寻找元素theElement
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
int index = 0;
while (currentNode != NULL && currentNode->element != theElement)
{
index++;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
if (index == listSize)
return -1;
else
return index;
}
/*删除索引为theIndex的元素;若该元素不存在,则抛出异常*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::erase(int theIndex)
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
chainNode<T>* deleteNode = nullptr;
if (theIndex == 0)
{
deleteNode = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
}
else
{
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++)
{
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
deleteNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = currentNode->next->next;
}
delete deleteNode;
listSize--;
}
/*插入元素theElement并使其索引为theIndex*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{
//无效索引
if (theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize)
{
ostringstream s("");
s << "index = " << theIndex << "size = " << listSize;
throw illegalIndex(s.str());
}
//在链表头插入
if (theIndex == 0)
firstNode = new chainNode<T>(theElement, firstNode);
else
{
//寻找新元素的前驱
chainNode<T>* p = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++)
p = p->next;
//在p之后插入
p->next = new chainNode<T>(theElement, p->next);
}
listSize++;
}
/*方法output*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{
for (chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
currentNode != nullptr;
currentNode = currentNode->next)
out << currentNode->element << " ";
}
/*重载<<操作符*/
template<class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const chain<T>& x)
{
x.output(out);
return out;
}
/*清空链表*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::clear()
{
chainNode<T>* nextNode = nullptr;
while (firstNode != nullptr)
{
nextNode = firstNode->next;
delete firstNode;
firstNode = nextNode;
}
listSize = 0;
}
/*在链表末尾插入元素theElement的节点*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::push_back(const T& theElement)
{
chainNode<T>* newNode = new chainNode<T>(theElement, nullptr);
if (firstNode == nullptr)
firstNode = newNode;
else
{
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
while (currentNode->next != nullptr)
currentNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = newNode;
}
listSize++;
}
/*使得线性表的大小等于theSize;若初始线性表的大小小于theSize,则不增加元素;
* 若初始线性表的大小大于theSize,则删除多余的元素。
*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::setSize(int theSize)
{
if (listSize > theSize)
{
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < theSize-1; i++)
currentNode = currentNode->next;//使得currentNode指向第theSize个元素
chainNode<T>* deleteNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = nullptr;//将第theSize个指向nullptr
//删除所有多余的元素,重复利用了currentNode,可行
while (deleteNode != nullptr)
{
currentNode = deleteNode->next;
delete deleteNode;
deleteNode = currentNode;
}
listSize = theSize;
}
}
/*用元素theElement替换索引为theIndex的元素;若索引theIndex超出范围,则抛出异常*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::set(int theIndex, const T& theElement)
{
checkIndex(theIndex);
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++)
currentNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->element = theElement;
}
/*删除指定索引范围内的所有元素:(fromIndex,toIndex)---前开后开
如果给定范围超出链表范围,则抛出异常。*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
{
checkIndex(fromIndex+1);
checkIndex(toIndex-1);
chainNode<T>* fromNode = firstNode;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < fromIndex; i++)
fromNode = fromNode->next;//存住fromIndex的指针
chainNode<T>* toNode = fromNode->next;//不删除fromIndex的结点
i++;
chainNode<T>* deleteNode = nullptr;
//存住toIndex的指针并delete其间的结点
while (i < toIndex)
{
deleteNode = toNode;
toNode = toNode->next;
delete deleteNode;//要注意后删,不然toNode会指向nullptr
i++;
}
fromNode->next = toNode;
listSize = listSize - (toIndex - fromIndex - 1);
}
/*返回值是指定元素最后出现时的索引;若这样的元素不存在,则返回-1。*/
template<class T>
int chain<T>::lastIndexOf(const T& theElement)
{
int index = -1;
int loc = 0;
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
while (currentNode != nullptr)
{
//找到就更新index,没找到就不更新
if (currentNode->element == theElement)
index = loc;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
loc++;
}
return index;
}
/*交换链表*this和theChain的所有元素*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::swap(chain<T>& theChain)
{
chainNode<T>* temp = firstNode;
firstNode = theChain.firstNode;
theChain.firstNode = temp;
int tempnum = listSize;
listSize = theChain.listSize;
theChain.listSize = tempnum;
}
/*将链表*this转换为数组theArray*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::toArray(arrayList<T>& theArray)
{
theArray.clear();//首先要清空数组
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++)
{
theArray.push_back(currentNode->element);
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
}
/*将表中的元素向左移动i个位置*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::leftShift(int i)
{
chainNode<T>* deleteNode = nullptr;
for (int j = 0; j < i && j < listSize; j++)
{
deleteNode = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
delete deleteNode;
}
listSize -= i;
}
/*颠倒*this中的元素的顺序*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::reverse()
{
/*让第二个节点指向第一个节点*/
chainNode<T>* beforeNode = firstNode;
chainNode<T>* currentNode = beforeNode->next;
chainNode<T>* nextNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = beforeNode;
beforeNode->next = nullptr;
/*让第二个节点以后,最后一个节点以前的所有节点指向它前面的节点*/
while (nextNode->next != nullptr)
{
beforeNode = currentNode;
currentNode = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode->next;
currentNode->next = beforeNode;
}
/*让最后一个节点指向倒数第二个节点*/
beforeNode = currentNode;
currentNode = nextNode;
currentNode->next = beforeNode;
/*firstNode指向最后一个节点*/
firstNode = currentNode;
}
/*
meld():*this为新的扩展的链表,它从a的首元素开始,交替地包含a和b的元素。
如果一个链表的元素取完了,就把另一个链表的剩余元素附加到新的扩展链表c中。
合并后的链表使用的应该是链表a和b的节点空间,合并之后,输入链表a和b是空表
*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::meld(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b)
{
//先清空本链表
(*this).clear();
chainNode<T>* currentNode = nullptr;
/*当前a,b链表都不为nullptr时*/
while (a.firstNode != nullptr && b.firstNode != nullptr)
{
if (listSize == 0)
{
//如果a,b链表都不为空,则在c中先插入a,b的一个元素
firstNode = a.firstNode;
a.firstNode = (a.firstNode)->next;
(a.listSize)--;
firstNode->next = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = (b.firstNode)->next;
(b.listSize)--;
listSize += 2;
currentNode = firstNode->next;//当前结点指向第二个元素
}
else
{
currentNode->next = a.firstNode;
a.firstNode = (a.firstNode)->next;
(a.listSize)--;
listSize++;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
currentNode->next = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = (b.firstNode)->next;
(b.listSize)--;
listSize++;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
}
/*当前b链表为nullptr时*/
if (a.firstNode != nullptr)
{
if (listSize == 0)
{
//如果当前a链表不为空,则在c中插入a的所有元素
firstNode = a.firstNode;
a.firstNode = nullptr;
listSize += a.listSize;
a.listSize = 0;
}
else
{
currentNode->next = a.firstNode;
listSize += a.listSize;
a.firstNode = nullptr;
a.listSize = 0;
}
}
/*当前a链表为nullptr时*/
if (b.firstNode != nullptr)
{
if (listSize == 0)
{
//如果当前a链表不为空,则在c中插入a的所有元素
firstNode = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = nullptr;
listSize += b.listSize;
b.listSize = 0;
}
else
{
currentNode->next = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = nullptr;
listSize+=b.listSize;
b.listSize = 0;
}
}
}
/*merge():有序链表a和b,合并生成有序链表(*this),此后a,b链表都为空表*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::merge(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b)
{
//先清空本链表
(*this).clear();
chainNode<T>* currentNode = nullptr;
/*当前a,b链表都不为nullptr时*/
while (a.firstNode != nullptr && b.firstNode != nullptr)
{
//首先解决第一个元素
if (listSize == 0)
{
//如果a,b链表都不为空,则在c中首先插入a,b中小的一个元素
if ((a.firstNode)->element <= (b.firstNode)->element)
{
firstNode = a.firstNode;
a.firstNode = (a.firstNode)->next;
listSize++;
a.listSize--;
currentNode = firstNode;//当前结点指向第一个元素
}
else
{ //如果a,b链表都不为空,则在c中首先插入a,b中小的一个元素
firstNode = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = (b.firstNode)->next;
listSize++;
b.listSize--;
currentNode = firstNode;//当前结点指向第一个元素
}
}
//然后解决后面的元素
else
{
if ((a.firstNode)->element <= (b.firstNode)->element)
{
currentNode->next = a.firstNode;
a.firstNode = (a.firstNode)->next;
listSize++;
a.listSize--;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
else
{
currentNode->next = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = (b.firstNode)->next;
listSize++;
b.listSize--;
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
}
}
/*当前b链表为nullptr时*/
if (a.firstNode != nullptr)
{
if (listSize == 0)
{
//如果当前a链表不为空,则在c中插入a的所有元素
firstNode = a.firstNode;
a.firstNode = nullptr;
listSize += a.listSize;
a.listSize = 0;
}
else
{
currentNode->next = a.firstNode;
listSize += a.listSize;
a.firstNode = nullptr;
a.listSize = 0;
}
}
/*当前a链表为nullptr时*/
while (b.firstNode != nullptr)
{
if (listSize == 0)
{
//如果当前a链表为空,则在c中插入b的所有元素
firstNode = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = nullptr;
listSize += b.listSize;
b.listSize = 0;
}
else
{
currentNode->next = b.firstNode;
b.firstNode = nullptr;
listSize += b.listSize;
b.listSize = 0;
}
}
}
/*split():生成两个扩展链表a和b,a包含*this中索引为奇数的元素,b包含*this中其他的元素,此后*this链表为空表*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::split(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b)
{
chainNode<T>* currentNodeA = nullptr;
chainNode<T>* currentNodeB = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 1)
{
if (b.listSize == 0)
{
b.firstNode = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
(b.listSize)++;
currentNodeB = b.firstNode;
}
else
{
currentNodeB->next = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
(b.listSize)++;
currentNodeB = currentNodeB->next;
}
}
else
{
if (a.listSize == 0)
{
a.firstNode = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
(a.listSize)++;
currentNodeA = a.firstNode;
}
else
{
currentNodeA->next = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
(a.listSize)++;
currentNodeA = currentNodeA->next;
}
}
}
listSize = 0;
currentNodeA->next = nullptr;
currentNodeB->next = nullptr;
}
/*循环移动 [0,1,2,3,4]循环移动两位是[2,3,4,0,1]*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::circularShift(int i)
{
//存住原始第一个节点
chainNode<T>* originalNode = firstNode;
chainNode<T>* lastNode = nullptr;
//找到循环移动结束后的第一个节点
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
firstNode = firstNode->next;
//找到循环移动结束后的最后一个节点
if (j == i - 2)
lastNode = firstNode;
}
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
//找到原始链表的最后一个节点
while (currentNode->next != nullptr)
currentNode = currentNode->next;
//原始链表的最后一个结点指向原始链表的第一个结点
currentNode->next = originalNode;
//循环结束后的最后一个结点指向nullptr
lastNode->next = nullptr;
}
/*重载操作符*/
/*重载[]操作符*/
template<class T>
T& chain<T>::operator[](int i)
{
checkIndex(i);
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
currentNode = currentNode->next;//先获取到地址
return currentNode->element;//然后返回元素
}
template<class T>
const T& chain<T>::operator[](int i) const
{
checkIndex(i);
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
currentNode = currentNode->next;//先获取到地址
return currentNode->element;//然后返回元素
}
/*重载==操作符*/
template<class T>
bool chain<T>::operator==(chain<T>& right) const
{
if (listSize == right.listSize)
{
int i = listSize;
chainNode<T>* leftNode = firstNode;
chainNode<T>* rightNode = right.firstNode;
while (i--)
{
//只要有不相等就返回false
if (leftNode->element != rightNode->element)
return false;
leftNode = leftNode->next;
rightNode = rightNode->next;
}
//只有全部相等时才返回true
return true;
}
else //长度不相等直接返回false
return false;
}
/*重载!=操作符*/
template<class T>
bool chain<T>::operator!=(chain<T>& right) const
{
if (listSize == right.listSize)
{
int i = listSize;
chainNode<T>* leftNode = firstNode;
chainNode<T>* rightNode = right.firstNode;
while (i--)
{
//只要有不相等就返回true
if (leftNode->element != rightNode->element)
return true;
leftNode = leftNode->next;
rightNode = rightNode->next;
}
//只有全部相等时才返回false
return false;
}
else //长度不相等直接返回true
return true;
}
/*重载<操作符,要求左边链表所有的元素都小于右边链表的元素*/
template<class T>
bool chain<T>::operator<(chain<T>& right) const
{
//左边链表长度大于右边链表时,直接返回false
if (listSize > right.listSize)
return false;
else
{
chainNode<T>* leftNode = firstNode;
chainNode<T>* rightNode = right.firstNode;
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++)
{
//存在左边链表的元素大于右边链表的元素时,直接返回false
if (leftNode->element >= rightNode->element)
return false;
leftNode = leftNode->next;
rightNode = rightNode->next;
}
return true;
}
}
/*排序*/
/*冒泡排序*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::bubbleSort()
{
for (int i = listSize; i > 1; i--)
{
int j = 1;
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
while (j < i)
{
if (currentNode->element > currentNode->next->element)
Swap<T>(currentNode->element, currentNode->next->element);
currentNode = currentNode->next;
j++;
}
}
}
/*按名次排序*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::rankSort()
{
int* r = new int[listSize];
//初始化名次
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++)
r[i] = 0;
//计算名次
for (int i = listSize - 1; i >= 0; i--) //从右往左拿出每个元素与其他元素比较
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
if ((*this)[i]>(*this)[j])
r[i]++;
else
r[j]++;
}
}
//按名次排序
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++)
{
if (i != r[i])
{
Swap<T>((*this)[i], (*this)[r[i]]);
Swap<T>(r[i], r[r[i]]);
}
}
delete[] r;
}
/*返回链表的最大元素*/
template<class T>
T chain<T>::maxOfList()
{
chain<T>::iterator it = (*this).begin();
T tempMax = *it;//存储最大元素
for (int i = 1; i < listSize; i++)
{
it++;
if ((*it) > tempMax)
{
tempMax = *it;
}
}
return tempMax;
}
/*选择排序*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::selectionSort()
{
int indexMax = 0;
bool is_sorted = false;
for (int i = listSize; i > 1 && !is_sorted; i--)
{
is_sorted = true;
indexMax = 0;
chain<T>::iterator it = (*this).begin();
T tempMax = *it;//存储最大元素
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
{
it++;
if ((*it) > tempMax)
{
tempMax = *it;
indexMax = j;
}
else
is_sorted = false;
}
Swap<T>((*this)[i - 1], (*this)[indexMax]);
}
}
/*插入排序*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::insertSort()
{
for (int i = 1; i < listSize; i++)
{
chainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode;
int tempData = (*this)[i];
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < i ; j++)
{
if (tempData < currentNode->element)
break;
else
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
if (j != i)
{
(*this).insert(j, tempData);
(*this).erase(i + 1);
}
}
}
/*箱子排序,range指定了链表元素的最大范围,适合数据集中的情况*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::binSort(int range)
{
//对链表中的结点排序
//创建初始化箱子
chainNode<T>** bottom, ** top;//bottom指向箱子的底部,top指向箱子的顶部
bottom = new chainNode<T>*[range + 1];
top = new chainNode<T>*[range + 1];
for (int b = 0; b <= range; b++)
bottom[b] = nullptr;
//把链表的结点分配到箱子
for (; firstNode != nullptr; firstNode = firstNode->next)
{//把首结点firstNode加入到箱子中
int data = firstNode->element;//元素类型转换为整型
if (bottom[data] == nullptr) //箱子为空
bottom[data] = top[data] = firstNode;
else //箱子不空
{
top[data]->next = firstNode;
top[data] = firstNode;
}
}
//把箱子中的结点收集到有序链表
chainNode<T>* y = nullptr;
for (int bin = 0; bin <= range; bin++)
{
if (bottom[bin] != nullptr)
{
if (y == nullptr) //第一个非空箱子
firstNode = bottom[bin];
else
y->next = bottom[bin];
y = top[bin];
}
}
if (y->next != nullptr)
y->next = nullptr;
delete[] bottom;
delete[] top;
}
/*基数排序*/
template<class T>
void chain<T>::baseBinSort(int range)
{
//对链表中的结点排序
chainNode<T>** bottom, ** top;//bottom指向箱子的底部,top指向箱子的顶部
bottom = new chainNode<T>*[range + 1];
top = new chainNode<T>*[range + 1];
//获取链表中数据的最大值
int maxData = maxOfList();
cout << "maxData = " << maxData << endl;
int binNum = 1;//计算要进行箱子排序的次数
while (maxData / (range + 1))
{
maxData /= 10;
binNum++;
}
for(int i = 0;i< binNum;i++)
{
//每一次都要初始化箱子
for (int b = 0; b <= range; b++)
bottom[b] = nullptr;
//把链表的结点分配到箱子
for (; firstNode != nullptr; firstNode = firstNode->next)
{//把首结点firstNode加入到箱子中
int data = int((firstNode->element)/pow(10,i)) % 10;//元素类型转换为整型
if (bottom[data] == nullptr) //箱子为空
bottom[data] = top[data] = firstNode;
else //箱子不空
{
top[data]->next = firstNode;
top[data] = firstNode;
}
}
//把箱子中的结点收集到有序链表
chainNode<T>* y = nullptr;
for (int bin = 0; bin <= range; bin++)
{
if (bottom[bin] != nullptr)
{
if (y == nullptr) //第一个非空箱子
firstNode = bottom[bin];
else
y->next = bottom[bin];
y = top[bin];
}
}
if (y->next != nullptr)
y->next = nullptr;
cout << "(*this) = " << *this << endl;
}
delete[] bottom;
delete[] top;
}
/*非成员方法*/
/*meld():生成一个新的扩展的链表c,它从a的首元素开始,交替地包含a和b的元素。
如果一个链表的元素取完了,就把另一个链表的剩余元素附加到新的扩展链表c中。*/
template<class T>
void meld(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b, chain<T>& c)
{
c.clear();//先清空链表C
typename chain<T>::iterator pointerA = a.begin();
typename chain<T>::iterator pointerB = b.begin();
while (pointerA != nullptr && pointerB != nullptr)
{
c.push_back(*pointerA);
pointerA++;
c.push_back(*pointerB);
pointerB++;
}
while (pointerA != nullptr)
{
c.push_back(*pointerA);
pointerA++;
}
while (pointerB != nullptr)
{
c.push_back(*pointerB);
pointerB++;
}
}
/*方法merge()---生成一个新的有序链表c,包含了a和b的所有元素,且函数后a,b链表不为空*/
template<class T>
void merge(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b, chain<T>& c)
{
c.clear();//先清空链表C
typename chain<T>::iterator pointerA = a.begin();
typename chain<T>::iterator pointerB = b.begin();
while (pointerA != nullptr && pointerB != nullptr)
{
/*插入小的那一个*/
if (*pointerA > *pointerB)
{
c.push_back(*pointerB);
pointerB++;
}
else
{
c.push_back(*pointerA);
pointerA++;
}
}
while (pointerA != nullptr)
{
c.push_back(*pointerA);
pointerA++;
}
while (pointerB != nullptr)
{
c.push_back(*pointerB);
pointerB++;
}
}
/*生成两个扩展链表a和b,a包含c中索引为奇数的元素,b包含c中其他的元素,且函数后c链表不为空*/
template<class T>
void split(chain<T>& a, chain<T>& b, chain<T>& c)
{
//先清空链表a和链表b
a.clear();
b.clear();
typename chain<T>::iterator pointerC = c.begin();
for (int i = 0; i < c.size(); i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 1)
{
a.push_back(*pointerC);
pointerC++;
}
else
{
b.push_back(*pointerC);
pointerC++;
}
}
}
#endif
main.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: main()函数,控制运行所有的测试函数
*/
#include <iostream>
#include "_2myFunctions.h"
#include "_5arrayList.h"
#include "_6chain.h"
int main()
{
arrayListTest();
return 0;
}
_2myFunctions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue
{
public:
illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal input data
class illegalInputData
{
public:
illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal index
class illegalIndex
{
public:
illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds
{
public:
matrixIndexOutOfBounds
(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch
{
public:
matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage =
"The size of the two matrics doesn't match")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// stack is empty
class stackEmpty
{
public:
stackEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty stack")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// queue is empty
class queueEmpty
{
public:
queueEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty queue")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// hash table is full
class hashTableFull
{
public:
hashTableFull(string theMessage =
"The hash table is full")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight
{
public:
undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage =
"No edge weights defined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// method undefined
class undefinedMethod
{
public:
undefinedMethod(string theMessage =
"This method is undefined")
{message = theMessage;}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
#endif
_2myFunctions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种非成员函数
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYFUNCTIONS_H_
#define _MYFUNCTIONS_H_
#include<iostream>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include<cmath>
#include <exception>
using std::min;
using std::endl;
using std::cout;
using std::bad_alloc;
/*交换两数据*/
template<class V>
void Swap(V& a, V& b)
{
V temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
/*
作用:将数组的长度加倍
输入:指针a指向需要改变长度的数组,oldLength表示数组原来的长度,newLength表示需要改变的新长度
结果:将数组扩容/缩容 为newLength
*/
template<class T>
void changeLength(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{
if (newLength < 0)
throw illegalParameterValue("new length must be >= 0");
T* temp = new T[newLength];
int number = min(oldLength, newLength);
copy(a, a + number, temp);
delete[] a;
a = temp;
}
/*遍历一维数组*/
template<class T>
void traverse1dArray(T* x, int length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
cout << x[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
/*创建二维数组*/
template <class T>
bool make2dArray(T**& x, int numberOfRows, int numberOfColumns)
{
try {
//行指针
x = new T * [numberOfRows];
//为每一行分配内存
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfRows; i++)
x[i] = new int[numberOfColumns];
return true;
}
catch (bad_alloc) { return false; }
}
/*遍历二维数组*/
template<class T>
void traverse2dArray(T**& x, int numberOfRows, int numberOfColumns)
{
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfRows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < numberOfColumns; j++)
{
cout.width(4);
cout << x[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
/*myFunctions的测试函数*/
void myFunctionsTest();
/*汉诺塔的递归解决方案*/
void towersOfHanoiRecursion(int n, int x, int y, int z);
#endif
_2myFunctions.cpp
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 测试_2myFunctions.h头文件中的所有函数
*/
#include "_2myFunctions.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
/*myFunctions的测试函数*/
void myFunctionsTest()
{
cout << endl << "********************************myFunctionsTest()函数开始*************************************" << endl;
//cout << "汉诺塔*************************************************" << endl;
//towersOfHanoiRecursion(4, 1, 2, 3);
cout << "********************************myFunctionsTest()函数结束*************************************" << endl;
}
/*汉诺塔的递归解决方案*/
/*执行搬运次数为2^n-1次*/
void towersOfHanoiRecursion(int n, int x, int y, int z)
{
static int numberOfMove = 0;
if (n > 0)
{
towersOfHanoiRecursion(n - 1, x, z, y);
cout << "Move top disk from tower " << x << " to top of tower " << y << endl;
numberOfMove++;
towersOfHanoiRecursion(n - 1, z, y, x);
}
else
cout << "numberOfMove = " << numberOfMove << endl;
}
运行结果
********************************arrayListTest()函数开始***************************************
成员函数测试********************************************************************
测试使用chain初始化数组的构造函数***********
chainData = 99 22 8
arrayData = 99 22 8
插入元素8***********************************
data.capacity() = 10
data.size() = 1
获取第一个元素******************************
data.get(0) = 8
移除第一个元素******************************
此时无元素**********************************
data.size() = 0
data.capacity() = 1
插入6个元素*********************************
data.size() = 6
data.capacity() = 8
data.indexOf(1) = 5
8 6 5 4 3 1
插满元素并将数组长度设置为10***************
data.size() = 9
data.capacity() = 10
8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
入栈元素99*********************************
8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1 99
出栈元素99*********************************
popback = 99
8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
生成新数组data3****************************
data = 8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
data3 = 99 99
交换数组data和data3************************
data = 99 99
data3 = 8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
函数reserve()******************************
data3.size() = 9
data3.capacity() = 12
data3 = 8 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
函数set()**********************************
data3 = 99 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
交换数组data和data3************************
data = 99 6 99 99 5 4 99 3 1
data3 = 99 99
清空数组data3******************************
data3.size() = 0
data3.capacity() = 1
data3 =
删除数组data索引为[0,2]的元素**************
data.size() = 6
data.capacity() = 12
data = 99 5 4 99 3 1
指定元素最后出现的索引*********************
data.lastIndexOf(99) = 3
data.lastIndexOf(1) = 5
data.lastIndexOf(4) = 2
原地颠倒线性表元素*************************
data = 1 3 99 4 5 99
data数组左移2位****************************
data = 99 4 5 99
data数组循环左移2位************************
data = 5 99 99 4
data数组隔元素删除元素*********************
data原 = 6 9 8 2 3 5 5 99 99 4
data后 = 6 8 3 5 99
合并两数组的元素***************************
data = 2 3 6 8 3 5 99
data3 = 6 9 8 2 3 5
data4.meld(data,data3) = 2 6 3 9 6 8 8 2 3 3 5 5 99
合并两有序数组****************************
data4.merge(data,data3) = 2 3 6 6 8 3 5 9 8 2 3 5 99
按奇偶索引拆分数组************************
data = 2 6 8 5 8 3 99
data3 = 3 6 3 9 2 5
迭代器*************************************************************************
it指向data.begin()**************
*it = 2
it后++之后**********************
*it = 6
it前++之后**********************
*it = 8
it后--之后**********************
*it = 6
it前--之后**********************
*it = 2
it指向data.end()****************
*it = -842150451
it1指向data.end()***************
(it1 == it) = false
(it1 != it) = true
重载操作符*********************************************************************
测试[]操作符*********************
data[2] = 8
data = 2 6 9 5 8 3 99
data1 = 2 6 9 5 8 3 99
测试==操作符*********************
data == data1!
测试!=操作符*********************
测试<操作符**********************
data2 < data!
排序***************************************************************************
冒泡排序**********************************
data = 2 3 5 6 8 9 99
data3 = 2 3 3 5 6 9
rankSort()排序****************************
data = 99 9 8 6 5 3 2
data = 2 3 5 6 8 9 99
indexOfMax()******************************
data.indexOfMax() = 6
selectionSort()排序***********************
data = 99 9 8 6 5 3 2
data = 2 3 5 6 8 9 99
insertSort()排序**************************
data = 99 9 8 6 5 3 2
data = 2 3 5 6 8 9 99
友元函数***********************************************************************
cin>>*************************************
Please enter the number of elements:
4
Please enter the element: 1
1
Please enter the element: 2
2
Please enter the element: 3
3
Please enter the element: 4
4
cindata = 1 2 3 4
reversedata = 4 3 2 1
********************************arrayListTest()函数结束***************************************
D:\Prj\_Algorithm\test\x64\Debug\test.exe (进程 5056)已退出,代码为 0。
要在调试停止时自动关闭控制台,请启用“工具”->“选项”->“调试”->“调试停止时自动关闭控制台”。
按任意键关闭此窗口. . .


![[附源码]Nodejs计算机毕业设计基于图书管理系统Express(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1efb016b7e45426f8570ef9870d2dba3.png)