- 待完善: 第6-8
谁做出来了,麻烦指下路,谢谢!
- 第6-7: 连蒙带猜🤣
- 第8: 猜不出来😂
coursera链接
文章目录
- 第1题
- 第2题
- 第3题
- 第4题
- 第5题-8
- 求解 θ3-θ1的 Python 代码
- 第8题
- 求解 θ4 - θ6的 Python 代码
- Matlab代码_参考
第1题
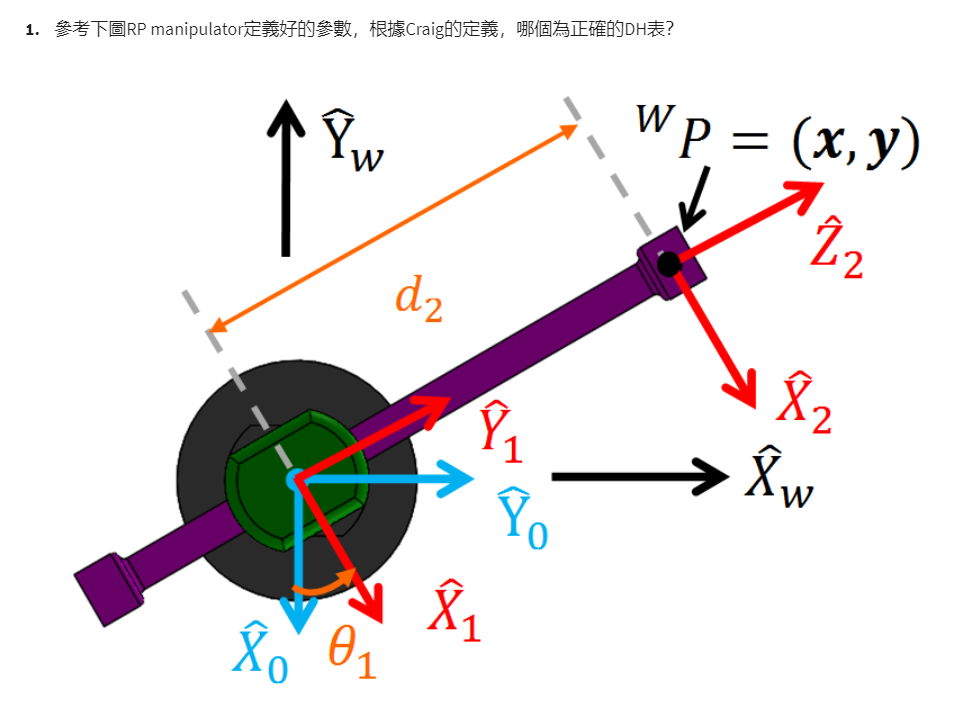
i = 2
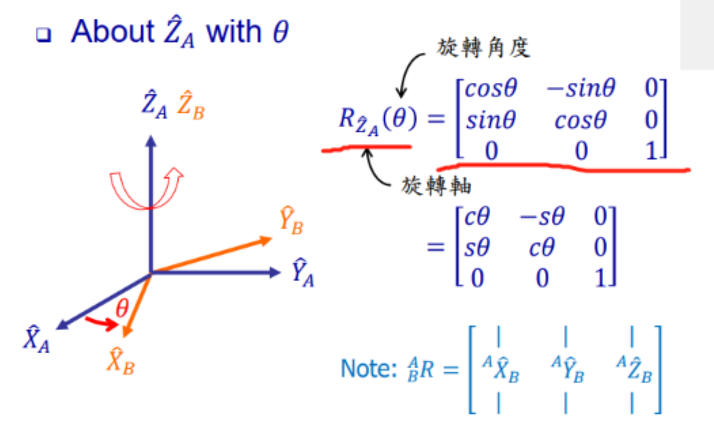
1)、根据右手定则 : 右手拇指(Z), 四指(X),掌心朝向(Y)
- Z 为 垂直 纸面 朝外
2)、右手拇指指向 X ^ 1 \hat{X}_{1} X^1,将 Z ^ 1 \hat{Z}_{1} Z^1旋转到 Z ^ 2 \hat{Z}_{2} Z^2的方向,旋转方向与四指弯曲方向相反,为负, α为 -90。
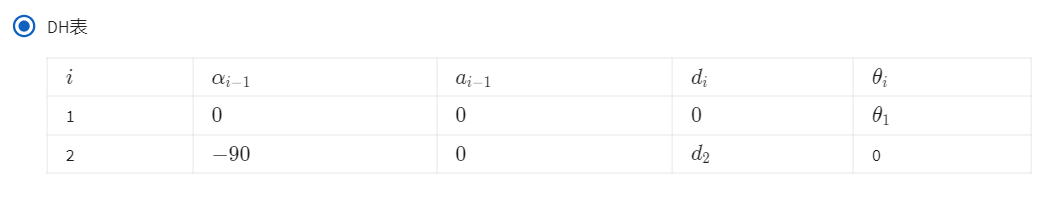
第2题
2、
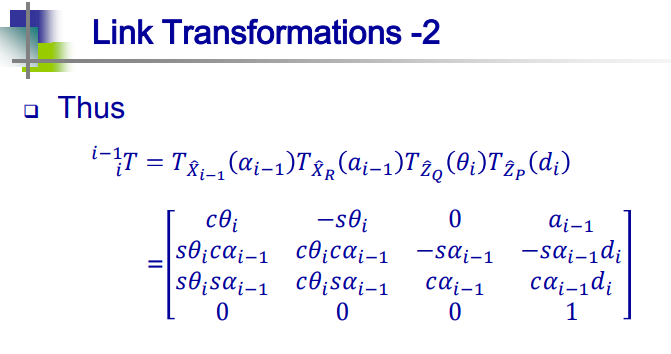
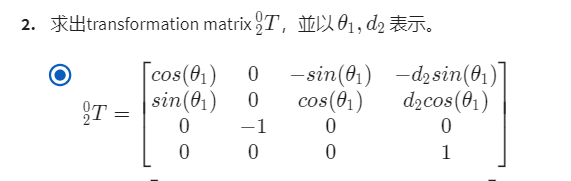
第3题
3、


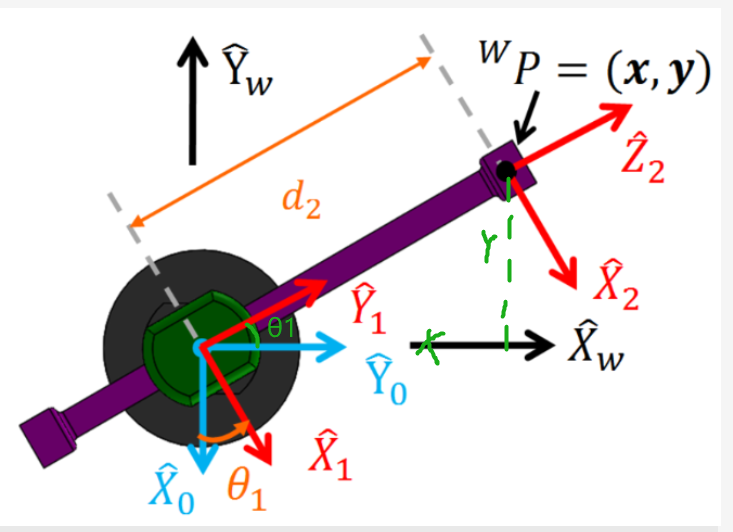
t
a
n
(
θ
1
)
=
Y
X
tan(θ_1)=\frac{Y}{X}
tan(θ1)=XY
import math
θ1 = 180 * math.atan(40/69.28)/ math.pi ## 弧度转角度
print(θ1) ## 30
答案: 30
找了半天公式的我🤣
第4题


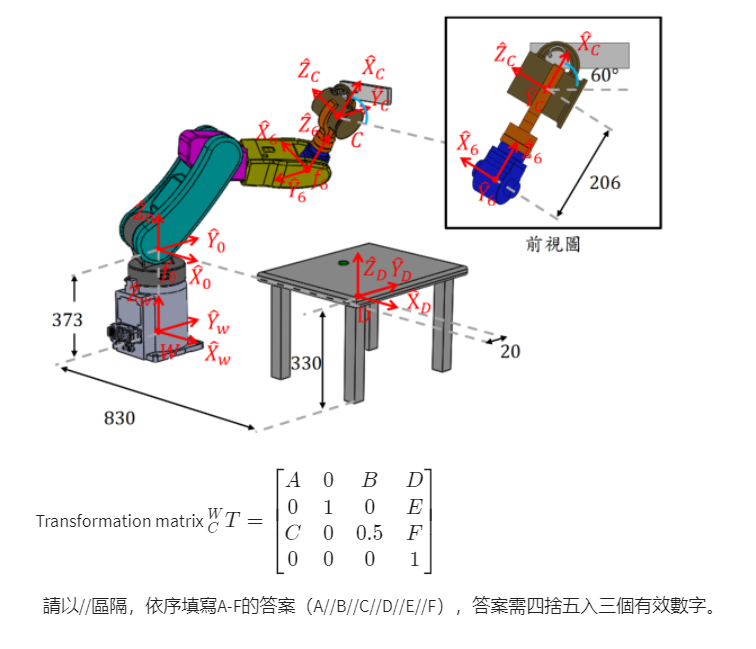
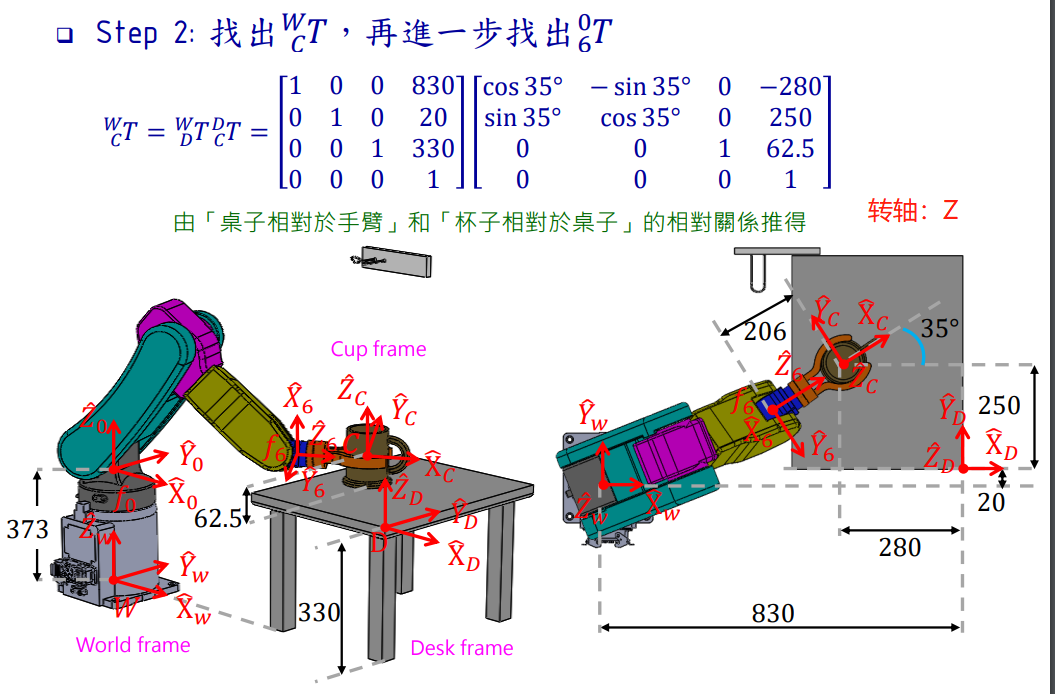
参考点: D(桌角) Desk
杯子——> 桌角——> 机械手
易于找到P, 用这个公式:

求R:
这里的转轴为 Y
注意角度的正负判断: 右手拇指指向Y, 四指弯曲方向为正
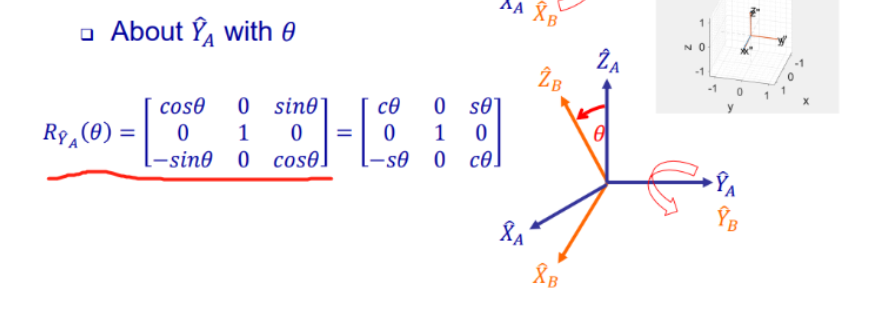
题中 右手拇指指向 Y ^ C \hat{Y}_C Y^C , X ^ C \hat{X}_C X^C 相对于 X ^ D \hat{X}_D X^D 转向 与四指弯曲方向相反, 为负
import numpy as np
## 无转动
R_WD = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]]
a = np.row_stack((R_WD,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行
P = np.array([[830, 20, 330, 1]])
T_WD = np.column_stack((a,P.T)) ## 扩展 列, 注意 转置
# print(T_WD)
## 绕 Y轴 转
θ = np.pi * (-60)/180 ## 注意 正负 判断
R_DC = [[np.cos(θ), 0, np.sin(θ)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(θ), 0, np.cos(θ)]]
# print(R_DC)
a = np.row_stack((R_DC,[[0, 0, 0]]))
P = np.array([[-500, 452, 410, 1]])
T_DC = np.column_stack((a,P.T))
T_WC = np.dot(T_WD, T_DC)
T_WC = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_WC[i]] for i in range(len(T_WC))] ## 保留 3位有效数字
print(T_WC)

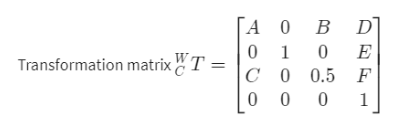
答案: 0.5//-0.866//0.866//330//472//740
############################
补充: 课件里 是沿着 Z轴转
############################
第5题-8

参考 PPT Pieper’s Solution 部分, 题5-8一起做,因为由于 θ1的范围限制,可以排除一些 θ3 值。 但 θ2, θ1的选项仍有很多。
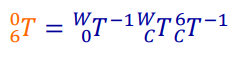
求解 θ3-θ1的 Python 代码
最终版本:
import numpy as np
########################## 求 T_WC
## 无转动
R_WD = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]]
a = np.row_stack((R_WD,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行
P = np.array([[830, 20, 330, 1]])
T_WD = np.column_stack((a,P.T)) ## 扩展 列, 注意 zhuan
# print(T_WD)
## 绕 Y轴 转
θ = np.pi * (-60)/180 ## 注意 正负 判断
R_DC = [[np.cos(θ), 0, np.sin(θ)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(θ), 0, np.cos(θ)]]
# print(R_DC)
a = np.row_stack((R_DC,[[0, 0, 0]]))
P = np.array([[-500, 452, 410, 1]])
T_DC = np.column_stack((a,P.T))
T_WC = np.dot(T_WD, T_DC)
# T_WC = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_WC[i]] for i in range(len(T_WC))]
# print(T_WC) ## 第 4 题答案
#############################################
### 求 T_06
# 求 T_W0
# α, a, d, θ = 0, 0, 373, 0
## 无转动
T_W0 = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 373],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# print(T_W0)
# 求 T_6C Xc 和 Z6 方向相同, Yc和 Y6 反向, Zc 和 X6 同向
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
T = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(T_W0), T_WC)
T_06 = np.dot(T, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
# print(T_06)
P_04 = P_06 = np.array([[227, 472, 188.59876682, 1]])
x, y, z = 227, 472, 188.59876682
##################
α2, a2, d3 = 0, 340, 0 ## θ3
α3, a3, d4 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -40, 338 ## θ4
'''
## 仅与 θ3 有关
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
#f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) -\
# d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
#f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + \
# d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
# print(f3)
'''
# 对 i= 1 i= 2
α0, a0, d1 = 0, 0, 0 ## θ1
α1, a1, d2 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -30, 0 ## θ2
'''
## 和 θ2,θ3有关
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
# g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
# np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
## 化简
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3
# g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
# np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
## 化简
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3
'''
'''
## a1 不等于 0
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
#k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
#k4 = f3 * np.cos(α1) + d2 * np.cos(α1)
k4 = 0
'''
##
r = x**2 + y**2 + z**2 ## 可解
'''
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
k4 = 0
'''
from sympy import *
θ3 = symbols('θ3')
f = (r-a1**2- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2 )**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2 \
- (d4 * cos(α3))**2 )**2/(4 * a1**2) \
+ z**2/(sin(α1))**2 \
- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2)**2 \
- (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2
# f = ((r - k3)**2)/(4*a1**2) + ((z-k4)**2)/(np.sin(α1))**2 - k1**2 - k2**2
root3 = solve([f],[θ3])
print('θ3(弧度值): ', root3)
# lis = [(-3.05085978803173,), (-2.76035600105476,), (-0.616827296276209,), (-0.326323509299240,)]
θ3_du = [180 * root3[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root3))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ3(以度为单位): ', θ3_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
## 求解 θ2
# 结果汇总
# θ3(以度为单位): [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
# θ3 = -3.05085978803173(无满足要求的θ1), -2.76035600105476(符合), -0.616827296276209(符合), -0.326323509299240(无满足要求的θ1)
# θ2 =[-2.82490122970046, -2.09516142685496],\
# [0.207932140057394, 0.864458274997230]
# [-0.864458274997158, -0.207932140057458]
# θ3的有效解 -2.76035600105476 , -0.616827296276209
θ3 = -0.616827296276209
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
θ2 = symbols('θ2')
f = (k1 * cos(θ2) + k2 * sin(θ2)) * 2 * a1 + k3 - r
root2 = solve([f],[θ2])
θ2 = [root2[i][0] for i in range(len(root2))]
print(θ2)
# lis = [(-3.05085978803173,), (-2.76035600105476,), (-0.616827296276209,), (-0.326323509299240,)]
θ2_du = [180 * root2[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root2))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ2(以度为单位): ', θ2_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
## 求解 θ1 [-90, 90]
## 结果汇总
# θ2 = -2.82490122970046(不满足要求)
# θ1 = θ1(以度为单位): [-115.684399755325, 115.684399755325]
###
# θ2 = -2.09516142685496(不满足要求)
# θ1 = θ1(以度为单位): [-115.684399755325, 115.684399755325]
################## θ31 满足
# θ2(以度为单位): [11.9136340504118, 49.5298107225008]
# θ2 = 0.207932140057394
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446740, 64.3156002446740]
# θ2 = 0.864458274997230
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446740, 64.3156002446740]
################## θ32
# [-0.864458274997158, -0.207932140057458]
# θ2(以度为单位): [-49.5298107224966, -11.9136340504155]
# θ2 = -0.864458274997158
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446747, 64.3156002446747]
# θ2 = -0.207932140057458
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446747, 64.3156002446747]
# θ33
θ2 = -0.207932140057458
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
θ1 = symbols('θ1')
f = g1 * cos(θ1) - g2 * sin(θ1) - x
root1 = solve([f],[θ1])
θ1 = [root1[i][0] for i in range(len(root1))]
print(θ1)
# lis = [(-3.05085978803173,), (-2.76035600105476,), (-0.616827296276209,), (-0.326323509299240,)]
θ1_du = [180 * root1[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root1))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ1(以度为单位): ', θ1_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
### 根据实际,应使 θ1 = 64°
帮助理解
import numpy as np
########################## 求 T_WC
## 无转动
R_WD = [[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]]
a = np.row_stack((R_WD,[[0, 0, 0]])) ## 扩展 行
P = np.array([[830, 20, 330, 1]])
T_WD = np.column_stack((a,P.T)) ## 扩展 列, 注意 zhuan
# print(T_WD)
## 绕 Y轴 转
θ = np.pi * (-60)/180 ## 注意 正负 判断
R_DC = [[np.cos(θ), 0, np.sin(θ)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(θ), 0, np.cos(θ)]]
# print(R_DC)
a = np.row_stack((R_DC,[[0, 0, 0]]))
P = np.array([[-500, 452, 410, 1]])
T_DC = np.column_stack((a,P.T))
T_WC = np.dot(T_WD, T_DC)
# T_WC = [[float(format(x, '.3g')) for x in T_WC[i]] for i in range(len(T_WC))]
# print(T_WC) ## 第 4 题答案
#############################################
### 求 T_06
# 求 T_W0
# α, a, d, θ = 0, 0, 373, 0
## 无转动
T_W0 = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 373],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# print(T_W0)
# 求 T_6C Xc 和 Z6 方向相同, Yc和 Y6 反向, Zc 和 X6 同向
T_6C = [[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, -1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 206],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
T = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(T_W0), T_WC)
T_06 = np.dot(T, np.linalg.inv(T_6C))
# print(T_06)
P_04 = P_06 = np.array([[227, 472, 188.59876682, 1]])
x, y, z = 227, 472, 188.59876682,
##################
### 针对 i = 3, i = 4
α2, a2, d3 = 0, 340, 0 ## θ3
α3, a3, d4 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -40, 338 ## θ4
"""
## 仅与 θ3 有关
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.sin(θ3) + a2
# f2_θ3 = a3 * np.cos(α2)*np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3)*np.cos(α2)*np.cos(θ3) -\
# d4 * np.sin(α2)*np.cos(α3) - d3 * np.sin(α2)
## 化简:
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
# f3 = a3 * np.sin(α2)* np.sin(θ3)- d4 * np.sin(α3)* np.sin(α2) * np.cos(θ3) + \
# d4 * np.cos(α2) * np.cos(α3) + d3 * np.cos(α2)
## 化简
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3) ## 2.069653090559027e-14 ## 可求
# print(f3)
"""
# 对 i= 1 i= 2
α0, a0, d1 = 0, 0, 0 ## θ1
α1, a1, d2 = np.pi*(-90)/180, -30, 0 ## θ2
"""
## 和 θ2,θ3有关
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
# g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
# np.sin(α1) * f3 - d2 * np.sin(α1)
## 化简
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3
# g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
# np.cos(α1) * f3 + d2 * np.cos(α1)
## 化简
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3
## a1 不等于 0
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
# k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2 + d2**2 + 2*d2*f3
## 化简
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
# k4 = f3 * np.cos(α1) + d2 * np.cos(α1)
## 化简
k4 = 0
"""
##
r = x**2 + y**2 + z**2 ## 可解
# from scipy.optimize import fsolve
# def func(θ3):
# return
# root = solve([func], [θ3] )
# print(root)
from sympy import *
θ3 = symbols('θ3')
f = (r-a1**2- (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2 )**2 - (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2 - (d4 * cos(α3))**2 )**2/(4 * a1**2) + z**2/(sin(α1))**2 - (a3 * cos(θ3) + d4 * sin(α3)*sin(θ3) + a2)**2 - (a3 * sin(θ3) - d4 * sin(α3) * cos(θ3))**2
root3 = solve([f],[θ3])
print('θ3(弧度值): ', root3)
# lis = [(-3.05085978803173,), (-2.76035600105476,), (-0.616827296276209,), (-0.326323509299240,)]
θ3_du = [180 * root3[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root3))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ3(以度为单位): ', θ3_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
## 求解 θ2
# 结果汇总
# θ3(以度为单位): [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
# θ3 = -3.05085978803173(无满足要求的θ1), -2.76035600105476(符合), -0.616827296276209(符合), -0.326323509299240(无满足要求的θ1)
# θ2 =[-2.82490122970046, -2.09516142685496],\
# [0.207932140057394, 0.864458274997230]
# [-0.864458274997158, -0.207932140057458]
θ3 = -0.326323509299240
f1 = a3 * np.cos(θ3) + d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.sin(θ3) + a2
f2 = a3 * np.sin(θ3) - d4 * np.sin(α3) * np.cos(θ3)
f3 = d4 * np.cos(α3)
k1 = f1
k2 = -f2
k3 = f1**2 + f2**2 + f3**2 + a1**2
θ2 = symbols('θ2')
f = (k1 * cos(θ2) + k2 * sin(θ2))*2 * a1 + k3 - r
root2 = solve([f],[θ2])
θ2 = [root2[i][0] for i in range(len(root2))]
print(θ2)
# lis = [(-3.05085978803173,), (-2.76035600105476,), (-0.616827296276209,), (-0.326323509299240,)]
θ2_du = [180 * root2[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root2))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ2(以度为单位): ', θ2_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
## 求解 θ1 [-90, 90]
## 结果汇总
# θ2 = -2.82490122970046(不满足要求)
# θ1 = θ1(以度为单位): [-115.684399755325, 115.684399755325]
###
# θ2 = -2.09516142685496(不满足要求)
# θ1 = θ1(以度为单位): [-115.684399755325, 115.684399755325]
## θ31 满足
# θ2(以度为单位): [11.9136340504118, 49.5298107225008]
# θ2 = 0.207932140057394
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446740, 64.3156002446740]
# θ2 = 0.864458274997230
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446740, 64.3156002446740]
# θ32
# θ2 = -0.864458274997158
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446747, 64.3156002446747]
# θ2 = -0.207932140057458
# θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446747, 64.3156002446747]
# θ33
θ2 = 2.82490122970057
g1 = np.cos(θ2)* f1 - np.sin(θ2) * f2 + a1
g2 = np.sin(θ2)* np.cos(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.cos(α1)* f2 -\
np.sin(α1) * f3
g3 = np.sin(θ2)* np.sin(α1) * f1 + np.cos(θ2) * np.sin(α1)* f2 +\
np.cos(α1) * f3
θ1 = symbols('θ1')
f = g1 * cos(θ1) - g2 * sin(θ1) - x
root1 = solve([f],[θ1])
θ1 = [root1[i][0] for i in range(len(root1))]
print(θ1)
# lis = [(-3.05085978803173,), (-2.76035600105476,), (-0.616827296276209,), (-0.326323509299240,)]
θ1_du = [180 * root1[i][0] / np.pi for i in range(len(root1))] ## θ3 弧度换角度
print('θ1(以度为单位): ', θ1_du ) # [-174.801389740395, -158.156748814047, -35.3416007650924, -18.6969598387445]
答案:-158//-35
第6题和第7题不理解正负怎么定的
答案: 12//-50

答案: 64
第8题

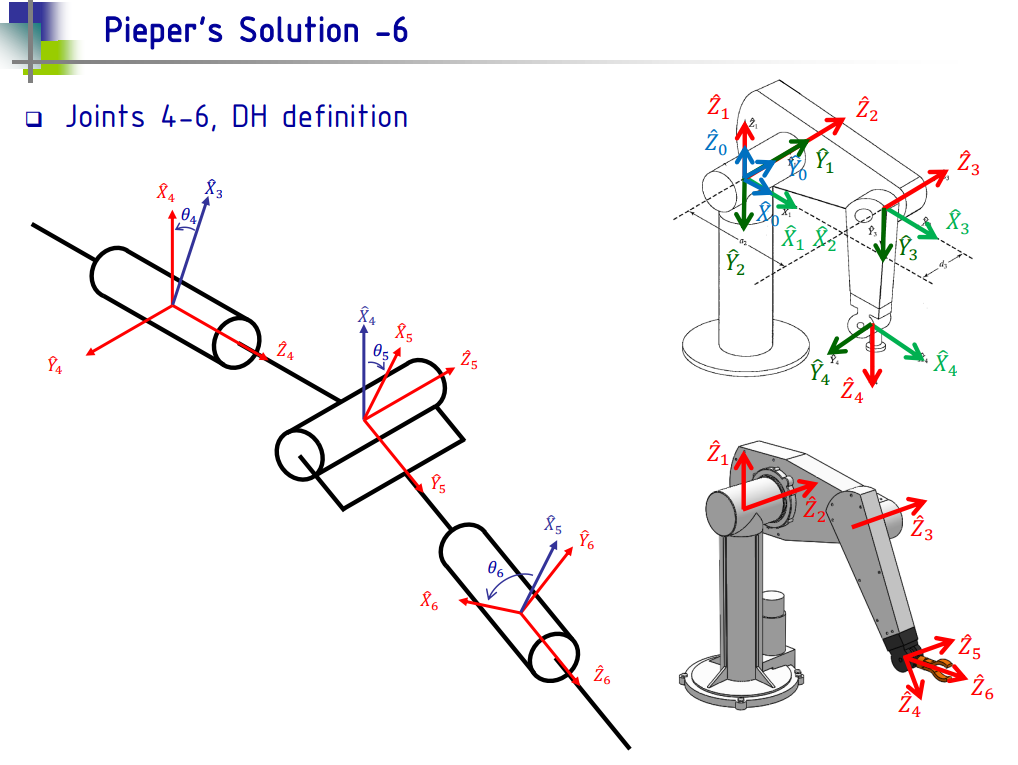

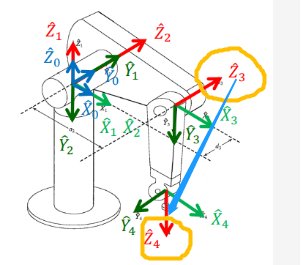


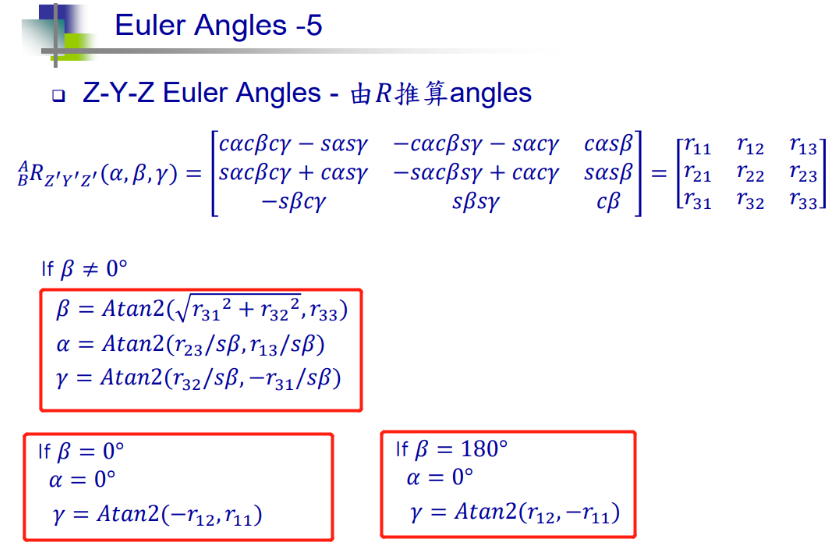
求解 θ4 - θ6的 Python 代码
import numpy as np
# 求解 θ4, θ5, θ6 [-90, 90]
## 沿着 Z 旋转 x, 先旋转θ1, 再旋转 θ2, 再旋转 θ3,
# θ1 θ1(以度为单位): [-64.3156002446747, 64.3156002446747]
θ = -1.12251898466604 ## 可选 [-1.12251898466604, 1.12251898466604]
α = 0
R_01 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
# θ2 = np.pi * (-52.2)/180 ## 12//-50 -12 50
# 可选 4个
# [-0.864458274997158, -0.207932140057458]
# θ2(以度为单位): [-49.5298107224966, -11.9136340504155]
# [0.864458274997158, 0.207932140057458]
# θ2(以度为单位): [49.5298107224966, 11.9136340504155]
θ = -0.864458274997158 ##
α = np.pi * (-90)/180
R_12 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
# θ3 = np.pi * (2.5)/180 ## -158//-35
## 可选 2个
θ = -0.616827296276209 ## -2.76035600105476(符合), -0.616827296276209(符合)
α = 0
R_23 = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(α), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
R = np.dot(R_01, R_12)
R_03 = np.dot(R, R_23)
# print(R_03)
## 由之前 计算的 T_06
R_06 = [[ -0.8660254, 0. ,0.5],
[ 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0.5, 0., 0.8660254]]
R_36 = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(R_03), R_06)
# print(R_36)
r31 = R_36[2][0]
r32 = R_36[2][1]
r33 = R_36[2][2]
r23 = R_36[1][2]
r13 = R_36[0][2]
import math
β = math.atan2(math.sqrt(r31**2 + r32**2), r33) ## 此外, 当 β 选负时,还有 一种 姿态选项, 而后续的θ4和 θ6 仅与 β的选值有关
β = -β ## 另一组姿态
print(β) ## 1.1033617668479667 63
## 由PPT P25 DH定义 与 ZYZ 欧拉角度 转换关系
print('θ5:',180*β/np.pi)
# β = 1.1033617668479667
α = math.atan2(r23/np.sin(β), r13/np.sin(β))
print(α) ##
print('θ4:',180*α/np.pi + 180)
γ = math.atan2(r32/np.sin(β), -r31/np.sin(β))
print(γ) ##
print('θ6:', 180*γ/np.pi + 180)
# β1 = - 180*β/np.pi
# α1 = 180*α/np.pi + 180
# γ1 = 180*γ/np.pi + 180
| θ3 | θ2 | θ1 | θ5 | θ4 | θ6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2.76035600105476(-158) | 0.864458274997230(50) | 1.12251898466603(64) | -61° | 31° | -77° | ❌ |
| -2.76035600105476(-158) | 0.864458274997230(50) | -1.12251898466603(-64) | -61° | -31° | 77° | ❌ |
| -0.616827296276209(-35) | -0.864458274997230 (-50) | -1.12251898466603(-64) | -82° | -27° | 65° | |
| -0.616827296276209(-35) | -0.864458274997230(-50) | 1.12251898466603(64) | -82° | 27 | -65 |
❌(-27,-82,65)//(27,-82,-65)
## 通过 R_06 再次验证
def getR(α, θ):
α = np.pi * α / 180
θ = np.pi * θ / 180
R = [[np.cos(θ), -np.sin(θ), 0],
[np.sin(θ)*np.cos(α), np.cos(θ)*np.cos(θ), -np.sin(α)],
[np.sin(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(θ)*np.sin(α), np.cos(α)]]
return R
R_01 = getR(0, -64)
R_12 = getR(-90, 50)
R = np.dot(R_01, R_12)
R_23 = getR(0, -158)
R = np.dot(R, R_23)
R_34 = getR(-90, 33)
R = np.dot(R, R_34)
R_45 = getR(90, 63)
R = np.dot(R, R_45)
R_56 = getR(-90, -29)
R_06 = np.dot(R, R_56)
print(R_06)
# R_06 = [[ -0.8660254, 0. ,0.5],
# [ 0., -1., 0.],
# [ 0.5, 0., 0.8660254]]
Matlab代码_参考
github链接