文章目录
- 一、定义:中介者模式
- 二、模拟场景:中介者模式
- 三、违背方案:中介者模式
- 3.1 工程结构
- 3.2 创建数据库
- 3.3 JDBC工具类
- 3.4 单元测试
- 四、改善代码:中介者模式
- 4.1 工程结构
- 4.2 中介者工程结构图
- 4.3 资源和配置类
- 4.3.1 XML配置对象
- 4.3.2 资源工具类
- 4.3.3 配置类
- 4.4 SqlSession实现
- 4.4.1 定义SqlSession接口
- 4.4.2 SqlSession具体实现类
- 4.4.3 定义 SqlSession 工厂接口
- 4.4.4 SqlSessionFactory工厂接口具体实现类
- 4.4.5 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 建造者工厂实现
- 4.5 数据库对象类和持久层
- 4.5.1 用户类
- 4.5.2 学校类
- 4.5.3 用户持久层接口
- 4.5.4 学校持久层接口
- 4.5.5 用户持久层配置文件
- 4.5.6 学校持久层配置文件
- 4.6 单元测试
- 4.6.1 配置文件
- 4.6.2 单条数据查询单元测试
- 4.6.3 集合数据查询单元测试
- 五、总结:中介者模式
一、定义:中介者模式

- 中介者模式:当复杂功能应用之间重复调用,在中间添加一层中介者包装服务,对外提供简单、通用和易扩展的服务能力。
- 中介者模式的使用场景:
- 十字路口有交警指挥交通。
- 飞机降落时有营运人员在搭台喊话。
- 无论哪个方向来的候车都从站台上下。
- 公司系统中有中台系统包装所有接口和提供统一的服务。
- 平时用到的一些中间件,他们包装了底层的多种数据库的差异化,对外提供非常简单的调用
二、模拟场景:中介者模式

- 模拟 MyBatis 手写 ORM 框架,通过操作数据库学习中介者模式。
- 除了中间件层使用场景,对于一些外部接口,例如 N 中奖品服务,也可以由中台系统统一包装,再对外提供服务能力。
- 这也是一种中介者模式思想方案的落地体现。
- 本案例将对 JDBC 层包装,让用户在使用数据库服务时像使用 MyBatis 一样简单方便,通过对 ORM 框架源码技术迁移运用的方式学习中介者模式,更能增强和扩展知识栈。
三、违背方案:中介者模式
3.1 工程结构
design-17.0-1
|——src
|——main
|--java
|--com.lino.design
|--JDBCUtil.java
3.2 创建数据库
design.sql
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0;
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for school
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `school`;
CREATE TABLE `school` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '主键',
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '名称',
`address` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '地址',
`createTime` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`updateTime` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of school
-- ----------------------------
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for user
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
`age` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
`createTime` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`updateTime` datetime NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (1, '张三', 18, '2023-01-31 16:52:03', '2023-01-31 16:52:06');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES (2, '李四', 18, '2023-01-31 16:52:16', '2023-01-31 16:52:18');
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1;
3.3 JDBC工具类
JDBCUtil.java
package com.lino.design;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* @description: JDBC工具类
*/
public class JDBCUtil {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JDBCUtil.class);
public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/design";
public static final String USER = "root";
public static final String PASSWORD = "123456";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2.获得数据库连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
// 3.操作数据库,实现增删改查
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT id, name, age, createTime, updateTime FROM user");
// 4.如果有数据,rs.next()返回true
while (resultSet.next()) {
logger.info("测试结果:姓名:{} 年龄:{}", resultSet.getString("name"), resultSet.getInt("age"));
}
}
}
- 直接使用 JDBC 方式直接操作数据库,整个过程分为:加载驱动程序、获得数据库连接、操作数据库和获取执行结果。
3.4 单元测试
测试结果
21:46:53.615 [main] INFO com.lino.design.JDBCUtil - 测试结果:姓名:张三 年龄:30
21:46:53.619 [main] INFO com.lino.design.JDBCUtil - 测试结果:姓名:李四 年龄:18
- 从测试结果可以看到,已经查询到了数据库中的数据。
- 但如果全部的业务开发都这样实现,会非常麻烦。实际的开发中,会使用相应的框架,比如 MyBatis、IBatis 和 Hibernate 等。
四、改善代码:中介者模式
- 使用中介者模式模仿 MyBatis 的 ORM 框架的开发。
- MyBatis 的源码涉及内容较多,虽然在使用时非常方便,直接使用注解或者 XML 配置就可以操作数据库返回结果。
- 但在实现上,MyBatis 作为中间层已经处理了 SQL 语句的获取、数据库连接、执行和返回封装结果等。
- 接下来把 MyBatis 最核心的部分抽离出来,手动实现一个 ORM 框架。
4.1 工程结构
design-17.0-2
|——src
|——main
|--java
|--com.lino.design
|--dao
| |--ISchoolDao.java
| |--IUserDao.java
|--mediator
| |--Configuration.java
| |--DefaultSqlSession.java
| |--Resources.java
| |--SqlSession.java
| |--SqlSessionFactory.java
| |--SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java
| |--XNode.java
|--po
| |--School.java
| |--User.java
|--resources
|--mapper
| |--School_Mapper.xml
| |--User_Mapper.xml
|--mybatis-config-datasource.xml
|--test
|--java
|--com.lino.design.test
|--ApiTest.java
4.2 中介者工程结构图
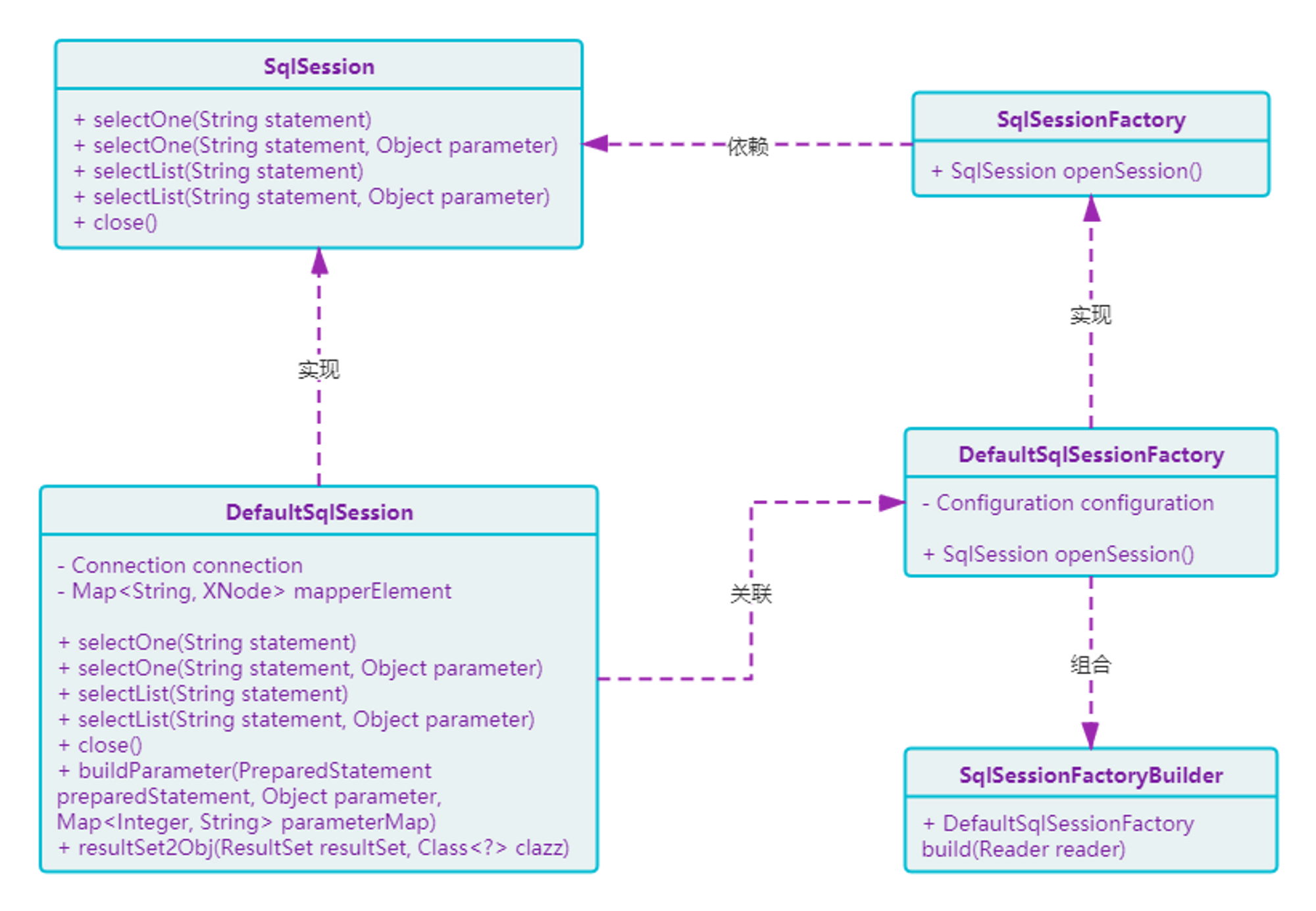
- ORM 框架实现的核心类,包括:加载配置文件、解析 XML、获取数据库 Session、操作数据库及返回结果。
- 左上方是对数据库的定义和处理,基本包括常用的方法:
<T> T selectOne、<T> List<T> selectList。 - 右侧是对数据库配置开启 Session 的工厂处理类,这里的工厂会操作
DefaultSqlSession。 - 之后是工厂建造者类
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,是对数据库操作的核心类:处理工厂、解析文件和获取 Session 等。
4.3 资源和配置类
4.3.1 XML配置对象
XNode.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @description: xml配置对象
*/
public class XNode {
private String namespace;
private String id;
private String parameterType;
private String resultType;
private String sql;
private Map<Integer, String> parameter;
public String getNamespace() {
return namespace;
}
public void setNamespace(String namespace) {
this.namespace = namespace;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getParameterType() {
return parameterType;
}
public void setParameterType(String parameterType) {
this.parameterType = parameterType;
}
public String getResultType() {
return resultType;
}
public void setResultType(String resultType) {
this.resultType = resultType;
}
public String getSql() {
return sql;
}
public void setSql(String sql) {
this.sql = sql;
}
public Map<Integer, String> getParameter() {
return parameter;
}
public void setParameter(Map<Integer, String> parameter) {
this.parameter = parameter;
}
}
4.3.2 资源工具类
Resources.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.Reader;
/**
* @description: 资源类
*/
public class Resources {
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(String resource) throws IOException {
return new InputStreamReader(getResourceAsStream(resource));
}
private static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource) throws IOException {
ClassLoader[] classLoaders = getClassLoaders();
for (ClassLoader classLoader : classLoaders) {
InputStream inputStream = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(resource);
if (null != inputStream) {
return inputStream;
}
}
throw new IOException("Could not find resource " + resource);
}
private static ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders() {
return new ClassLoader[]{
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()};
}
}
4.3.3 配置类
Configuration.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @description: 配置类
*/
public class Configuration {
protected Connection connection;
protected Map<String, String> dataSource;
protected Map<String, XNode> mapperElement;
public void setConnection(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public void setDataSource(Map<String, String> dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public void setMapperElement(Map<String, XNode> mapperElement) {
this.mapperElement = mapperElement;
}
}
4.4 SqlSession实现
4.4.1 定义SqlSession接口
SqlSession.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @description: 定义sqlsession接口
*/
public interface SqlSession {
/**
* 查询单条记录
*
* @param statement SQL语句
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 泛型结果对象
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statement);
/**
* 查询单条记录
*
* @param statement SQL语句
* @param parameter 查询参数
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 泛型结果对象
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* 查询多条记录
*
* @param statement SQL语句
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 泛型集合对象
*/
<T> List<T> selectList(String statement);
/**
* 查询多条记录
*
* @param statement SQL语句
* @param parameter 查询参数
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 泛型集合对象
*/
<T> List<T> selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* 关闭连接
*/
void close();
}
- 定义了操作数据库的查询接口,分为查询一个结果和多个结果,同时包括有参数方法和无参数方法。
4.4.2 SqlSession具体实现类
DefaultSqlSession.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @description: 默认SqlSession实现类
*/
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Connection connection;
private Map<String, XNode> mappperElement;
public DefaultSqlSession(Connection connection, Map<String, XNode> mappperElement) {
this.connection = connection;
this.mappperElement = mappperElement;
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement) {
try {
XNode xNode = mappperElement.get(statement);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(xNode.getSql());
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<T> objects = resultSet2Obj(resultSet, Class.forName(xNode.getResultType()));
return objects.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
XNode xNode = mappperElement.get(statement);
Map<Integer, String> parameterMap = xNode.getParameter();
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(xNode.getSql());
buildParameter(preparedStatement, parameter, parameterMap);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<T> objects = resultSet2Obj(resultSet, Class.forName(xNode.getResultType()));
return objects.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> List<T> selectList(String statement) {
XNode xNode = mappperElement.get(statement);
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(xNode.getSql());
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
return resultSet2Obj(resultSet, Class.forName(xNode.getResultType()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> List<T> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
XNode xNode = mappperElement.get(statement);
Map<Integer, String> parameterMap = xNode.getParameter();
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(xNode.getSql());
buildParameter(preparedStatement, parameter, parameterMap);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
return resultSet2Obj(resultSet, Class.forName(xNode.getResultType()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
private void buildParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, Object parameter, Map<Integer, String> parameterMap) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException {
int size = parameterMap.size();
// 单个参数
if (parameter instanceof Long) {
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
preparedStatement.setLong(i, Long.parseLong(parameter.toString()));
}
return;
}
if (parameter instanceof Integer) {
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
preparedStatement.setInt(i, Integer.parseInt(parameter.toString()));
}
return;
}
if (parameter instanceof String) {
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(i, parameter.toString());
}
return;
}
Map<String, Object> fieldMap = new HashMap<>();
// 对象参数
Field[] declaredFields = parameter.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
String name = field.getName();
field.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = field.get(parameter);
field.setAccessible(false);
fieldMap.put(name, obj);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
String parameterDefine = parameterMap.get(i);
Object obj = fieldMap.get(parameterDefine);
if (obj instanceof Short) {
preparedStatement.setShort(i, Short.parseShort(obj.toString()));
continue;
}
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
preparedStatement.setInt(i, Integer.parseInt(obj.toString()));
continue;
}
if (obj instanceof Long) {
preparedStatement.setLong(i, Long.parseLong(obj.toString()));
continue;
}
if (obj instanceof String) {
preparedStatement.setString(i, obj.toString());
continue;
}
if (obj instanceof Date) {
preparedStatement.setDate(i, (java.sql.Date) obj);
}
}
}
private <T> List<T> resultSet2Obj(ResultSet resultSet, Class<?> clazz) {
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
// 每次遍历行值
while (resultSet.next()) {
T obj = (T) clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
Object value = resultSet.getObject(i);
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
String setMethod = "set" + columnName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + columnName.substring(1);
Method method;
if (value instanceof Timestamp) {
method = clazz.getMethod(setMethod, Date.class);
} else {
method = clazz.getMethod(setMethod, value.getClass());
}
method.invoke(obj, value);
}
list.add(obj);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
}
- 这里包括了接口定义的方法实现,即包装了 JDBC 层的使用。
- 通过这种包装,可以隐藏数据库的 JDBC 操作,当外部调用时,对入参、出参都由内部处理。
4.4.3 定义 SqlSession 工厂接口
SqlSessionFactory.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
/**
* @description: SqlSession工厂
*/
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 开启会话
*
* @return 会话
*/
SqlSession openSession();
}
4.4.4 SqlSessionFactory工厂接口具体实现类
DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
/**
* @description: 默认SqlSession工厂实现类
*/
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration.connection, configuration.mapperElement);
}
}
- DefaultSqlSessionFactory 事 MyBatis 最常用的类,这里简单地实现了一个版本。
- 虽然是简单版本,但包括了最基本的核心思路。
- 当开启 SqlSession 时,会返回一个 DefaultSqlSession。
- 这个构造函数向下传递了 Configuration 配置文件,包括:
Connection connectionMap<String, String> dataSourceMap<String, XNode> mapperElement
4.4.5 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 建造者工厂实现
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java
package com.lino.design.mediator;
import org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperEntityResolver;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
import org.xml.sax.InputSource;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import static java.util.regex.Pattern.*;
/**
* @description: SqlSession工厂建造者类
*/
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
saxReader.setEntityResolver(new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
Document document = saxReader.read(new InputSource(reader));
Configuration configuration = parseConfiguration(document.getRootElement());
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(configuration);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private Configuration parseConfiguration(Element root) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.setDataSource(dataSource(root.selectNodes("//dataSource")));
configuration.setConnection(connection(configuration.dataSource));
configuration.setMapperElement(mapperElement(root.selectNodes("mappers")));
return configuration;
}
private Map<String, String> dataSource(List<Element> list) {
Map<String, String> dataSource = new HashMap<>(4);
Element element = list.get(0);
List content = element.content();
for (Object o : content) {
Element e = (Element) o;
String name = e.attributeValue("name");
String value = e.attributeValue("value");
dataSource.put(name, value);
}
return dataSource;
}
private Connection connection(Map<String, String> dataSource) {
try {
Class.forName(dataSource.get("driver"));
return DriverManager.getConnection(dataSource.get("url"), dataSource.get("username"), dataSource.get("password"));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private Map<String, XNode> mapperElement(List<Element> list) {
Map<String, XNode> map = new HashMap<>(16);
Element element = list.get(0);
List content = element.content();
for (Object o : content) {
Element e = (Element) o;
String resource = e.attributeValue("resource");
try {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read(new InputSource(reader));
Element root = document.getRootElement();
// 命名空间
String namespace = root.attributeValue("namespace");
// SELECT
List<Element> selectNodes = root.selectNodes("select");
for (Element node : selectNodes) {
String id = node.attributeValue("id");
String parameterType = node.attributeValue("parameterType");
String resultType = node.attributeValue("resultType");
String sql = node.getText();
// ? 匹配
Map<Integer, String> parameter = new HashMap<>(16);
Pattern pattern = compile("(#\\{(.*?)})");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(sql);
for (int i = 1; matcher.find(); i++) {
String g1 = matcher.group(1);
String g2 = matcher.group(2);
parameter.put(i, g2);
sql = sql.replace(g1, "?");
}
XNode xNode = new XNode();
xNode.setNamespace(namespace);
xNode.setId(id);
xNode.setParameterType(parameterType);
xNode.setResultType(resultType);
xNode.setSql(sql);
xNode.setParameter(parameter);
map.put(namespace + "." + id, xNode);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return map;
}
}
- 这个类包括的核心方法有:
build:构建实例化元素。- 这个类主要用于创建解析 XML 文件的类,以及初始化 SqlSession 工厂类 DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
- 另外,需要注意代码
saxReader.setEntityResolver(new XMLMapperEntityResolver()),是为了保证在不联网时同样可以解析 XML,否则会需要从互联网获取 dtd 文件。
parseConfiguration:解析配置。- 这个类时对 XML 中的元素进行获取,这里主要获取了
dataSource、mappers两个配置。dataSource:数据库的链接信息。mappers:对数据库操作语句的解析。
- 这个类时对 XML 中的元素进行获取,这里主要获取了
dataSource:获取数据库配置。connection(Map<String, String> dataSource):连接数据库。- 数据库连接开启操作的地方和常见的方式是一样的:
Class.forName(dataSource.get("driver"))。 - 但是这样包装以后,外部不需要知道具体是如何操作的。
- 同时,当需要连接多套数据库时,也可以在这里扩展。
- 数据库连接开启操作的地方和常见的方式是一样的:
mapperElement:解析 SQL 语句。- 核心是为了解析 XML 中的 SQL 语句配置。
- 在平常的使用中,基本都会配置一些 SQL 语句,也有一些入参的占位符。这里使用正则表达式的方式解析操作。
- 解析完成的 SQL 语句就有了一个名称和 SQL 的映射关系,当操作数据库时,这个组件就可以通过映射关系获取对应的 SQL 语句。
4.5 数据库对象类和持久层
4.5.1 用户类
User.java
package com.lino.design.po;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @description: 用户类
*/
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public Date getUpdateTime() {
return updateTime;
}
public void setUpdateTime(Date updateTime) {
this.updateTime = updateTime;
}
}
4.5.2 学校类
School.java
package com.lino.design.po;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @description: 学校类
*/
public class School {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public Date getUpdateTime() {
return updateTime;
}
public void setUpdateTime(Date updateTime) {
this.updateTime = updateTime;
}
}
4.5.3 用户持久层接口
IUserDao.java
package com.lino.design.dao;
import com.lino.design.po.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @description: 用户持久层接口
*/
public interface IUserDao {
/**
* 根据用户ID查询用户信息
*
* @param id 用户ID
* @return 用户信息对象
*/
User queryUserInfoById(Long id);
/**
* 查询用户列表
*
* @param user 用户对象
* @return 用户列表
*/
List<User> queryUserList(User user);
}
4.5.4 学校持久层接口
ISchoolDao.java
package com.lino.design.dao;
import com.lino.design.po.School;
/**
* @description: 学校持久层接口
*/
public interface ISchoolDao {
/**
* 根据学校ID查询学校信息
*
* @param treeId 学校ID
* @return 学校信息对象
*/
School querySchoolInfoById(Long treeId);
}
4.5.5 用户持久层配置文件
User_Mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lino.design.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="queryUserInfoById" parameterType="java.lang.Long" resultType="com.lino.design.po.User">
SELECT id, name, age, createTime, updateTime
FROM user
where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="queryUserList" parameterType="com.lino.design.po.User" resultType="com.lino.design.po.User">
SELECT id, name, age, createTime, updateTime
FROM user
where age = #{age}
</select>
</mapper>
4.5.6 学校持久层配置文件
School_Mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.lino.design.dao.ISchoolDao">
<select id="querySchoolInfoById" resultType="com.lino.design.po.School">
SELECT id, name, address, createTime, updateTime
FROM school
where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
4.6 单元测试
4.6.1 配置文件
mybatis-config-datasource.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/design?useUnicode=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/User_Mapper.xml" />
<mapper resource="mapper/School_Mapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 配置文件包括了数据库的连接池信息及需要引入的 mapper 映射文件。
4.6.2 单条数据查询单元测试
ApiTest.java
@Test
public void test_queryUserInfoById() {
String resource = "mybatis-config-datasource.xml";
Reader reader;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
DefaultSqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
try {
User user = session.selectOne("com.lino.design.dao.IUserDao.queryUserInfoById", 1L);
logger.info("测试结果:{}", JSON.toJSONString(user));
} finally {
session.close();
reader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 单元测试包括:资源加载和解析、SqlSession 工厂构建、开启 SqlSession 以及最后执行查询操作
selectOne。
测试结果
08:37:28.528 [main] INFO com.lino.design.test.ApiTest - 测试结果:{"age":18,"createTime":1675155123000,"id":1,"name":"张三","updateTime":1675155126000}
4.6.3 集合数据查询单元测试
ApiTest.java
@Test
public void test_queryUserList() {
String resource = "mybatis-config-datasource.xml";
Reader reader;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
DefaultSqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
try {
User req = new User();
req.setAge(18);
List<User> userList = session.selectList("com.lino.design.dao.IUserDao.queryUserList", req);
logger.info("测试结果:{}", JSON.toJSONString(userList));
} finally {
session.close();
reader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 集合测试内容与以上的查询方法有所不同。
session.selectList是查询一个集合结果。
测试结果
08:37:41.751 [main] INFO com.lino.design.test.ApiTest - 测试结果:[{"age":18,"createTime":1675155123000,"id":1,"name":"张三","updateTime":1675155126000},{"age":18,"createTime":1675155136000,"id":2,"name":"李四","updateTime":1675155138000}]
五、总结:中介者模式
- 运用中介者模式的设计思想手写了一个 ORM 框架,隐去了对数据库的复杂操作,让外部的调用方能够非常简单地操作数据库,这也是平常使用 Mybatis 的效果。
- 中介者模式还可以实现服务接口的包装。
- 比如:公司有很多的奖品接口需要在营销活动中对接,可以把这些奖品接口统一汇总到中台再开发一个奖品中心,对外提供服务。
- 这样就不需要每一位研发人员都去找奖品接口提供方,而是找中台服务即可。
- 中介者模式:满足了单一职责和开闭,也就符合了迪米特法则,即越少人知道越好。
- 外部的人只需要按照需求调用,不需要知道具体是如何实现的,复杂的内容由组件合作服务平台处理即可。