链表

逻辑结构
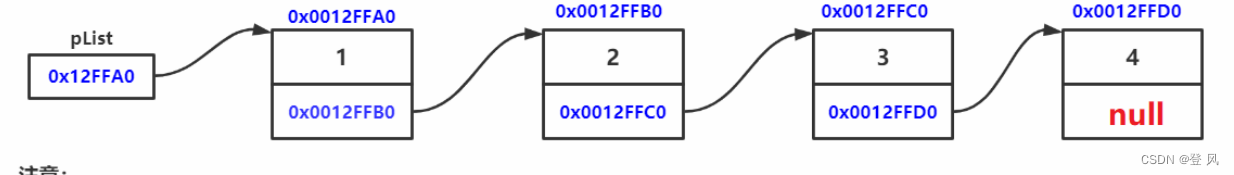

无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。
无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
链表的实现

创建一个链表


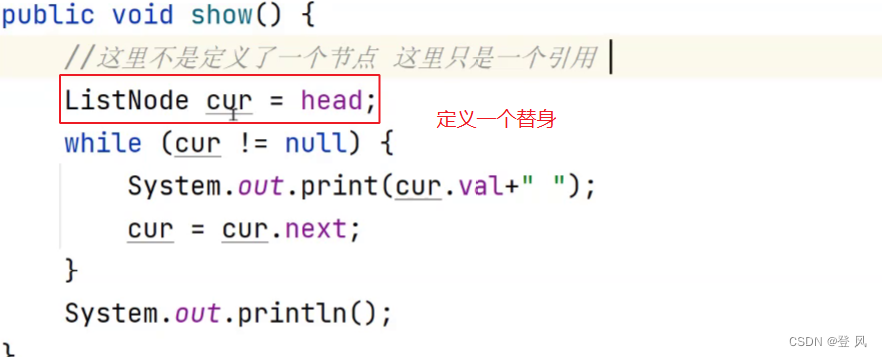
遍历单链表
、
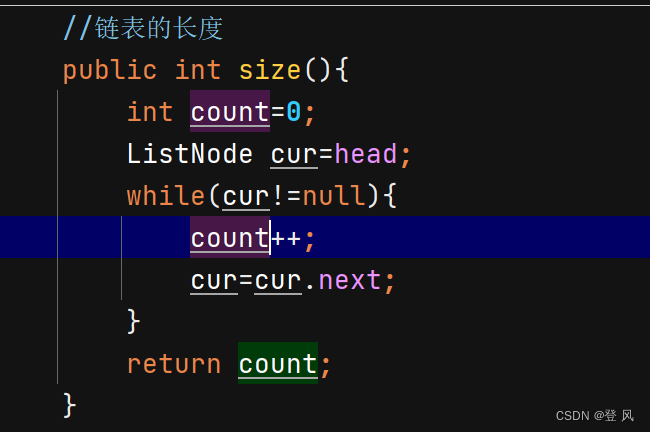
得到单链表的长度 链表中节点的个数
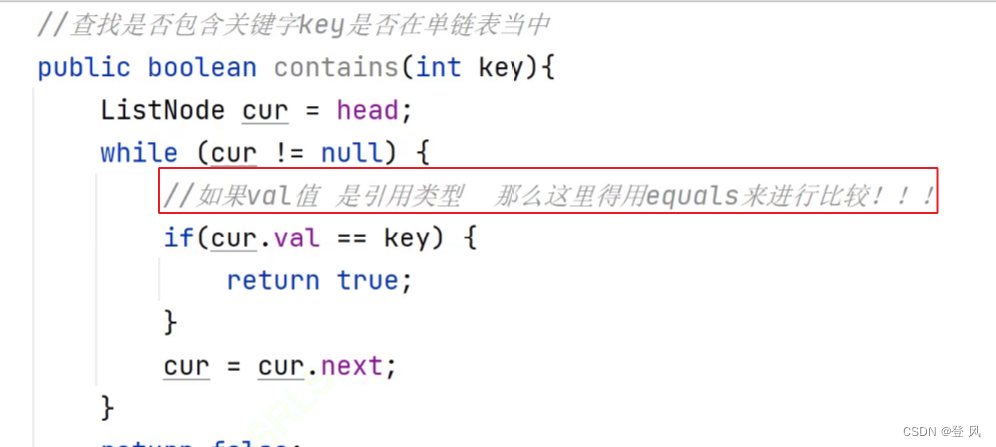
查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中

头插和尾插

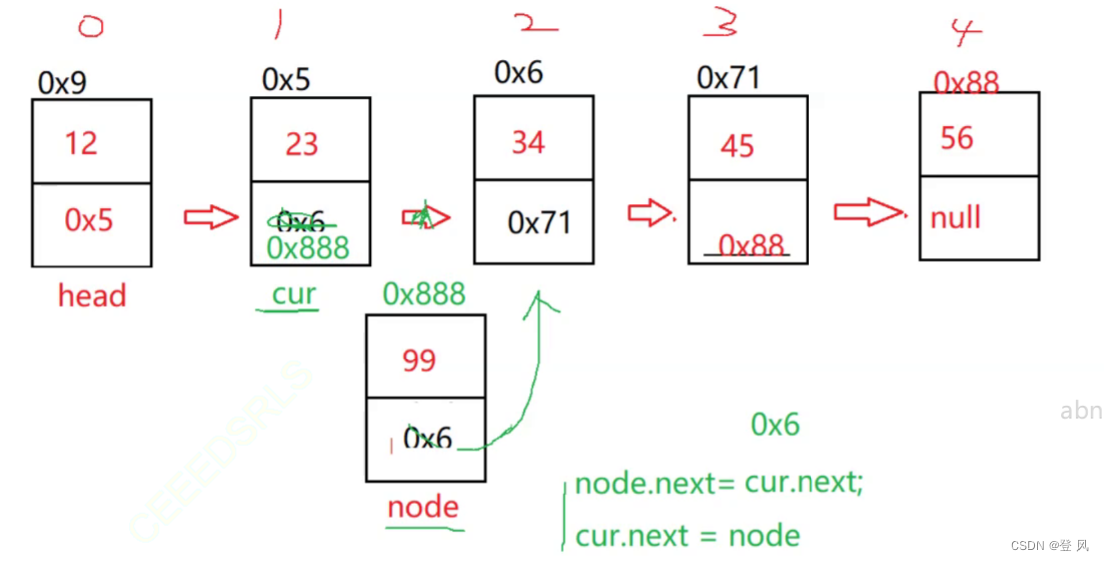
任意位置的插入

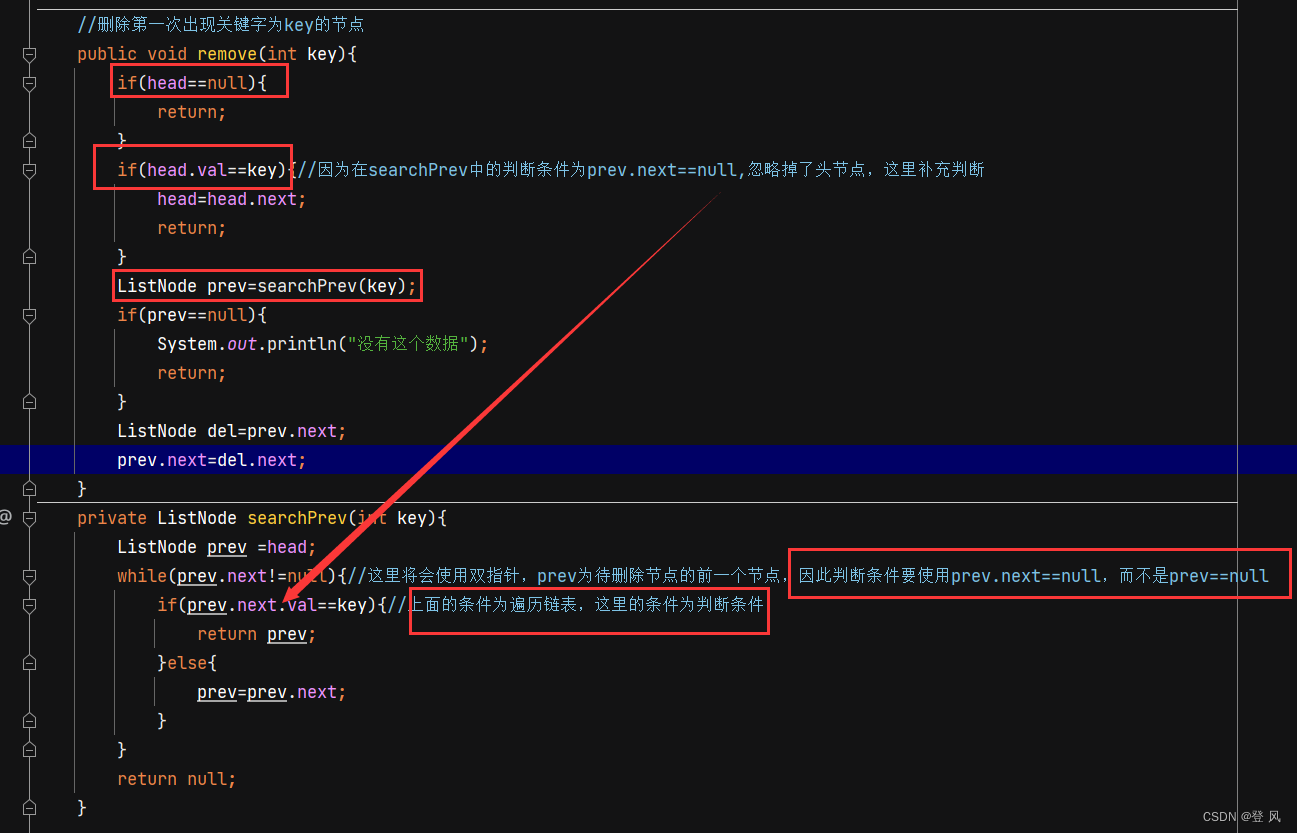
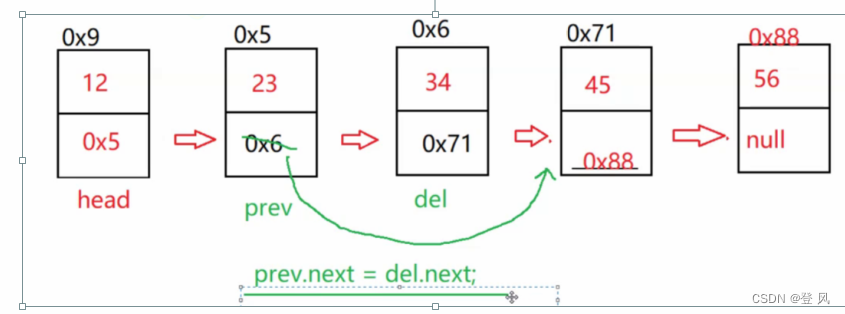
删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点

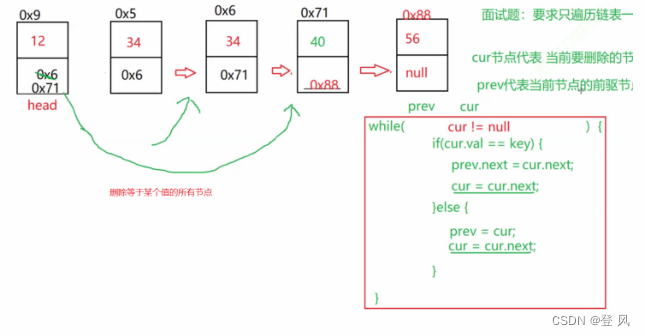
删除所有值为key的节点

clear

上述单链表的所有代码
MySingleList
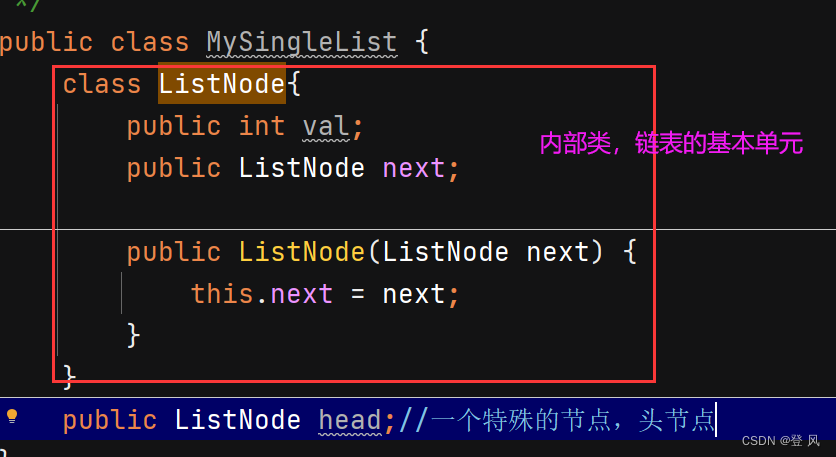
public class MySingleList {
class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;//一个特殊的节点,头节点
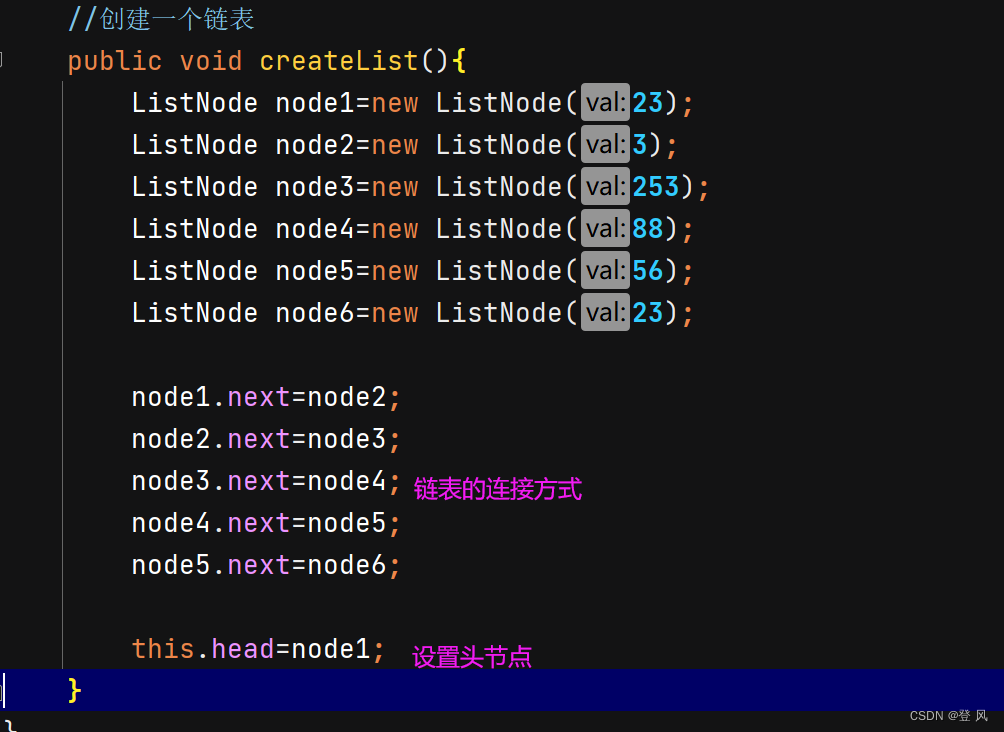
//创建一个链表
public void createList(){
ListNode node1=new ListNode(23);
ListNode node2=new ListNode(3);
ListNode node3=new ListNode(253);
ListNode node4=new ListNode(88);
ListNode node5=new ListNode(56);
ListNode node6=new ListNode(23);
node1.next=node2;
node2.next=node3;
node3.next=node4;
node4.next=node5;
node5.next=node6;
this.head=node1;
}
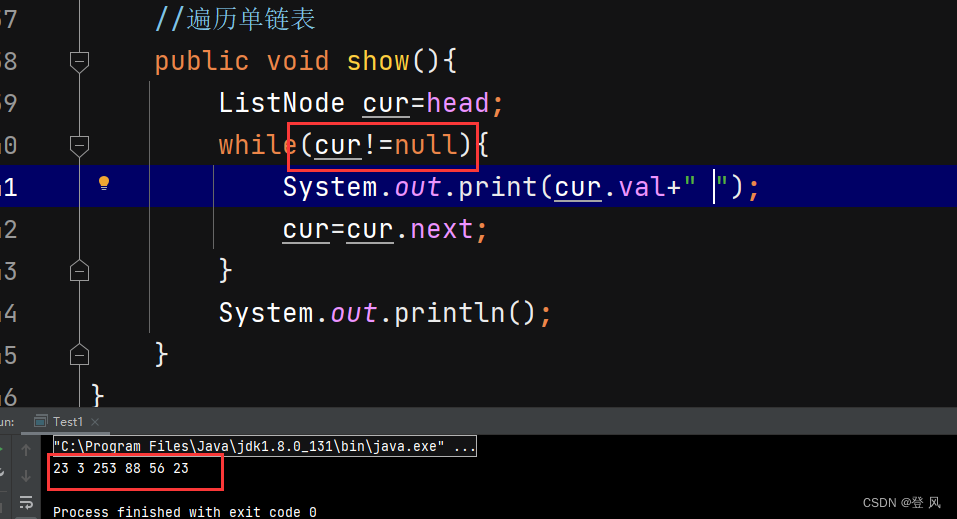
//遍历单链表
public void show(){
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//链表的长度
public int size(){
int count=0;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
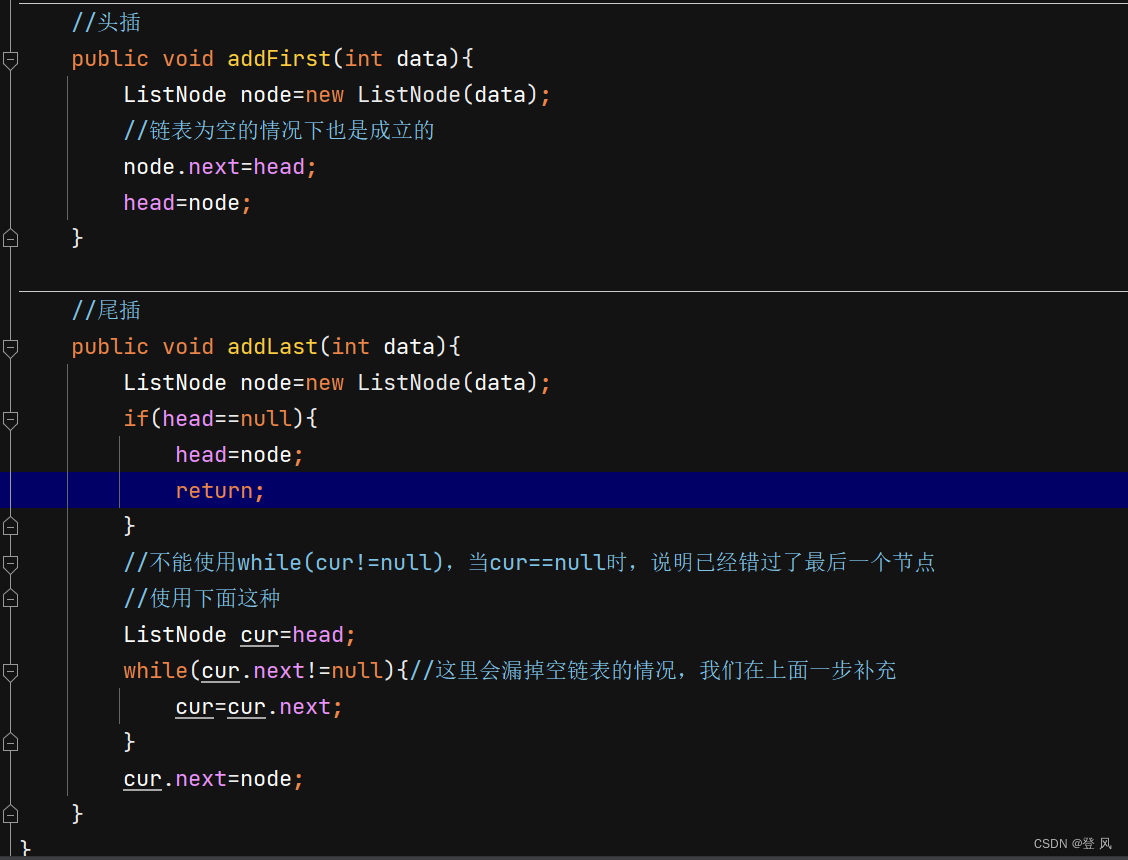
//头插
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
//链表为空的情况下也是成立的
node.next=head;
head=node;
}
//尾插
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
if(head==null){
head=node;
return;
}
//不能使用while(cur!=null),当cur==null时,说明已经错过了最后一个节点
//使用下面这种
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur.next!=null){//这里会漏掉空链表的情况,我们在上面一步补充
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=node;
}
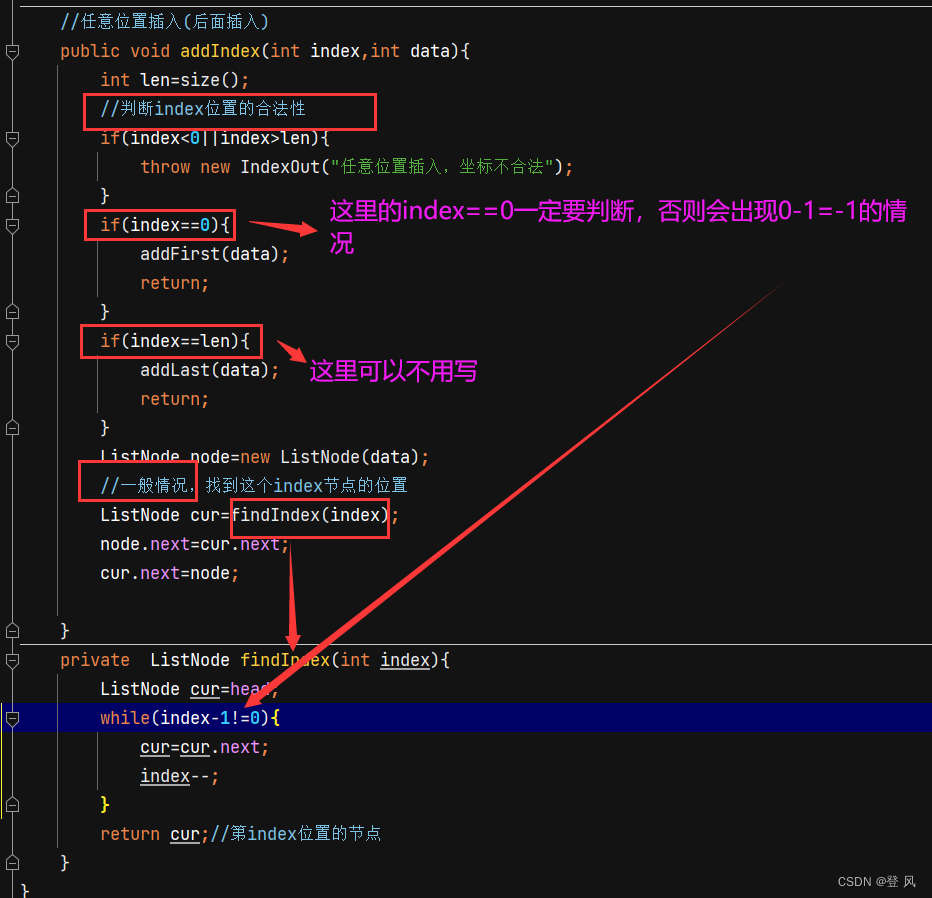
//任意位置插入(后面插入)
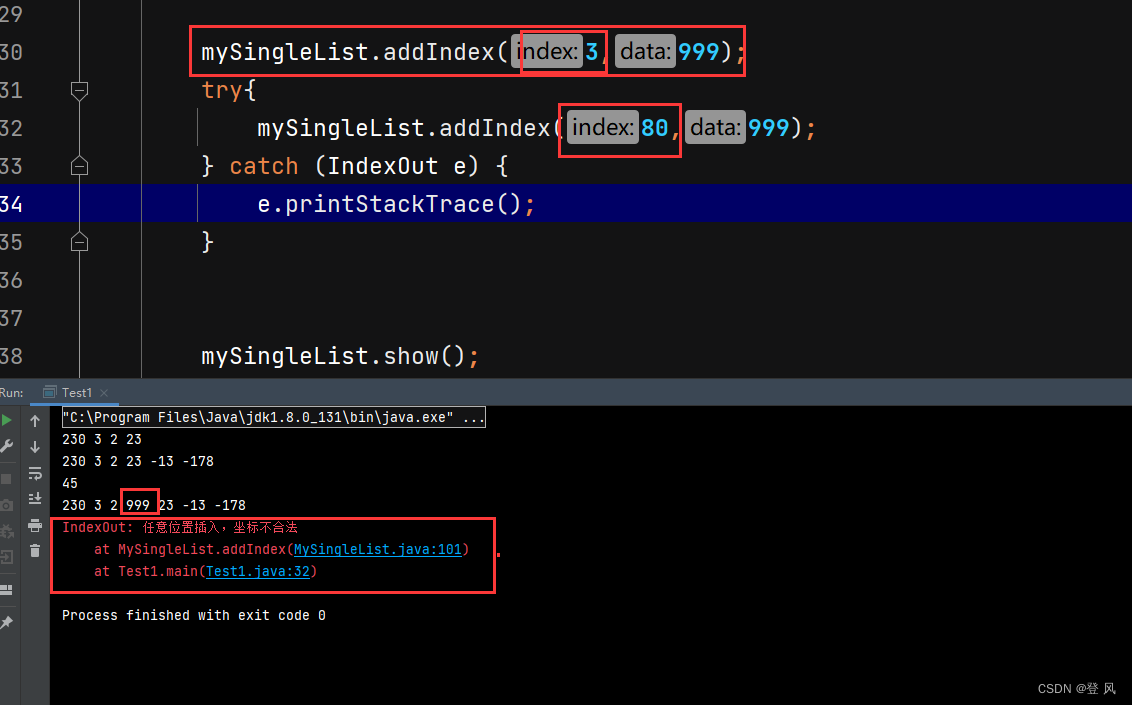
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
int len=size();
//判断index位置的合法性
if(index<0||index>len){
throw new IndexOut("任意位置插入,坐标不合法");
}
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
/* if(index==len){
addLast(data);
return;
}*/
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
//一般情况,找到这个index节点的位置
ListNode cur=findIndex(index);
node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
}
private ListNode findIndex(int index){
ListNode cur=head;
while(index-1!=0){
cur=cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;//第index位置的节点
}
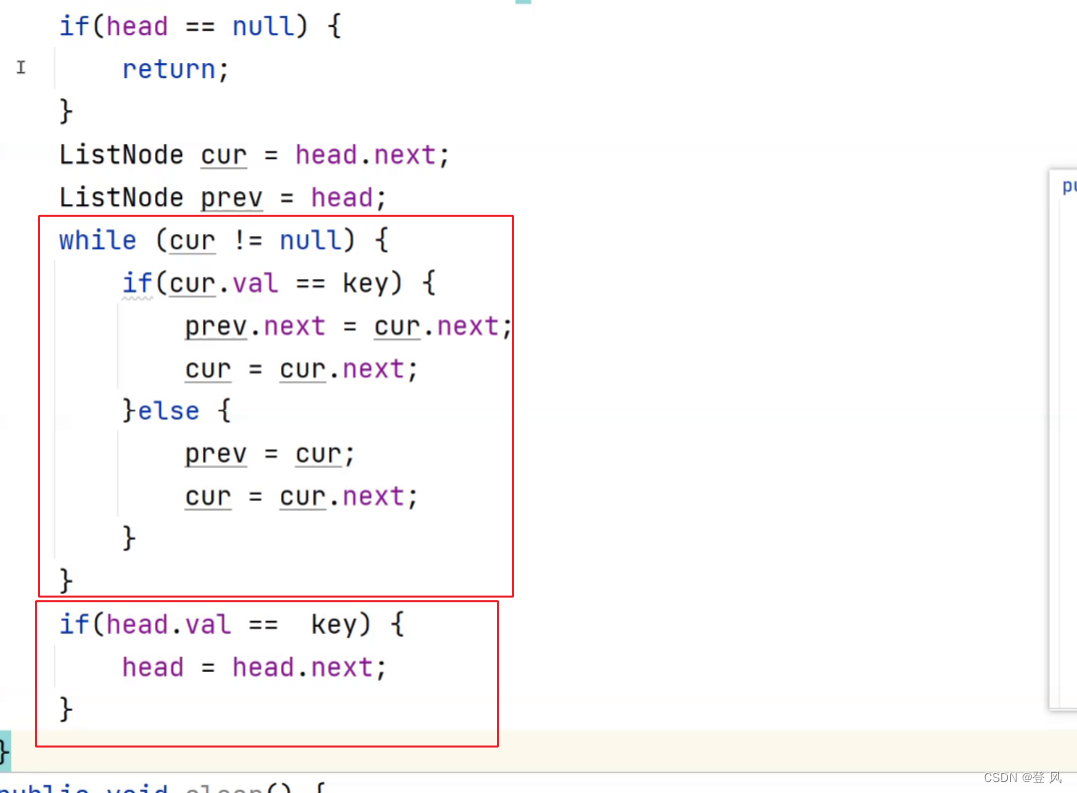
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
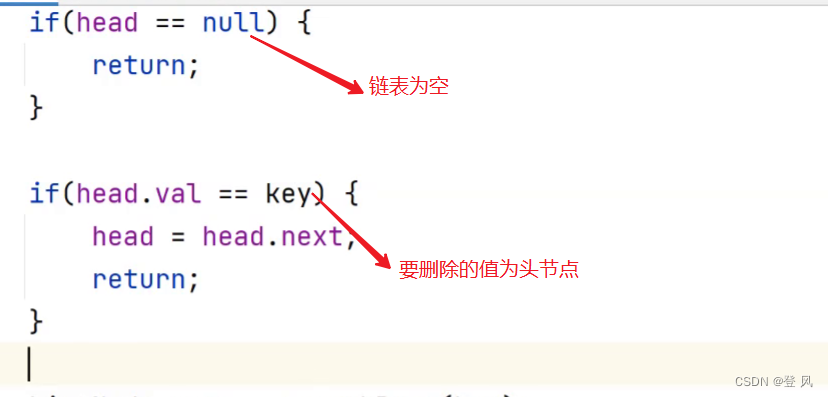
public void remove(int key){
if(head==null){
return;
}
if(head.val==key){//因为在searchPrev中的判断条件为prev.next==null,忽略掉了头节点,这里补充判断
head=head.next;
return;
}
ListNode prev=searchPrev(key);
if(prev==null){
System.out.println("没有这个数据");
return;
}
ListNode del=prev.next;
prev.next=del.next;
}
private ListNode searchPrev(int key){
ListNode prev =head;
while(prev.next!=null){//这里将会使用双指针,prev为待删除节点的前一个节点,因此判断条件要使用prev.next==null,而不是prev==null
if(prev.next.val==key){//上面的条件为遍历链表,这里的条件为判断条件
return prev;
}else{
prev=prev.next;
}
}
return null;
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if(head==null){
return;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
ListNode prev=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
prev.next=cur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val==key){//观察到前面的cur为head.next,漏掉了对head的val值的判断,这里补充上
head=head.next;
}
}
//clear
public void clear(){
this.head=null;
}
}
IndexOut
public class IndexOut extends RuntimeException {
public IndexOut() {
}
public IndexOut(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
Test1
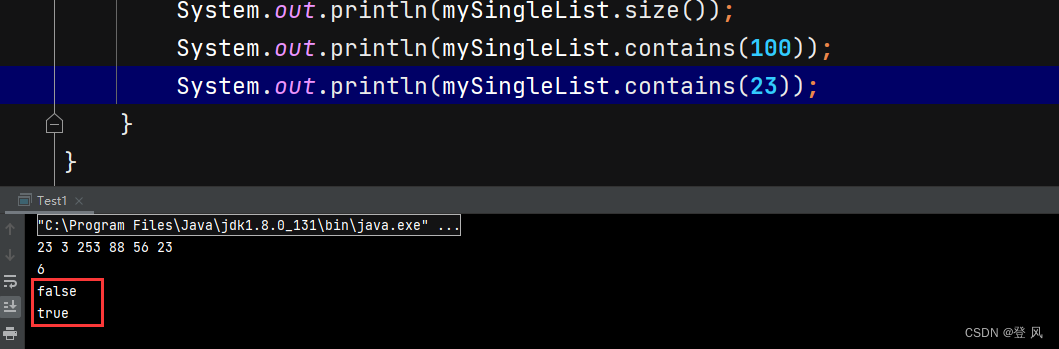
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySingleList mySingleList=new MySingleList();
/* mySingleList.createList();
mySingleList.show();
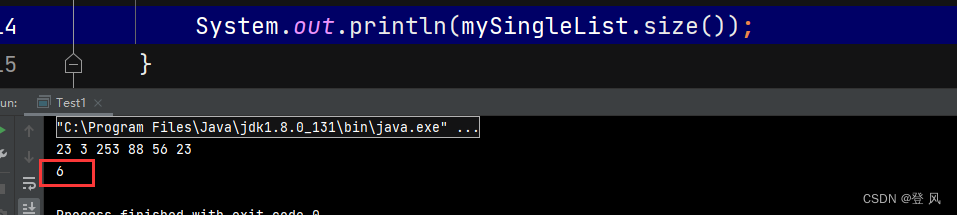
System.out.println(mySingleList.size());
System.out.println(mySingleList.contains(100));
System.out.println(mySingleList.contains(23));
mySingleList.show();*/
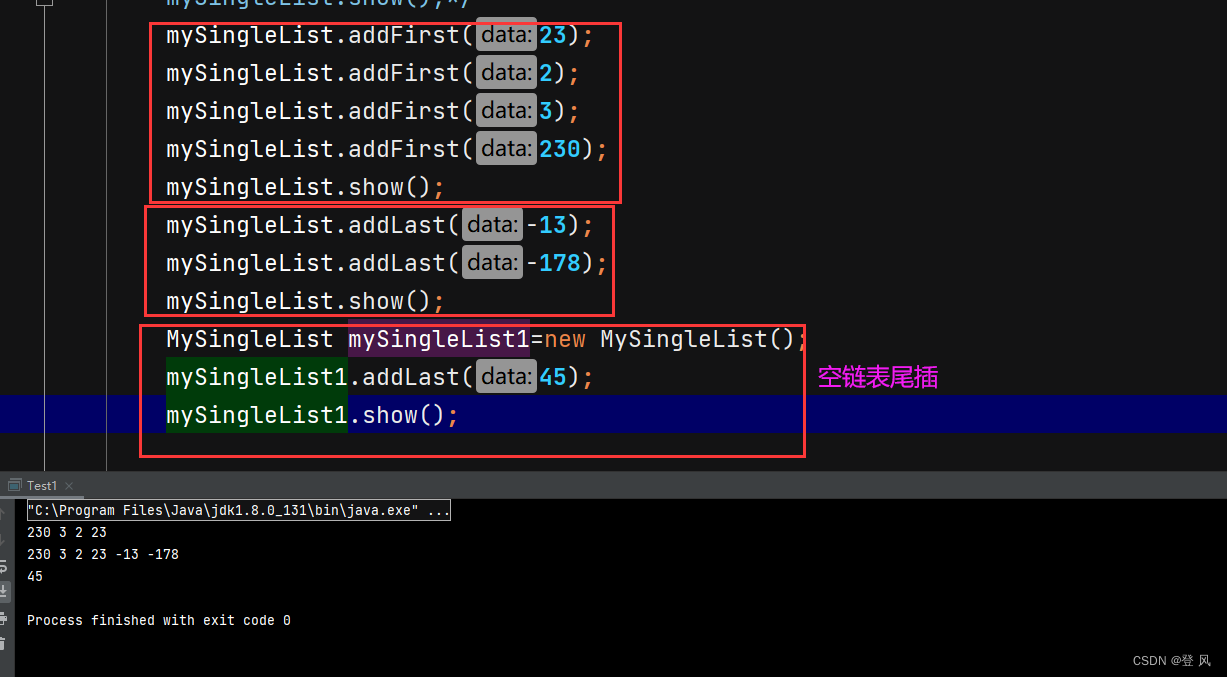
mySingleList.addFirst(23);
mySingleList.addFirst(2);
mySingleList.addFirst(3);
mySingleList.addFirst(230);
mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.addLast(-13);
mySingleList.addLast(-178);
mySingleList.show();
MySingleList mySingleList1=new MySingleList();
mySingleList1.addLast(45);/*
mySingleList1.show();
mySingleList.addIndex(3,999);
try{
mySingleList.addIndex(4,999);
} catch (IndexOut e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySingleList.addIndex(mySingleList.size(), 56);*/
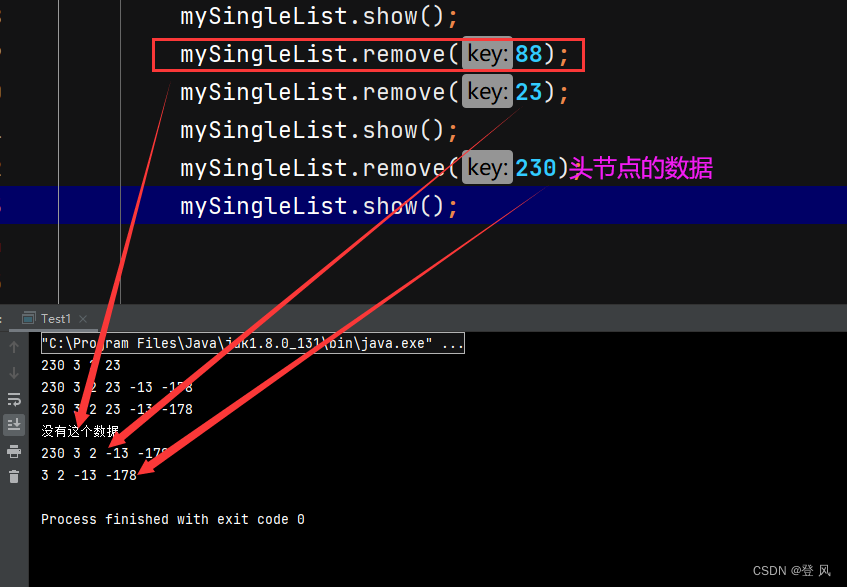
/* mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.remove(88);
mySingleList.remove(23);
mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.remove(230);*/
/* mySingleList.show();
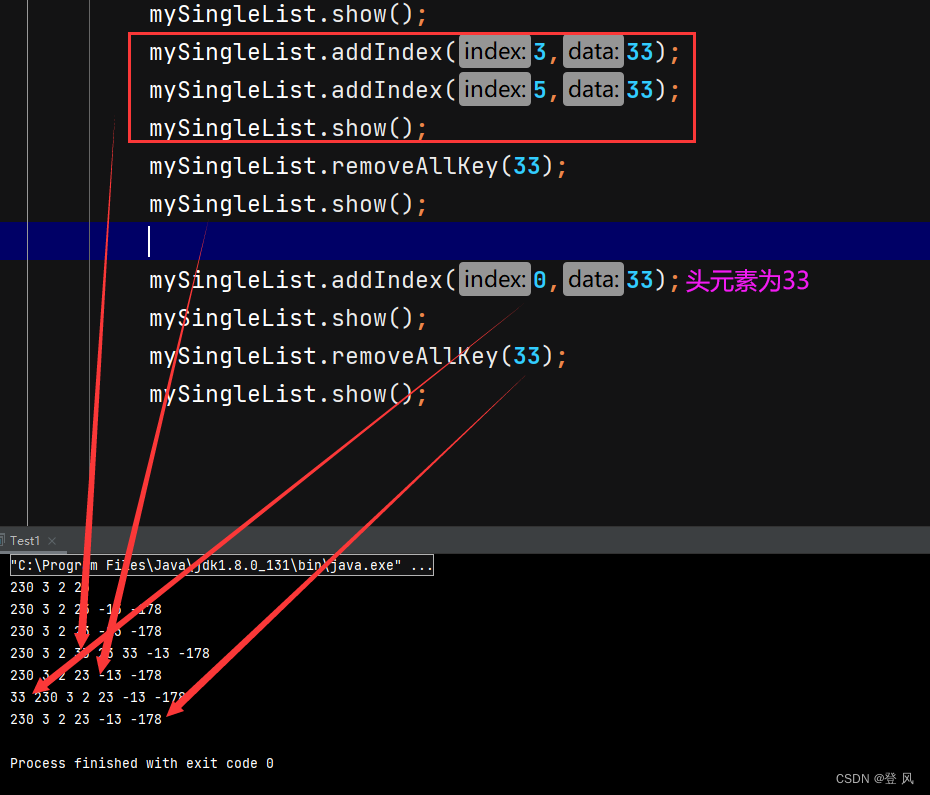
mySingleList.addIndex(3,33);
mySingleList.addIndex(5,33);
mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.removeAllKey(33);
mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.addIndex(0,33);
mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.removeAllKey(33);*/
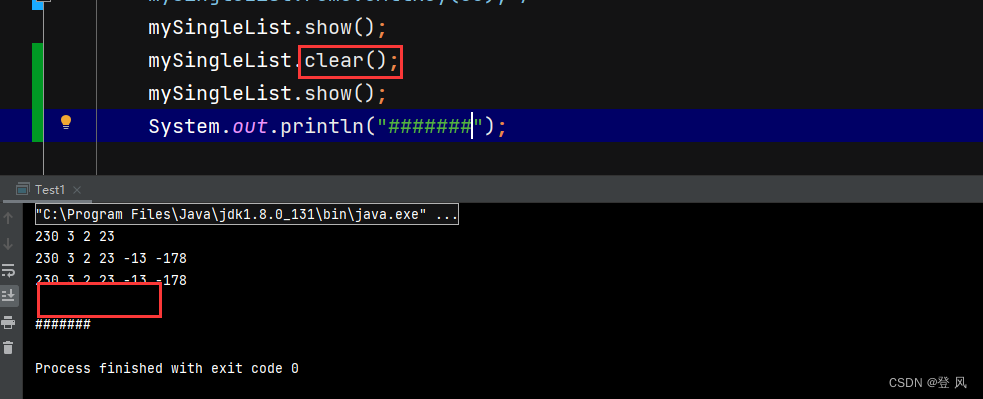
mySingleList.show();
mySingleList.clear();
mySingleList.show();
System.out.println("#######");
}
}