1. 时钟组件:AnalogClock与DigitalClock
1.1 知识点
(1)掌握AnalogClock与DigitalClock的使用;
1.2 具体内容

package com.example.clockproject;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.Menu;
public class ClockActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_clock);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.clock, menu);
return true;
}
}时钟组件没有什么太复杂的操作,不过在后面讲解线程操作的时候,会用的此种组件。
1.3 小结
(1)AnalogClock可以完成指针时钟的显示;
(2)DigitalClock可以完成数字时钟的显示。
2. 计时器:Chronometer
2.1 知识点
(1)掌握Chronometer组件的使用及操作;
(2)可以在手机开发中使用震动服务;
2.2 具体内容


<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".ChronometerActivity" >
<Chronometer
android:id="@+id/myChronometer"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/butStart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="开始计时"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/butStop"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="停止计时"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/butReset"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="复位"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/butFormat"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="格式化显示"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.chronometerproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Chronometer;
public class ChronometerActivity extends Activity {
Button butStart,butStop,butReset,butFormat = null;
Chronometer myChronometer = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_chronometer);
butStart = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butStart);
butStop = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butStop);
butReset = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butReset);
butFormat = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butFormat);
myChronometer = (Chronometer) super.findViewById(R.id.myChronometer);
butStart.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
butStop.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
butReset.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
butFormat.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
}
private class OnClickListenerImpl implements OnClickListener{
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.butStart:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.start();
break;
case R.id.butStop:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.stop();
break;
case R.id.butReset:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());//设置基准时间
break;
case R.id.butFormat:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.setFormat("新的格式:%s");//格式化
}
}
}
}
计时器的功能并不复杂,但是可以结合一些系统服务,实现一些有意思的操作。
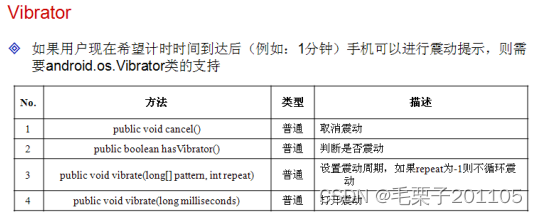
震动必须用真机进行测试。
package com.example.chronometerproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.os.Vibrator;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Chronometer;
import android.widget.Chronometer.OnChronometerTickListener;
public class ChronometerActivity extends Activity {
Button butStart,butStop,butReset,butFormat = null;
Chronometer myChronometer = null;
Vibrator vb = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_chronometer);
butStart = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butStart);
butStop = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butStop);
butReset = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butReset);
butFormat = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.butFormat);
myChronometer = (Chronometer) super.findViewById(R.id.myChronometer);
butStart.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
butStop.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
butReset.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
butFormat.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListenerImpl());
myChronometer.setOnChronometerTickListener(new OnChronometerTickListener() {
@Override
public void onChronometerTick(Chronometer chronometer) {
String time = chronometer.getText().toString();
if("0:30".equals(time)){
ChronometerActivity.this.vb.vibrate(new long[]{1000,10,1000,100}, 0);//设置震动周期震动的形式
}
}
});
vb = (Vibrator) super.getApplication().getSystemService(Service.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
}
private class OnClickListenerImpl implements OnClickListener{
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch(v.getId()){
case R.id.butStart:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.start();
break;
case R.id.butStop:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.stop();
ChronometerActivity.this.vb.cancel();
break;
case R.id.butReset:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());//设置基准时间
break;
case R.id.butFormat:
ChronometerActivity.this.myChronometer.setFormat("新的格式:%s");//格式化
}
}
}
}
手机震动为系统服务,需要获取权限
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE"
/>2.3 小结
(1)Chronometer可以完成计时器的操作;
(2)如果手机要想完成震动的操作,则可以使用“Service.VIBRATOR_SERVICE ”服务。
3. 标签:TabHost
3.1 知识点
(1)掌握标签组件的使用,并可以使用标签组件进行程序界面分割;
(2)可以通过配置文件完成标签组件的显示;
(3)可以通过程序完成标签组件的显示。
3.2 具体内容

有了标签之后,在一定的屏幕空间就可以显示更多的内容,在这样的界面中,有多个Tab,多个Tab就组成了一个TabHost。
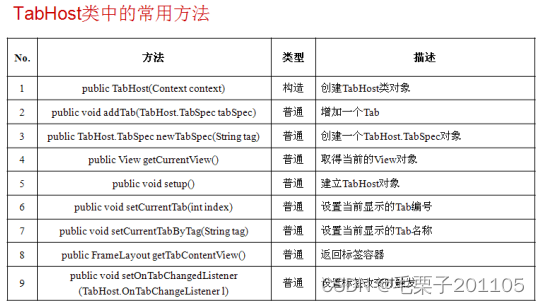

我们先使用第一种方式来完成,注意观察操作形式。
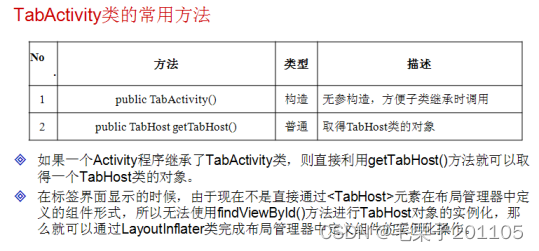
要继TabActivity的原因在于这种Activity提供两个关键的方法可以让我们完成标签页的创建。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".TabHostActivity" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_edit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="input here..."
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/but"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Serach"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_clock"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/clock"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_sex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/sex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:checkedButton="@+id/woman"
>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/man"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="MAN"
/>
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/woman"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="WOMAN"
/>
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.tabhostproject;
import android.app.TabActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class TabHostActivity extends TabActivity {
TabHost tabHost = null;
int layRes[]={R.id.tab_edit,R.id.tab_clock,R.id.tab_sex};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.tabHost = super.getTabHost();
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.activity_tab_host, //定义要转换的布局管理局
this.tabHost.getTabContentView(),//指定标签添加的容器
true);//实例化布局管理器中的组件
for(int i = 0;i<layRes.length;i++){
TabHost.TabSpec myTab = this.tabHost.newTabSpec("tab"+i);
myTab.setIndicator("标签"+i);//标签文字
myTab.setContent(layRes[i]);
this.tabHost.addTab(myTab);//添加标签
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.tab_host, menu);
return true;
}
}以上的代码是采用直接集成TabActivity来实现的标签页效果,如果你还继承Activity同时还能实现标签页,那么就需要第二种形式。
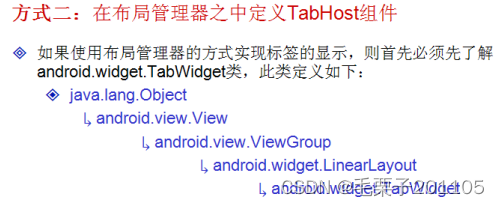
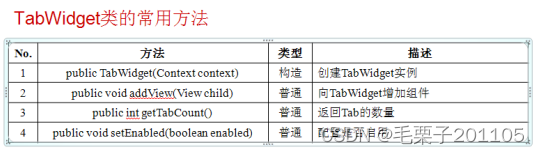

package com.example.tabhostproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class TabHostActivity extends Activity {
TabHost tabHost = null;
int layRes[]={R.id.tab_edit,R.id.tab_clock,R.id.tab_sex};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.tab_host_widget);
tabHost = (TabHost) super.findViewById(R.id.tabhost);
this.tabHost.setup();//创建TabHost对象
for(int i=0;i<layRes.length;i++){
TabHost.TabSpec myTab = this.tabHost.newTabSpec("tab"+i);
myTab.setIndicator("标签"+(i+1));//设置标签文字
myTab.setContent(layRes[i]);
this.tabHost.addTab(myTab);
}
this.tabHost.setCurrentTab(0);//设置开始索引
}
}
<TabHost
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_edit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="input here..." />
<Button
android:id="@+id/but"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Serach" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_clock"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/clock"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_sex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/sex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checkedButton="@+id/woman"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/man"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="MAN" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/woman"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="WOMAN" />
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost>我们现在实现了和第一种方式同样的显示效果,现在呢我们想要把标签放到屏幕的下方,那么只需要修改两个地方。
<TabHost
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_edit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edt"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="input here..." />
<Button
android:id="@+id/but"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Serach" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_clock"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/clock"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tab_sex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/sex"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checkedButton="@+id/woman"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/man"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="MAN" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/woman"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="WOMAN" />
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
</FrameLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
</TabHost>3.3 小结
(1)使用Tab标签可以实现程序的分栏显示;
(2)Tab的实现可以通过继承TabActivity类实现也可以通过配置实现;
(3)通过配置实现的Tab较为麻烦。





![[论文分享]VOLO: Vision Outlooker for Visual Recognition](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/66aca6a3aea648df8876cc9df3b44d8d.png)