一、前言
之前我们学习了布尔查询,知道了filter查询只在乎查询条件和文档的匹配程度,但不会根据匹配程度对文档进行打分,而对于must、should这两个布尔查询会对文档进行打分,那如果我想在查询的时候同时不去在乎文档的打分(对搜索结果的排序),只想过滤文本字段是否包含这个词,除了filter查询,我们还会介绍Constant Score查询。相反,如果想干预这个分数,我们会使用Function Score查询,这些都会在后面介绍到。
二、Constant Score查询
如果不想让检索词频率TF(Term Frequency)对搜索结果排序有影响,只想过滤某个文本字段是否包含某个词,可以使用Constant Score将查询语句包装起来。
假设需要查询city字段是否包含关键词“上海”的酒店,则请求的DSL如下:
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": { //满足条件即打分为1(默认值是1)
"filter": {
"term": { //term查询city中是上海的城市
"city": "上海"
}
}
}
}
}
查询结果如下:
{
...
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "hotel",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "004",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "京盛集团酒店",
"city" : "上海",
"price" : "800.00",
"create_time" : "2021-05-29 21:35:00",
"amenities" : "浴池(假日需预订),室内游泳池,普通停车场/充电停车场",
"full_room" : true,
"location" : {
"lat" : 36.940243,
"lon" : 120.394
},
"praise" : 100
}
},
{
"_index" : "hotel",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "006",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "京盛集团精选酒店",
"city" : "上海",
"price" : "500.00",
"create_time" : "2022-01-29 22:50:00",
"full_room" : true,
"location" : {
"lat" : 40.918229,
"lon" : 118.422011
},
"praise" : 20
}
}
]
}
}
通过结果可以看到,使用Constant Score搜索时,命中的酒店文档对应的city字段都包含“上海”一词。但是不论该词在文档中出现多少次,这些文档的得分都是一样的1.0.
PS:很多人可能会把constant_score查询中的filter和布尔查询的filter搞混,constant_score中的filter可以把它想象成普通的query,它后面接的就是各种各样的查询子句。如term,terms,exists,bool等等。
比如我想同时使用must查询创建时间大于等于2022-01-29 22:50:00的hotel且不在乎打分,那么可以使用下面的DSL:
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"range": {
"create_time": {
"gte": "2022-01-29 22:50:00"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
在Constant Score搜索中,参数boost可以控制命中文档的得分,默认值都是1.0,以下为更改boost参数为2.0的例子:
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"boost":2.0,
"filter": {
"term": {
"city": "上海"
}
}
}
}
}
查询结果如下:
{
...
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 2.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "hotel",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "004",
"_score" : 2.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "京盛集团酒店",
"city" : "上海",
"price" : "800.00",
"create_time" : "2021-05-29 21:35:00",
"amenities" : "浴池(假日需预订),室内游泳池,普通停车场/充电停车场",
"full_room" : true,
"location" : {
"lat" : 36.940243,
"lon" : 120.394
},
"praise" : 100
}
},
{
"_index" : "hotel",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "006",
"_score" : 2.0,
"_source" : {
"title" : "京盛集团精选酒店",
"city" : "上海",
"price" : "500.00",
"create_time" : "2022-01-29 22:50:00",
"full_room" : true,
"location" : {
"lat" : 40.918229,
"lon" : 118.422011
},
"praise" : 20
}
}
]
}
}
根据搜索结果可以看到,设定Boost值为2.0后,所有的命中的文档得分都为2.0。
然后对于Constant Score的效率问题,我们拿它和上一节讲到的filter查询做一个对比:
- Constant Score查询实际上就是一个没有分值函数的查询,它会将所有匹配文档的分值设置为一个常量。这种查询不需要计算每个匹配文档的相关度,所以效率会比普通查询高。
- 但是Constant Score查询还需要执行查询本身,比如匹配查询条件、过滤文档等步骤。而filter查询仅仅过滤文档,不计算分值,所以整体效率比Constant Score查询更高。
- Constant Score查询不会像filter查询那样缓存过滤结果。因为Constant Score查询还需要计算每个匹配文档的分值,而这一步不受过滤结果缓存的影响。
- 所以总的来说,在效率方面: filter查询 > Constant Score查询 > 普通查询
在java客户端上构建Constant Score搜索时,可以使用ConstantScoreQueryBuilder类的实例进行构建,它接收一个QueryBuilder参数,即可以接收termQueryBuilder,termsQueryBuilder,boolQueryBuilder等等,和之前的DSL是一样的,那么比如我们查询一个城市是上海或者北京的酒店,代码如下:
Service层,getQueryResult()可以看往期的博客,有具体的方法实现:
public List<Hotel> constantScore(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException {
//新建搜索请求
String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest);
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder1 = QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "北京");
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder2 = QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "上海");
BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
boolQueryBuilder.should(termQueryBuilder1).should(termQueryBuilder2);
//构建ConstantScoreBuilder
ConstantScoreQueryBuilder constantScoreQueryBuilder = new ConstantScoreQueryBuilder(boolQueryBuilder);
//设置固定分数2.0
constantScoreQueryBuilder.boost(2.0f);
searchSourceBuilder.query(constantScoreQueryBuilder);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
return getQueryResult(searchRequest);
}
Controller层:
@PostMapping("/query/constant_score")
public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> constantScoreQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) {
try {
List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.constantScore(hotelDocRequest);
if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) {
return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList);
} else {
return FoundationResponse.error(100,"no data");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());
return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());
return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());
}
}
Postman实现:
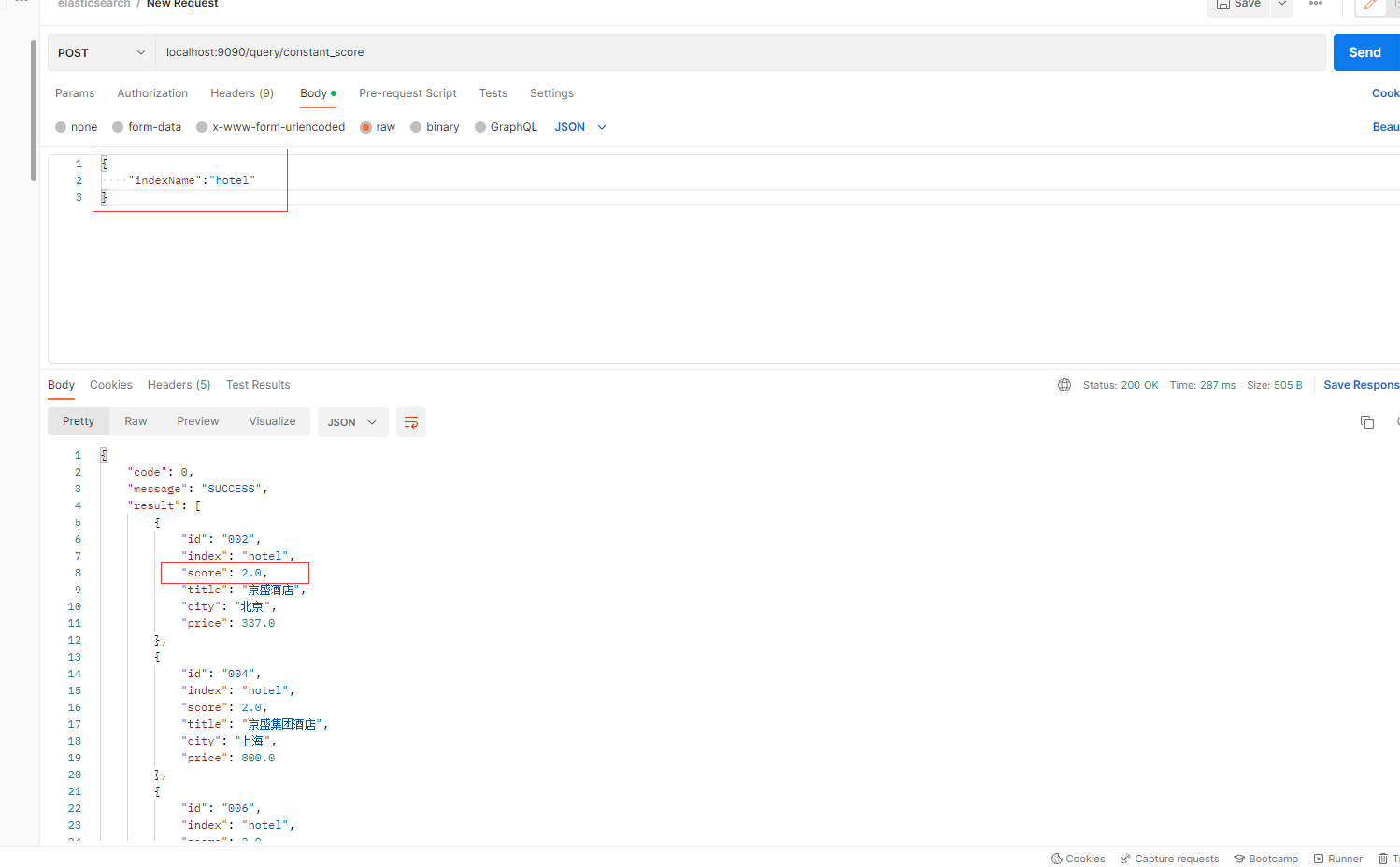
三、Function Score查询
当你使用ES进行搜索时,命中的文档默认按照相关度进行排序,有些场景下用户需要干预该“相关度”,此时就可以使用Function Score查询。使用时,用户必须定义一个查询以及一个或多个函数,这些函数为每一个文档计算一个新分数。
它允许每个主查询query匹配的文档应用加强函数,以达到改变原始查询评分_score的目的。
3.1、function_score 查询模板
function_score 查询模板可以分为两类,分别为单个加强函数的查询和多个加强函数的查询。
单个加强函数的查询模板:
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {.....}, // 主查询,查询完后会有一个 _score 评分
"field_value_factor": {...}, // 在 _score 的基础上进行强化评分
"boost_mode": "multiply", // 指定用哪种方式结合 _score 和 强化 score
"max_boost": 1.5 // 限制强化 score 的最高分,但是不会限制 _score
}
}
}
多个加强函数的查询模板:
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {.....},
"functions": [ // 可以有多个加强函数(或是 filter+加强函数),每一个加强函数会产生一个加强 score
{ "field_value_factor": ... },
{ "gauss": ... },
{ "filter": {...}, "weight": ... }
],
"score_mode": "sum", // 决定加强 score 们如何整合
"boost_mode": "multiply" // 决定最后的 functions 中 score 和 query score 的结合方式
}
}
}
3.2、function_score 参数
强化 _score 计算的函数
function_score 提供了几种内置加强 _score 计算的函数功能:
weight:设置一个简单而不被规范化的权重提升值。
weight 加强函数和 boost 参数比较类似,可以用于任何查询,不过有一点差别是 weight 不会被 Lucene 规范化(normalize)成难以理解的浮点数,而是直接被应用。
例如,当 weight 为 2 时,最终得分为 new_score = 2 * _score。
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"term": {
"city": {
"value": "上海"
}
}
},
"weight":2
}
}
}
输出后可以对比一下不加weight的默认分数,基本分数都翻了2倍
field_value_factor:指定文档中某个字段的值结合 _score 改变分数
属性如下:
field:指定字段名
factor:对字段值进行预处理,乘以(或者加,取决于boost_mode)指定的数值(默认为1)
modifier:将字段值进行加工,有以下的几个选项:
none:不处理log:计算对数log1p:先将字段值+1,再计算对数log2p:先将字段值+2,再计算对数ln:计算自然对数ln1p:先将字段值+1,再计算自然对数ln2p:先将字段值+2,再计算自然对数square:计算平方sqrt:计算平方根reciprocal:计算倒数
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {.....},
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "price",
"modifier": "none",
"factor": 1.2
},
"boost_mode": "multiply",
"max_boost": 1.5
}
}
}
调整后的 function 分数公式为,factor * doc['price'].value;如果boos_mode设定为sum,那么分数公式为factor + doc['price'].value;
例如我们让最终的分数以price字段进行增强,在原分数基础上*1.2
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"term": {
"city": {
"value": "上海"
}
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field":"price",
"factor": 1.2
},
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
再例如我想对字段值先乘1.2再+1再取对数,那么DSL如下:
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"term": {
"city": {
"value": "上海"
}
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field":"price",
"modifier": "ln1p",
"missing":1.0,
"factor": 1.2
},
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
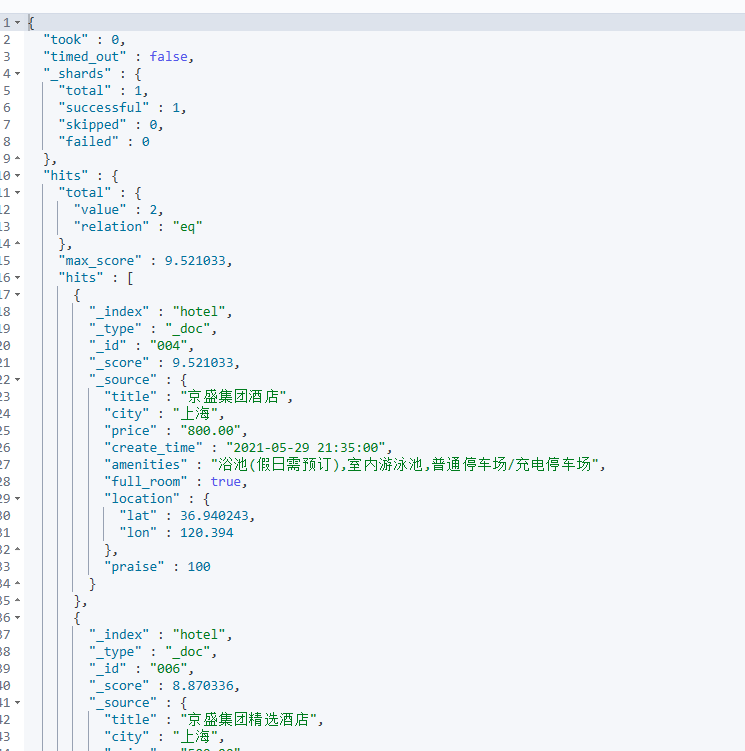
function 分数为,ln1p(1.2 * doc['view_cnt'].value),如果指定字段缺失用 missing 对应的值,至于和匹配的相关性分数 _score 如何结合需要下面的 boost_mode 参数来决定。
random_score:使用一致性随机分值计算来对每个用户采用不同的结果排序方式,对相同用户仍然使用相同的排序方式,其本质上用的是seed 种子参数,用户相关的 id 与 seed 构造映射关系,就可千人千面的效果,seed 不同排序结果也不同。具体示例如下:
①字段值相同,例如通过full_room,由上面查询结果可知,两个结果的full_room相同,此时使用random_score,两个的排序结果仍然是一致的:
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"term": {
"city": {
"value": "上海"
}
}
},
"random_score": {
"field":"full_room",
"seed": 10
},
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
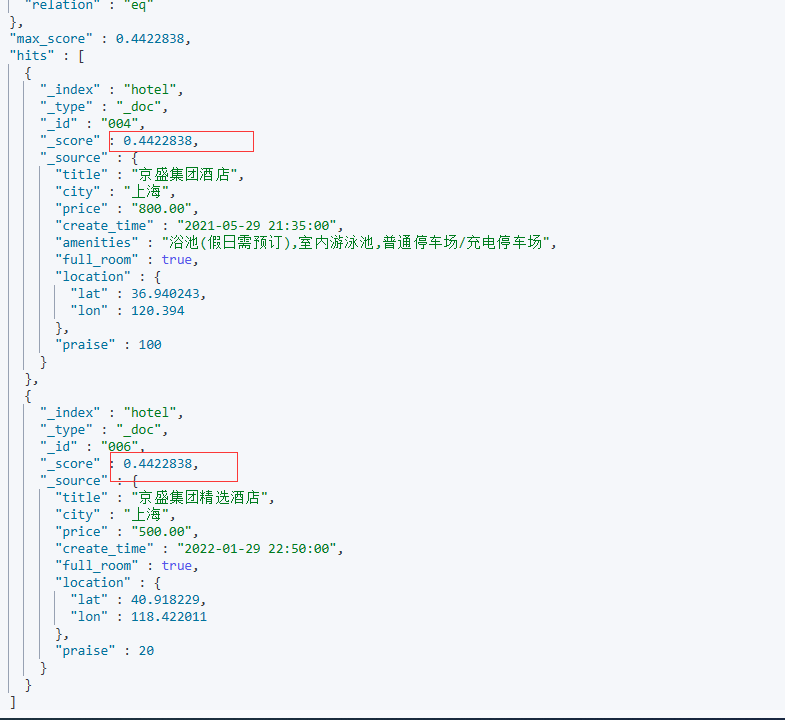
如果对price进行随机加强,那么排序就会不一样:
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"term": {
"city": {
"value": "上海"
}
}
},
"random_score": {
"field":"price",
"seed": 10
},
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}

我们可以调整seed,就会发现排序不一样。
衰减函数(decay function):es 内置了三种衰减函数,分别是 linear、exp 和 gauss;
三种衰减函数的差别只在于衰减曲线的形状,在 DSL 的语法上的用法完全一样;
linear : 线性函数是条直线,一旦直线与横轴0香蕉,所有其他值的评分都是0
exp : 指数函数是先剧烈衰减然后变缓
guass(最常用) : 高斯函数则是钟形的,他的衰减速率是先缓慢,然后变快,最后又放缓
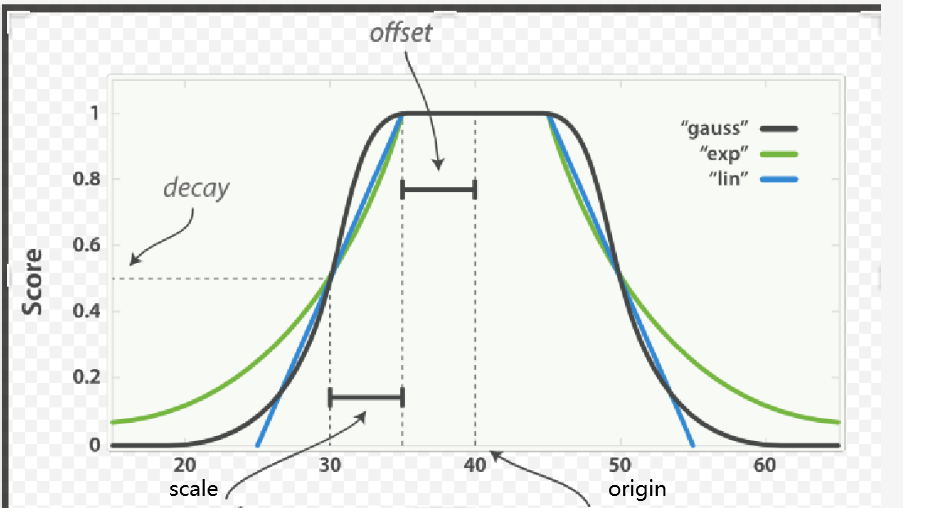
origin:中心点 或字段可能的最佳值,落在原点 origin 上的文档评分 _score 为满分 1.0 。
scale:衰减率,即一个文档从原点 origin 下落时,评分 _score 改变的速度。(例如,每 £10 欧元或每 100 米)。
decay:从原点 origin 衰减到 scale 所得的评分 _score ,默认值为 0.5 。
offset:以原点 origin 为中心点,为其设置一个非零的偏移量 offset 覆盖一个范围,而不只是单个原点。在范围 -offset <= origin <= +offset 内的所有评分 _score 都是 1.0 。不设置默认是0
POST /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"term": {
"city": {
"value": "上海"
}
}
},
"gauss": {
"price": {
// 如果不设置offset,offset默认为0 公式 : origin-offset <= value <= origin+offset
// 范围在800-0 <= value <= 800+0的文档的评分_score都是满分1.0
//而在此范围之外,评分会开始衰减,衰减率由scale值(此处是300)和decay值(此处是0.2)决定
// 也就是说,在origin + offset + scale或是origin - offset - scale的点上,得到的分数仅有decay分
"origin": "800",
"scale": "300",
"decay": 0.2
}
},
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}
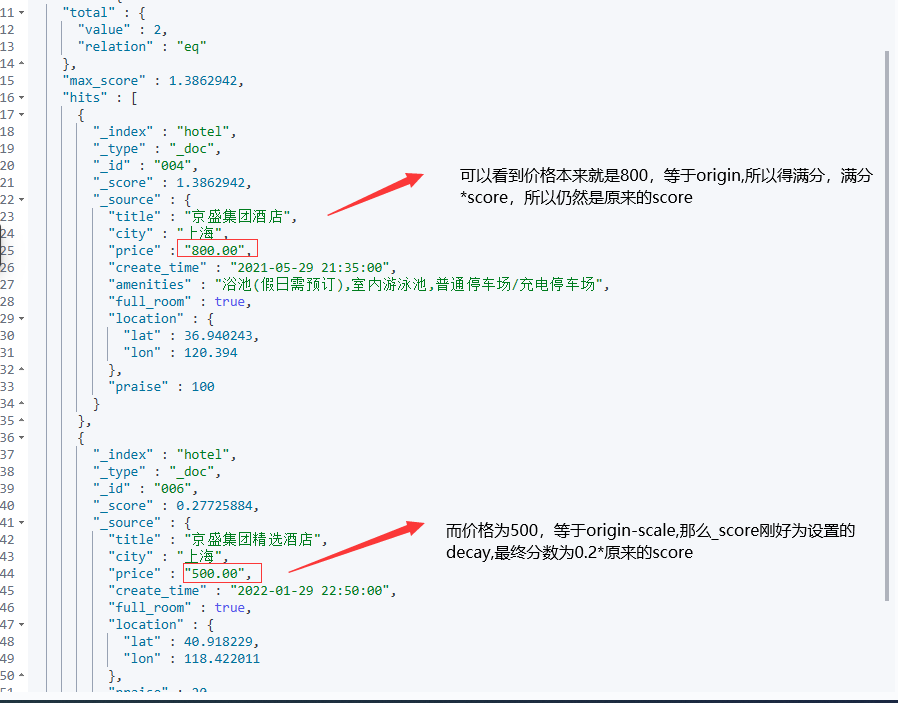
对衰减函数感兴趣的小伙伴可以浏览这篇文章,讲的很详细,尤其是最后对于用户同时对于酒店的地理位置和价格去做一个筛选。
script_score:当需求超出以上范围时,可以用自定义脚本完全控制评分计算。
3.3、其它辅助函数
boost_mode参数:决定 query 中的相关性分数和加强的函数分数的结合方式。
multiply:默认的配置,两者分数相乘,new_score = _score * boost_score;
sum:两者相加,new_score = _score + boost_score;
min:取两者最小值,new_score = min(_score, boost_score);
max:取两者最大值,new_score = max(_score, boost_score);
replace:用 boost_score 替换 _score 值。有时候我们可以通过replace看具体的函数得分是多少,便于我们排查问题
score_mode参数决定 functions 里面的强化 score 如何结合
function_score 先会执行 score_mode 的设置,即先整合所有的强化计算,再执行 boost_mode 的配置,就是将 query 相关性分数和整合强化分数的结合。
multiply:默认的配置,多个强化分数相乘;
sum:多个强化分数相加;
min:取多个强化分数最小值;
max:取多个强化分数最大值;
avg:取多个强化分数平均值;
first:使用首个函数的结果作为最终结果。
max_boost:限制加强函数的最大效果,就是限制加强 score 最大能多少,但要注意不会限制 old_score。
如果加强 score 超过了 max_boost 限制的值,会把加强 score 的值设成 max_boost 的值;
假设加强 score 是5,而 max_boost 是2,因为加强 score 超出了 max_boost 的限制,所以 max_boost 就会把加强 score 改为2。简单的说,就是 final_score = min(整合后的 score, max_boost)。
3.4、java实现
funtion_score的参数我们可以通过ScoreFunctionBuilders.xxx构筑
Service层实现:
public List<Hotel> functionScoreScore(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException {
//新建搜索请求
String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest);
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);
SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
TermQueryBuilder termQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "上海");
//构建FunctionScoreBuilder,比如这里构筑高斯函数(衰减函数)
GaussDecayFunctionBuilder gaussDecayFunctionBuilder = ScoreFunctionBuilders.gaussDecayFunction(hotelDocRequest.getPropertiesName(), 800, 200, 0, 0.2);
//构建Function Score查询
FunctionScoreQueryBuilder functionScoreQueryBuilder = new FunctionScoreQueryBuilder(termQueryBuilder, gaussDecayFunctionBuilder).boostMode(CombineFunction.MULTIPLY);
searchSourceBuilder.query(functionScoreQueryBuilder);
searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);
return getQueryResult(searchRequest);
}
controller层实现:
@PostMapping("/query/function_score")
public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> functionScoreQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) {
try {
List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.functionScoreScore(hotelDocRequest);
if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) {
return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList);
} else {
return FoundationResponse.error(100,"no data");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());
return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());
return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());
}
}
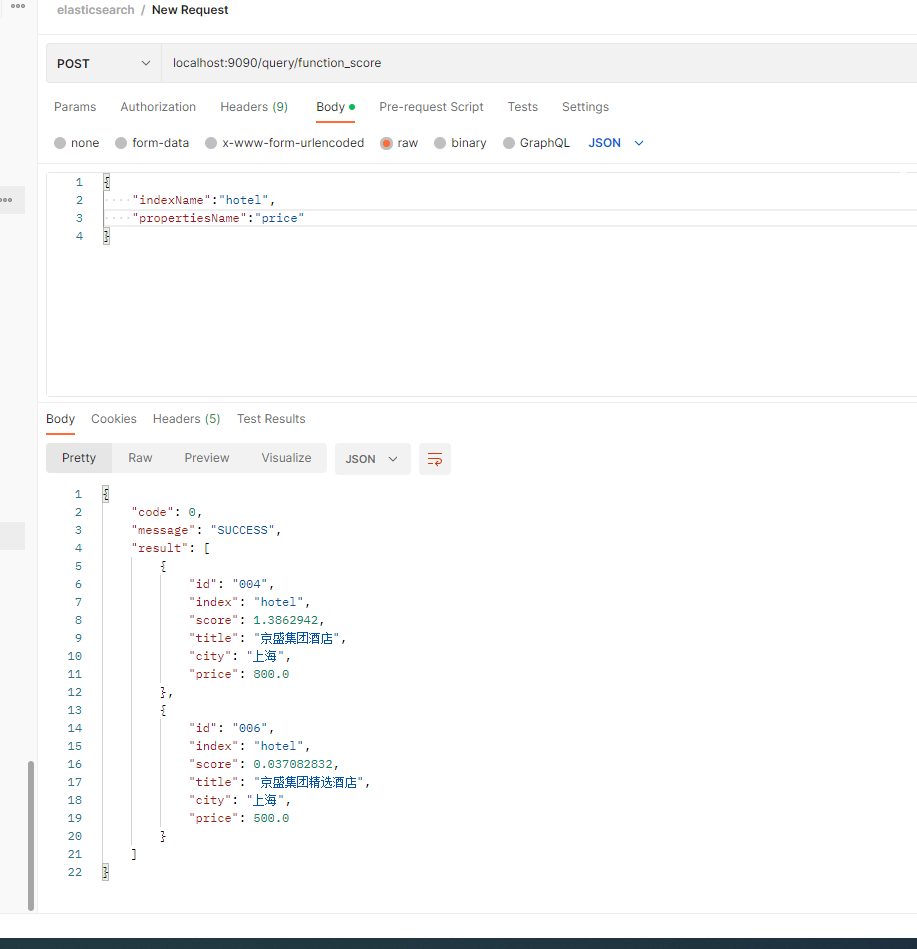
postman实现截图:



![[Mac软件]Pixelmator Pro 3.3.12 专业图像编辑中文版](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/dd42514c0c36a2778cd2eaeeaad43fb5.png)