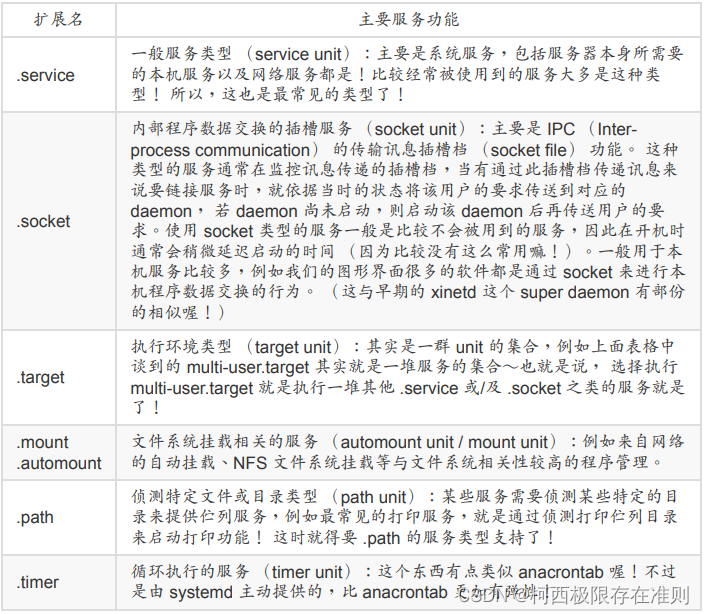
目录
- 1 C entOS 6 的启动管理
- 1.1 Linux 组成
- 1.2 内核设计流派
- 1.3 CentOS 6启动流程
- 1.3.1 CentOs 6 启动流程
- 1.3.1 硬件启动POST
- 1.3.2 bootloader 启动/引导加载器
- 1.3.2.1 grub 功能和组成
- 1.3.2.2 CentOS 6 grub 安装
- 1.3.2.3 grub legacy 管理
- 1.3.3 加载 kernel
- 1.3.4 init 初始化
- 1.3.4.1 运行级别
- 1.3.4.2 初始化脚本 sysinit
- 1.3.4.3 服务管理
- 1.3.4.4 非独立服务
- 1.3.4.5 开机启动文件 rc.local
- 1.3.5 Centos 启动过程总结
- 1.4 自制linux系统
- 1.4.0为当前Linux系统增加硬盘
- 1.4.1 分区并创建文件系统
- 1.4.2 挂载boot
- 1.4.3 安装grub
- 1.4.4 准备内核和initramfs文件
- 1.4.5 手动建立grub.conf
- 1.4.6 准备根下面相关程序和库
- 1.4.7 准备新的虚拟机
- 1.5 启动过程的故障排错
- 1.5.1 实战案例
- 1.5.2 实战案例
- 2 /proc 目录和内核参数管理
- 3 /sys 目录
- 4 内核模块管理和编译
- 4.1 内核版本
- 4.2 内核模块命令
- 4.3 编译内核
- 4.3.1 编译准备
- 4.3.1.1.目标主机硬件设备相关信息
- 4.3.1.2 开发环境相关包
- 4.3.1.3 内核编译安装实现
- 4.3.1.4 编译安装内核实战案例
- 4.3.1.4 内核编译说明
- 4.3.1.5 卸载内核
- 5 Busybox
- 5.1 Busybox介绍
- 5.2 Busybox使用
- 5.3 busybox编译安装
- 6 systemd
- 6.1 systemd 特性
- 6.2 systemctl管理系统服务service unit
- 6.3 service unit文件格式
- 6.4 运行级别
- 6.5 Centos 7之后版本引导顺序
- 6.6 设置内核参数
- 6.7 破解 CentOS 7和8的 root 密码
- 6.8 实现GRUB2安全
- 6.9 修复GRUB2
- 6.10 故障排错实战案例
- 6.10.1 实战案例1: centos 7,8 破坏MBR后进行恢复
- 6.10.2 实战案例2: entos 7,8删除/boot/grub2/*所有内容进行恢复
- 6.10.3 实战案例3: Centos 7,8 删除/boot/下所有文件后进行恢复
1 C entOS 6 的启动管理
1.1 Linux 组成
-
kernel 实现进程管理、内存管理、网络管理、驱动程序、文件系统、安全功能等功能
-
rootfs 包括程序和 glibc 库
程序:二进制执行文件
库: 函数集合,function, 调用接口 (头文件负责描述)
1.2 内核设计流派
-
宏内核(monolithic kernel): 又称单内核和强内核,Unix,Linux
把所有系统服务都放到内核里,所有功能集成于同一个程序,分层实现不同功能,系统庞大复杂Linux其实在单内核内核实现了模块化,也就相当于吸收了微内核的优点
-
微内核(micro kernel): Windows,Solaris,HarmonyOS
简化内核功能,在内核之外的用户态尽可能多地实现系统服务,同时加入相互之间的安全保护,每种功能使用一个单独子系统实现,将内核功能移到用户空间,性能差
1.3 CentOS 6启动流程
1.3.1 CentOs 6 启动流程
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dOSQIoTw-1692688111216)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817112929369.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/04f5532051814e0cb0f6f20c4453d90e.png)
- 加载BIOS的硬件信息,获取第一个启动设备
- 读取第一个启动设备MBR的引导加载程序(grub)的启动信息
- 加载核心操作系统的核心信息,核心开始解压缩,并尝试驱动所有的硬件设备
- 核心执行init程序,并获取默认的运行信息
- init程序执行/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit文件,重新挂载根文件系统
- 启动核心的外挂模块
- init执行运行的各个批处理文件(scripts)
- init执行/etc/rc.d/rc.local
- 执行/bin/login程序,等待用户登录
- 登录之后开始以shell控制主机
1.3.1 硬件启动POST
POST:Power-On-Self-Test,加电自检,是BIOS功能的一个主要部分。负责完成对CPU、主板、内存、硬盘子系统、显示子系统、串并行接口、键盘等硬件情况的检测
主板的ROM:BIOS,Basic lnput and Output System 基本输入输出系统,保存着有关计算机系统最重要的基本输入输出程序,系统信息设置、开机加电自检程序和系统启动自举程序等
主板的RAM:CMOS 互补金属氧化物半导体,保存各项参数的设定,按次序查找引导设备,第一个有引导程序的设备为本次启动设备
1.3.2 bootloader 启动/引导加载器
1.3.2.1 grub 功能和组成
bootloader:引导加载器,引导程序
- windows:ntloader,仅是启动OS
- Linux:功能丰富,提供菜单,允许用户选择要启动系统或不同的内核版本,把用户选定的内核装载到内存中的特定空间中,解压、展开,并把系统控制权移交给内核
Linux的bootloader
- LILO:LInux LOader,早期的bootloader,功能单一,已淘汰
- GRUB:GRand Unified Bootloader,C5/6 使用GRUB 0.97: GRUB Legacy,C7 以后使用GRUB 2.02
GRUB 启动阶段
- primary boot loader:
- 1st stage:MBR的前446个字节)
- 1.5 stage:mbr 之后的扇区,让stage1中的bootloader能识别stage2所在的分区上的文件
- secondary boot loader:2nd stage,分区文件/boot/grub/
例:
[root@CentOS8 ~]#rpm -qa grub*
grub2-tools-minimal-2.02-106.el8.x86_64
grub2-common-2.02-106.el8.noarch
grub2-tools-2.02-106.el8.x86_64
grub2-pc-2.02-106.el8.x86_64
grub2-pc-modules-2.02-106.el8.noarch
grub2-tools-extra-2.02-106.el8.x86_64
grubby-8.40-42.el8.x86_64
[root@CentOS8 ~]#rpm -qi grub2-pc
Name : grub2-pc
Epoch : 1
Version : 2.02
Release : 106.el8
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: Tue 30 May 2023 11:33:23 PM CST
Group : System Environment/Base
Size : 0
1.3.2.2 CentOS 6 grub 安装
安装grub:
(1)grub-install 安装grub stage1和stage1_5到/dev/DISK磁盘上,并复制GRUB相关文件到 DIR/boot
目录下
grub-install --root-directory=DIR /dev/DISK
(2) grub
grub> root (hd#,#)
@第#个硬盘第#个分区
grub> setup (hd#)
例1:破坏C6系统的启动文件的第一阶段的446字节,然后使用救援模式修复
[root@CentOS6 ~]#hexdump -C -n 512 /dev/sda
00000000 eb 48 90 10 8e d0 bc 00 b0 b8 00 00 8e d8 8e c0 |.H..............|
00000010 fb be 00 7c bf 00 06 b9 00 02 f3 a4 ea 21 06 00 |...|.........!..|
00000020 00 be be 07 38 04 75 0b 83 c6 10 81 fe fe 07 75 |....8.u........u|
00000030 f3 eb 16 b4 02 b0 01 bb 00 7c b2 80 8a 74 03 02 |.........|...t..|
00000040 80 00 00 80 a0 0c 05 00 00 08 fa 90 90 f6 c2 80 |................|
00000050 75 02 b2 80 ea 59 7c 00 00 31 c0 8e d8 8e d0 bc |u....Y|..1......|
00000060 00 20 fb a0 40 7c 3c ff 74 02 88 c2 52 f6 c2 80 |. ..@|<.t...R...|
00000070 74 54 b4 41 bb aa 55 cd 13 5a 52 72 49 81 fb 55 |tT.A..U..ZRrI..U|
00000080 aa 75 43 a0 41 7c 84 c0 75 05 83 e1 01 74 37 66 |.uC.A|..u....t7f|
00000090 8b 4c 10 be 05 7c c6 44 ff 01 66 8b 1e 44 7c c7 |.L...|.D..f..D|.|
000000a0 04 10 00 c7 44 02 01 00 66 89 5c 08 c7 44 06 00 |....D...f.\..D..|
000000b0 70 66 31 c0 89 44 04 66 89 44 0c b4 42 cd 13 72 |pf1..D.f.D..B..r|
000000c0 05 bb 00 70 eb 7d b4 08 cd 13 73 0a f6 c2 80 0f |...p.}....s.....|
000000d0 84 f0 00 e9 8d 00 be 05 7c c6 44 ff 00 66 31 c0 |........|.D..f1.|
000000e0 88 f0 40 66 89 44 04 31 d2 88 ca c1 e2 02 88 e8 |..@f.D.1........|
000000f0 88 f4 40 89 44 08 31 c0 88 d0 c0 e8 02 66 89 04 |..@.D.1......f..|
00000100 66 a1 44 7c 66 31 d2 66 f7 34 88 54 0a 66 31 d2 |f.D|f1.f.4.T.f1.|
00000110 66 f7 74 04 88 54 0b 89 44 0c 3b 44 08 7d 3c 8a |f.t..T..D.;D.}<.|
00000120 54 0d c0 e2 06 8a 4c 0a fe c1 08 d1 8a 6c 0c 5a |T.....L......l.Z|
00000130 8a 74 0b bb 00 70 8e c3 31 db b8 01 02 cd 13 72 |.t...p..1......r|
00000140 2a 8c c3 8e 06 48 7c 60 1e b9 00 01 8e db 31 f6 |*....H|`......1.|
00000150 31 ff fc f3 a5 1f 61 ff 26 42 7c be 7f 7d e8 40 |1.....a.&B|..}.@|
00000160 00 eb 0e be 84 7d e8 38 00 eb 06 be 8e 7d e8 30 |.....}.8.....}.0|
00000170 00 be 93 7d e8 2a 00 eb fe 47 52 55 42 20 00 47 |...}.*...GRUB .G|
00000180 65 6f 6d 00 48 61 72 64 20 44 69 73 6b 00 52 65 |eom.Hard Disk.Re|
00000190 61 64 00 20 45 72 72 6f 72 00 bb 01 00 b4 0e cd |ad. Error.......|
000001a0 10 ac 3c 00 75 f4 c3 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |..<.u...........|
000001b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 05 7f 0d 00 00 00 80 20 |............... |
000001c0 21 00 83 aa 28 82 00 08 00 00 00 00 20 00 00 aa |!...(....... ...|
000001d0 29 82 83 fe ff ff 00 08 20 00 00 00 80 0c 00 fe |)....... .......|
000001e0 ff ff 83 fe ff ff 00 08 a0 0c 00 80 1a 06 00 fe |................|
000001f0 ff ff 05 fe ff ff 00 88 ba 12 00 78 45 06 55 aa |...........xE.U.|
00000200
[root@CentOS6 ~]#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1 count=446 #将前446字节写为0
446+0 records in
446+0 records out
446 bytes (446 B) copied, 0.000366533 s, 1.2 MB/s
[root@CentOS6 ~]#hexdump -C -n 512 /dev/sda -v
00000000 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000040 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000050 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000060 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000070 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000080 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000090 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000000a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000000b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000000c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000000d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000000e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000000f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000100 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000110 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000120 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000130 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000140 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000150 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000160 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000170 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000180 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000190 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000001a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000001b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 80 20 |............... |
000001c0 21 00 83 aa 28 82 00 08 00 00 00 00 20 00 00 aa |!...(....... ...|
000001d0 29 82 83 fe ff ff 00 08 20 00 00 00 80 0c 00 fe |)....... .......|
000001e0 ff ff 83 fe ff ff 00 08 a0 0c 00 80 1a 06 00 fe |................|
000001f0 ff ff 05 fe ff ff 00 88 ba 12 00 78 45 06 55 aa |...........xE.U.|
00000200
[root@CentOS6 ~]#reboot
有光盘的情况下:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ADm7L1J9-1692688111217)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120203401.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8d8cb079b50b42e7916a95d14a769beb.png)
**无光盘的情况下:**先尝试网络启动,失败后提示没有操作系统
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kYuLp9D2-1692688111217)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120333842.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dc2311292c36451a919e9e83b43fc8e5.png)
修复:
连接光盘,重启加载时按下ESC显示boot menu,选择光盘启动
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Tx2IWxQa-1692688111218)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120550979.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1584d2a8553e4e7087b0afaddfc82a2b.png)
选择救援模式
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1sB0G8t4-1692688111219)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120627264.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b689c932e58f4aeba89f923a50609bcd.png)
配置语言、键盘、网络等
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DYfTFS7p-1692688111219)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120735142.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ecdfaf2dd8084b35ac184cc666ec5b24.png)
回车启动一个shell
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QxHE4VYJ-1692688111220)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120824643.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7f253618e4e640bd9b329733d88a3d13.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rJAEFDVD-1692688111220)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817120842025.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/776de0723c1d48dd9581bfef4adee077.png)
bash-4.1#df #查看我们系统真正的硬盘被挂载到/mnt/sysimage
bash-4.1#chroot /mnt/sysimage/ #切换到系统的硬盘下
bash-4.1#grub-install /dev/sda #修复sda
#提示成功
bash-4.1#sync #将缓冲区内容写入到磁盘,防止直接重启而未写入磁盘
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EmpM0THp-1692688111221)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817121137643.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fbc95c0a9fc644478da528b9c94c3950.png)
bash-4.1#hexdump -C -n 512 /dev/sda #查看sda的前512字节内容,已经修复
bash-4.1#reboot #重启
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-v5RNbyKY-1692688111221)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817121358831.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/24f7d41496e045cd9a682c7dd14f9e0c.png)
成功启动
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9rTotLEj-1692688111222)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817121630243.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e664935f9b5a41f684c7cc771362aeeb.png)
例2:破坏C6系统的启动文件的第一阶段的446字节,然后使用grub修复
[root@CentOS6 ~]#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1 count=446 #将前446字节写为0
446+0 records in
446+0 records out
446 bytes (446 B) copied, 0.000366533 s, 1.2 MB/s
[root@CentOS6 ~]#grub
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
GNU GRUB version 0.97 (640K lower / 3072K upper memory)
[ Minimal BASH-like line editing is supported. For the first word, TAB
lists possible command completions. Anywhere else TAB lists the possible
completions of a device/filename.]
grub> root (hd0,0)
root (hd0,0)
Filesystem type is ext2fs, partition type 0x83
grub> setup (hd0)
setup (hd0)
Checking if "/boot/grub/stage1" exists... no
Checking if "/grub/stage1" exists... yes
Checking if "/grub/stage2" exists... yes
Checking if "/grub/e2fs_stage1_5" exists... yes
Running "embed /grub/e2fs_stage1_5 (hd0)"... 27 sectors are embedded.
succeeded
Running "install /grub/stage1 (hd0) (hd0)1+27 p (hd0,0)/grub/stage2 /grub/grub.conf"... succeeded
Done.
[root@CentOS6 ~]#hexdump -C -n 512 /dev/sda
00000000 eb 48 90 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.H..............|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
*
00000030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 02 |................|
00000040 ff 00 00 20 01 00 00 00 00 02 fa 90 90 f6 c2 80 |... ............|
00000050 75 02 b2 80 ea 59 7c 00 00 31 c0 8e d8 8e d0 bc |u....Y|..1......|
00000060 00 20 fb a0 40 7c 3c ff 74 02 88 c2 52 f6 c2 80 |. ..@|<.t...R...|
00000070 74 54 b4 41 bb aa 55 cd 13 5a 52 72 49 81 fb 55 |tT.A..U..ZRrI..U|
00000080 aa 75 43 a0 41 7c 84 c0 75 05 83 e1 01 74 37 66 |.uC.A|..u....t7f|
00000090 8b 4c 10 be 05 7c c6 44 ff 01 66 8b 1e 44 7c c7 |.L...|.D..f..D|.|
000000a0 04 10 00 c7 44 02 01 00 66 89 5c 08 c7 44 06 00 |....D...f.\..D..|
000000b0 70 66 31 c0 89 44 04 66 89 44 0c b4 42 cd 13 72 |pf1..D.f.D..B..r|
000000c0 05 bb 00 70 eb 7d b4 08 cd 13 73 0a f6 c2 80 0f |...p.}....s.....|
000000d0 84 f0 00 e9 8d 00 be 05 7c c6 44 ff 00 66 31 c0 |........|.D..f1.|
000000e0 88 f0 40 66 89 44 04 31 d2 88 ca c1 e2 02 88 e8 |..@f.D.1........|
000000f0 88 f4 40 89 44 08 31 c0 88 d0 c0 e8 02 66 89 04 |..@.D.1......f..|
00000100 66 a1 44 7c 66 31 d2 66 f7 34 88 54 0a 66 31 d2 |f.D|f1.f.4.T.f1.|
00000110 66 f7 74 04 88 54 0b 89 44 0c 3b 44 08 7d 3c 8a |f.t..T..D.;D.}<.|
00000120 54 0d c0 e2 06 8a 4c 0a fe c1 08 d1 8a 6c 0c 5a |T.....L......l.Z|
00000130 8a 74 0b bb 00 70 8e c3 31 db b8 01 02 cd 13 72 |.t...p..1......r|
00000140 2a 8c c3 8e 06 48 7c 60 1e b9 00 01 8e db 31 f6 |*....H|`......1.|
00000150 31 ff fc f3 a5 1f 61 ff 26 42 7c be 7f 7d e8 40 |1.....a.&B|..}.@|
00000160 00 eb 0e be 84 7d e8 38 00 eb 06 be 8e 7d e8 30 |.....}.8.....}.0|
00000170 00 be 93 7d e8 2a 00 eb fe 47 52 55 42 20 00 47 |...}.*...GRUB .G|
00000180 65 6f 6d 00 48 61 72 64 20 44 69 73 6b 00 52 65 |eom.Hard Disk.Re|
00000190 61 64 00 20 45 72 72 6f 72 00 bb 01 00 b4 0e cd |ad. Error.......|
000001a0 10 ac 3c 00 75 f4 c3 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |..<.u...........|
000001b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 80 20 |............... |
000001c0 21 00 83 aa 28 82 00 08 00 00 00 00 20 00 00 aa |!...(....... ...|
000001d0 29 82 83 fe ff ff 00 08 20 00 00 00 80 0c 00 fe |)....... .......|
000001e0 ff ff 83 fe ff ff 00 08 a0 0c 00 80 1a 06 00 fe |................|
000001f0 ff ff 05 fe ff ff 00 88 ba 12 00 78 45 06 55 aa |...........xE.U.|
00000200
例3:破坏1.5阶段的第2至第25个扇区,将内容置为0,然后修复
[root@CentOS6 ~]#dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=512 count=25 seek=1
25+0 records in
25+0 records out
12800 bytes (13 kB) copied, 0.00245147 s, 5.2 MB/s
[root@CentOS6 ~]#hexdump -C -n 5120 /dev/sda -v
00000000 eb 48 90 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.H..............|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 02 |................|
00000040 ff 00 00 20 01 00 00 00 00 02 fa 90 90 f6 c2 80 |... ............|
00000050 75 02 b2 80 ea 59 7c 00 00 31 c0 8e d8 8e d0 bc |u....Y|..1......|
00000060 00 20 fb a0 40 7c 3c ff 74 02 88 c2 52 f6 c2 80 |. ..@|<.t...R...|
00000070 74 54 b4 41 bb aa 55 cd 13 5a 52 72 49 81 fb 55 |tT.A..U..ZRrI..U|
00000080 aa 75 43 a0 41 7c 84 c0 75 05 83 e1 01 74 37 66 |.uC.A|..u....t7f|
00000090 8b 4c 10 be 05 7c c6 44 ff 01 66 8b 1e 44 7c c7 |.L...|.D..f..D|.|
000000a0 04 10 00 c7 44 02 01 00 66 89 5c 08 c7 44 06 00 |....D...f.\..D..|
000000b0 70 66 31 c0 89 44 04 66 89 44 0c b4 42 cd 13 72 |pf1..D.f.D..B..r|
000000c0 05 bb 00 70 eb 7d b4 08 cd 13 73 0a f6 c2 80 0f |...p.}....s.....|
000000d0 84 f0 00 e9 8d 00 be 05 7c c6 44 ff 00 66 31 c0 |........|.D..f1.|
000000e0 88 f0 40 66 89 44 04 31 d2 88 ca c1 e2 02 88 e8 |..@f.D.1........|
000000f0 88 f4 40 89 44 08 31 c0 88 d0 c0 e8 02 66 89 04 |..@.D.1......f..|
00000100 66 a1 44 7c 66 31 d2 66 f7 34 88 54 0a 66 31 d2 |f.D|f1.f.4.T.f1.|
00000110 66 f7 74 04 88 54 0b 89 44 0c 3b 44 08 7d 3c 8a |f.t..T..D.;D.}<.|
00000120 54 0d c0 e2 06 8a 4c 0a fe c1 08 d1 8a 6c 0c 5a |T.....L......l.Z|
00000130 8a 74 0b bb 00 70 8e c3 31 db b8 01 02 cd 13 72 |.t...p..1......r|
00000140 2a 8c c3 8e 06 48 7c 60 1e b9 00 01 8e db 31 f6 |*....H|`......1.|
00000150 31 ff fc f3 a5 1f 61 ff 26 42 7c be 7f 7d e8 40 |1.....a.&B|..}.@|
00000160 00 eb 0e be 84 7d e8 38 00 eb 06 be 8e 7d e8 30 |.....}.8.....}.0|
00000170 00 be 93 7d e8 2a 00 eb fe 47 52 55 42 20 00 47 |...}.*...GRUB .G|
00000180 65 6f 6d 00 48 61 72 64 20 44 69 73 6b 00 52 65 |eom.Hard Disk.Re|
00000190 61 64 00 20 45 72 72 6f 72 00 bb 01 00 b4 0e cd |ad. Error.......|
000001a0 10 ac 3c 00 75 f4 c3 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |..<.u...........|
000001b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 80 20 |............... |
000001c0 21 00 83 aa 28 82 00 08 00 00 00 00 20 00 00 aa |!...(....... ...|
000001d0 29 82 83 fe ff ff 00 08 20 00 00 00 80 0c 00 fe |)....... .......|
000001e0 ff ff 83 fe ff ff 00 08 a0 0c 00 80 1a 06 00 fe |................|
000001f0 ff ff 05 fe ff ff 00 88 ba 12 00 78 45 06 55 aa |...........xE.U.|
00000200 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000210 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000220 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000230 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000240 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000250 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000260 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000270 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000280 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000290 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000002a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000002b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000002c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000002d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000002e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000002f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000300 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000310 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000320 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000330 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000340 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000350 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000360 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000370 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000380 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000390 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000003a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000003b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000003c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000003d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000003e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000003f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000400 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000410 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000420 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000430 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000440 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000450 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000460 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000470 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000480 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000490 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000004a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000004b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000004c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000004d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000004e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000004f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000500 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000510 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000520 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000530 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000540 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000550 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000560 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000570 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000580 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000590 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000005a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000005b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000005c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000005d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000005e0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000005f0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000600 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000610 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000620 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000630 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000640 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000650 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000660 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000670 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000680 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000690 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000006a0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000006b0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000006c0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
000006d0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
[root@CentOS6 ~]#reboot
重启后系统无法打开,但错误提示不同:

此时1阶段正常,系统认为硬盘可以启动,所以一直在加载,而不去寻找光盘等设备来启动,就会卡在这里
**修复:**同样的,进入救援模式,然后切换根,然后grub-install /dev/sda即可
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-faBAOoEz-1692688111222)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230817123704463.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f84ff2357a95437b9bda032fd636f874.png)
1.3.2.3 grub legacy 管理
配置文件: /boot/grub/grub.conf <-- /etc/grub.conf
stage2及内核等通常放置于一个基本磁盘分区
grub legacy 功用:
- 提供启动菜单、并提供交互式接口
- a:内核参数
- e:编辑模式,用于编辑菜单
- c:命令模式,交互式接口
- 加载用户选择的内核或操作系统
- 允许传递参数给内核
- 可隐藏启动菜单
- 为菜单提供了保护机制
- 为编辑启动菜单进行认证
- 为启用内核或操作系统进行认证
grub的命令行接口
help: 获取帮助列表
help KEYWORD: 详细帮助信息
find (hd#,#)/PATH/TO/SOMEFILE:
root (hd#,#)
kernel /PATH/TO/KERNEL_FILE: 设定本次启动的内核文件,额外还可添加许多内核支持使用的cmdline参数
例如: max_loop=100 selinux=0 init=/path/to/init
initrd /PATH/TO/INITRAMFS_FILE: 设定为选定的内核提供额外文件的ramdisk
boot: 引导启动选定的内核
cat /proc/cmdline 内核参数
内核参数文档:
/usr/share/doc/kernel-doc-2.6.32/Documentation/kernel-parameters.txt
grub legacy识别硬盘设备
(hd#,#)
hd# 磁盘编号,用数字表示;从0开始编号
# 分区编号,用数字表示,从0开始编号
示例:
(hd0,0) 第一块硬盘,第一个分区
手动在grub命令行接口启动系统
grub> root (hd#,#)
grub> kernel /vmlinuz-VERSION-RELEASE ro root=/dev/DEVICE
grub> initrd /initramfs-VERSION-RELEASE.img
grub> boot
grub legacy配置文件: /boot/grub/grub.conf
default=#: 设定默认启动的菜单项;落单项(title)编号从0开始
timeout=#: 指定菜单项等待选项选择的时长
splashimage=(hd#,#)/PATH/XPM_FILE: 菜单背景图片文件路径
password [--md5 | encrypt] STRING: 启动菜单编辑认证
hiddenmenu: 隐藏菜单
title TITLE: 定义菜单项“标题”,可出现多次
root (hd#,#): 查找stage2及kernel文件所在设备分区;为grub的根
kernel /PATH/TO/VMLINUZ_FILE [PARAMETERS]: 启动的内核
initrd /PATH/TO/INITRAMFS_FILE: 内核匹配的ramfs文件
password [--md5|--encrypted ] STRING: 启动选定的内核或操作系统时进行认证
grub加密生成grub口令
grub-md5-crypt
grub-crypt
破解root口令:
(1)编辑grub菜单(选定要编辑的title,而后使用a 或 e 命令)
(2)在选定的kernel后附加1,s,S,single 都可以进入单用户模式
(3)在kernel所在行,键入“b”命令
范例: 给grub 添加密码,防止破解root密码
[root@centos6 ~]#grub-crypt
Password:
Retype password:
S6SRedtvBe0DOsM8yKqSykwmmnHsDb9WDRUuZbC3H1ZNwITf/Mh88MXa3JzXToxyyohXIXFWLIOMdgmYFfkwxxkP.VW3ypITa4P5zUKuT.
[root@centos6 ~]#vim /boot/grub/grub.conf
default=0
timeout=5
password --encrypt #加上这一行
56SRedtvBe0DOsM8ykqSykwmmnHSDb9WDRUuZbC3H1ZNwI1f/Mh88MXa3JzX1oxyyohXIXFWLIOMdgmYFfkwxxkP.VW3ypI1a4P5zUKuT.
splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub /splash.xpm.gz
hiddenmenu
title Centos 6 (2.6.32-754.e16.x86_64)
#然后在系统选择时输入口令才能进入编辑
#不过进入救援模式,仍然可以跳过这些安全步骤,并修改密码
1.3.3 加载 kernel
kernel自身初始化过程:
- 探测可识别到的所有硬件设备
- 加载硬件动程序 (借助于ramdisk加载动)
- 以只读方式挂载根文件系统
- 运行用户空间的第一个应用程序:/sbin/init
Linux内核特点:
- 支持模块化:.ko (内核对象),如: 文件系统,硬件驱动,网络协议等
- 支持内核模块的动态装载和卸载
内核组成部分:
-
核心文件: /boot/vmlinuz-VERSION-release
ramdisk:辅助的伪根系统,加载相应的硬件驱动,ramdisk --> ramfs 提高速度
C 5 /boot/initrd-VERSION-release.img
C 6以后版本 /boot/initramfs-VERSION-release.img
-
模块文件: /ib/modules/VERSION-release
ramdisk文件的制作:
mkinitrd命令
mkinitrd /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img $(uname -r)
dracut命令
dracut /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img $(uname -r)
例:误删除/boot/initramfs-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64.img文件,导致系统无法启动,修复
[root@CentOS6 boot]#rm -f initrd-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64kdump.img
[root@CentOS6 boot]#reboot
#进入救援模式
#chroot /mnt/sysimage #切根
#mkinitrd /boot/initramfs-`uname -r`.img `uname -r`
#sync
#reboot
例:误删除/boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64文件,即内核文件,导致系统无法启动,修复
[root@CentOS6 boot]#rm -f /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64
#方式1
[root@CentOS6 boot]#reboot
#进入救援模式
#chroot /mnt/sysimage #切根
#mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/ #挂载光盘
#cp /mnt/isolinux/vmlinuz /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64
#sync
#reboot
#方式2
#由于vmlinuz文件来源于光盘里的kernel包,直接重装即可
[root@CentOS6 boot]#rpm -qf vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64
kernel-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64
例:误删除/boot/*,grub和内核都被删除,进行故障恢复
#先修复内核,再修复Grub
范例:生成背景图片
[root@centos6 ~]#convert -resize 640x480 -colors 14 winner.png splash.xpm
[root@centos6 ~]#more splash.xpm
#生成splash.xpm.gz
[rootacentos6 ~]#qzip splash.xpm
[root@centos6 ~]#mv splash.xpm.gz /boot/grub
1.3.4 init 初始化
使POST --> BootSeguence (BIOS) -->Bootloader(MBR) --> kernel(ramdisk) --> rootfs(只读) -->init(systemd)
init程序的类型:
-
SysV: init,C5之前
配置文件:/etc/inittab
-
Upstart: init,C 6
配置文件:/etc/inittab,/etc/init/*.conf
-
Systemd:systemd,C 7
配置文件: /usr/lib/systemd/system;/etc/systemd/system
1.3.4.1 运行级别
运行级别: 为系统运行或维护等目的而设定,0-6:7个级别,一般使用3,5做为默认级别
0:关机
1:单用户模式(root自动登录),single,维护模式
2:多用户模式,启动网络功能,但不会启动NFS: 维护模式
3:多用户模式,正常模式:文本界面
4:预留级:可同3级别
5:多用户模式,正常模式:图形界面
6:重启
切换级别:
init #
查看级别:
runlevel
who -r
定义运行级别
/etc/inittab
C 5的inittab文件还定义以下内容
初始运行级别(RUN LEVEL)
系统初始化脚本
对应运行级别的脚本目录
捕获某个关键字顺序
定义UPS电源终端/恢复脚本
在虚拟控制台生成getty
在运行级别5初始化X
C 5的inittab文件每一行格式
id:runlevel:action:process
id:是惟一标识该项的字符序列
runlevels: 定义了操作所使用的运行级别
action:指定了要执行的特定操作
wait: 切换至此级别运行一次
respawn: 此process终止,就重新启动之
initdefault:设定默认运行级别;process省略
sysinit:设定系统初始化方式
process:定义了要执行的进程
例:CentOS 6 /etc/inittab和相关文件
C6 init程序为 upstart, 其配置文件/etc/inittab,/etc/init/*.conf,配置文件的语法 遵循 upstart配置文件语法格式,和C 5不同
[root@CentOS6 ~]#cat /etc/inittab
# inittab is only used by upstart for the default runlevel.
#
# ADDING OTHER CONFIGURATION HERE WILL HAVE NO EFFECT ON YOUR SYSTEM.
#
# System initialization is started by /etc/init/rcS.conf
#
# Individual runlevels are started by /etc/init/rc.conf
#
# Ctrl-Alt-Delete is handled by /etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf
#
# Terminal gettys are handled by /etc/init/tty.conf and /etc/init/serial.conf,
# with configuration in /etc/sysconfig/init.
#
# For information on how to write upstart event handlers, or how
# upstart works, see init(5), init(8), and initctl(8).
#
# Default runlevel. The runlevels used are:
# 0 - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
# 1 - Single user mode
# 2 - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as 3, if you do not have networking)
# 3 - Full multiuser mode
# 4 - unused
# 5 - X11
# 6 - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
#
id:3:initdefault:
例:control -alt-delete键默认行为是重启,工作中可以将其注释以防止误触
[root@CentOS6 init]#cat /etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf
# control-alt-delete - emergency keypress handling
#
# This task is run whenever the Control-Alt-Delete key combination is
# pressed. Usually used to shut down the machine.
#
# Do not edit this file directly. If you want to change the behaviour,
# please create a file control-alt-delete.override and put your changes there.
start on control-alt-delete
exec /sbin/shutdown -r now "Control-Alt-Delete pressed"
例:ntsysv图形界面修改服务,空格开启或关闭
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HbLCqmRt-1692688111223)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230818231950485.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f2e4a36ec67b4eeab5a42b0d30c077ed.png)
例:一次性修改atd的7种模式
[root@CentOS6 init]#chkconfig --list atd
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
[root@CentOS6 init]#chkconfig --level 34 atd off
[root@CentOS6 init]#chkconfig --list atd
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:on 6:off
[root@CentOS6 init]#chkconfig atd on
[root@CentOS6 init]#chkconfig --list atd
atd 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
例:设置服务开机不启动
[root@CentOS6 init]#service iptables stop #关闭服务
[root@CentOS6 init]#chkconfig iptables off #设置开机不启动,开机启动则on
1.3.4.2 初始化脚本 sysinit
在所有服务加载之前执行初始化的脚本
/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit
#由 rcS.conf文件调用
[root@CentOS6 init]#cat /etc/init/rcS.conf
exec /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit
系统初始化脚本功能
- 设置主机名
- 设置欢迎信息
- 激活udev和selinux
- 挂载/etc/fstab文件中定义的文件系统
- 检测根文件系统,并以读写方式重新挂载根文件系统
- 设置系统时钟
- 激活swap设备
- 根据/etc/sysctl.conf文件设置内核参数
- 激活lvm及software raid设备
- 加载额外设备的驱动程序
- 清理操作
1.3.4.3 服务管理
service 命令:手动管理服务
service 服务 start|stop|restart
service --status-all
由rc.conf文件调用rc.d,rc调用服务脚本
[root@CentOS6 init]#cat /etc/init/rc.conf
exec /etc/rc.d/rc $RUNLEVEL
/etc/rc.d/rc 控制服务脚本的开机自动运行
for srv in /etc/rc.d/rcN.d/k*; do
$srv stop
done
for srv in /etc/rc.d/rcN.d/s*; do
$srv start
done
说明: rc N --> 意味着读取/etc/rc.d/rcN.d/
- K: K##: ##运行次序,数字越小,越先运行,数字越小的服务,通常为依赖到别的服务
- s: S##: ##运行次序,数字越小,越先运行,数字越小的服务,通常为被依赖到的服务
配置服务开机启动
- chkconfig命令
- ntsysv命令
chkconfig 命令管理服务
#查看服务在所有级别的启动或关闭设定情形:
chkconfig [--list] [name]
#添加服务
Sysv的服务脚本放置于/etc/rc.d/init.d (/etc/init.d)
#!/bin/bash
chkconfig: LLLL nn nn #LLLL 表示初始在哪个级别下启动,-表示都不启动
description :描述信息
chkconfig --add name
#删除服务
chkconfig --del name
#修改指定的运行级别
chkconfig [--level levels] name <onlofflreset>
说明: --level LLLL: 指定要设置的级别;省略时表示2345
1.3.4.4 非独立服务
服务分为独立服务和非独立服务
瞬态 (Transient) 服务被超级守护进程 xinetd 进程所管理,也称为非独立服务,即用户不访问/使用该服务时,服务关闭,被xinetd进程所监控,当有用户访问某非独立服务时,则唤醒该非独立服务,使用结束则关闭服务
进入的请求首先被xinetd代理
配置文件:
etc/xinetd.conf
/etc/xinetd.d/<service>
用chkconfig控制非独立服务开机启动
示例: chkconfig tftp on
1.3.4.5 开机启动文件 rc.local
/etc/rc.d/rc.local
注意: 正常级别下,最后启动一个服务S99local没有链接至/etc/rc.d/init.d一个服务脚本,而是指向了/etc/rc.d/rc.local脚本
不便或不需写为服务脚本放置于/etc/rc.d/init.d/目录,且又想开机时自动运行的命令,可直接放警于/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件中
/etc/rc.d/rc.local在指定运行级别脚本后运行
1.3.5 Centos 启动过程总结
/sbin/init --> (/etc/inittab) --> 设置默认运行级别 --> 运行系统初始脚本/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit、完成系统初始化 -->(关闭对应下需要关闭的服务)启动需要启动服务/etc/rc#.d/Sxxx,/etc/rc.d/rc.local --> 设置登录终端
参看: http://s4.51cto.com/wyfs02/M02/87/20/wKiom1fVBELjXsvaAAUkuL83t2Q304.jpg

1.4 自制linux系统
1.4.0为当前Linux系统增加硬盘
在现有Linux系统上构建系统,所以先在其上面加一块硬盘,上面存放文件系统与数据
在VMware上增加硬盘
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-eP8rc43Y-1692688111224)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230820184900325.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/16ead1b8f409494f8cf5460ffbf3a223.png)
默认当前无法找到硬盘
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2GQhIH7k-1692688111225)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230820184934789.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1d844e65dc52478c9548ed3774fe470d.png)
使用命令扫描一下磁盘
[root@CentOS6 ~]#lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 3.7G 0 rom
sda 8:0 0 200G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 100G 0 part /
├─sda3 8:3 0 48.8G 0 part /data
├─sda4 8:4 0 1K 0 part
└─sda5 8:5 0 4G 0 part [SWAP]
[root@CentOS6 ~]#echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
[root@CentOS6 ~]#echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host1/scan
[root@CentOS6 ~]#echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/host2/scan
[root@CentOS6 ~]#lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 3.7G 0 rom
sda 8:0 0 200G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 100G 0 part /
├─sda3 8:3 0 48.8G 0 part /data
├─sda4 8:4 0 1K 0 part
└─sda5 8:5 0 4G 0 part [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
1.4.1 分区并创建文件系统
fdisk /dev/sdb
#分两个必要的分区:
[root@centos6 ~]#echo -e 'n\np\n1\n\n+1G\nw\n' fdisk /dev/sdb #\n表示回车,给第一个分区分1G空间
[root@centos6 ~]#echo -e 'n\np\n2\n\n\n\nw\n' fdisk /dev/sdb #将剩下空间给第二个分区
/dev/sdb1对应/boot /dev/sdb2对应根/
[root@centos6 ~]#mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
[root@centos6 ~]#mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2
例:
#1手动添加
[root@CentOS6 ~]#fdisk /dev/sdb
Device contains neither a valid DOS partition table, nor Sun, SGI or OSF disklabel
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x85b35a65.
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
After that, of course, the previous content won't be recoverable.
Warning: invalid flag 0x0000 of partition table 4 will be corrected by w(rite)
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help):
Command (m for help): n
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p
Partition number (1-4): 1
First cylinder (1-2610, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-2610, default 2610): +1G
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
#2非交互式直接添加
[root@CentOS6 ~]#echo -e 'n\np\n2\n\n\n\nw\n' | fdisk /dev/sdb
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u').
Command (m for help): Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
Partition number (1-4): First cylinder (133-2610, default 133): Using default value 133
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (133-2610, default 2610): Using default value 2610
Command (m for help): Command (m for help): The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
[root@CentOS6 ~]#lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sr0 11:0 1 3.7G 0 rom
sda 8:0 0 200G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
├─sda2 8:2 0 100G 0 part /
├─sda3 8:3 0 48.8G 0 part /data
├─sda4 8:4 0 1K 0 part
└─sda5 8:5 0 4G 0 part [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 20G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 1G 0 part
└─sdb2 8:18 0 19G 0 part
#格式化
[root@CentOS6 ~]#mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
66384 inodes, 265064 blocks
13253 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=272629760
9 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
7376 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (8192 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 34 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
[root@CentOS6 ~]#mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb2
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
1245184 inodes, 4976133 blocks
248806 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=4294967296
152 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 22 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
1.4.2 挂载boot
[root@centos6 ~]#mkdir /mnt/boot #子目录必须为boot
[root@centos6 ~]#mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/
1.4.3 安装grub
[root@centos6 ~]#grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb
例:
[root@CentOS6 ~]#mkdir /mnt/boot
[root@CentOS6 ~]#mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/boot/
[root@CentOS6 ~]#grub-install --root-directory=/mnt /dev/sdb
Probing devices to guess BIOS drives. This may take a long time.
Installation finished. No error reported.
This is the contents of the device map /mnt/boot/grub/device.map.
Check if this is correct or not. If any of the lines is incorrect,
fix it and re-run the script `grub-install'.
(fd0) /dev/fd0
(hd0) /dev/sda
(hd1) /dev/sdb
[root@CentOS6 ~]#ls /mnt/boot
grub lost+found
[root@CentOS6 ~]#ls /mnt/boot/grub
device.map fat_stage1_5 iso9660_stage1_5 minix_stage1_5 stage1 ufs2_stage1_5 xfs_stage1_5
e2fs_stage1_5 ffs_stage1_5 jfs_stage1_5 reiserfs_stage1_5 stage2 vstafs_stage1_5
1.4.4 准备内核和initramfs文件
[root@CentOS6 ~]#cp /boot/vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64 /mnt/boot/vmlinuz
[root@CentOS6 ~]#cp /boot/initramfs-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64.img /mnt/boot/initramfs
1.4.5 手动建立grub.conf
[root@CentOS6 ~]#cat /mnt/boot/grub/grub.conf
default=0
timeout=5
title joyce linux
root (hd0,0)
kernel /vmlinuz root=/dev/sda2 selinux=0 init=/bin/bash
initrd /initramfs
[root@CentOS6 ~]#tree /mnt/boot
/mnt/boot
├── grub
│ ├── device.map
│ ├── e2fs_stage1_5
│ ├── fat_stage1_5
│ ├── ffs_stage1_5
│ ├── grub.conf
│ ├── iso9660_stage1_5
│ ├── jfs_stage1_5
│ ├── minix_stage1_5
│ ├── reiserfs_stage1_5
│ ├── stage1
│ ├── stage2
│ ├── ufs2_stage1_5
│ ├── vstafs_stage1_5
│ └── xfs_stage1_5
├── initramfs
├── lost+found
└── vmlinuz
1.4.6 准备根下面相关程序和库
mkdir /mnt/sysroot
mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt/sysroot
mkdir -pv /mnt/sysroot/{etc,lib,lib64,bin,sbin,tmp,var,usr,sys,proc,opt,home,root,boot,dev,mnt,media}
复制bash等命令和相关库文件,如: bash,ifconfig,insmod,ping,mount,ls,cat,df,lsblk,blkid,fdisk,tree,ip,ps等
#查询网卡驱动并拷贝
[root@CentOS6 ~]#ethtool -i eth0
driver: e1000
version: 7.3.21-k8-NAPI
firmware-version:
bus-info: 0000:02:01.0
supports-stalistics: yes
supports-test: yes
supports-eeprom-access: yes
supports-register-dump: yes
supports-priv-flags: no
[root@CentOS6 ~]#modinfo -n e1000
/lib/modules/2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/e1000/e1000.ko
[root@CentOS6 ~]#cp /lib/modules/2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64/kernel/drivers/net/e1000/e1000.ko /mnt/sysroot/lib/ #将网卡驱动放在/mnt/sysroot/lib下
[root@centos6 ~]#chroot /mnt/sysroot
1.4.7 准备新的虚拟机
将当前C6机器关机,将刚创建的硬盘拷贝到test文件夹中
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yNjXPyrD-1692688111226)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230820201128691.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/932f065e1ec34ea9afc44e8776e23941.png)
创建一个新的Linux6虚拟机,将前一虚拟机sdb硬盘对应的vmdk文件增加进去,删除原有磁盘
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-BZLgdncj-1692688111226)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230820201515816.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/033e4526e6b8460fbeea61da889d8c4e.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bozx9Yha-1692688111227)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230820201618680.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6f21279501a44e7686c7c828810bc6ec.png)
开机
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0GAmAOmD-1692688111227)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230820201712535.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/825c7ed67b144580bc37d4ea296bddeb.png)
1.5 启动过程的故障排错
1.5.1 实战案例
故障:删除 /sbin/init 无法启动
恢复过程
先进入grub菜单,在kernel参数后加 selinux=0 init=/bin/bash
mount -o remount,rw /
mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/
rpm2cpio /mnt/Packages/upstart.xxx.rpm cpio -idv ./sbin/init
mv ./sbin/init /sbin/
1.5.2 实战案例
故障:rm -rf /boot/* 和 /etc/fstab 进行恢复
恢复过程
1.用光盘进入 rescue mode,找到/ 所在分区并恢复/etc/fstab
进入救援模式,由于没有分区表,因此无法挂载操作系统的根
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qYr8fUCe-1692688111228)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230818164645440.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/637799b9772e426aa0c3c77c1cd22b4e.png)
fdisk -l
mkdir /mnt/rootdir
mount /dev/sdaN /mnt/rootdir
ls /mnt/rootdir
mount /dev/sda2 /mnt/rootdir
vim /mnt/rootdir/etc/fstab
/dev/sda1 /boot ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/sda2 / ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/sda3 /data ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/sda5 swap swap defaults 0 0
reboot
2.rescue mode 恢复内核和initrd 文件
/dev/sda2 --> /mnt/sysimage
chroot /mnt/sysimage
mount /dev/srO /mnt/
#方法1
rpm -ivh /mnt/Packages/kernel.xxxx.rpm --force
#方法2
cp /mnt/isolinux/vmlinuz /boot/
mkinitrd /boot/initramfs.img `uname -r`
3.修复grub
grub-install /dev/sda
vim /boot/grub/grub.conf 方法2
[root@centos6 ~]#cat /boot/grub/grub.conf
default=0
timeout=5
title centos
kernel /vmlinuz root=/dev/sda2
initrd /initramfs.img
4.reboot
2 /proc 目录和内核参数管理
/proc目录: 内核把自己内部状态信息及统计信息,以及可配置参数通过proc伪文件系统加以输出帮助: man proc
内核参数:
- 只读:只用于输出信息
- 可写: 可接受用户指定“新值”来实现对内核某功能或特性的配置
/proc/sys 设置:
sysctl命令用于查看或设定此目录中诸多参数
sysctl -w path.to.parameter=VALUE
例:
[root@CentOS6 ~]#cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
0
[root@CentOS6 ~]#echo 1 >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
#等价于:
[root@CentOS6 ~]#sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
不过这是临时修改,无法持久保存
默认配置文件:/etc/sysct.conf (总文件)及以下文件
/run/sysctl.d/*.conf
/etc/sysctl.d/*.conf
/usr/local/lib/sysctl.d/* .conf
/usr/lib/sysctl.d/*.conf
lib/sysctl.d/* .conf
etc/sysctl.conf
最好是分类,单独放一个,或者放总文件里
范例:修改主机名
sysctl -w kernel.hostname=mail.joyce.com
echo命令通过重定向方式也可以修改大多数参数的值
echo "VALUE”> /proc/sys/path/to/parameter
范例:
echo “websrv” > /proc/sys/kernel/hostname
sysctl命令
-
临时设置某参数
sysctl -w parameter=VALUE -
通过读取配置文件设置参数
sysctl -p [/path/to/conf_filel -
查看所有生效参数
sysctl -a
常用的内核参数
net.ipv4.ip_forward
net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_all #设置1则其他主机无法ping通本主机
net.ipv4.ip_nonocal_bind #允许应用程序可以监听本地不存在的IP
vm.drop_caches #可以释放缓冲区
fs.file-max = 1020000 #最多可以打开的文件数,打开一个文件分配一个文件描述符
例:
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all
0
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /etc/sysctl.d/test.conf
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /etc/sysctl.d/test.conf
net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_all=1
[root@centos8 ~]#sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/test.conf
net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_all =1
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/icmp_echo_ignore_all
1
3 /sys 目录
/sys目录:
使用sysfs文件系统,为用户使用的伪文件系统,输出内核识别出的各硬件设备的相关属性信息,也有内核对硬件特性的设定信息,有些参数是可以修改的,用于调整硬件工作特性
udev通过此路径下输出的信息动态为各设备创建所需要设备文件,udev是运行用户空间程序专用工具: udevadmin,hotplug
udev为设备创建设备文件时,会读取其事先定义好的规则文件,一般在/etc/udev/rules.d及/usr/lib/udev/rules.d目录下
4 内核模块管理和编译
单内核体系设计、但充分借鉴了微内核设计体系的优点,为内核引入模块化机制
内核组成部分:、
- kernel: 内核核心,一般为bzlmage,通常在/boot目录下,名称为 vmlinuz-VERSION-RELEASE
- kernel object: 内核对象,一般放置于/lib/modules/VERSION-RELEASE/
- 辅助文件: ramdisk、initrd(C5及以前,模拟磁盘,进入后还要进入文件系统)、initramfs(C6及以后,模拟文件系统,直接接触文件)
4.1 内核版本
运行中的内核
uname命令
uname - print system information
uname [OPTION]..
选项:
-n: 显示节点名称
-r: 显示VERSION-RELEASE
-a: 显示所有信息
4.2 内核模块命令
lsmod命令
- 显示由核心已经装载(已被使用的)的内核模块
- 显示的内容来自于: /proc/modules文件
modinfo命令
功能:管理内核模块
配置文件: /etc/modprobe.conf,/etc/modprobe.d/*.conf
显示模块的详细描述信息
modinfo [ -k kernel ] [ modulename | filename... ]
常用选项:
-n:只显示模块文件路径-
-p:显示模块参数
-a:作者
-d:描述
装载或卸载内核模块
modprobe [ -C config-file ] [ modulename ] [ module parame-ters... ]
modprobe [ -r ] modulename...
depmod命令: 内核模块依赖关系文件及系统信息映射文件的生成工具
insmod命令: 指定模块文件,不能自动解决依赖模块
insmod [ filename ] [ module options...]
范例:
insmod modinfo -n exportfs
Insmod modinfo -n xfs
rmmod命令:卸载模块,类似于modprobe -r
rmmod [ modulename ]
范例:
rmmod xfs
rmmod exportfs
4.3 编译内核
编译安装内核准备:
- 准备好开发环境
- 获取目标主机上硬件设备的相关信息
- 获取目标主机系统功能的相关信息,例如:需要启用相应的文件系统
- 获取内核源代码包,www.kernel.org
4.3.1 编译准备
4.3.1.1.目标主机硬件设备相关信息
CPU:
cat /proc/cpuinfo
x86info -a
lscpu
lsblk 块设备
全部硬件设备信息: hal-device: Centos 6
4.3.1.2 开发环境相关包
安装相对应包:gcc make ncurses-devel flex bison openssl-devel elfutils-libelf-devel
4.3.1.3 内核编译安装实现
-
下载源码文件
-
准备文本配置文件/boot/config-`uname-r`
-
make menuconfig: 配置内核选项,相当于./configure
[ ] : N #未启用 [M] : M #存放在lib下的独立模块 [*] : Y #存放在核心里 -
make [-j #] 或者用以下两步实现
make -j # bzlmage #编译内核文件vmlinuz make -i # modules #编译lib/modules下的文件 -
安装模块: make modules_install
-
安装内核相关文件: make install
-
安装bzlmage为 /boot/vmlinuz-VERSION-RELEASE
-
生成initramfs文件
-
编辑grub的配置文件
-
4.3.1.4 编译安装内核实战案例
简述:
[root@CentOS8 ~]#yum -y install gcc make ncurses-devel flex bison openssl-devel elfutils-libelf-devel
[root@centos8 ~]#tar xf linux-5.4.13.tar.xz -C /usr/src
[root@centos8 ~]#cd /usr/src
[root@centos8 ~]#In -sv Tinux-5.4.13 Tinux
[rootacentos8 ~]#cd /usr/src/Tinux
[root@centos8 ~]#cp /boot/config-$(uname -r) ./.config
[root@centos8 ~]#vim .config
# CONFIG MODULE SIG is not set
CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRUSTED KEYS="
# CONFIG DEBUG INFO is not set
[rootacentos8 ~]#make hep
[rootacentos8 ~]#make menuconfig
[rootacentos8 ~]#make -j 2或者 make -j 2 bzImage ; make -j 2 modules
[rootacentos8 ~]#make modules install
[root@centos8 ~]#make install
[root@centos8 ~]#reboot
例:为C8安装最新内核6.4.11
[root@CentOS8 ~]#yum -y install gcc make ncurses-devel flex bison openssl-devel elfutils-libelf-devel
Last metadata expiration check: 1:31:08 ago on Sun 20 Aug 2023 10:37:38 PM CST.
Package gcc-8.5.0-4.el8_5.x86_64 is already installed.
Package make-1:4.2.1-10.el8.x86_64 is already installed.
Package ncurses-devel-6.1-9.20180224.el8.x86_64 is already installed.
Package openssl-devel-1:1.1.1k-5.el8_5.x86_64 is already installed.
Dependencies resolved.
===================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
===================================================================================================
Installing:
bison x86_64 3.0.4-10.el8 AppStream 688 k
elfutils-libelf-devel x86_64 0.185-1.el8 BaseOS 59 k
flex x86_64 2.6.1-9.el8 AppStream 320 k
Transaction Summary
===================================================================================================
Install 3 Packages
Total download size: 1.0 M
Installed size: 3.0 M
Downloading Packages:
(1/3): elfutils-libelf-devel-0.185-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 131 kB/s | 59 kB 00:00
(2/3): flex-2.6.1-9.el8.x86_64.rpm 339 kB/s | 320 kB 00:00
(3/3): bison-3.0.4-10.el8.x86_64.rpm 569 kB/s | 688 kB 00:01
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 878 kB/s | 1.0 MB 00:01
Running transaction check
Transaction check succeeded.
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded.
Running transaction
Preparing : 1/1
Installing : elfutils-libelf-devel-0.185-1.el8.x86_64 1/3
Installing : flex-2.6.1-9.el8.x86_64 2/3
Running scriptlet: flex-2.6.1-9.el8.x86_64 2/3
Installing : bison-3.0.4-10.el8.x86_64 3/3
Running scriptlet: bison-3.0.4-10.el8.x86_64 3/3
Verifying : bison-3.0.4-10.el8.x86_64 1/3
Verifying : flex-2.6.1-9.el8.x86_64 2/3
Verifying : elfutils-libelf-devel-0.185-1.el8.x86_64 3/3
Installed:
bison-3.0.4-10.el8.x86_64 elfutils-libelf-devel-0.185-1.el8.x86_64 flex-2.6.1-9.el8.x86_64
Complete!
[root@CentOS8 ~]#tar xvf linux-6.4.11.tar.xz -C /usr/local/src
[root@CentOS8 ~]#cd /usr/local/src
[root@CentOS8 src]#ls
httpd-2.4.57 httpd-2.4.57.tar.bz2 linux-6.4.11
[root@CentOS8 src]#du -sh . #查看目录总大小
1.5G
[root@CentOS8 src]#find -name "*.c" | wc -l #.c后缀文件个数
32793
[root@CentOS8 src]#find -name "*.c" | xargs cat|wc -l #所有.c文件总行数
23223391
[root@CentOS8 src]#cd linux-6.4.11/
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#ls
arch CREDITS fs ipc lib mm samples tools
block crypto include Kbuild LICENSES net scripts usr
certs Documentation init Kconfig MAINTAINERS README security virt
COPYING drivers io_uring kernel Makefile rust sound
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#cp /boot/config-4.18.0-348.el8.x86_64 .config
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#ls -a
. .config .get_maintainer.ignore Kbuild Makefile scripts
.. COPYING .gitattributes Kconfig mm security
arch CREDITS .gitignore kernel net sound
block crypto include lib README tools
certs Documentation init LICENSES rust usr
.clang-format drivers io_uring .mailmap .rustfmt.toml virt
.cocciconfig fs ipc MAINTAINERS samples
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#vim .config
# CONFIG_MODULE_SIG is not set #将其注释
CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRUSTED KEYS="" #删除中间内容
# CONFIG DEBUG INFO is not set
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#make hel p
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#make menuconfig
HOSTCC scripts/basic/fixdep
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/mconf.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/checklist.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/inputbox.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/menubox.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/textbox.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/util.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lxdialog/yesno.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/confdata.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/expr.o
LEX scripts/kconfig/lexer.lex.c
YACC scripts/kconfig/parser.tab.[ch]
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/lexer.lex.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/menu.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/parser.tab.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/preprocess.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/symbol.o
HOSTCC scripts/kconfig/util.o
HOSTLD scripts/kconfig/mconf
.config:569:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for I8K
.config:3027:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for ISDN_CAPI
.config:6142:warning: symbol value 'm' invalid for VFIO_VIRQFD
configuration written to .config
*** End of the configuration.
*** Execute 'make' to start the build or try 'make help'.
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#make -j 2或者 make -j 8 bzImage ; make -j 8 modules
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#time make -j 16 ;date #计时
real 71m7.093s
user 315m20.782s
sys 57m0.485s
Mon Aug 21 01:45:32 CST 2023
[rootacentos8 ~]#make modules_install
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]# ls /lib/modules/
4.18.0-348.el8.x86_64 6.4.11joyce-linux-6-4-11
[root@CentOS8 linux-6.4.11]#du -sh /lib/modules/6.4.11joyce-linux-6-4-11/
4.7G /lib/modules/6.4.11joyce-linux-6-4-11/
[root@centos8 ~]#make install
[root@centos8 ~]#reboot
make menuconfig:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-n01g4qBu-1692688111229)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230821002421885.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e9907894e3714123b77ea56a52c8f3cb.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-XfWUghek-1692688111229)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230821002538383.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/21bfd361f20d481b8e7862f97d14a6ba.png)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gumYllcx-1692688111230)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230821002721884.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/05382ffa11934a58a1ebcc766600926f.png)
修改完后查看.config文件,NTFS已经被修改
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-tTrJ2Y9f-1692688111232)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230821003030496.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/25aa981784f3483083cd7ab17ecfe4b5.png)
4.3.1.4 内核编译说明
1.配置内核选项:
支持“更新”模式进行配置: make help
- (a) make config: 基于命令行以遍历的方式配置内核中可配置的每个选项
- (b) make menuconfig: 基于curses的文本窗口界面
- © make gconfig: 基于GTK(GNOME) 环境窗口界面
- (d) make xconfig: 基于QT(KDE)环境的窗口界面
支持“全新配置”模式进行配置
- (a)make defconfig: 基于内核为目标平台提供的“默认”配置进行配置
- (b) make allyesconfig: 所有选项均回答为"yes"
- © make allnoconfig: 所有选项均回答为"no"
2.编译内核
-
全编译:
make [-j #] -
编译内核的一部分功能:
(a)只编译某子目录中的相关代码
cd /usr/src/linux; make dir/(b) 只编译一个特定的模块
cd /usr/src/linux; make dir/file.ko -
范例: 只为e1000编译驱动:
make drivers/net/ethernet/intel/e1000/e1000.ko
3 交叉编译内核
编译的目标平台与当前平台不相同
make ARCH=arch name
要获取特定目标平台的使用帮助
make ARCH=arch_name help
示例:
make ARCH=arm help
4重新编译需要事先清理操作
make clean: 清理大多数编译生成的文件,但会保留.config文件等
make mrproper: 清理所有编译生成的文件、config及某些备份文件
make distclean: 包含make mrproper,并清理patches以及编辑器备份文件
4.3.1.5 卸载内核
- 删除/usr/src/linux/目录下不需要的内核源码
- 删除/lib/modules/目录下不需要的内核库文件
- 删除/boot目录下启动的内核和内核映像文件
- 更改grub的配置文件,删除不需要的内核启动列表 grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
- CentOS 8 还需要删除 /boot/loader/entries/5b85fc7444b240a992c42ce2a9f65db5-新内核版本.conf
5 Busybox
5.1 Busybox介绍

Busybox 最初是由 Bruce Perens 在 1996 年为 Debian GNU/Linux 安装盘编写的。其目标是在一张软盘(存储空间只有1MB多)上创建一个GNU/Linux 系统,可以用作安装盘和急救盘
Busybox 是一个开源项目,遵循GPL 2协议。Busybox将众多的UNIX命令集合进一个很小的可执行程序中,可以用来替代GNU fileutils、shellutils 等工具集。Busybox中各种命令与相应的GNU工具相比所能提供的选项比较少,但是也足够一般的应用了。Busybox主要用于嵌入式系统
Busybox 是一个集成了三百多个最常用Linux命令和工具的软件。BusyBox 包含了一些简单的工具,例如Is、cat和echo等等,还包含了一些更大、更复杂的工具,例grep、find、mount以及telnet。有些人将BusyBox 称为 Linux 工具里的瑞士军刀。简单的说BusyBox就好像是个大工具箱,它集成压缩了Linux 的许多工具和命令,也包含了 Android 系统的自带的shell
定制小型的Linux操作系统: inux内核+busybox
官方网站: https://busybox.net/
5.2 Busybox使用
busybox 的编译过程与Linux内核的编译类似
busybox的使用有三种方式
- busybox后直接跟命令,如 busybox ls
- 直接将busybox重命名,如 p busybox tar
- 创建符号链接,如 In -s busybox rm
busybox的安装
以上方法中,第三种方法最方便,但为busybox中每个命令都创建一个软链接,相当费事,busybox提供自动方法: busybox编译成功后,执行make install,则会产生一个 install目录,其中包含了busybox及每个命令的软链接
5.3 busybox编译安装
[root@centos7 ~]#yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ glibc glibc-devel make pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel systemd-devel zlib-devel glibc-static ncurses-devel
[root@centos7 ~]#wget https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.36.1.tar.bz2
[root@centos7 ~]#tar xvf busybox-1.36.1.tar.bz2
[root@centos7 ~]#cd busybox-1.36.1/
[root@centos7 ~]#make menuconfig 按下面选择,把busybox编译也静态二进制、不用共享库
#Settings -->Build options -->[*] Build BusyBox as a static binary (no sharedTibs)
[root@centos7 ~]#make && make install#如果出错,执行make clean后,重新执行上面命令
[root@centos7 ~]#mkdir /mnt/sysroot/
[root@centos7 ~]#cp -a _install/* /mnt/sysroot/
6 systemd
6.1 systemd 特性
Systemd: 从 C 7 版本之后开始用 systemd 实现init进程,系统启动和服务器守护进程管理器,负责在系统启动或运行时,激活系统资源,服务器进程和其它进程
Systemd新特性
- 系统引导时实现服务并行启动
- 按需启动守护进程
- 自动化的服务依赖关系管理
- 完全代替xinetd
- 同时采用socket式与D-Bus总线式激活服务
- socket与服务程序分离
- 向后兼容sysv init脚本
- 使用systemctl 命令管理,systemctl命令固定不变,不可扩展,非由systemd启动的服务
- systemctl无法与之通信和控制
- 系统状态快照
systemd核心概念: unit
unit表示不同类型的systed对象,通过配置文件进行标识和配置;文件中主要包含了系统服务、监听socket、保存的系统快照以及其它与init相关的信息
Unit类型
#查看unit类型
systemctl -t help
[root@CentOS7 yum.repos.d]#systemctl -t help
Available unit types:
service
socket
busname
target
snapshot
device
mount
automount
swap
timer
path
slice
scope
- service unit: 文件扩展名为.service,用于定义系统服务
- Target unit: 文件扩展名为.target,用于模拟实现运行级别
- Device unit: .device,用于定义内核识别的设备
- Mount unit:.mount, 定义文件系统挂载点
- Socket unit:.socket, 定义进程间通信用的socket文件,也可在系统启动时,延迟启动服务,实现按需启动
- Snapshot unit: .snapshot,管理系统快照
- Swap unit: .swap,用于标识swap设备
- Automount unit: .automount,文件系统的自动挂载点
- Path unit:.path,用于定义文件系统中的一个文件或目录使用,常用于当文件系统变化时,延时激活服务,如: spool 目录
unit的配置文件
/usr/lib/systemd/system;每个服务最主要的启动脚本设置,类似于之前的/etc/init.d/
/lib/systemd/system; :Ubuntu的对应目录
/run/systemd/system; 系统执行过程中所产生的服务脚本,比上面目录优先运行
/etc/systemd/system; 管理员建立的执行脚本,类似于/etc/rcN.d/sxx的功能,比上面目录优先运行
6.2 systemctl管理系统服务service unit
命令
systemctl COMMAND name.service
例:
#启动:相当于service name start
systemctl start name.service
#停止: 相当于service name stop
systemctl stop name.service
#重启:相当于service name restart
systemctl restart name.service
#查看状态: 相当于service name status
systemctl status name.service
#禁止自动和手动启动:
systemctl mask name.service
#取消禁止
systemctl unmask name.service
#查看某服务当前激活与否的状态:
systemctl is-active name.service
#查看所有已经激活的服务:
systemctl list-units --type-t service
#查看所有服务:
systemctl list-units --type service --all|-a
#设定某服务开机自启,相当于chkconfig name on
systemctl enable name.service
#设定某服务开机禁止启动: 相当于chkconfig name off
systemctl disable name.service
#立即启动某服务,并设置为开机自启
systemctl enable --now name.service
#立即关闭某服务,并设置为开机不启动
systemctl disable --now name.service
#查看所有服务的开机自启状态,相当于chkconfig --list
systemctl list-unit-files --type service
#用来列出该服务在哪些运行级别下启用和禁用: chkconfig -list name
Is /etc/systemd/system/*.wants/name.service
#查看服务是否开机自启:
systemctl is-enabled name.service
#列出失败的服务
systemctl --failed --type=service
#查看服务的依赖关系:
systemctl list-dependencies name.service
#杀掉进程:
systemctl kill unitname
服务状态
#显示状态
systemctl list-unit-files --type service --all
- loaded Unit配置文件已处理
- active(running) 一次或多次持续处理的运行
- active(exited) 成功完成一次性的配置
- active(waiting) 运行中,等待一个事件
- inactive 不运行
- enabled 开机启动
- disabled 开机不启动
- static 开机不启动,但可被另一个启用的服务激活
- indirect 重定向到别处
例:
#显示所有单元状态
systemctl 或 systemctl list-units
#只显示服务单元的状态
systemctl --type=service
#显示sshd服务单元
systemctl -l status sshd.service
#验证sshd服务当前是否活动
systemctl is-active sshd
#启动,停止和重启sshd服务
systemct] start sshd.service
systemctl stop sshd.service
systemctT restart sshd.service
#重新加载配置
systemct reload sshd.service
#列出活动状态的所有服务单元
systemctl list-units --type=service
#列出所有服务单元
systemctl list-units --type=service --all
#查看服务单元的启用和禁用状态
systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
#列出依赖的单元
systemctl list-dependencies sshd
#验证sshd服务是否开机启动
systemctl is-enabled sshd
#禁用network,使之不能自动启动,但手动可以
systemctl disable network
#启用network
systemct] enabe network
#禁用network,使之不能手动或自动启动
systemctl mask network
#启用network
systemct] unmask network
6.3 service unit文件格式
/etc/systemd/system: 系统管理员和用户使用
/usr/lib/systemd/system: 发行版打包者使用
帮助参考:
systemd.directives (7),systemd.unit(5),systemd.service(5), systemd.socket(5),systemd.target(5),systemd.exec(5)
unit 格式说明:
- 以“#”开头的行后面的内容会被认为是注释
- 相关布尔值,1、yes、on、true 都是开启,0、no、off、false 都是关闭
- 时间单位默认是秒,所以要用毫秒 (ms)分钟 (m) 等须显式说明
service unit file文件通常由三部分组成**
[Unit]: 定义与Unit类型无关的通用选项;用于提供unit的描述信息、unit行为及依赖关系等
[Service]: 与特定类型相关的专用选项; 此处为Service类型
[Install]: 定义由“systemctl enable”以及”systemctl disable”命令在实现服务启用或禁用时用到的一些选项
Unit段的常用选项:
Description: 描述信息
After: 定义unit的启动次序,表示当前unit应该晚于哪些unit启动,其功能与Before相反
Requires: 依赖到的其它units,强依赖,被依赖的units无法激活时,当前unit也无法激活
Wants:依赖到的其它units,弱依赖
Conflicts: 定义units间的冲突关系
Service段的常用选项:
Type:定义影响ExecStart及相关参数的功能的unit进程启动类型
simple: 默认值,这个daemon主要由ExecStart接的指令串来启动,启动后常驻于内存中
forking: 由ExecStart启动的程序透过spawns延伸出其他子程序来作为此daemon的主要服务。原生父程序在启动结束后就会终止
oneshot: 与simple类似,不过这个程序在工作完毕后就结束了,不会常驻在内存中
dbus: 与simple类似,但这个daemon必须要在取得一个D-Bus的名称后,才会继续运作.因此
通常也要同时设定BusNname= 才行
onotify: 在启动完成后会发送一个通知消息。还需要配合 NotifyAccess 来让Systemd 接收消息
idle: 与simple类似,要执行这个daemon必须要所有的工作都顺利执行完毕后才会执行。这类的daemon通常是开机到最后才执行即可的服务
EnvironmentFile:环境配置文件
ExecStart:指明启动unit要运行命令或脚本的绝对路径
ExecStartPre:ExecStant前运行
ExecStartPost:ExecStart后运行
ExecStop:指明停止unit要运行的命令或脚本
Restart: 当设定Restart=1 时,则当次daemon服务意外终止后,会再次自动启动此服务
PrivateTmp: 设定为yes时,会在生成/tmp/systemd-private-UUID-NAME.service-XXXXX/tmp/目录
Install段的常用选项:
Alias: 别名,可使用systemctl command Alias.service
RequiredBy: 被哪些units所依赖,强依赖
WantedBy:被哪些units所依赖,弱依赖
Also: 安装本服务的时候还要安装别的相关服务
注意:对于新创建的unit文件,或者修改了的unit文件,要通知systemd重载此配置文件,而后可以选择重启
systemctl daemon-reToad
范例: 服务Unit文件——http
[unit]
Description=The Nginx HTTP Server daemon # 描述信息
After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target # 指定启动nginx之前需要其他的其他服务,如network.target等
[service]
# Type为服务类型,仅启动一个主进程的服务为simple,需要启动若干子进程的服务为forking
Type=forking
# 设置执行systemctl start nginx后需要启动的具体命令
Execstart=/usr/ocal/nginx/sbin/nginx
# 设置执行systemctl reload nginx后需要执行的具体命令
ExecReToad=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
# 设置执行systemctl stop nginx后需要执行的具体命令
Execstop=/bin/kill -s OUIT ${MAINPID}
[Install]
# 设置在什么模式下被安装,设置开机启动的时候需要
wantedBy=multi-user.target
范例: 服务Unit文件示例——tomcat
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/tomcat.service
[unit]
Description=java tomcat project
After=sysTog.target network.target
[service]
Type=forking
EnvironmentFile=/usr/local/tomcat/conf/tomcat.conf
Execstart=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
Execstop=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
PrivateTmp=true
User=tomcat
[Install]
wantedBy=multi-user.target
**范例: 服务Unit文件示例——**bak
vim /etc/systemd/system/bak.service
[unit]
Description=backup /etc
Requires=atd.service
[service]
Type=simple
Execstart=/bin/bash -c "echo /data/bak.sh | at now"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start bak
范例: Ubutun实现开机自动运行程序
[root@ubuntu1804 ~]#vim /etc/rc.local
[root@ubuntu1804 ~]#cat /etc/rc.local
#!/bin/bash
echo -e ' E[31;1mstarting test service E[Om
sleep 10
[root@ubuntu1804 ~]#chmod +x /etc/rc.local
6.4 运行级别
target units: 相当于CentOS 6之前的runlevel,unit配置文件: target
ls /usr/lib/systemd/system/*.target
systemctl list-unit-files --type target --a77
和运行级别对应关系
0 ==> runlevel0.target,poweroff.target
1 ==> runlevel1.target,rescue.target
2 ==> runlevel2.target,multi-user.target
3 ==> runlevel3.target,multi-user.target
4 ==> runlevel4.target,multi-user.target
5 ==> runlevel5.target,graphical.target
6 ==> runlevel6.target,reboot.target
查看依赖性:
systemct1 1ist-dependencies graphical.target
级别切换: 相当于 init N
systemct1 isolate name.target
进入默认target
systemct7 defau7t
范例:
#切换至字符模式
systemct] isolate multi-user.target
注意:只有/lib/systemd/system/*.target文件中Allowlsolate=yes 才能切换(修改文件需执行systemd daemon-reload才能生效)
获取默认运行级别:相当于查看 /etc/inittab
systemct1 get-defaut
修改默认级别: 相当于修改 /etc/inittab
systemct1 set-default name.target
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#systemctl set-default multi-user.target
[root@centos8 ~]#ls -l /etc/systemd/system/default.target
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 37 NoV 7 19:32 /etc/systemd/system/default.target -> /1ib/systemd/system/multi-user.target
切换至紧急救援模式
systemct1 rescue
切换至emergency模式
systemctl emergency
说明: rescue.target 比emergency 支持更多的功能,例如日志等
传统命令init,poweroff,halt,reboot都成为systemctl的软链接
#关机
systemct1 halt、systemct1 poweroff
#重启:
systemctl reboot
#挂起:
systemct1 suspend
#休眠:
systemct7
hibernate
#休眠并挂起:
systemct1 hybrid-sTeep
范例: 禁用ctrl+alt+delete 重启快捷键
[root@centos8 ~]#ls -l /1ib/systemd/system/ctrl-alt-del.target
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 13 May 23 2019 /1ib/systemd/system/ctrl-alt-del.target -> reboot.target
[root@centos8 ~]#systemct1 mask ctrl-alt-de1.target
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/ctr]-alt-del.target - /dev/nul1
[root@centos8 ~]#init q
[root@centos8 ~]#systemctl daemon-reload
6.5 Centos 7之后版本引导顺序
-
UEFi或BIOS初始化,运行POST开机自检
-
选择启动设备
-
引导装载程序,centos7是grub2,加载装载程序的配置文件
/etc/grub.d/
/etc/default/grub
/boot/grub2/grub.cfg
-
加载initramfs驱动模块
-
加载内核选项
-
内核初始化,centos7使用systemd代替init
-
执行initrd.target所有单元,包括挂载/etc/fstab
-
从initramfs根文件系统切换到磁盘根目录
-
systemd执行默认target配置,配置文件/etc/systemd/system/default.target
-
systemd执行sysinit.target初始化系统及basic.target准备操作系统
-
systemd启动multi-user.target下的本机与服务器服务
-
systemd执行multi-user.target下的/etc/rc.d/rc.local
-
Systemd执行multi-user.target下的getty.target及登录服务
-
systemd执行graphical需要的服务
通过systemd-analyze 工具可以了解启动的详细过程
[root@CentOS8 ~]#systemd-analyze blame
40.827s dnf-makecache.service
6.374s plymouth-quit-wait.service
5.407s cockpit-motd.service
3.263s unbound-anchor.service
2.570s mysqld.service
1.543s tuned.service
1.443s postfix.service
1.373s systemd-udev-settle.service
1.329s vdo.service
1.038s sssd.service
796ms polkit.service
777ms ModemManager.service
679ms initrd-switch-root.service
674ms lvm2-monitor.service
553ms NetworkManager-wait-online.service
516ms avahi-daemon.service
429ms NetworkManager.service
426ms smartd.service
425ms dracut-initqueue.service
258ms autofs.service
202ms cups.service
180ms packagekit.service
175ms accounts-daemon.service
171ms udisks2.service
168ms systemd-udev-trigger.service
163ms bluetooth.service
159ms systemd-logind.service
143ms systemd-tmpfiles-clean.service
133ms systemd-udevd.service
125ms user@0.service
116ms sysroot.mount
100ms sshd.service
100ms rsyslog.service
83ms initrd-parse-etc.service
82ms gdm.service
74ms systemd-tmpfiles-setup-dev.service
69ms systemd-vconsole-setup.service
68ms cockpit.service
68ms sysstat-summary.service
68ms systemd-modules-load.service
61ms auditd.service
59ms systemd-journald.service
58ms nis-domainname.service
57ms kmod-static-nodes.service
56ms sys-kernel-debug.mount
56ms boot.mount
53ms dev-disk-by\x2duuid-80ee59c8\x2db184\x2d4f49\x2d9039\x2d5150257143b8.swap
53ms systemd-remount-fs.service
48ms plymouth-switch-root.service
47ms systemd-fsck@dev-disk-by\x2duuid-54ead45a\x2d7577\x2d4b54\x2d9de2\x2d501aef04207a>
42ms dracut-pre-pivot.service
41ms dracut-cmdline.service
41ms data.mount
40ms dev-hugepages.mount
37ms iscsi-shutdown.service
36ms dev-mqueue.mount
33ms systemd-user-sessions.service
33ms systemd-journal-flush.service
33ms systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service
31ms rtkit-daemon.service
40.827s dnf-makecache.service
6.374s plymouth-quit-wait.service
5.407s cockpit-motd.service
3.263s unbound-anchor.service
2.570s mysqld.service
1.543s tuned.service
1.443s postfix.service
1.373s systemd-udev-settle.service
1.329s vdo.service
1.038s sssd.service
796ms polkit.service
777ms ModemManager.service
679ms initrd-switch-root.service
674ms lvm2-monitor.service
553ms NetworkManager-wait-online.service
516ms avahi-daemon.service
429ms NetworkManager.service
426ms smartd.service
425ms dracut-initqueue.service
258ms autofs.service
202ms cups.service
180ms packagekit.service
175ms accounts-daemon.service
171ms udisks2.service
168ms systemd-udev-trigger.service
163ms bluetooth.service
159ms systemd-logind.service
143ms systemd-tmpfiles-clean.service
133ms systemd-udevd.service
125ms user@0.service
116ms sysroot.mount
100ms sshd.service
100ms rsyslog.service
83ms initrd-parse-etc.service
82ms gdm.service
74ms systemd-tmpfiles-setup-dev.service
69ms systemd-vconsole-setup.service
68ms cockpit.service
68ms sysstat-summary.service
68ms systemd-modules-load.service
61ms auditd.service
59ms systemd-journald.service
58ms nis-domainname.service
57ms kmod-static-nodes.service
56ms sys-kernel-debug.mount
56ms boot.mount
53ms dev-disk-by\x2duuid-80ee59c8\x2db184\x2d4f49\x2d9039\x2d5150257143b8.swap
53ms systemd-remount-fs.service
48ms plymouth-switch-root.service
47ms systemd-fsck@dev-disk-by\x2duuid-54ead45a\x2d7577\x2d4b54\x2d9de2\x2d501aef04207a>
42ms dracut-pre-pivot.service
41ms dracut-cmdline.service
41ms data.mount
40ms dev-hugepages.mount
37ms iscsi-shutdown.service
36ms dev-mqueue.mount
33ms systemd-user-sessions.service
33ms systemd-journal-flush.service
33ms systemd-tmpfiles-setup.service
31ms rtkit-daemon.service
30ms sysstat.service
30ms systemd-random-seed.service
28ms systemd-sysctl.service
22ms import-state.service
20ms dracut-pre-udev.service
19ms plymouth-read-write.service
18ms initrd-cleanup.service
17ms plymouth-start.service
17ms cockpit.socket
15ms plymouth-quit.service
14ms proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount
14ms cockpit-wsinstance-https-factory.socket
14ms systemd-fsck-root.service
13ms systemd-rfkill.service
12ms sys-fs-fuse-connections.mount
11ms cockpit-wsinstance-http.socket
9ms systemd-update-utmp.service
9ms user-runtime-dir@0.service
7ms systemd-update-utmp-runlevel.service
6ms dracut-shutdown.service
5ms initrd-udevadm-cleanup-db.service
5ms sysstat-collect.service
2ms sys-kernel-config.mount
1ms cockpit-wsinstance-http-redirect.socket
lines 61-84/84 (END)
30ms sysstat.service
30ms systemd-random-seed.service
28ms systemd-sysctl.service
22ms import-state.service
20ms dracut-pre-udev.service
19ms plymouth-read-write.service
18ms initrd-cleanup.service
17ms plymouth-start.service
17ms cockpit.socket
15ms plymouth-quit.service
14ms proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount
14ms cockpit-wsinstance-https-facto>
14ms systemd-fsck-root.service
13ms systemd-rfkill.service
lines 61-74/84 87%
30ms sysstat.service
30ms systemd-random-seed.service
28ms systemd-sysctl.service
22ms import-state.service
20ms dracut-pre-udev.service
19ms plymouth-read-write.service
18ms initrd-cleanup.service
17ms plymouth-start.service
17ms cockpit.socket
15ms plymouth-quit.service
14ms proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount
14ms cockpit-wsinstance-https-factory.socket
14ms systemd-fsck-root.service
13ms systemd-rfkill.service
12ms sys-fs-fuse-connections.mount
11ms cockpit-wsinstance-http.socket
9ms systemd-update-utmp.service
9ms user-runtime-dir@0.service
7ms systemd-update-utmp-runlevel.service
6ms dracut-shutdown.service
5ms initrd-udevadm-cleanup-db.service
5ms sysstat-collect.service
2ms sys-kernel-config.mount
1ms cockpit-wsinstance-http-redirect.socket
lines 61-84/84 (END)
#或xml文件
[root@CentOS8 ~]#systemd-analyze plot > boot.xml
然后传到win下,用浏览器打开
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xvJxmwXs-1692688111234)(C:\Users\HUIO\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230822120113748.png)]
6.6 设置内核参数
设置内核参数,只影响当次启动
启动时,到启动菜单,按e键,找到在linux 开头的行后添加systemd.unit=desired.target
例如:
systemd.unit=emergency.target 或 systemd.unit=rescue.target
6.7 破解 CentOS 7和8的 root 密码
方法一
启动时任意键暂停启动
按e键进入编辑模式
将光标移动linux 开始的行(C7是Linux16那行 ),添加内核参数rd.break
按ctrl-x启动
mount -o remount,rw /sysroot
chroot /sysroot
passwd root
#如果SELinux是启用的,才需要执行下面操作,如查没有启动,不需要执行
touch /.autorelabel
exit
reboot
方式二
启动时任意键暂停启动
按e键进入编辑模式
将光标移动linux 开始的行,改为rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh
按ctrl-x启动
chroot /sysroot
passwd root
#如果SELinux是启用的,才需要执行下面操作,如查没有启动,不需要执行
touch /.autorelabel
exit
reboot
6.8 实现GRUB2安全
#添加grub密码
[root@CentOS8 ~]#grub2-setpassword
Enter password:
Confirm password:
#查看文件
[root@CentOS8 ~]#ll /boot/grub2/
total 340
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 64 May 30 23:36 device.map
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 May 30 23:36 fonts
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 6590 Jul 25 15:05 grub.cfg
-rw------- 1 root root 1024 Aug 16 13:51 grubenv
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 12288 May 30 23:36 i386-pc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 309444 Aug 18 21:48 logo.xpm
-rw------- 1 root root 298 Aug 22 12:21 user.cfg
[root@CentOS8 ~]#cat /boot/grub2/user.cfg
GRUB2_PASSWORD=grub.pbkdf2.sha512.10000.0DCB0C5B0F0A9B3021C99E920A0731164C713BCA004314B049811590E32A84348686B899E6D161D11D6C663C10A0C33100BE582B7BA5CF39C5919E845D9AEA6B.4AF8E233565BF8508115991D41FCCB2B3387E35807D5BE510744A86AD64F7C0CB79CE1166AFAB1186E957D10060DFAD1CA6B57C067815CE744175070E5FD501D
#清空grub密码
[root@centos8 ~]#at /dev/null > /boot/grub2/user.cfg
6.9 修复GRUB2
GRUB2: Centos 7,8及ubuntu1804都使用
引导提示时可以使用命令行界面,可从文件系统引导
主要配置文件: /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
修复配置文件: grub2-mkconfig > /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
修复grub
grub2-install /dev/sda #BIOS环境
grub2-insta77 #UEFI环境
调整默认启动内核
#以下命令是修改 /boot/grub2/grubenv 实现
grub2-set-default 0 #适合C7,因为C8配置文件中不再存储内核对应的数字,不知道0、1对应的是哪个内核
或者
vim /etc/default/grub
GRUB_DEFAULT=0
[root@CentOS8 ~]#cat /boot/grub2/grubenv #默认启动内核
# GRUB Environment Block
saved_entry=34f09f8df29847998143d560b2af24fb-4.18.0-348.el8.x86_64 #修改为需要的内核即可,适合C8
kernelopts=root=UUID=f2c173be-7848-43e9-9d0b-da0f1841f93f ro resume=UUID=80ee59c8-b184-4f49-9039-5150257143b8 rhgb quiet net.ifnames=0
boot_success=1
boot_indeterminate=0
########################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################################[root@CentOS8 ~]#cd
[root@CentOS8 ~]#ls /boot/loader/entries/ #查看所有内核
34f09f8df29847998143d560b2af24fb-0-rescue.conf
34f09f8df29847998143d560b2af24fb-4.18.0-348.el8.x86_64.conf
6.10 故障排错实战案例
6.10.1 实战案例1: centos 7,8 破坏MBR后进行恢复
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1 count=446
光盘进入救援模式
grub2-instal1 --root-directory=/mnt/sysimage /dev/sda
6.10.2 实战案例2: entos 7,8删除/boot/grub2/*所有内容进行恢复
#光盘进入救援模式
chroot /mnt/sysimage
grub2-install /dev/sda
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
6.10.3 实战案例3: Centos 7,8 删除/boot/下所有文件后进行恢复
#1 光盘救援模式下安装grub2
特别说明: centos8 必须先grub,再安装kernel,否则安装kernel-core时会提示grub出错
chroot /mnt/sysimage
mount /dev/sr0 /mnt
grub2-install /dev/sda
#2 安装kernel
#Centos 7
rpm -ivh /mnt/Packages/kernel-3.10.0-1062.e17.x86_64.rpm --force
#Centos 8
rpm -ivh /mnt/Baseos/Packages/kernel-core-4.18.0-147.e18.x86_64.rpm --force
#3 修复grub配置文件
生成grub2.cfg文件
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
#4 退出重启
exit
exit
![[PyTorch][chapter 51][Auto-Encoder -1]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ad287288c7c942129815f6fced4716db.png)