文章目录
- 一.并查集
- 二.并查集的实现
- 三.并查集的基本应用
一.并查集
-
并查集的逻辑结构:由多颗不相连通的多叉树构成的森林(一个这样的多叉树就是森林的一个连通分量)
- 并查集的元素(树节点)用
0~9的整数表示,并查集可以表示如下: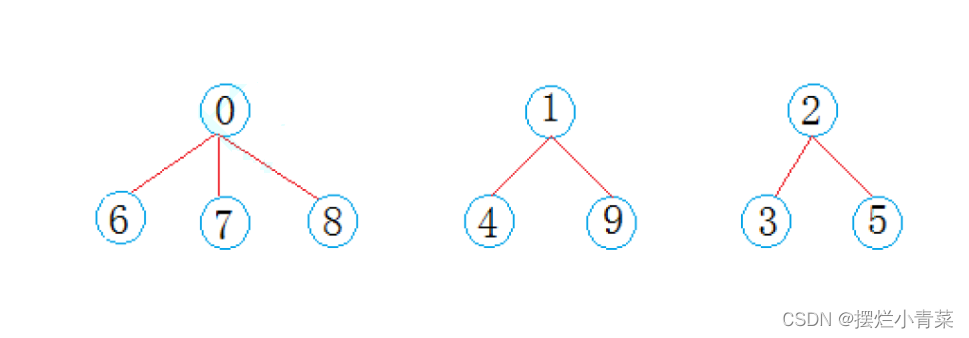
- 并查集的元素(树节点)用
-
并查集的物理存储结构:并查集一般采用顺序结构实现,用数组下标表示并查集的元素,数组元素用于记录并查集中的元素间的关系:
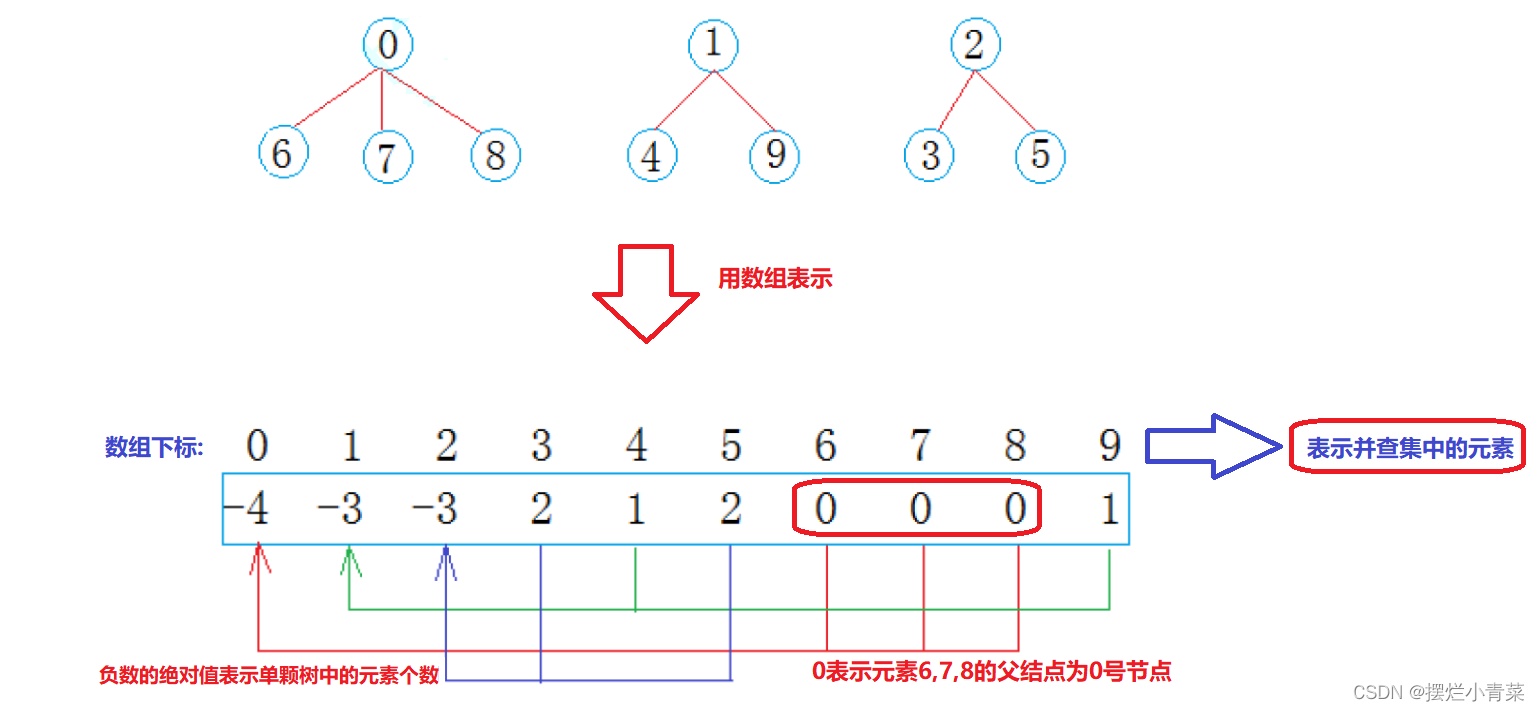
- 若并查集的元素对应的数组元素为负数,则表示该并查集元素为某颗多叉树的根且没有前驱结点,负数的绝对值表示该颗多叉树(并查集的连通分量)的元素个数
- 若并查集的元素对应的数组元素为非负数,这个非负数则表示该并查集的元素的前驱结点
-
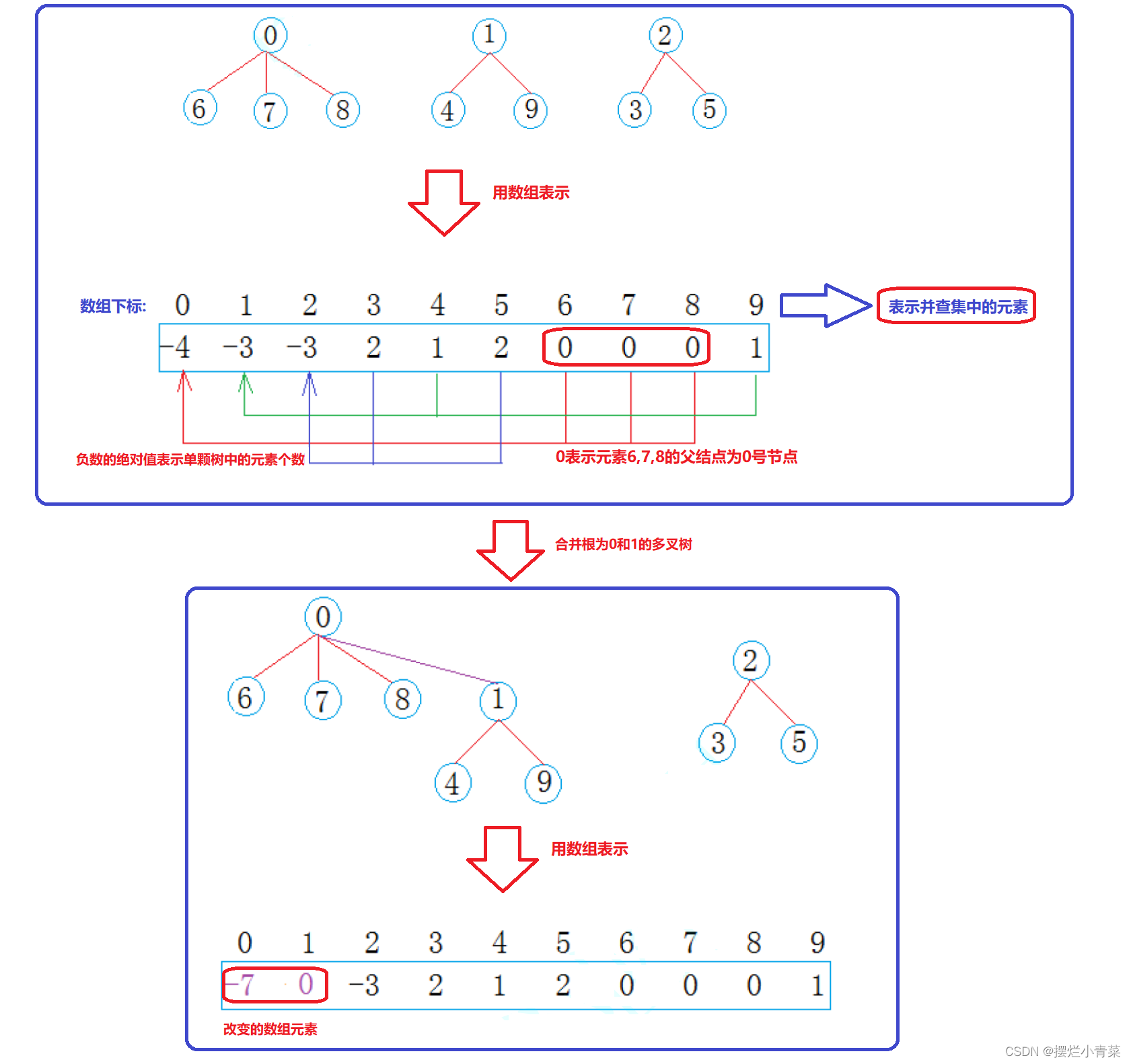
并查集数据结构常用的运算就是==(连通分量)多叉树间的合并算法==:
二.并查集的实现
- 并查集的初始状态设置:

- 简单的代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
//采用适配器模式实现并查
class UnionFindSet
{
public:
//构造函数参数为并查集中的元素个数,并查集的初始状态为size颗树构成的森林(size个连通分量)
UnionFindSet(size_t size)
:_SetMap(size,-1)
{}
//给定一个并查集元素找到其所在的(连通分量)多叉树的根结点
size_t FindRoot(int Node) const throw(std :: string)
{
//越界检查
if (Node < 0 || Node >= _SetMap.size())throw "Label out of range";
while (_SetMap[Node] >= 0)
{
Node = _SetMap[Node];
}
return static_cast<size_t>(Node);
}
//给定两个并查集元素,将它们所在的(连通分量)多叉树进行合并运算
void Union(int Node1, int Node2) throw(std::string)
{
//越界检查
if (Node1 < 0 || Node1 > _SetMap.size()|| Node2 < 0 || Node2 > _SetMap.size())
throw "Label out of range";
//先找到两个元素所在的(连通分量)多叉树的根
size_t root1 = FindRoot(Node1);
size_t root2 = FindRoot(Node2);
//进行多叉树合并操作
if (root1 != root2)
{
_SetMap[root1] += _SetMap[root2];
_SetMap[root2] = static_cast<int>(root1);
}
}
//计算并查集中多叉树的颗数(连通分量的个数)
size_t SetCount() const noexcept
{
//并查集中多叉树的颗数就是vector中负数元素的个数
size_t count = 0;
for (auto e : _SetMap)
{
if (e < 0)++count;
}
return count;
}
private:
std::vector<int> _SetMap;
};
- 并查集是一种经常用于划分等价类的数据结构.以树形逻辑结构为基础,以一颗多叉树(一个连通分量)表示一个等价类,多个互相不连通的多叉树(连通分量)构成的森林用于表示多个等价类构成的集合,使用并查集可以很好地解决等价类的划分和计数问题(即图的连通分量的求解问题)
三.并查集的基本应用
LeetCoed : LCR 116. 省份数量
- 这个问题就是一个等价类集合的构建和计数问题,可以使用并查集解决.(题目中的相连关系就是一种相对于相同省份性质的等价关系)
- 问题的本质可以抽象为:以城市为元素依据相连关系形成的图结构的最小生成树的个数(即连通分量的个数),可以采用
dfs或bfs遍历算法,此处提供使用并查集的一种写法. - 借助
vector和lambda表达式建立简单的并查集最后返回并查集中多叉树的个数:
class Solution
{
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected)
{
//创建简易的并查集
vector<int> UnionSet(isConnected.size(),-1);
//定义Find函数,根据结点找到多叉树的根
auto Find = [&UnionSet](int Node){
while(UnionSet[Node] >=0)
{
Node = UnionSet[Node];
}
return Node;
};
for(int i = 0; i < isConnected.size(); ++i)
{
for(int j = i+1; j < isConnected.size(); ++j)
{
if(isConnected[i][j] == 1)
{
//多叉树合并
int root1 = Find(i);
int root2 = Find(j);
if(root1 != root2)
{
UnionSet[root1] += UnionSet[root2];//这句代码用于修改结点计数,此题中可以不加
UnionSet[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
}
int count = 0;
//统计并查集中多叉树的个数
for(auto e : UnionSet)
{
if(e < 0 ) ++count;
}
return count;
}
};
LeetCode:990. 等式方程的可满足性
- 这同样是一个等价类划分的问题:将
0~25的各个编号与a~z二十六个字母建立映射关系,根据字母间相等关系构建并查集:
class Solution
{
public:
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations)
{
vector<int> UionSet(26,-1);
auto FindRoot = [&UionSet](int Node){
while(UionSet[Node] >= 0)
{
Node = UionSet[Node];
}
return Node;
};
//先遍历等式方程中的字母,在并查集中将它们归类到各个多叉树中(构建相等关系等价类集合)
for(auto str : equations)
{
//遇到等式,等式两边字母应该属于并查集中同一颗多叉树
if(str[1] == '=')
{
int root1 = FindRoot(str[0]-'a');
int root2 = FindRoot(str[3]-'a');
if(root1 != root2)
{
UionSet[root1] += UionSet[root2];
UionSet[root2] = root1;
}
}
}
//再处理不等式方程,检验相容性
for(auto str : equations)
{
//遇到不等式,不等式两边字母不能属于并查集中同一颗多叉树
if(str[1] == '!')
{
int root1 = FindRoot(str[0]-'a');
int root2 = FindRoot(str[3]-'a');
if(root1 == root2)
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};