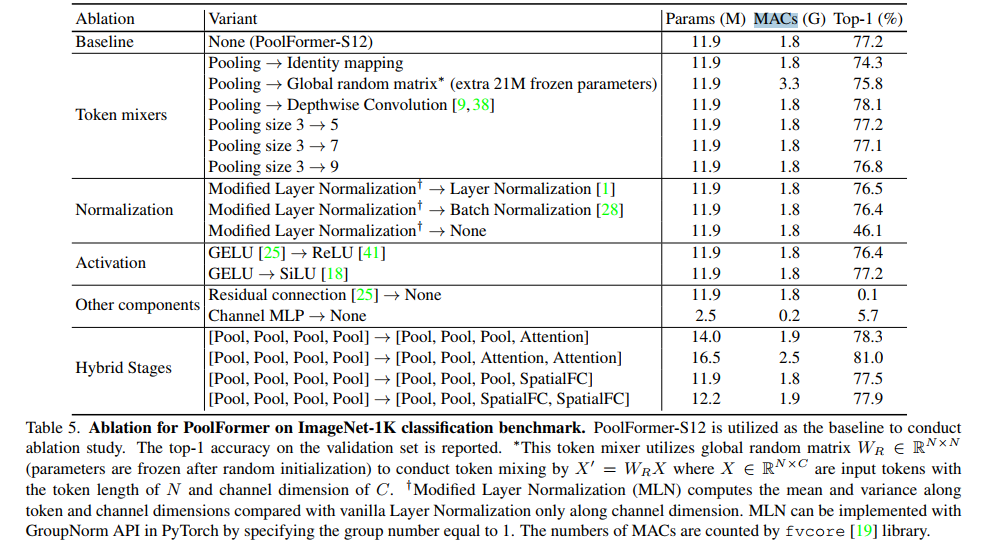
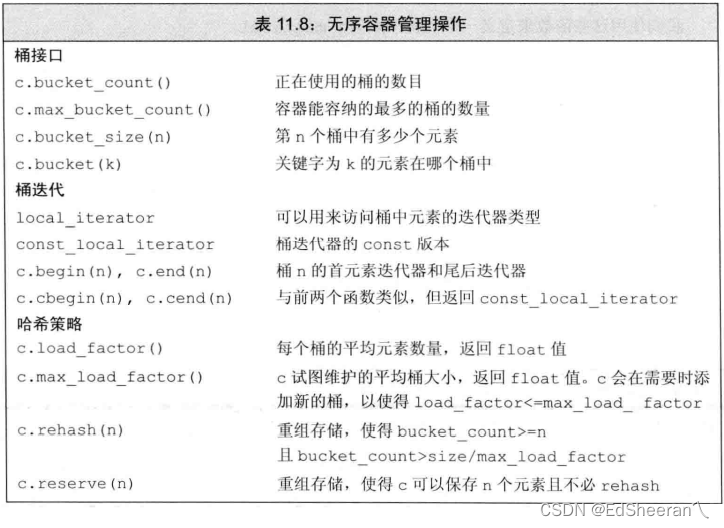
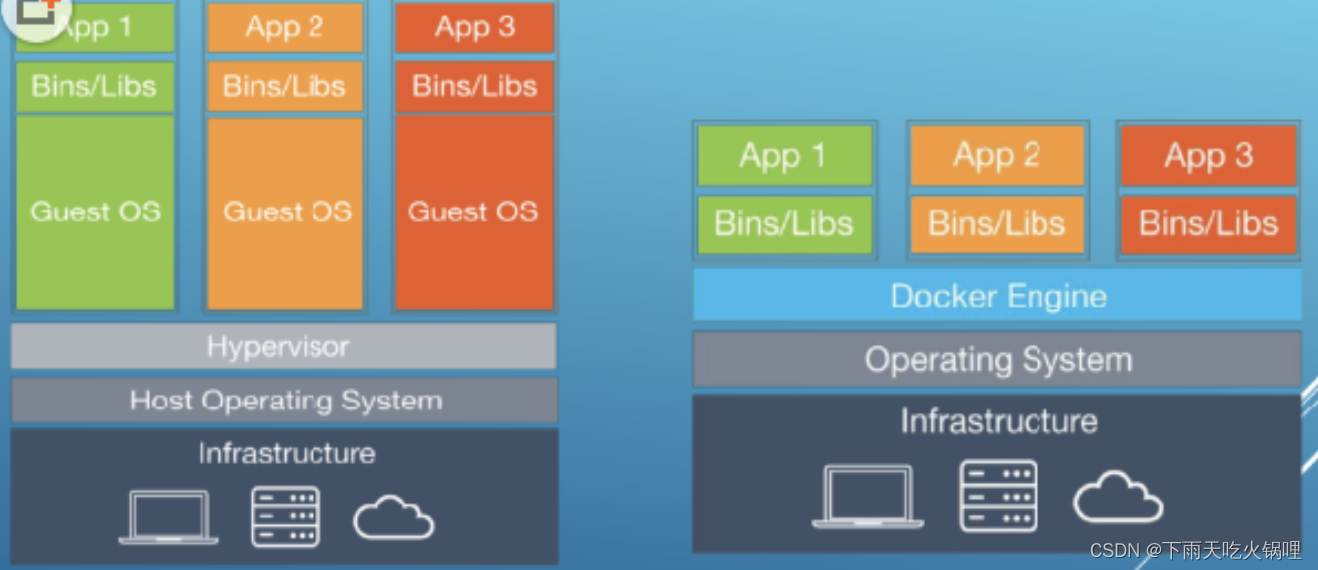
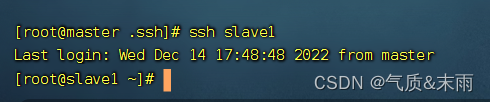
先看源码
template<typename _Tp>
class shared_ptr : public __shared_ptr<_Tp>
{
template<typename... _Args>
using _Constructible = typename enable_if<
is_constructible<__shared_ptr<_Tp>, _Args...>::value>::type;
template<typename _Arg>
using _Assignable = typename enable_if<
is_assignable<__shared_ptr<_Tp>&, _Arg>::value, shared_ptr&>::type;
public:
/// The type pointed to by the stored pointer, remove_extent_t<_Tp>
using element_type = typename __shared_ptr<_Tp>::element_type;
#if __cplusplus >= 201703L
#define __cpp_lib_shared_ptr_weak_type 201606L
/// The corresponding weak_ptr type for this shared_ptr
/// @since C++17
using weak_type = weak_ptr<_Tp>;
#endif
constexpr shared_ptr() noexcept : __shared_ptr<_Tp>() { }
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr&) noexcept = default; ///< Copy constructor
template<typename _Yp, typename = _Constructible<_Yp*>>
explicit shared_ptr(_Yp* __p) : __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p) { }
template<typename _Yp, typename _Deleter,
typename = _Constructible<_Yp*, _Deleter>>
shared_ptr(_Yp* __p, _Deleter __d)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p, std::move(__d)) { }
template<typename _Deleter>
shared_ptr(nullptr_t __p, _Deleter __d)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p, std::move(__d)) { }
template<typename _Yp, typename _Deleter, typename _Alloc,
typename = _Constructible<_Yp*, _Deleter, _Alloc>>
shared_ptr(_Yp* __p, _Deleter __d, _Alloc __a)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p, std::move(__d), std::move(__a)) { }
template<typename _Deleter, typename _Alloc>
shared_ptr(nullptr_t __p, _Deleter __d, _Alloc __a)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__p, std::move(__d), std::move(__a)) { }
template<typename _Yp>
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Yp>& __r, element_type* __p) noexcept
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, __p) { }
#if __cplusplus > 201703L
template<typename _Yp>
shared_ptr(shared_ptr<_Yp>&& __r, element_type* __p) noexcept
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(std::move(__r), __p) { }
#endif
template<typename _Yp,
typename = _Constructible<const shared_ptr<_Yp>&>>
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<_Yp>& __r) noexcept
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r) { }
shared_ptr(shared_ptr&& __r) noexcept
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(std::move(__r)) { }
template<typename _Yp, typename = _Constructible<shared_ptr<_Yp>>>
shared_ptr(shared_ptr<_Yp>&& __r) noexcept
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(std::move(__r)) { }
template<typename _Yp, typename = _Constructible<const weak_ptr<_Yp>&>>
explicit shared_ptr(const weak_ptr<_Yp>& __r)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r) { }
#if _GLIBCXX_USE_DEPRECATED
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
template<typename _Yp, typename = _Constructible<auto_ptr<_Yp>>>
shared_ptr(auto_ptr<_Yp>&& __r);
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
// _GLIBCXX_RESOLVE_LIB_DEFECTS
// 2399. shared_ptr's constructor from unique_ptr should be constrained
template<typename _Yp, typename _Del,
typename = _Constructible<unique_ptr<_Yp, _Del>>>
shared_ptr(unique_ptr<_Yp, _Del>&& __r)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(std::move(__r)) { }
#if __cplusplus <= 201402L && _GLIBCXX_USE_DEPRECATED
// This non-standard constructor exists to support conversions that
// were possible in C++11 and C++14 but are ill-formed in C++17.
// If an exception is thrown this constructor has no effect.
template<typename _Yp, typename _Del,
_Constructible<unique_ptr<_Yp, _Del>, __sp_array_delete>* = 0>
shared_ptr(unique_ptr<_Yp, _Del>&& __r)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(std::move(__r), __sp_array_delete()) { }
#endif
/**
* @brief Construct an empty %shared_ptr.
* @post use_count() == 0 && get() == nullptr
*/
constexpr shared_ptr(nullptr_t) noexcept : shared_ptr() { }
shared_ptr& operator=(const shared_ptr&) noexcept = default;
template<typename _Yp>
_Assignable<const shared_ptr<_Yp>&>
operator=(const shared_ptr<_Yp>& __r) noexcept
{
this->__shared_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(__r);
return *this;
}
#if _GLIBCXX_USE_DEPRECATED
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
template<typename _Yp>
_Assignable<auto_ptr<_Yp>>
operator=(auto_ptr<_Yp>&& __r)
{
this->__shared_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(std::move(__r));
return *this;
}
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
shared_ptr&
operator=(shared_ptr&& __r) noexcept
{
this->__shared_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(std::move(__r));
return *this;
}
template<class _Yp>
_Assignable<shared_ptr<_Yp>>
operator=(shared_ptr<_Yp>&& __r) noexcept
{
this->__shared_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(std::move(__r));
return *this;
}
template<typename _Yp, typename _Del>
_Assignable<unique_ptr<_Yp, _Del>>
operator=(unique_ptr<_Yp, _Del>&& __r)
{
this->__shared_ptr<_Tp>::operator=(std::move(__r));
return *this;
}
private:
// This constructor is non-standard, it is used by allocate_shared.
template<typename _Alloc, typename... _Args>
shared_ptr(_Sp_alloc_shared_tag<_Alloc> __tag, _Args&&... __args)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__tag, std::forward<_Args>(__args)...)
{ }
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc, typename... _Args>
friend shared_ptr<_NonArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared(const _Alloc&, _Args&&...);
template<typename _Yp, typename... _Args>
friend shared_ptr<_NonArray<_Yp>>
make_shared(_Args&&...);
#if __cpp_lib_shared_ptr_arrays >= 201707L
// This constructor is non-standard, it is used by allocate_shared<T[]>.
template<typename _Alloc, typename _Init = const remove_extent_t<_Tp>*>
shared_ptr(const _Sp_counted_array_base<_Alloc>& __a,
_Init __init = nullptr)
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__a, __init)
{ }
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc>
friend shared_ptr<_UnboundedArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared(const _Alloc&, size_t);
template<typename _Yp>
friend shared_ptr<_UnboundedArray<_Yp>>
make_shared(size_t);
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc>
friend shared_ptr<_UnboundedArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared(const _Alloc&, size_t, const remove_extent_t<_Yp>&);
template<typename _Yp>
friend shared_ptr<_UnboundedArray<_Yp>>
make_shared(size_t, const remove_extent_t<_Yp>&);
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc>
friend shared_ptr<_BoundedArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared(const _Alloc&);
template<typename _Yp>
friend shared_ptr<_BoundedArray<_Yp>>
make_shared();
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc>
friend shared_ptr<_BoundedArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared(const _Alloc&, const remove_extent_t<_Yp>&);
template<typename _Yp>
friend shared_ptr<_BoundedArray<_Yp>>
make_shared(const remove_extent_t<_Yp>&);
#if __cpp_lib_smart_ptr_for_overwrite
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc>
friend shared_ptr<_NotUnboundedArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared_for_overwrite(const _Alloc&);
template<typename _Yp>
friend shared_ptr<_NotUnboundedArray<_Yp>>
make_shared_for_overwrite();
template<typename _Yp, typename _Alloc>
friend shared_ptr<_UnboundedArray<_Yp>>
allocate_shared_for_overwrite(const _Alloc&, size_t);
template<typename _Yp>
friend shared_ptr<_UnboundedArray<_Yp>>
make_shared_for_overwrite(size_t);
#endif
#endif
// This constructor is non-standard, it is used by weak_ptr::lock().
shared_ptr(const weak_ptr<_Tp>& __r, std::nothrow_t) noexcept
: __shared_ptr<_Tp>(__r, std::nothrow) { }
friend class weak_ptr<_Tp>;
}从上面class shared_ptr的定义来看只是继承了class __shared_ptr,并没有涉及ref count相关的实现。下面来看看其父类class __shared_ptr的定义:
template<typename _Tp, _Lock_policy _Lp>
class __shared_ptr
{
public:
typedef _Tp element_type;
__shared_ptr()
: _M_ptr(0), _M_refcount() // never throws
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit
__shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p)
: _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p)
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
typedef int _IsComplete[sizeof(_Tp1)];
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __p, __p);
}
template<typename _Tp1, typename _Deleter>
__shared_ptr(_Tp1* __p, _Deleter __d)
: _M_ptr(__p), _M_refcount(__p, __d)
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
// TODO requires _Deleter CopyConstructible and __d(__p) well-formed
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __p, __p);
}
// generated copy constructor, assignment, destructor are fine.
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r)
: _M_ptr(__r._M_ptr), _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // never throws
{ __glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>) }
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit
__shared_ptr(const __weak_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r)
: _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount) // may throw
{
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
// It is now safe to copy __r._M_ptr, as _M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
// did not throw.
_M_ptr = __r._M_ptr;
}
#if (__cplusplus < 201103L) || _GLIBCXX_USE_DEPRECATED
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
// Postcondition: use_count() == 1 and __r.get() == 0
template<typename _Tp1>
explicit
__shared_ptr(std::auto_ptr<_Tp1>& __r)
: _M_ptr(__r.get()), _M_refcount()
{ // TODO requries delete __r.release() well-formed
__glibcxx_function_requires(_ConvertibleConcept<_Tp1*, _Tp*>)
typedef int _IsComplete[sizeof(_Tp1)];
_Tp1* __tmp = __r.get();
_M_refcount = __shared_count<_Lp>(__r);
__enable_shared_from_this_helper(_M_refcount, __tmp, __tmp);
}
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r, __static_cast_tag)
: _M_ptr(static_cast<element_type*>(__r._M_ptr)),
_M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r, __const_cast_tag)
: _M_ptr(const_cast<element_type*>(__r._M_ptr)),
_M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
{ }
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r, __dynamic_cast_tag)
: _M_ptr(dynamic_cast<element_type*>(__r._M_ptr)),
_M_refcount(__r._M_refcount)
{
if (_M_ptr == 0) // need to allocate new counter -- the cast failed
_M_refcount = __shared_count<_Lp>();
}
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr&
operator=(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __r) // never throws
{
_M_ptr = __r._M_ptr;
_M_refcount = __r._M_refcount; // __shared_count::op= doesn't throw
return *this;
}
#if (__cplusplus < 201103L) || _GLIBCXX_USE_DEPRECATED
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
template<typename _Tp1>
__shared_ptr&
operator=(std::auto_ptr<_Tp1>& __r)
{
__shared_ptr(__r).swap(*this);
return *this;
}
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
void
reset() // never throws
{ __shared_ptr().swap(*this); }
template<typename _Tp1>
void
reset(_Tp1* __p) // _Tp1 must be complete.
{
// Catch self-reset errors.
_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_ASSERT(__p == 0 || __p != _M_ptr);
__shared_ptr(__p).swap(*this);
}
template<typename _Tp1, typename _Deleter>
void
reset(_Tp1* __p, _Deleter __d)
{ __shared_ptr(__p, __d).swap(*this); }
// Allow class instantiation when _Tp is [cv-qual] void.
typename std::tr1::add_reference<_Tp>::type
operator*() const // never throws
{
_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_ASSERT(_M_ptr != 0);
return *_M_ptr;
}
_Tp*
operator->() const // never throws
{
_GLIBCXX_DEBUG_ASSERT(_M_ptr != 0);
return _M_ptr;
}
_Tp*
get() const // never throws
{ return _M_ptr; }
// Implicit conversion to "bool"
private:
typedef _Tp* __shared_ptr::*__unspecified_bool_type;
public:
operator __unspecified_bool_type() const // never throws
{ return _M_ptr == 0 ? 0 : &__shared_ptr::_M_ptr; }
bool
unique() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_unique(); }
long
use_count() const // never throws
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_use_count(); }
void
swap(__shared_ptr<_Tp, _Lp>& __other) // never throws
{
std::swap(_M_ptr, __other._M_ptr);
_M_refcount._M_swap(__other._M_refcount);
}
private:
void*
_M_get_deleter(const std::type_info& __ti) const
{ return _M_refcount._M_get_deleter(__ti); }
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1>
bool
_M_less(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp1>& __rhs) const
{ return _M_refcount < __rhs._M_refcount; }
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1> friend class __shared_ptr;
template<typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1> friend class __weak_ptr;
template<typename _Del, typename _Tp1, _Lock_policy _Lp1>
friend _Del* get_deleter(const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp1>&);
// Friends injected into enclosing namespace and found by ADL:
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool
operator==(const __shared_ptr& __a, const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __b)
{ return __a.get() == __b.get(); }
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool
operator!=(const __shared_ptr& __a, const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __b)
{ return __a.get() != __b.get(); }
template<typename _Tp1>
friend inline bool
operator<(const __shared_ptr& __a, const __shared_ptr<_Tp1, _Lp>& __b)
{ return __a._M_less(__b); }
_Tp* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.
__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.
}从__shared_ptr的定义来看,其中有两个重要的成员:
_Tp* _M_ptr; // Contained pointer.
__shared_count<_Lp> _M_refcount; // Reference counter.
template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class __shared_count
{
public:
__shared_count()
: _M_pi(0) // nothrow
{ }
template<typename _Ptr>
__shared_count(_Ptr __p) : _M_pi(0)
{
__try
{
typedef typename std::tr1::remove_pointer<_Ptr>::type _Tp;
_M_pi = new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Ptr, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>, _Lp>(
__p, _Sp_deleter<_Tp>());
}
__catch(...)
{
delete __p;
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
template<typename _Ptr, typename _Deleter>
__shared_count(_Ptr __p, _Deleter __d) : _M_pi(0)
{
__try
{
_M_pi = new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Ptr, _Deleter, _Lp>(__p, __d);
}
__catch(...)
{
__d(__p); // Call _Deleter on __p.
__throw_exception_again;
}
}
#if (__cplusplus < 201103L) || _GLIBCXX_USE_DEPRECATED
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wdeprecated-declarations"
// Special case for auto_ptr<_Tp> to provide the strong guarantee.
template<typename _Tp>
explicit
__shared_count(std::auto_ptr<_Tp>& __r)
: _M_pi(new _Sp_counted_base_impl<_Tp*,
_Sp_deleter<_Tp>, _Lp >(__r.get(), _Sp_deleter<_Tp>()))
{ __r.release(); }
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
// Throw bad_weak_ptr when __r._M_get_use_count() == 0.
explicit
__shared_count(const __weak_count<_Lp>& __r);
~__shared_count() // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_release();
}
__shared_count(const __shared_count& __r)
: _M_pi(__r._M_pi) // nothrow
{
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_add_ref_copy();
}
__shared_count&
operator=(const __shared_count& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != _M_pi)
{
if (__tmp != 0)
__tmp->_M_add_ref_copy();
if (_M_pi != 0)
_M_pi->_M_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
return *this;
}
void
_M_swap(__shared_count& __r) // nothrow
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
__r._M_pi = _M_pi;
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
long
_M_get_use_count() const // nothrow
{ return _M_pi != 0 ? _M_pi->_M_get_use_count() : 0; }
bool
_M_unique() const // nothrow
{ return this->_M_get_use_count() == 1; }
friend inline bool
operator==(const __shared_count& __a, const __shared_count& __b)
{ return __a._M_pi == __b._M_pi; }
friend inline bool
operator<(const __shared_count& __a, const __shared_count& __b)
{ return std::less<_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>*>()(__a._M_pi, __b._M_pi); }
void*
_M_get_deleter(const std::type_info& __ti) const
{ return _M_pi ? _M_pi->_M_get_deleter(__ti) : 0; }
private:
friend class __weak_count<_Lp>;
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;
}class __shared_count 中的重要成员:_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* _M_pi;
template<typename _Ptr, typename _Deleter, _Lock_policy _Lp>
class _Sp_counted_base_impl
: public _Sp_counted_base<_Lp>
{
public:
// Precondition: __d(__p) must not throw.
_Sp_counted_base_impl(_Ptr __p, _Deleter __d)
: _M_ptr(__p), _M_del(__d) { }
virtual void
_M_dispose() // nothrow
{ _M_del(_M_ptr); }
virtual void*
_M_get_deleter(const std::type_info& __ti)
{
#if __cpp_rtti
return __ti == typeid(_Deleter) ? &_M_del : 0;
#else
return 0;
#endif
}
private:
_Sp_counted_base_impl(const _Sp_counted_base_impl&);
_Sp_counted_base_impl& operator=(const _Sp_counted_base_impl&);
_Ptr _M_ptr; // copy constructor must not throw
_Deleter _M_del; // copy constructor must not throw
};从上面的定义来看,_Sp_counted_base_impl中并没有实现ref count的加,减。因此我们看看其父类_Sp_counted_base的定义:
template<_Lock_policy _Lp = __default_lock_policy>
class _Sp_counted_base
: public _Mutex_base<_Lp>
{
public:
_Sp_counted_base()
: _M_use_count(1), _M_weak_count(1) { }
virtual
~_Sp_counted_base() // nothrow
{ }
// Called when _M_use_count drops to zero, to release the resources
// managed by *this.
virtual void
_M_dispose() = 0; // nothrow
// Called when _M_weak_count drops to zero.
virtual void
_M_destroy() // nothrow
{ delete this; }
virtual void*
_M_get_deleter(const std::type_info&) = 0;
void
_M_add_ref_copy()
{ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, 1); }
void
_M_add_ref_lock();
void
_M_release() // nothrow
{
// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config.
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_use_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_use_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_use_count);
_M_dispose();
// There must be a memory barrier between dispose() and destroy()
// to ensure that the effects of dispose() are observed in the
// thread that runs destroy().
// See http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/libstdc++/2005-11/msg00136.html
if (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers)
{
__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);
}
// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config.
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count,
-1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);
_M_destroy();
}
}
}
void
_M_weak_add_ref() // nothrow
{ __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, 1); }
void
_M_weak_release() // nothrow
{
// Be race-detector-friendly. For more info see bits/c++config.
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_BEFORE(&_M_weak_count);
if (__gnu_cxx::__exchange_and_add_dispatch(&_M_weak_count, -1) == 1)
{
_GLIBCXX_SYNCHRONIZATION_HAPPENS_AFTER(&_M_weak_count);
if (_Mutex_base<_Lp>::_S_need_barriers)
{
// See _M_release(),
// destroy() must observe results of dispose()
__atomic_thread_fence (__ATOMIC_ACQ_REL);
}
_M_destroy();
}
}
long
_M_get_use_count() const // nothrow
{
// No memory barrier is used here so there is no synchronization
// with other threads.
return const_cast<const volatile _Atomic_word&>(_M_use_count);
}
private:
_Sp_counted_base(_Sp_counted_base const&);
_Sp_counted_base& operator=(_Sp_counted_base const&);
_Atomic_word _M_use_count; // #shared
_Atomic_word _M_weak_count; // #weak + (#shared != 0)
}类关系图
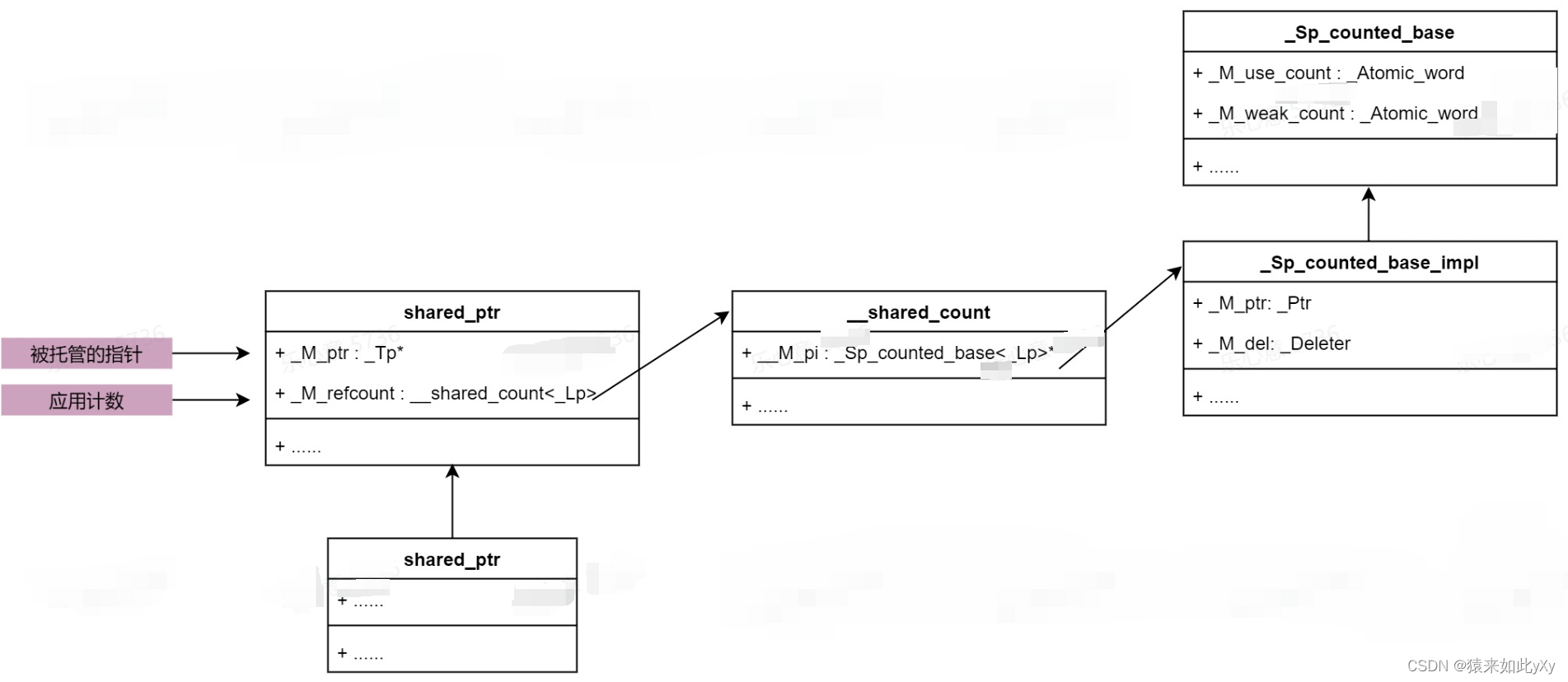
总结一下,shared_ptr的类关系图如上图所示,在_Sp_counted_base中成员_M_use_count是表示引用计数的值。其中加一有两个函数:
_Sp_counted_base<xxxx>::_M_add_ref_lock();
_Sp_counted_base<xxxx>::_M_add_ref_copy();
减一有函数:
_Sp_counted_base<xxxx>::_M_release();
下面我们来看看引用计数什么时候加一,什么时候减一。
引用计数加一
shared_ptr这个类构造,赋值,拷贝构造的时候
//构造时,赋值为1
_Sp_counted_base()
: _M_use_count(1), _M_weak_count(1) { }
//拷贝构造
__shared_count(const __shared_count& __r) noexcept: _M_pi(__r._M_pi)
{
if (_M_pi != nullptr)
_M_pi->_M_add_ref_copy();
}
//赋值
__shared_count&
operator=(const __shared_count& __r) noexcept
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != _M_pi)
{
if (__tmp != nullptr)
__tmp->_M_add_ref_copy();
if (_M_pi != nullptr)
_M_pi->_M_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
return *this;
}引用计数减一
shared_ptr这个类析构,赋值的时候。
//赋值
__shared_count&
operator=(const __shared_count& __r) noexcept
{
_Sp_counted_base<_Lp>* __tmp = __r._M_pi;
if (__tmp != _M_pi)
{
if (__tmp != nullptr)
__tmp->_M_add_ref_copy();
if (_M_pi != nullptr)
_M_pi->_M_release();
_M_pi = __tmp;
}
return *this;
}
//析构
~__shared_count() noexcept
{
if (_M_pi != nullptr)
_M_pi->_M_release();
}代码示例
示例1
#include<iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
node(int a) { age_ = a;}
~node() { cout << "destruct, age_:" << age_ << endl; }
private:
int age_ = 0;
};
int main() {
shared_ptr<node> p = make_shared<node>(1);
shared_ptr<node> q = make_shared<node>(2);
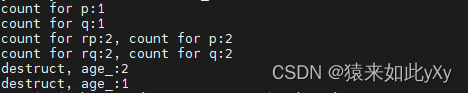
cout << "count for p:" << p.use_count() << endl;
cout << "count for q:" << q.use_count() << endl;
//拷贝构造函数,引用计数+1,被托管的指针分别被p 和 rp引用,所以引用计数是2
shared_ptr<node> rp(p);
cout << "count for rp:" << rp.use_count()
<< ", count for p:" << p.use_count() << endl;
//操作符 =, 引用计数+1, 被托管的指针分别被q 和 rq引用,所以引用计数是2
shared_ptr<node> rq = q;
cout << "count for rq:" << rq.use_count()
<< ", count for q:" << p.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
示例2
#include<iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
node(int a) { age_ = a;}
~node() { cout << "destruct, age_:" << age_ << endl; }
private:
int age_ = 0;
};
int main() {
shared_ptr<node> p = make_shared<node>(1);
shared_ptr<node> q = make_shared<node>(2);
cout << "count for p:" << p.use_count() << endl;
cout << "count for q:" << q.use_count() << endl;
//p原来托管的指针引用计数减一,q 托管的指针引用计数加一
//所以age = 1 的node指针对象因引用计数为0,被析构
p = q;
cout << "count for p:" << p.use_count()
<< ", count for q:" << p.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

示例3
#include<iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
node(int a) { age_ = a;}
~node() { cout << "destruct, age_:" << age_ << endl; }
private:
int age_ = 0;
};
int main() {
node* t = new node(3);
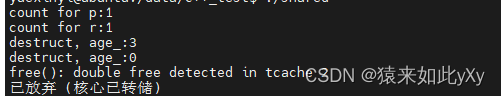
//将同一个原始指针给不同的shared_ptr对象,程序会异常,挂掉
shared_ptr<node> r(t);
shared_ptr<node> p(t);
cout << "count for p:" << p.use_count() << endl;
cout << "count for r:" << r.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
示例4
#include<iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class node
{
public:
node(int a) { age_ = a;}
~node() { cout << "destruct, age_:" << age_ << endl; }
private:
int age_ = 0;
};
int main() {
shared_ptr<node> r = make_shared<node>(1);
//运行shared_ptr的移动构造函数, r变成一个空shared_ptr
shared_ptr<node> p(move(r));
cout << "count for p:" << p.use_count() << endl;
cout << "count for r:" << r.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
![]()
更多细节: C++11 shared_ptr智能指针(超级详细)