目录
- 一 环境搭建
- 二 配置文件初始化
- 2.1 ClassLoader
- 2.2 获取配置文件
官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 简介
参考书籍:《通用源码阅读指导书:MyBatis源码详解》 易哥
参考文章:
- 一看你就懂,超详细java中的ClassLoader详解
- AppClassLoader/ExtClassLoader/BootstrapClassLoader
- Mybatis源码解析
上一篇文章我们介绍了Mybatis与SpringBoot的整合,我们可以掌握Mybatis的基本用法,到这我们需要来了解一条Sql的执行的基本处理过程
一 环境搭建
- 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.9</version>
</dependency>
- 编写Mapper
package com.shu;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.awt.print.Pageable;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @description:
* @author: shu
* @createDate: 2022/12/13 19:43
* @version: 1.0
*/
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
/**
* 通过ID查询单条数据
*
* @param id 主键
* @return 实例对象
*/
User queryById(Integer id);
/**
* 分页查询指定行数据
*
* @param user 查询条件
* @param pageable 分页对象
* @return 对象列表
*/
List<User> queryAllByLimit(User user);
/**
* 统计总行数
*
* @param user 查询条件
* @return 总行数
*/
long count(User user);
/**
* 新增数据
*
* @param user 实例对象
* @return 影响行数
*/
int insert(User user);
/**
* 批量新增数据
*
* @param entities List<User> 实例对象列表
* @return 影响行数
*/
int insertBatch(@Param("entities") List<User> entities);
/**
* 批量新增或按主键更新数据
*
* @param entities List<User> 实例对象列表
* @return 影响行数
*/
int insertOrUpdateBatch(@Param("entities") List<User> entities);
/**
* 更新数据
*
* @param user 实例对象
* @return 影响行数
*/
int update(User user);
/**
* 通过主键删除数据
*
* @param id 主键
* @return 影响行数
*/
int deleteById(Integer id);
}
- 编写mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.shu.UserMapper">
<resultMap type="com.shu.User" id="UserMap">
<result property="id" column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result property="name" column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="email" column="email" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="age" column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result property="schoolname" column="schoolName" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 通过ID查询单条数据 -->
<select id="queryById" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,name,email,age,sex,schoolName
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--分页查询指定行数据-->
<select id="queryAllByLimit" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,name,email,age,sex,schoolName
from user
<where>
<if test="id != null and id != ''">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="schoolname != null and schoolname != ''">
and schoolName = #{schoolname}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!--统计总行数-->
<select id="count" resultType="java.lang.Long">
select count(1)
from user
<where>
<if test="id != null and id != ''">
and id = #{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
and name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="schoolname != null and schoolname != ''">
and schoolName = #{schoolname}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!--新增数据-->
<insert id="insert" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into user(id,name,email,age,sex,schoolName)
values (#{id},#{name},#{email},#{age},#{sex},#{schoolname})
</insert>
<!-- 批量新增数据 -->
<insert id="insertBatch" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into user(id,name,email,age,sex,schoolName)
values
<foreach collection="entities" item="entity" separator=",">
(#{entity.id},#{entity.name},#{entity.email},#{entity.age},#{entity.sex},#{entity.schoolname})
</foreach>
</insert>
<!-- 批量新增或按主键更新数据 -->
<insert id="insertOrUpdateBatch" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into user(id,name,email,age,sex,schoolName)
values
<foreach collection="entities" item="entity" separator=",">
(#{entity.id},#{entity.name},#{entity.email},#{entity.age},#{entity.sex},#{entity.schoolname})
</foreach>
on duplicate key update
id=values(id),
name=values(name),
email=values(email),
age=values(age),
sex=values(sex),
schoolName=values(schoolName)
</insert>
<!-- 更新数据 -->
<update id="update">
update user
<set>
<if test="id != null and id != ''">
id = #{id},
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name},
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
email = #{email},
</if>
<if test="age != null and age != ''">
age = #{age},
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
sex = #{sex},
</if>
<if test="schoolname != null and schoolname != ''">
schoolName = #{schoolname},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!--通过主键删除-->
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from user where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
- 编写Mybatis-conf.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 别名-->
<!-- 环境 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 编写测试用例
package com.shu;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisDemo02ApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// 第一阶段:MyBatis的初始化阶段
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 得到配置文件的输入流
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 得到SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 第二阶段:数据读写阶段
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 找到接口对应的实现
UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 组建查询参数
User userParam = new User();
userParam.setSchoolname("Sunny School");
// 调用接口展开数据库操作
List<User> userList = userMapper.queryAllByLimit(userParam);
// 打印查询结果
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println("name : " + user.getName() + " ; email : " + user.getEmail());
}
}
}
}
到这我们的代码编写完毕,下一步我们来分析其执行过程
二 配置文件初始化
上面我们写了mybatis-config.xml文件,在代码开头我们可以看见进行配置文件的初始化
// 第一阶段:MyBatis的初始化阶段
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 得到配置文件的输入流
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
2.1 ClassLoader
- 我们从字面上理解就是类加载器,下面但是Jvm的类加载过程,类的加载就是 Java虚拟机将描述类的数据从 Class文件加载到 JVM的过程,在这一过程中会对 Class文件进行数据加载、连接和初始化,最终形成可以被虚拟机直接使用的 Java类。
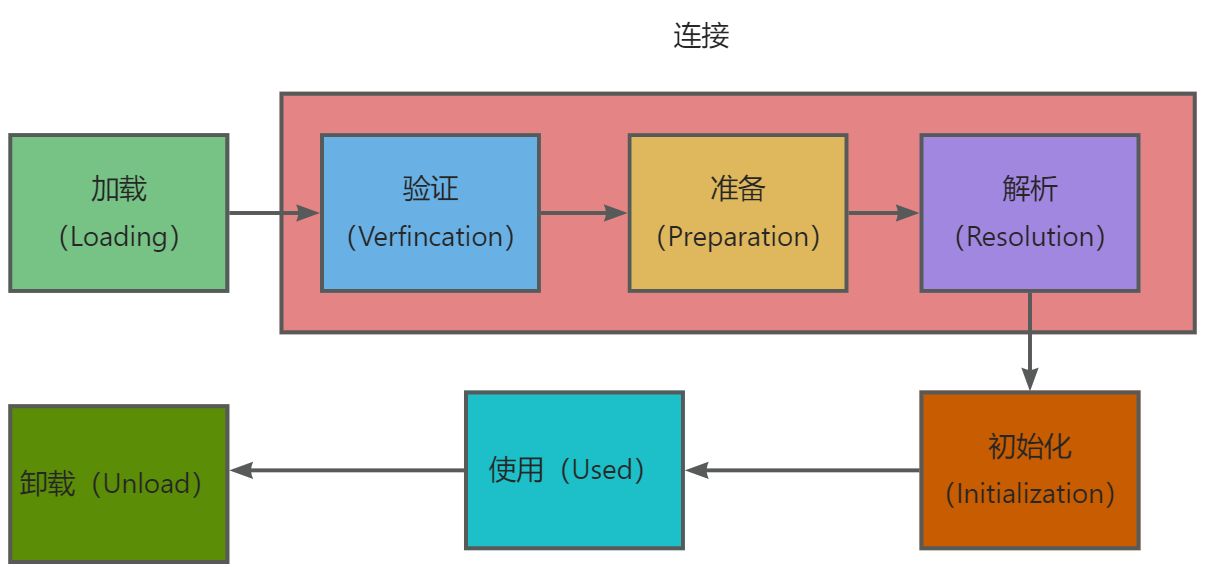
- 当然JVM 在一开始就可能把所有的类都加载,那么可能撑死,按需加载才是王道
Java 类加载器
1,引导类加载器 (BootstrapClassLoader)
负责加载系统类(通常从JAR的rt.jar中进行加载),它是虚拟机不可分割的一部分,通常使用C语言实现,引导类加载器没有对应的ClassLoader对象
2,扩展类加载器 (ExtClassLoader)
扩展类加载器用于从jre/lib/txt目标加载“标准的扩展”。可以将jar文件放入该目录,这样即使没有任何类路径,扩展类加载器也可以找到其中的各个类
3,系统类加载器 (AppClassLoader)
系统类加载器用于加载应用类,它在由ClASSPATH环境变量或者-classpath命令行选项设置的类路径的目录或者是jar/ZIP文件里查找这些类
加载顺序
- BootstrapClassLoader
- ExtClassLoader
- AppClassLoader
- 关于classLoader的详细信息请参考文章:一看你就懂,超详细java中的ClassLoader详解 博主讲得通俗易懂
- 关于JVM的的知识,推荐一本书《深入理解Java虚拟机:JVM高级特性与最佳实践(第3版)》 周志明,我后期也会整理相关知识,敬请期待
2.2 获取配置文件
// 第一阶段:MyBatis的初始化阶段
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 得到配置文件的输入流
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
- 我们可以看到调用了Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource)去获取配置文件的信息,调用getResourceAsStream()方法
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(ClassLoader loader, String resource) throws IOException {
// 去加载我们写的mybatis-config.xml 文件
InputStream in = classLoaderWrapper.getResourceAsStream(resource, loader);
// 没有找到,资源不存在
if (in == null) {
throw new IOException("Could not find resource " + resource);
}
return in;
}
- 到这我们可以看到他调用了classLoaderWrapper的方法,我们来看看这个类是啥?
public class ClassLoaderWrapper {
ClassLoader defaultClassLoader;
ClassLoader systemClassLoader;
ClassLoaderWrapper() {
try {
// AppClassLoader
systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
} catch (SecurityException ignored) {
// AccessControlException on Google App Engine
}
}
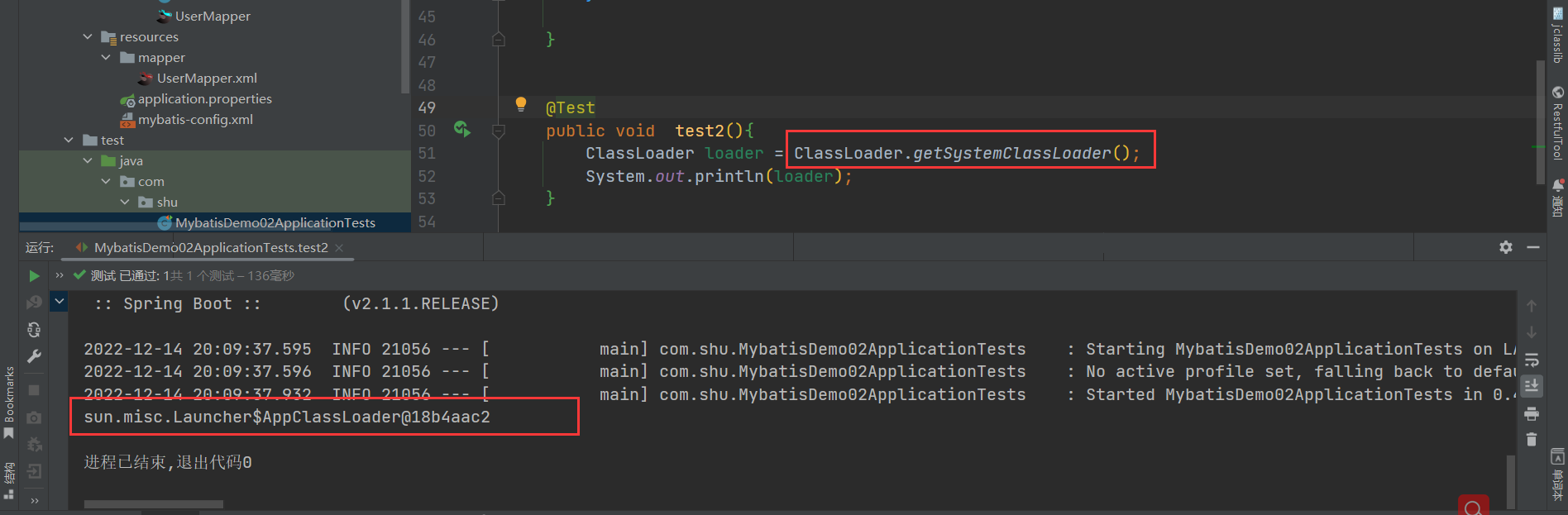
到这我们需要注意一下getClassLoaders(classLoader))方法,打个断点,调试一手
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return getResourceAsStream(resource, getClassLoaders(classLoader));
}
/**
* 获取多个ClassLoader,这一步是必须的,因为,我们就是从这个加载器中获取资源的流的
*五种类加载器:自己传入的、默认的类加载器、当前线程的类加载器、本类的类加载器、系统类加载器
* @param classLoader 我们定义的自己的类加载器
* @return 类加载器的数组
*/
ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new ClassLoader[]{
classLoader,
defaultClassLoader,
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
getClass().getClassLoader(),
systemClassLoader};
}
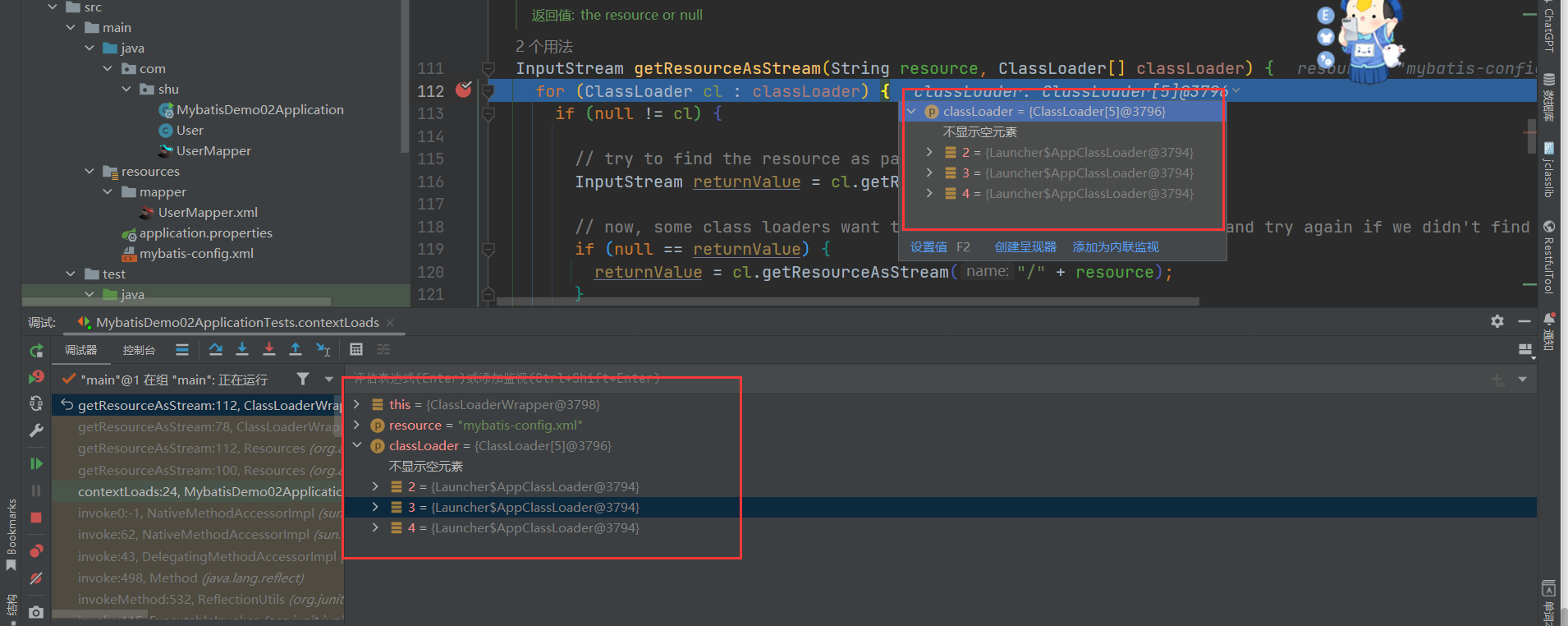
- 用一组 ClassLoader去找到我们写的mybatis-conf.xml文件,一般情况下,类加载器会将名称转换为文件名,然后从文件系统中读取该名称的类文件,因此,类加载器具有读取外部资源的能力,这里要借助的正是类加载器的这种能力。
/**
* 从一个ClassLoader中获取资源的流,这就是我们的目的
*
* @param resource 资源的地址
* @param classLoader 类加载器
* @return 流
*/
InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader[] classLoader) {
for (ClassLoader cl : classLoader) {
if (null != cl) {
// try to find the resource as passed
InputStream returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// now, some class loaders want this leading "/", so we'll add it and try again if we didn't find the resource
if (null == returnValue) {
returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream("/" + resource);
}
if (null != returnValue) {
return returnValue;
}
}
}
return null;
}
- getResourceAsStream 方法会依次调用传入的每一个类加载器的getResourceAsStream方法来尝试获取配置文件的输入流
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
// 找到文件
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
if (url == null) {
return null;
}
URLConnection urlc = url.openConnection();
InputStream is = urlc.getInputStream();
if (urlc instanceof JarURLConnection) {
JarURLConnection juc = (JarURLConnection)urlc;
JarFile jar = juc.getJarFile();
synchronized (closeables) {
if (!closeables.containsKey(jar)) {
closeables.put(jar, null);
}
}
} else if (urlc instanceof sun.net.www.protocol.file.FileURLConnection) {
synchronized (closeables) {
closeables.put(is, null);
}
}
return is;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
- 我们来看看getResource方法吧,相信你刚才看了文章,接下来看你理解没有刚才的知识
public URL getResource(String name) {
URL url;
// 父类加载器能够找到该文章,由前面我们知道AppClassLoader的父类加载器是ExtClassLoader
if (parent != null) {
url = parent.getResource(name);
} else {
// 通过双亲委派机制找到文件
url = getBootstrapResource(name);
}
// 没有的话
if (url == null) {
url = findResource(name);
}
return url;
}
- 由前面我们知道AppClassLoader的父类加载器是ExtClassLoader
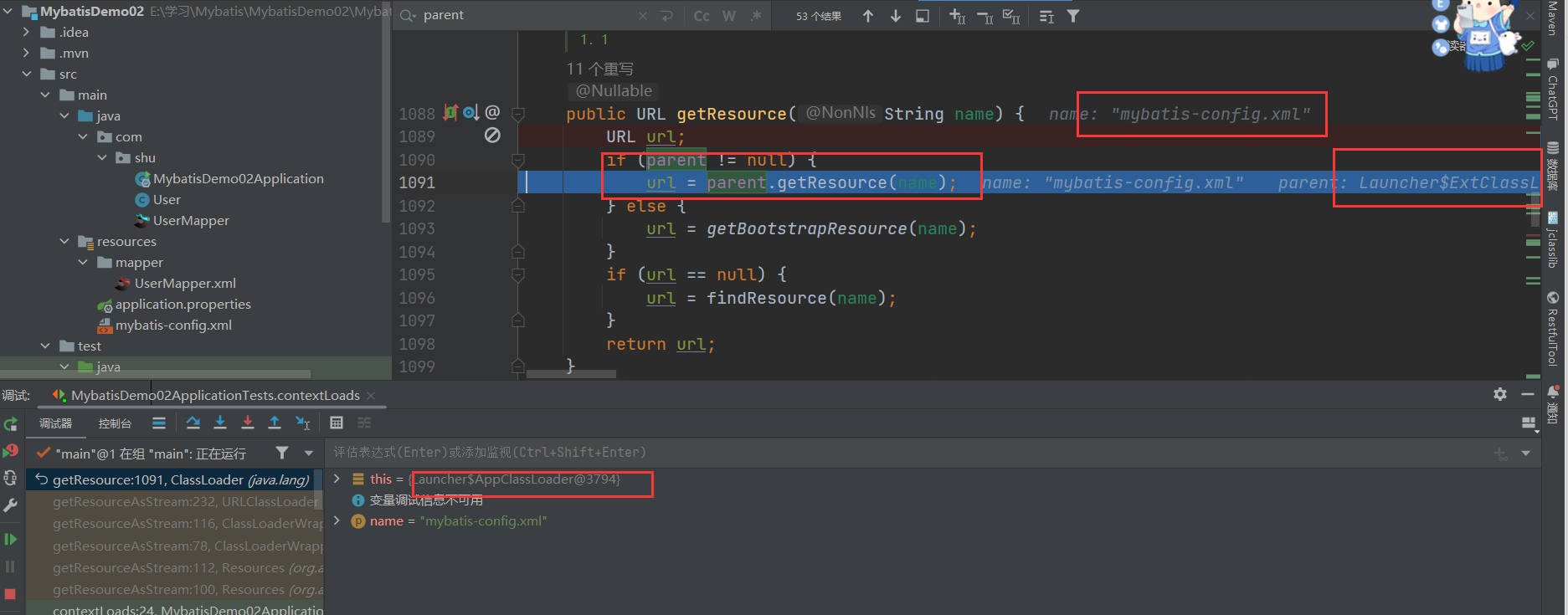
- ExtClassLoader的父类加载器为空,所以通过双亲委派机制去寻找该文件,相信我,后面你还会遇到的。
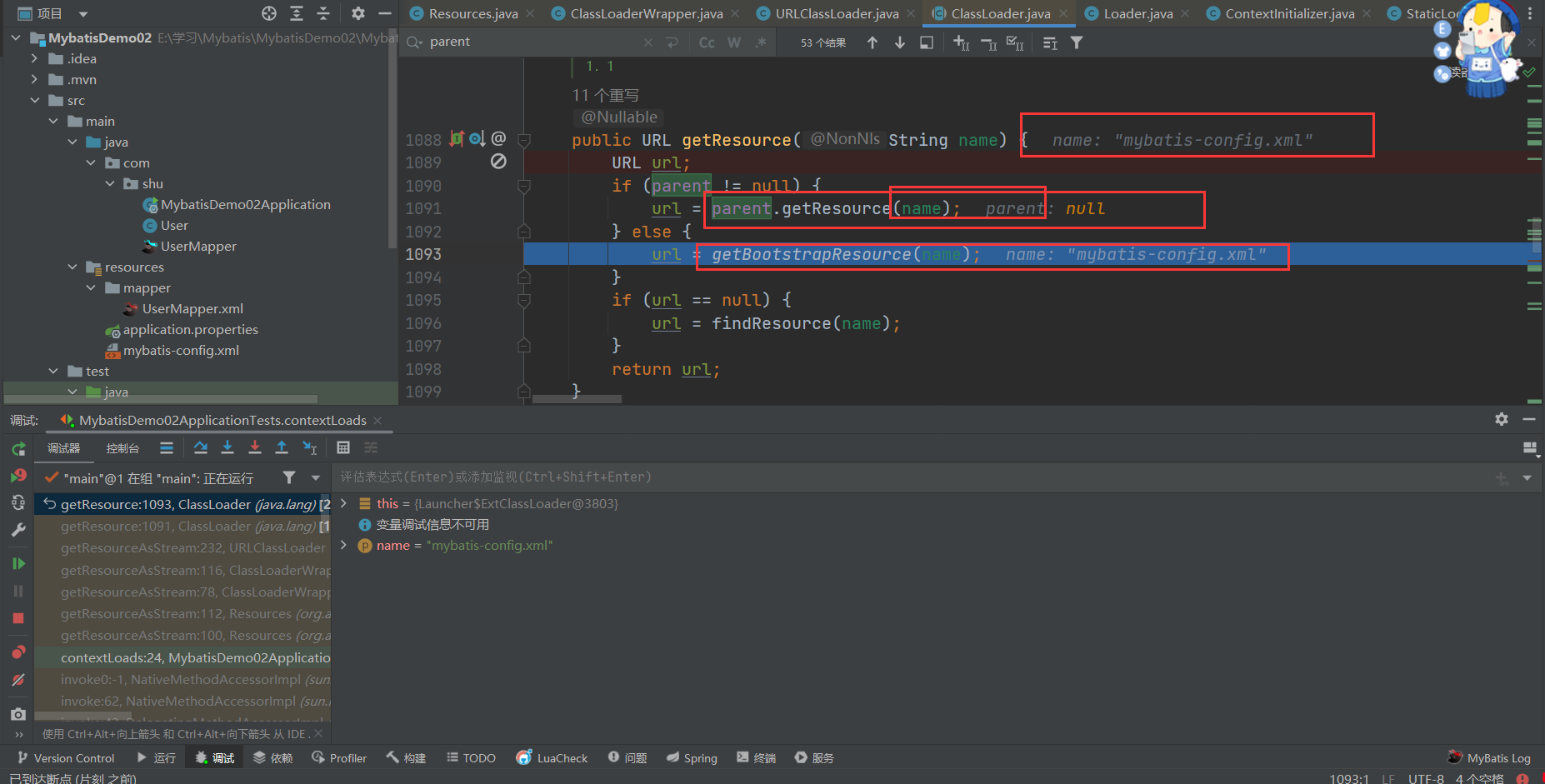
- 当前类加载器(一般是appclassloader)会让父类去加载,父类找不到再通过子类自身findResource(name)方法来找资源
- Java ClassLoader findResource() method with example
- AccessController.doPrivileged方法是一个native方法,无法通过IDE进去调试
public URL findResource(String var1, boolean var2) {
// 先去缓存查询一下
int[] var4 = this.getLookupCache(var1);
Loader var3;
// 这里有点不懂,有大神可以讲解?
for(int var5 = 0; (var3 = this.getNextLoader(var4, var5)) != null; ++var5) {
URL var6 = var3.findResource(var1, var2);
if (var6 != null) {
return var6;
}
}
return null;
}
- 找到了文件的URL路径,返回
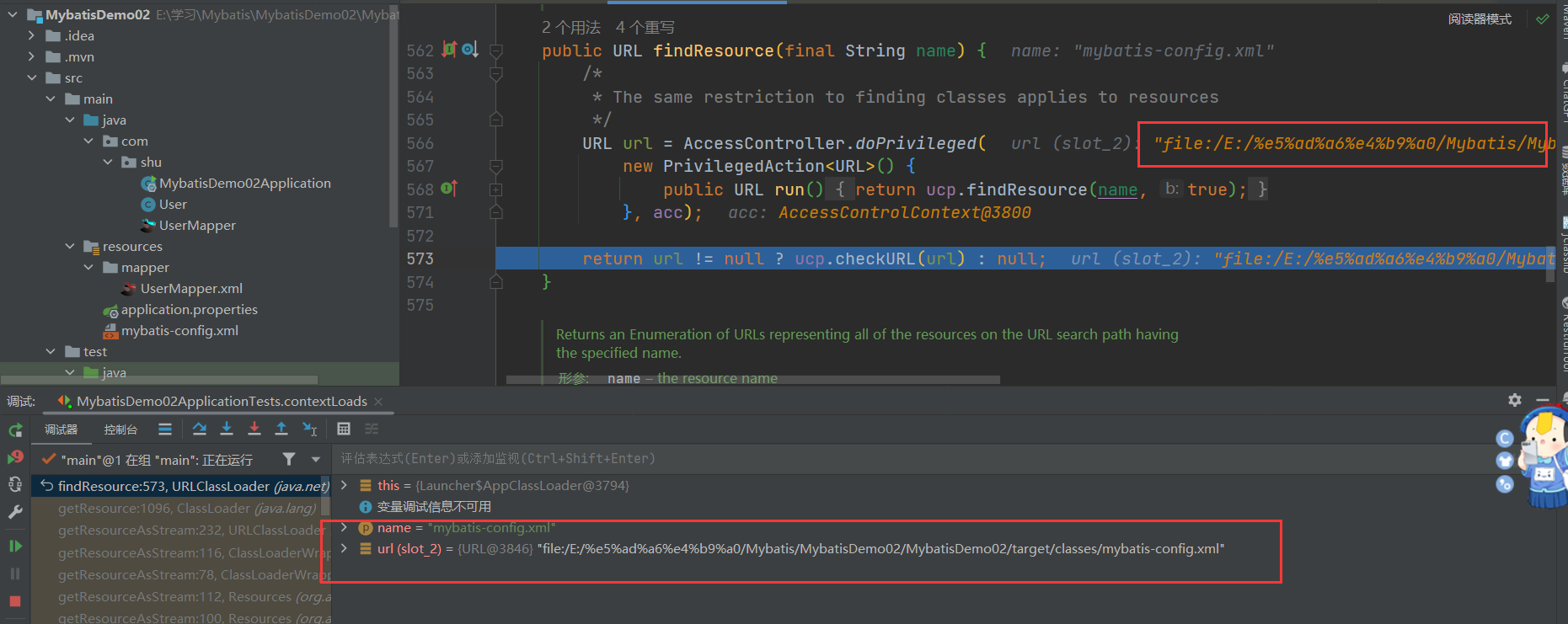
- 获取到了URL连接
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
// 找到文件
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
if (url == null) {
return null;
}
// 打开连接
URLConnection urlc = url.openConnection();
// 获取流数据
InputStream is = urlc.getInputStream();
// jar包连接
if (urlc instanceof JarURLConnection) {
JarURLConnection juc = (JarURLConnection)urlc;
JarFile jar = juc.getJarFile();
synchronized (closeables) {
if (!closeables.containsKey(jar)) {
closeables.put(jar, null);
}
}
}
// 文件连接
else if (urlc instanceof sun.net.www.protocol.file.FileURLConnection) {
synchronized (closeables) {
closeables.put(is, null);
}
}
return is;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
到这我们文件的解析就完毕了









![[附源码]Nodejs计算机毕业设计基于Web企业客户管理系统Express(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b83fdd37924a4cac8e508a223fe0b1d0.png)