目录
- 一、Exchange(交换机)的作用
- 二、Exchange(交换机)的类型
- 1.直连交换机:Direct Exchange
- 2.主题交换机:Topic Exchange
- 3.扇形交换机:Fanout Exchange
- 4.首部交换机:Headers exchange
- 5.默认交换机
- 6.Dead Letter Exchange(死信交换机)
- 三、交换机的属性
- 四、直连交换机
- 0.给子模块添加依赖
- 1.RabbitmqDirectConfig
- 2.SendMessageController
- 3.配置:application.yml
- 4.查看rabbitmq管理界面
- 5.创建消息接收监听类DirectReceiver
- 五、主题交换机(Topic Exchange)
- RabbitTopicConfig
- 交换机controller方法
- 消费者: TopicReceiver
- 六.扇形交换机(Fanout Exchange)
- RabbitmqFanoutConfig
- 生产者controller方法:
- 消费者:FanoutReceiver
一、Exchange(交换机)的作用
在RabbitMQ中,生产者发送消息不会直接将消息投递到队列中,而是先将消息投递到交换机中,在由交换机转发到具体的队列,
队列再将消息以推送或者拉取方式给消费者进行消费
创建消息 路由键 pull/push
生产者------------>交换机------------>队列------------>消费者
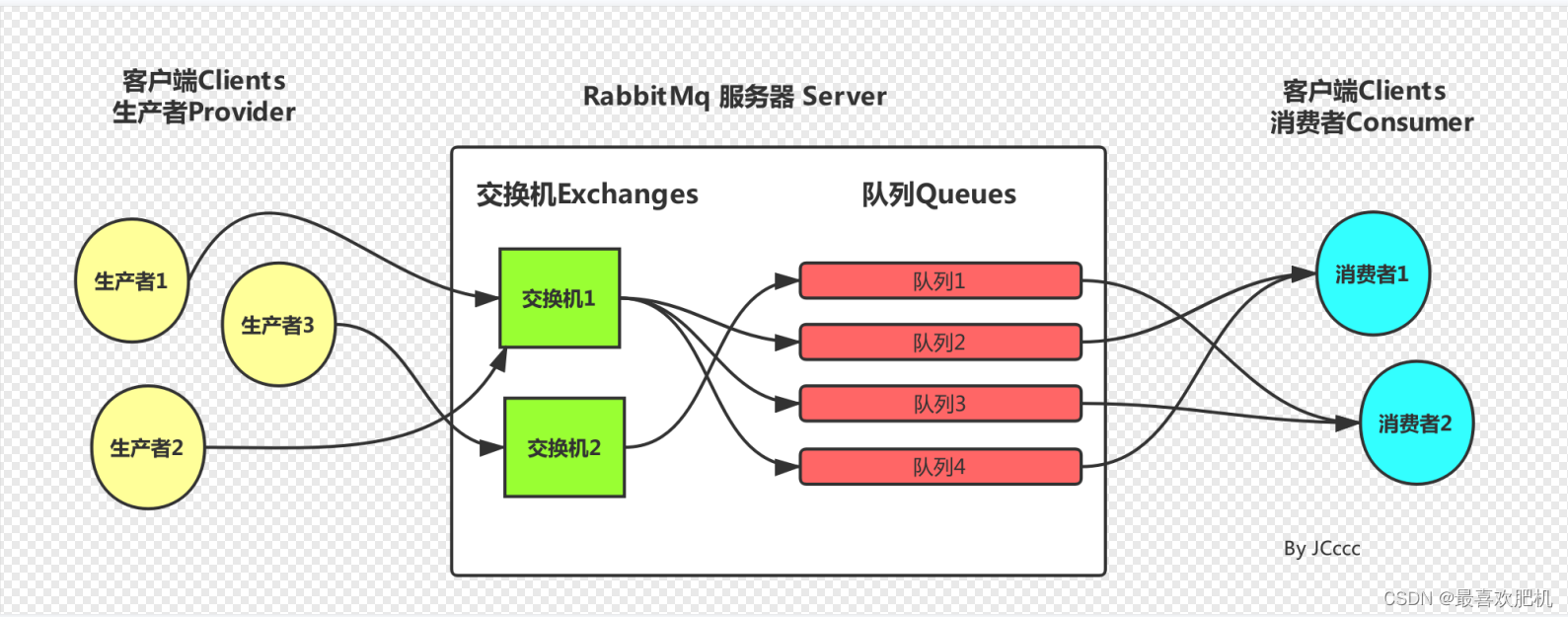
二、Exchange(交换机)的类型
1.直连交换机:Direct Exchange
直连交换机是一种带路由功能的交换机,一个队列会和一个交换机绑定,除此之外再绑定一个routing_key,当消息被发送的时候,需要指定一个binding_key,这个消息被送达交换机的时候,就会被这个交换机送到指定的队列里面去。同样的一个binding_key也是支持应用到多个队列中的。
这样当一个交换机绑定多个队列,就会被送到对应的队列去处理。
注1:什么是路由键
每个消息都有一个称为路由键(routing key)的属性,它其实就是一个简单的字符串
注2:直连交换机适用场景
有优先级的任务,根据任务的优先级把消息发送到对应的队列,这样可以指派更多的资源去处理高优先级的队列。
2.主题交换机:Topic Exchange
直连交换机的缺点!
直连交换机的routing_key方案非常简单,如果我们希望一条消息发送给多个队列,那么这个交换机需要绑定上非常多的routing_key,
假设每个交换机上都绑定一堆的routing_key连接到各个队列上。那么消息的管理就会异常地困难。
所以RabbitMQ提供了一种主题交换机,发送到主题交换机上的消息需要携带指定规则的routing_key,
主题交换机会根据这个规则将数据发送到对应的(多个)队列上。
主题交换机的routing_key需要有一定的规则,交换机和队列的binding_key需要采用*.#.*.....的格式,每个部分用.分开,其中
*表示一个单词
#表示任意数量(零个或多个)单词。
示例:
队列Q1绑定键为 *.TT.*
队列Q2绑定键为TT.#
如果一条消息携带的路由键为 A.TT.B,那么队列Q1将会收到
如果一条消息携带的路由键为TT.AA.BB,那么队列Q2将会收到
3.扇形交换机:Fanout Exchange
扇形交换机是最基本的交换机类型,它所能做的事情非常简单———广播消息。
扇形交换机会把能接收到的消息全部发送给绑定在自己身上的队列。因为广播不需要“思考”,
所以扇形交换机处理消息的速度也是所有的交换机类型里面最快的。
这个交换机没有路由键概念,就算你绑了路由键也是无视的。
4.首部交换机:Headers exchange
5.默认交换机
实际上是一个由RabbitMQ预先声明好的名字为空字符串的直连交换机(direct exchange)。它有一个特殊的属性使得它对于
简单应用特别有用处:那就是每个新建队列(queue)都会自动绑定到默认交换机上,绑定的路由键(routing key)名称与队列名称相同。
如:当你声明了一个名为”hello”的队列,RabbitMQ会自动将其绑定到默认交换机上,绑定(binding)的路由键名称也是为”hello”。
因此,当携带着名为”hello”的路由键的消息被发送到默认交换机的时候,此消息会被默认交换机路由至名为”hello”的队列中
类似amq.*的名称的交换机:
这些是RabbitMQ默认创建的交换机。这些队列名称被预留做RabbitMQ内部使用,不能被应用使用,否则抛出403 (ACCESS_REFUSED)错误
6.Dead Letter Exchange(死信交换机)
在默认情况,如果消息在投递到交换机时,交换机发现此消息没有匹配的队列,则这个消息将被悄悄丢弃。
为了解决这个问题,RabbitMQ中有一种交换机叫死信交换机。当消费者不能处理接收到的消息时,将这个消息重新发布到另外一个队列中,
等待重试或者人工干预。这个过程中的exchange和queue就是所谓的”Dead Letter Exchange 和 Que
三、交换机的属性
除交换机类型外,在声明交换机时还可以附带许多其他的属性,其中最重要的几个分别是:
Name:交换机名称
Durability:是否持久化。如果持久性,则RabbitMQ重启后,交换机还存在
Auto-delete:当所有与之绑定的消息队列都完成了对此交换机的使用后,删掉它
Arguments:扩展参数
四、直连交换机
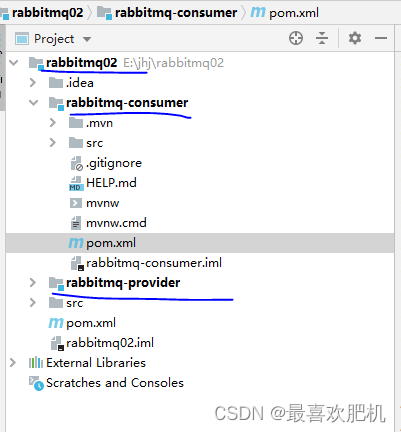
我们先建好工程:
rabbitmq02 #主模块maven项目
rabbitmq-provider #生产者springboot项目
rabbitmq-consumer #消费者springboot项目
0.给子模块添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
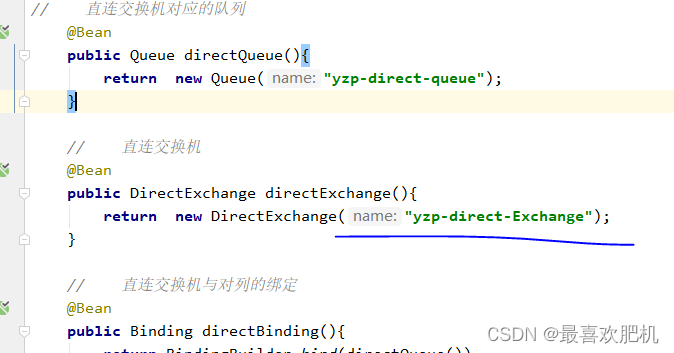
1.RabbitmqDirectConfig
package com.yzp.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author javaxy
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-14 18:31
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitmqDirectConfig {
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue directQueue(){
return new Queue("yzp-direct-queue");
}
// 直连交换机
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("yzp-direct-Exchange");
}
// 直连交换机与对列的绑定
@Bean
public Binding directBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue())
.to(directExchange())
.with("direct-routing-key");
}
}
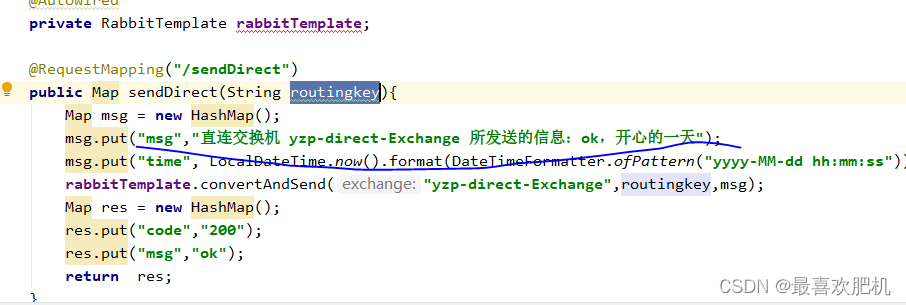
2.SendMessageController
package com.yzp.rabbitmqprovider.controller;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author javaxy
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-14 18:40
*/
@RestController
public class SendMessageController {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/sendDirect")
public Map sendDirect(String routingkey){
Map msg = new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","直连交换机 yzp-direct-Exchange 所发送的信息:ok,开心的一天");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("yzp-direct-Exchange",routingkey,msg);
Map res = new HashMap();
res.put("code","200");
res.put("msg","ok");
return res;
}
}
3.配置:application.yml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.113.129
password: 123
port: 5672
username: yzp
virtual-host: my_vhost
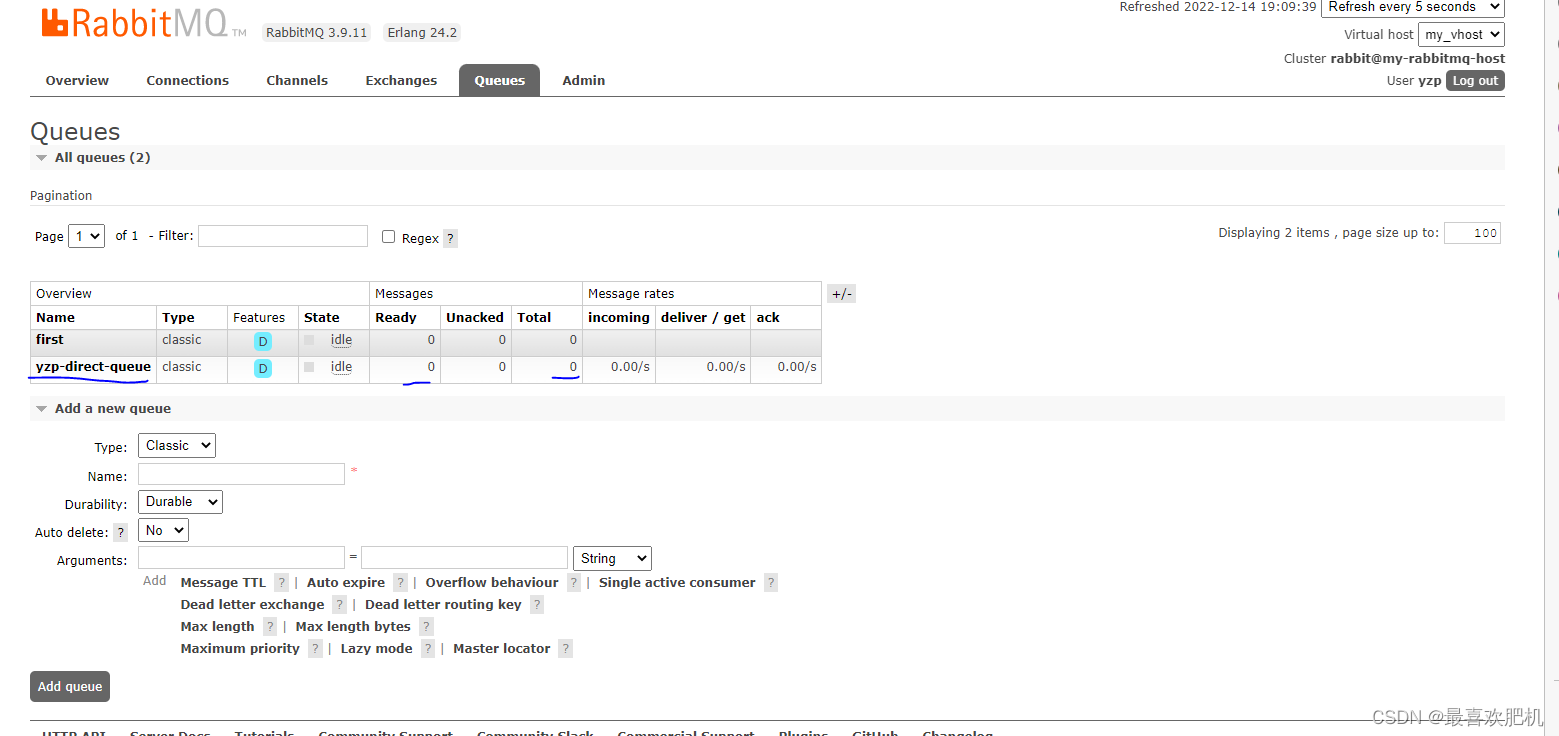
4.查看rabbitmq管理界面
我们目前还创建消费者rabbitmq-consumer,消息没有被消费的,我们去rabbitMq管理页面看看,是否推送成功
Overview选项卡,可以查看到刚刚创建的消息

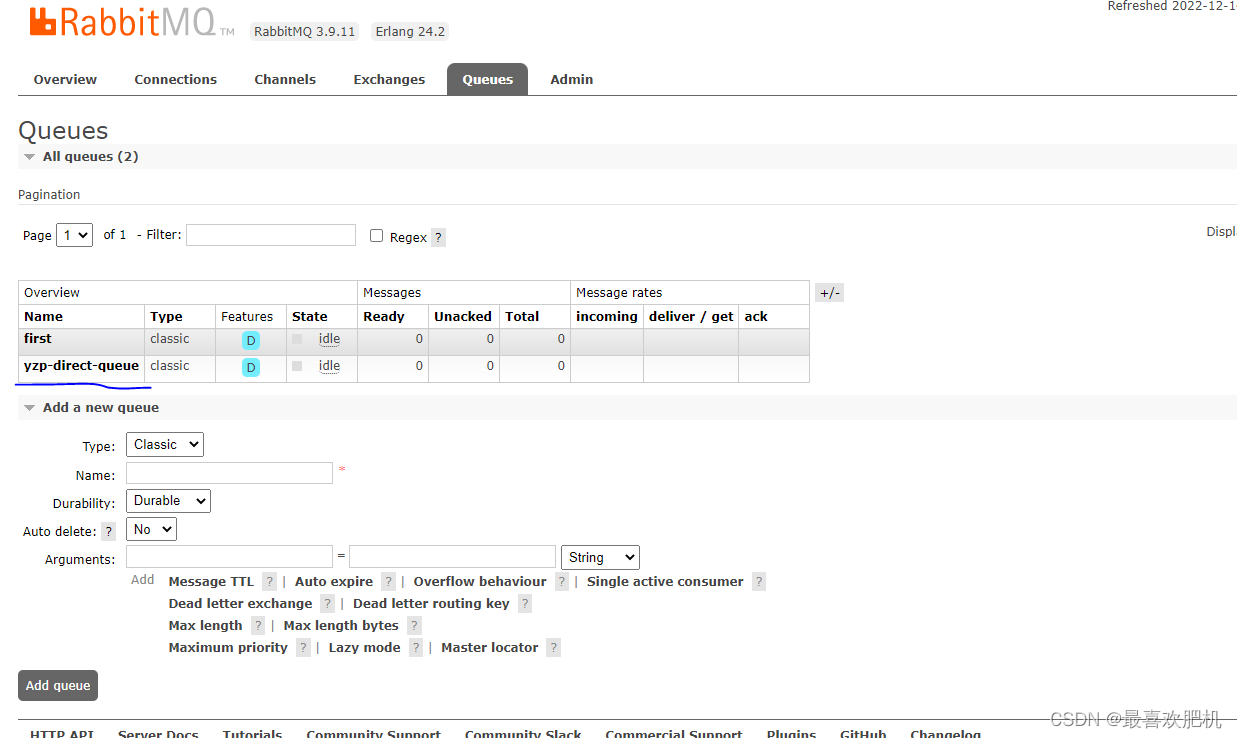
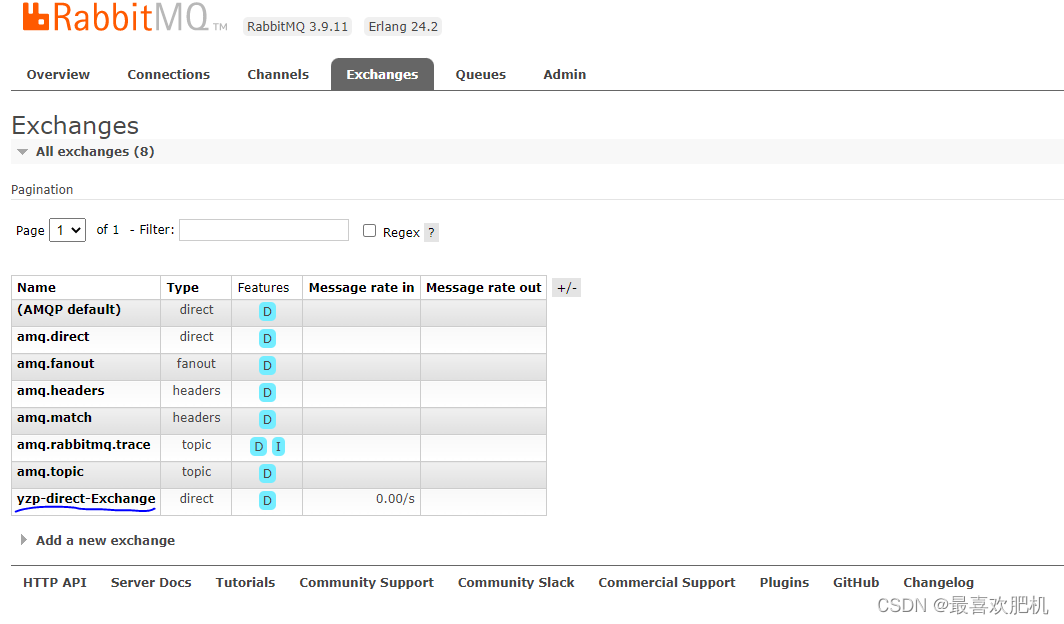
我们此时还没有创建信息,只是创建好了交换机和队列,接下来就是创建信息了:
我们在浏览器输入地址然后执行
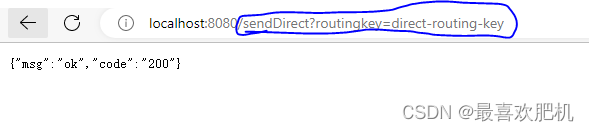
这里的routingkey=direct-routing-key是:

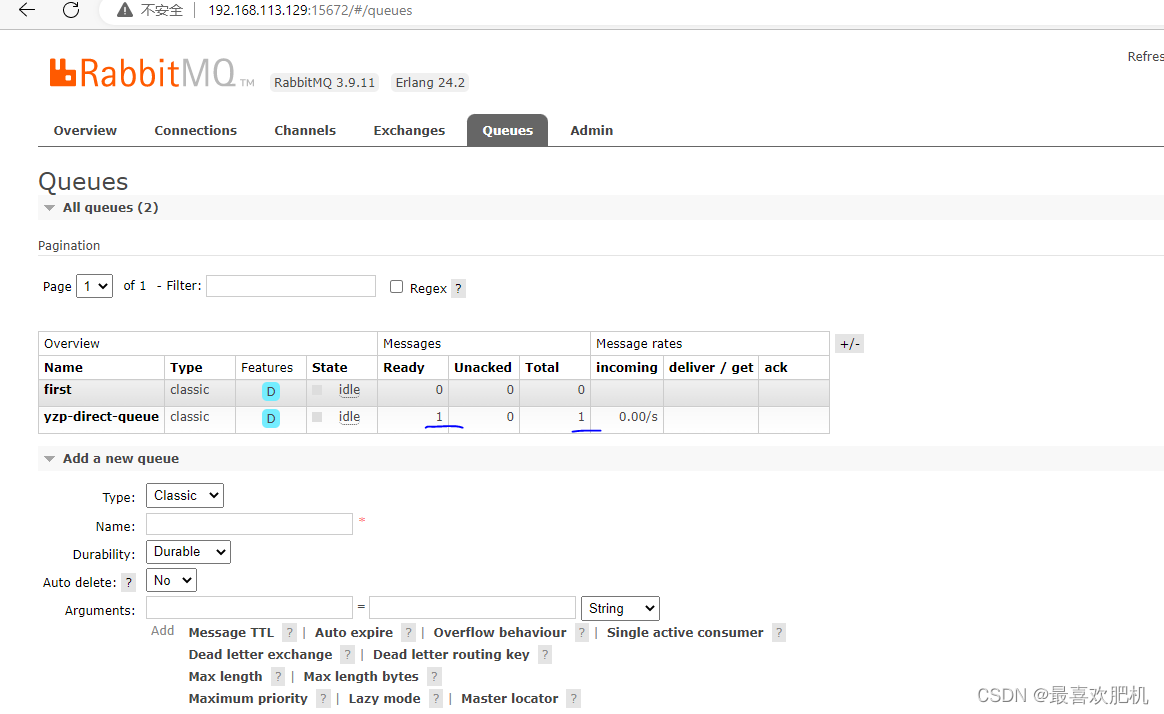
然后我们的队列里面就会有一条信息
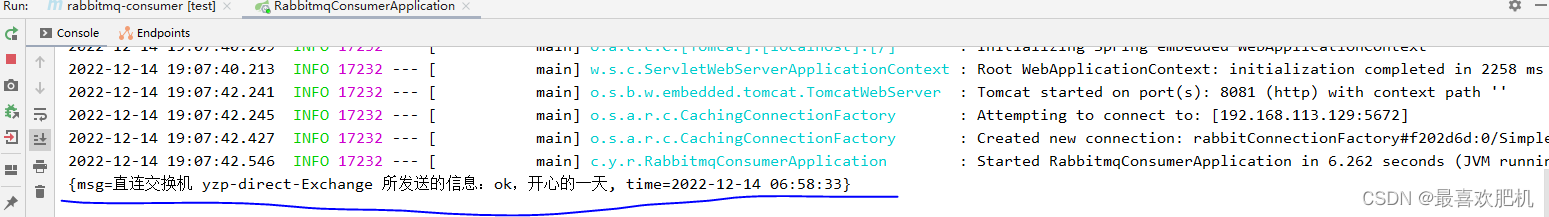
5.创建消息接收监听类DirectReceiver
package com.yzp.rabbitmqconsumer;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-direct-queue"})
public class DirectReceiver {
// @RabbitListener(queues = {"direct-queue"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
然后运行消费者服务即可
推送完信息之后我们的队列里面的信息也会清空
注1:新版jdk日期及格式化
LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
注2:rabbitTemplate和amqpTemplate有什么关系
查看源码中会发现rabbitTemplate实现自amqpTemplate接口,两者使用起来并无区别,功能一致
注3:不要@Configuration写成了@Configurable,这两个长得很像
@Configuration该注解是可以用来替代XML文件。
手动new出来的对象,正常情况下,Spring是无法依赖注入的,这个时候可以使用@Configurable注解
五、主题交换机(Topic Exchange)
RabbitTopicConfig
package com.yzp.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author javaxy
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-14 19:12
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitTopicConfig {
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueA(){
return new Queue("yzp-topic-queue-a");
}
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueB(){
return new Queue("yzp-topic-queue-b");
}
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueC(){
return new Queue("yzp-topic-queue-c");
}
// 直连交换机
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("yzp-topic-Exchange");
}
// 直连交换机与对列的绑定
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding1(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueA())
.to(topicExchange())
.with("yzp.person.yy");
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueB())
.to(topicExchange())
.with("yzp.person.xx");
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding3(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueC())
.to(topicExchange())
.with("yzp.person.*");
}
}
交换机controller方法
@RequestMapping("/sendTopic")
public Map sendTopic(String routingkey){
Map msg = new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","主题交换机 yzp-topic-Exchange 所发送的信息:ok,要开心哦");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("yzp-topic-Exchange",routingkey,msg);
Map res = new HashMap();
res.put("code","200");
res.put("msg","ok");
return res;
}
然后我们运行生产服务:
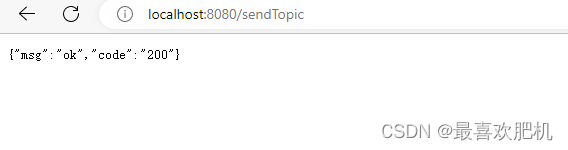
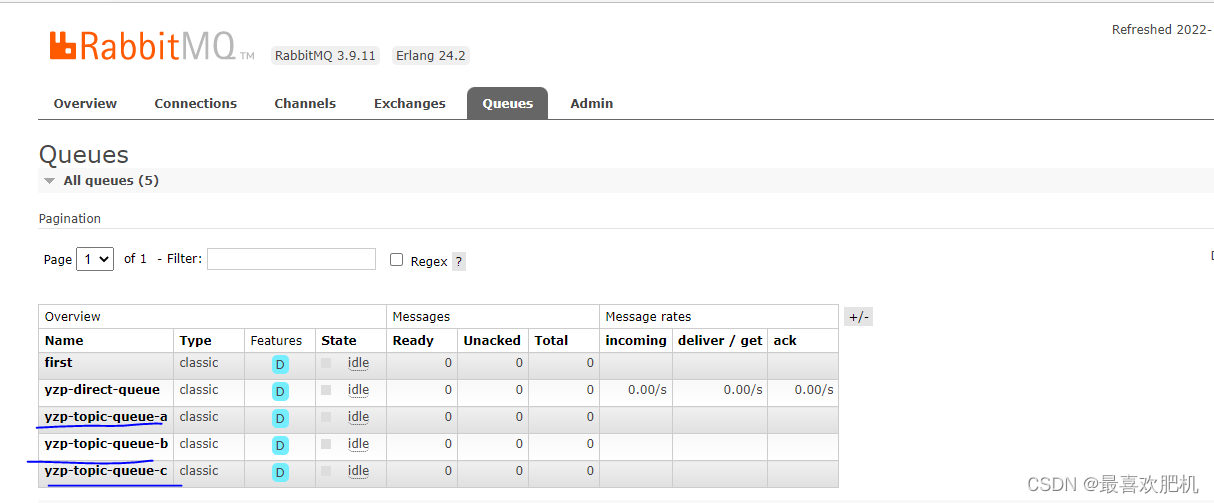
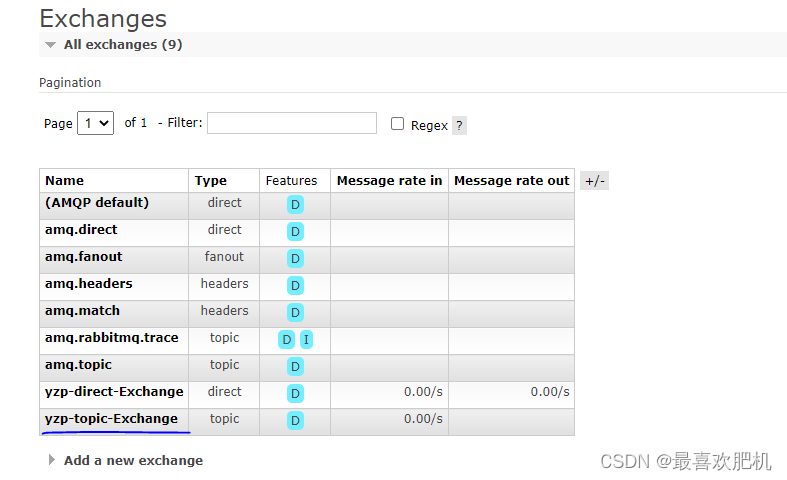
然后我们依次先执行下面这个路径
http://localhost:8080/sendTopic?routingkey=yzp.person.xx
http://localhost:8080/sendTopic?routingkey=yzp.person.yy
http://localhost:8080/sendTopic?routingkey=yzp.person.ss
测试结果:
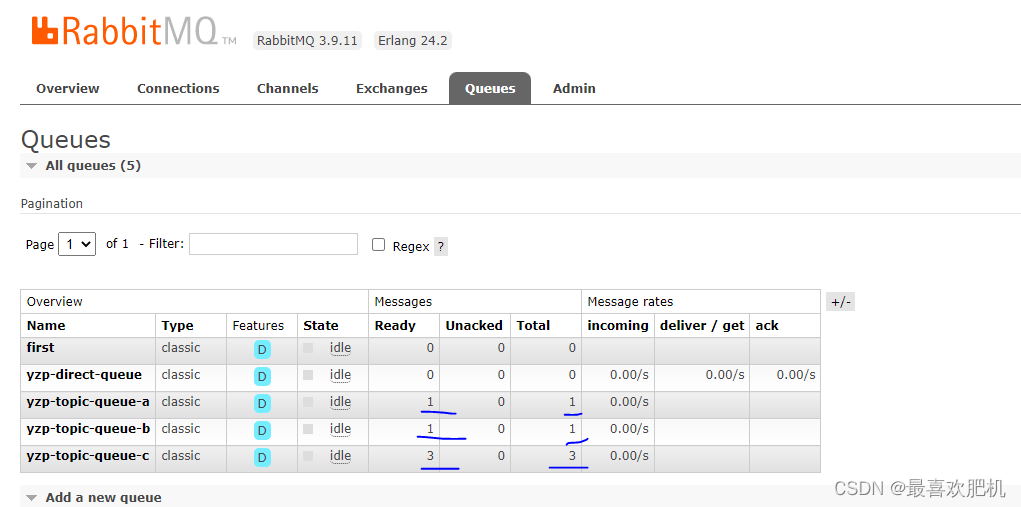
消费者: TopicReceiver
package com.yzp.rabbitmqconsumer;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author javaxy
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-14 19:24
*/
public class TopicReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-topic-queue-a"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler1(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-topic-queue-b"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler2(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-topic-queue-c"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler3(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
然后启动服务开始测试:
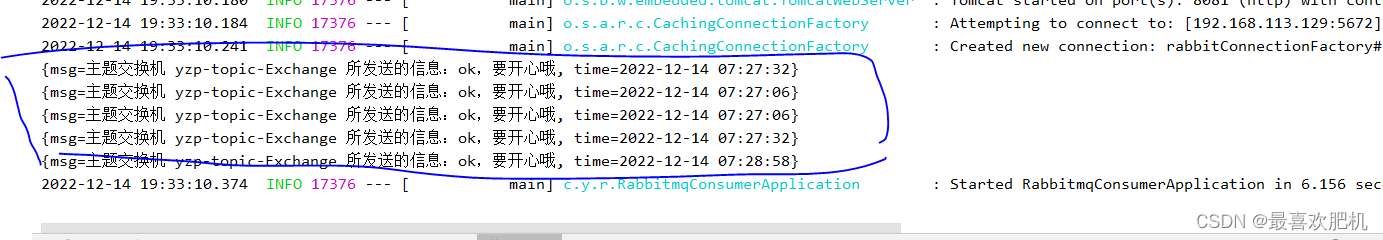
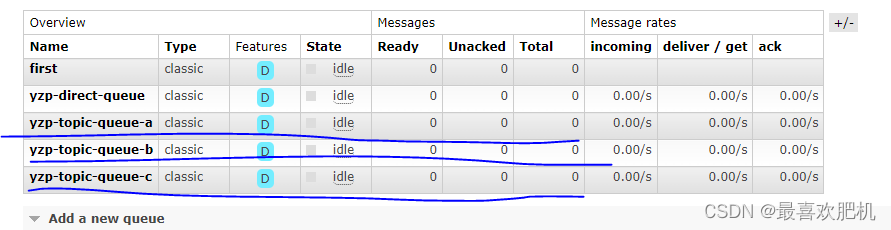
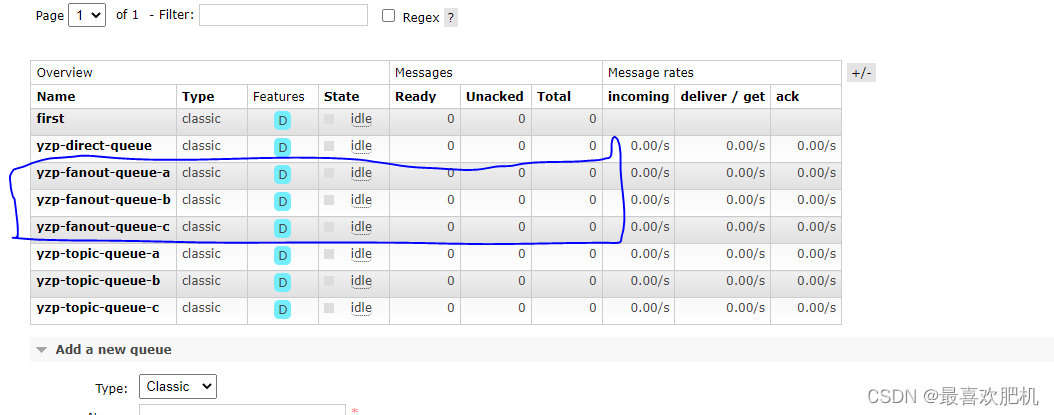
六.扇形交换机(Fanout Exchange)
RabbitmqFanoutConfig
package com.yzp.rabbitmqprovider.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author javaxy
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-14 19:34
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitmqFanoutConfig {
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueA(){
return new Queue("yzp-fanout-queue-a");
}
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueB(){
return new Queue("yzp-fanout-queue-b");
}
// 直连交换机对应的队列
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueC(){
return new Queue("yzp-fanout-queue-c");
}
// 直连交换机
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("yzp-fanout-Exchange");
}
// 直连交换机与对列的绑定
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding1(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueA())
.to(fanoutExchange());
}
// 直连交换机与对列的绑定
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueB())
.to(fanoutExchange());
}
// 直连交换机与对列的绑定
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding3(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueC())
.to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
生产者controller方法:
@RequestMapping("/sendFanout")
public Map sendFanout(String routingkey){
Map msg = new HashMap();
msg.put("msg","扇形交换机 yzp-fanout-Exchange 所发送的信息:ok,不要太开心哦");
msg.put("time", LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss")));
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("yzp-fanout-Exchange",null,msg);
Map res = new HashMap();
res.put("code","200");
res.put("msg","ok");
return res;
}
然后启动服务测试:
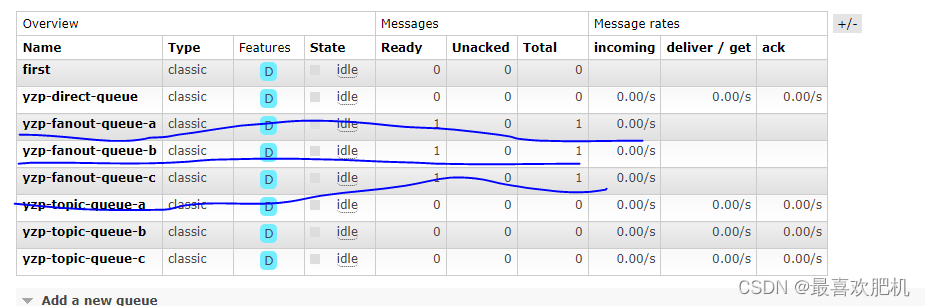
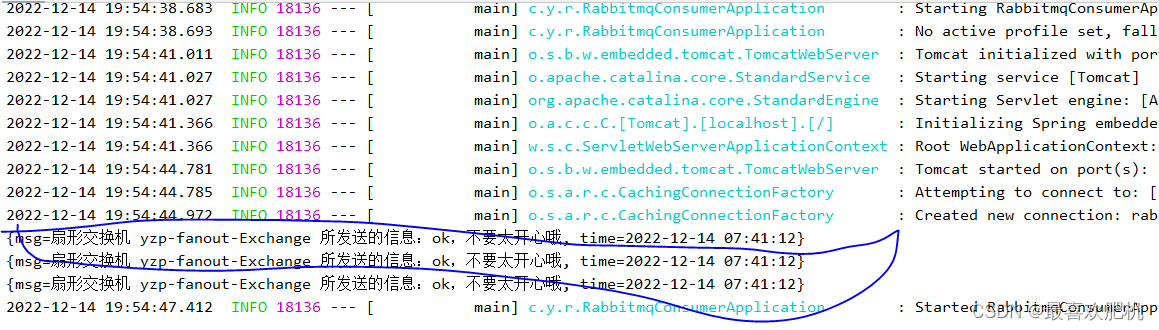
消费者:FanoutReceiver
package com.yzp.rabbitmqconsumer;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author javaxy
* @company xxx公司
* @create 2022-12-14 19:53
*/
@Component
public class FanoutReceiver {
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-fanout-queue-a"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler1(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-fanout-queue-b"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler2(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = {"yzp-fanout-queue-c"})
@RabbitHandler
public void handler3(Map msg){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
启动消费者服务进行测试: