作者简介
架构师李肯(全网同名),一个专注于嵌入式IoT领域的架构师。有着近10年的嵌入式一线开发经验,深耕IoT领域多年,熟知IoT领域的业务发展,深度掌握IoT领域的相关技术栈,包括但不限于主流RTOS内核的实现及其移植、硬件驱动移植开发、网络通讯协议开发、编译构建原理及其实现、底层汇编及编译原理、编译优化及代码重构、主流IoT云平台的对接、嵌入式IoT系统的架构设计等等。拥有多项IoT领域的发明专利,热衷于技术分享,有多年撰写技术博客的经验积累,连续多月获得RT-Thread官方技术社区原创技术博文优秀奖,荣获CSDN博客专家、CSDN物联网领域优质创作者、2021年度CSDN&RT-Thread技术社区之星、2022年RT-Thread全球技术大会讲师、RT-Thread官方嵌入式开源社区认证专家、RT-Thread 2021年度论坛之星TOP4、华为云云享专家(嵌入式物联网架构设计师)等荣誉。坚信【知识改变命运,技术改变世界】!
【C语言进阶】使用gettimeofday为你的程序运行时间做统计
有时候在编程调试的时候,会遇到个别性能问题需要调试,这时候我们需要比较精确地统计每段代码的耗时情况,这种情况下,你是怎么做的呢?本文介绍一种方法来实现此功能。
文章目录
- 1 需求背景
- 2 简要分析
- 2.1 算法分析
- 2.2 gettimeofday简介
- 3 源码实现
- 3.1 参考代码
- 3.2 代码简介
- 3.3 代码测试
- 4 小小总结
- 5 更多分享
1 需求背景
在项目编程中,如果遇到调试代码性能的时候,慢慢需要加时戳来观察,找出那些耗时的操作。这种情况大部分需要人工干涉,如果我们需要程序自动帮忙完成耗时分析呢?我们可以怎么做呢?
本文就这个场景问题,提供一种解决方案,欢迎大家参考。
2 简要分析
2.1 算法分析
根据我们的常识,我们知道,要想知道一个操作的耗时,一般的做法就是在操作前取一个时间,然后操作后取一个时间;最后两个时间相减,得到的就是这段操作的耗时。
根据这里方法论,我们可以比较快地实现逻辑代码,但是我们应该用哪个函数取当前时间点呢?
2.2 gettimeofday简介
在Linux C语言编程中,我们很容易会想到gettimeofday这个函数,下面我们将简单介绍一下这个函数。
参考Linux下的man说明,如下:
GETTIMEOFDAY(2) Linux Programmer’s Manual GETTIMEOFDAY(2)
NAME
gettimeofday, settimeofday - get / set timeSYNOPSIS
#include <sys/time.h>int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tv, struct timezone *tz); int settimeofday(const struct timeval *tv, const struct timezone *tz);Feature Test Macro Requirements for glibc (see feature_test_macros(7)):
settimeofday(): Since glibc 2.19: _DEFAULT_SOURCE Glibc 2.19 and earlier: _BSD_SOURCEDESCRIPTION
The functions gettimeofday() and settimeofday() can get and set the time as well as a timezone.The tv argument is a struct timeval (as specified in <sys/time.h>): struct timeval { time_t tv_sec; /* seconds */ suseconds_t tv_usec; /* microseconds */ }; and gives the number of seconds and microseconds since the Epoch (see time(2)). The tz argument is a struct timezone: struct timezone { int tz_minuteswest; /* minutes west of Greenwich */ int tz_dsttime; /* type of DST correction */ }; If either tv or tz is NULL, the corresponding structure is not set or returned. (However, compilation warnings will result if tv is NULL.) The use of the timezone structure is obsolete; the tz argument should normally be specified as NULL. (See NOTES below.) Under Linux, there are some peculiar "warp clock" semantics associated with the settimeofday() system call if on the very first call (after booting) that has a non-NULL tz argument, the tv argument is NULL and the tz_minuteswest field is nonzero. (The tz_dsttime field should be zero for this case.) In such a case it is assumed that the CMOS clock is on local time, and that it has to be incremented by this amount to get UTC system time. No doubt it is a bad idea to use this feature.RETURN VALUE
gettimeofday() and settimeofday() return 0 for success, or -1 for failure (in which case errno is set appropriately).
从这里我们可以知道,gettimeofday用于获取当前的时间是非常容易的,它会将时间结果存储在这个结构体中:
struct timeval {
time_t tv_sec; /* seconds /
suseconds_t tv_usec; / microseconds */
};
struct timeval 结构体中有 tv_sec 秒参数 和 tv_usec 微妙参数,非常有利于我们做时间的加减计算。
下面我们就用这个函数来实现下本期的功能。
3 源码实现
3.1 参考代码
本例给出一个参考代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <time.h>
static int get_cur_time_ms(void)
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL); //使用gettimeofday获取当前系统时间
return (tv.tv_sec * 1000 + tv.tv_usec / 1000); //利用struct timeval结构体将时间转换为ms
}
3.2 代码简介
代码的功能逻辑,正如上面 的函数描述所说,正是利用gettimeofday返回的struct timeval结构内的成员变量,通过秒、毫秒、微妙的数量转换,将当前时间转换成毫秒,然后以函数返回值的形式输出。
值得注意的是,虽然gettimeofday在结构体定义上 【号称】有微妙级的精度,但是实际大部分的平台是没法达到这样的精度的,所以我们取其中,转换成毫秒级的精度,这个已经满足我们绝大多数应用场景了。
3.3 代码测试
针对上面的功能代码,写了一段小代码来测试下。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <time.h>
static int get_cur_time_ms(void)
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL); //使用gettimeofday获取当前系统时间
return (tv.tv_sec * 1000 + tv.tv_usec / 1000); //利用struct timeval结构体将时间转换为ms
}
static void get_rand_bytes(unsigned char *data, int len)
{
int a;
int i;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //种下随机种子
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
data[i] = rand() % 255; //取随机数,并保证数在0-255之间
//printf("%02X ", data[i]);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{
int t1;
int t2;
unsigned char data[1024000];
t1 = get_cur_time_ms();
get_rand_bytes(data, sizeof(data));
t2 = get_cur_time_ms();
printf("random %d bytes, waste time: %dms\n", sizeof(data), t2 - t1); //打印耗时
return 0;
}
以下测试代码的逻辑还是很简单的,主要就是测试获取 1024000个随机数的耗时情况。
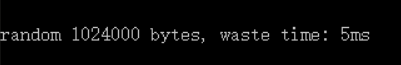
由于我本次测试使用的PC主机,其性能还是不错,所以测试出来的数据,还是耗时比较小的;如果这段代码放在嵌入式平台去运行的话,一个可能data数组的内存会爆,第二个耗时可能会大大增加。
感兴趣的朋友可以拿去一试。
注,本次测试的PC机情况如下:
4 小小总结
- 面对需求说明,尽快找到核心的功能要点,找到算法逻辑是关键;
- 明白要做什么,再去选择合适的函数来满足功能逻辑,这是比较好的思路;
- 考虑到gettimeofday的实际精度问题,牺牲部分不起眼的精度,依然可以满足大部分的需求。
5 更多分享
架构师李肯
架构师李肯(全网同名),一个专注于嵌入式IoT领域的架构师。有着近10年的嵌入式一线开发经验,深耕IoT领域多年,熟知IoT领域的业务发展,深度掌握IoT领域的相关技术栈,包括但不限于主流RTOS内核的实现及其移植、硬件驱动移植开发、网络通讯协议开发、编译构建原理及其实现、底层汇编及编译原理、编译优化及代码重构、主流IoT云平台的对接、嵌入式IoT系统的架构设计等等。拥有多项IoT领域的发明专利,热衷于技术分享,有多年撰写技术博客的经验积累,连续多月获得RT-Thread官方技术社区原创技术博文优秀奖,荣获CSDN博客专家、CSDN物联网领域优质创作者、2021年度CSDN&RT-Thread技术社区之星、2022年RT-Thread全球技术大会讲师、RT-Thread官方嵌入式开源社区认证专家、RT-Thread 2021年度论坛之星TOP4、华为云云享专家(嵌入式物联网架构设计师)等荣誉。坚信【知识改变命运,技术改变世界】!




![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于JAVA语言的宠物寄养管理(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b106f4b83f3141ec938f60d3336b7295.png)

![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM基于web的社团管理系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8ad3feb0d56b4a108c6490c7be94721b.png)

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计的小说阅读系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/73d5602892d74fe2828e44483b16f316.png)

