Dijstra算法优化
public static class NodeRecord {
public Node node;
public int distance;
public NodeRecord(Node node, int distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
public static class NodeHeap {
private Node[] nodes; // 实际的堆结构
// key 某一个node, value为上面堆中的位置
private HashMap<Node, Integer> heapIndexMap;
// key 某一个节点, value 从源节点出发到该节点的目前最小距离
private HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap;
private int size; // 堆上有多少个点
public NodeHeap(int size) {
nodes = new Node[size];
heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 有一个点叫node,现在发现了一个从源节点出发到达node的距离为distance
// 判断要不要更新,如果需要的话,就更新
public void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(Node node, int distance) {
//判断是否在堆上,如果在堆上则看是否更新
if (inHeap(node)) {
distanceMap.put(node, Math.min(distanceMap.get(node), distance));
//在堆上向上调整,因为只可能不变或者变小
insertHeapify(node, heapIndexMap.get(node));
}
//如果没有进来过则新增
if (!isEntered(node)) {
//先将点放到堆的最后
nodes[size] = node;
//表中加node给node下标和距离,看能否调整
heapIndexMap.put(node, size);
distanceMap.put(node, distance);
insertHeapify(node, size++);
}
}
public NodeRecord pop() {
//堆顶元素
NodeRecord nodeRecord = new NodeRecord(nodes[0], distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
//拿最后一个节点和0位置做交换
swap(0, size - 1);
//最后一个节点的下标改为-1代表已经从堆上弹出了
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size - 1], -1);
//距离表删除了
distanceMap.remove(nodes[size - 1]);
// free C++同学还要把原本堆顶节点析构,对java同学不必
//堆上将最后位置给清除
nodes[size - 1] = null;
heapify(0, --size);
return nodeRecord;
}
private void insertHeapify(Node node, int index) {
while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[(index - 1) / 2])) {
swap(index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
private void heapify(int index, int size) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < size) {
int smallest = left + 1 < size && distanceMap.get(nodes[left + 1]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[left])
? left + 1
: left;
smallest = distanceMap.get(nodes[smallest]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) ? smallest : index;
if (smallest == index) {
break;
}
swap(smallest, index);
index = smallest;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
/**
* 一个节点是否进入过堆里面
* @param node
* @return
*/
private boolean isEntered(Node node) {
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
/**
* 这个节点是否在堆上 如果点从堆上弹出则标记为-1
* @param node
* @return
*/
private boolean inHeap(Node node) {
return isEntered(node) && heapIndexMap.get(node) != -1;
}
private void swap(int index1, int index2) {
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index1], index2);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index2], index1);
Node tmp = nodes[index1];
nodes[index1] = nodes[index2];
nodes[index2] = tmp;
}
}
// 改进后的dijkstra算法
// 从head出发,所有head能到达的节点,生成到达每个节点的最小路径记录并返回,size代表图里面有多少个节点
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra2(Node head, int size) {
NodeHeap nodeHeap = new NodeHeap(size);
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(head, 0);
HashMap<Node, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
while (!nodeHeap.isEmpty()) {
//弹出堆顶元素
NodeRecord record = nodeHeap.pop();
//获取节点
Node cur = record.node;
//获取起始点到当前点的距离
int distance = record.distance;
for (Edge edge : cur.edges) {
//当前边发散出去的权重加上起始点到当前点的距离
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(edge.to, edge.weight + distance);
}
result.put(cur, distance);
}
return result;
}
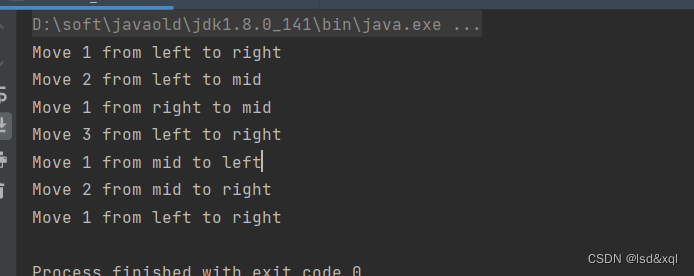
暴力递归
汉诺塔问题
public static void hanoi1(int n) {
leftToRight(n);
}
// 请把1~N层圆盘 从左 -> 右【除basecase外需要先从左移动到中间,再从中间移动到右边】
public static void leftToRight(int n) {
//将最下面的圆盘从左直接移到右
if (n == 1) { // base case
System.out.println("Move 1 from left to right");
return;
}
//剩余的n-1个圆盘从左移动到中
leftToMid(n - 1);
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from left to right");
//将剩余的圆盘从中移动到右
midToRight(n - 1);
}
// 请把1~N层圆盘 从左 -> 中【除basecase外需要先从左移动到右边再从右边移动到中间】
public static void leftToMid(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move 1 from left to mid");
return;
}
//将n-1个圆盘从左边移动到右边去
leftToRight(n - 1);
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from left to mid");
//再将n-1个圆盘从右边移动到中间
rightToMid(n - 1);
}
//除basecase外需要先从右边先移动到左边,再从左边移动到右边
public static void rightToMid(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move 1 from right to mid");
return;
}
rightToLeft(n - 1);
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from right to mid");
leftToMid(n - 1);
}
//除basecase外需要先将中间的移动到左边,再将左边的移动到右边
public static void midToRight(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move 1 from mid to right");
return;
}
midToLeft(n - 1);
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from mid to right");
leftToRight(n - 1);
}
//除basecase外需要先将中间的移动到右边,再将右边的移动到左边
public static void midToLeft(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move 1 from mid to left");
return;
}
midToRight(n - 1);
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from mid to left");
rightToLeft(n - 1);
}
//除basecase外需要先将右边的移动到中间,再将中间的移动到左边
public static void rightToLeft(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
System.out.println("Move 1 from right to left");
return;
}
rightToMid(n - 1);
System.out.println("Move " + n + " from right to left");
midToLeft(n - 1);
}
方法2:
定义from,to,other,这里的from,to和other都可能是左中右的任意一个,然后假设从from移动到to上,则需要经历以下三个流程
1)将1-n-1的圆盘从from移动到other,to成为了other
2)将剩余的一个n圆盘从from移动到to
3)将剩余的点从other移动到to区里面,这时的from作为上一步的other
public static void hanoi2(int n) {
if (n > 0) {
func(n, "left", "right", "mid");
}
}
//1-N 在:from
//去:to
//另一个:other
public static void func(int N, String from, String to, String other) {
if (N == 1) { // base
System.out.println("Move 1 from " + from + " to " + to);
} else {
//第一步将1~N-1的圆盘从from移动到other
func(N - 1, from, other, to);
//第二步是n圆盘自己直接挪动
System.out.println("Move " + N + " from " + from + " to " + to);
//第三步将圆盘从other移动到to
func(N - 1, other, to, from);
}
}
打印一个字符串的全部子序列
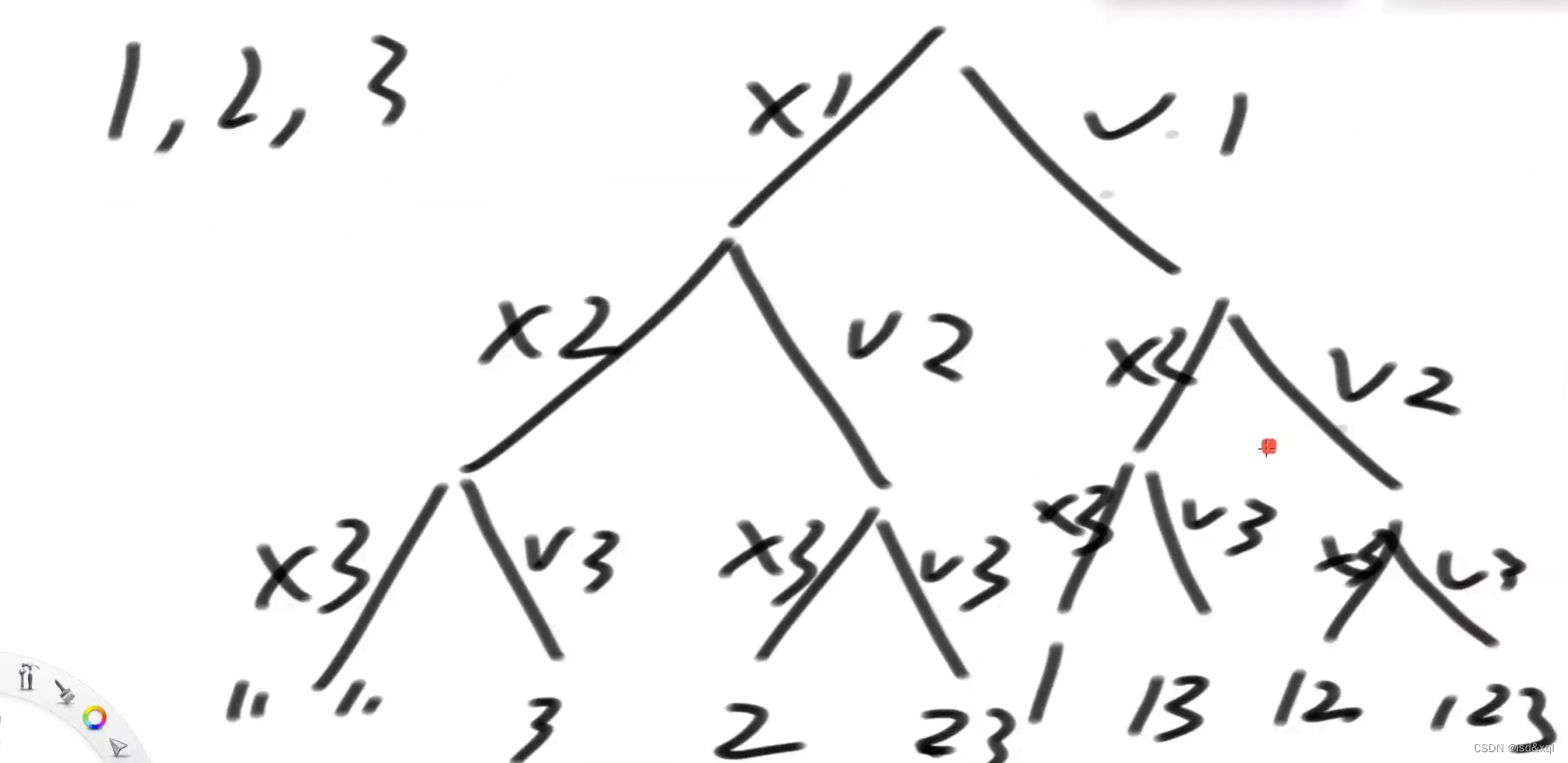
如上图为例,要找1,2,3这个序列的所有子序列,则可以规划为如上图的形式,关于每个数字是否需要来完成所有情况的获取
// s -> "abc"
public static List<String> subs(String s) {
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
String path = "";
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
process1(str, 0, ans, path);
return ans;
}
//规定递归的含义
// str 固定参数不变
// 来到了str[index]字符,index是位置
// str[0..index-1]已经走过了!之前的决定,都在path上
// 之前的决定已经不能改变了,就是path
// str[index....]还能决定,之前已经确定,而后面还能自由选择的话,
// 把所有生成的子序列,放入到ans里去
public static void process1(char[] str, int index, List<String> ans, String path) {
//index到终止位置了则直接结束
if (index == str.length) {
ans.add(path);
return;
}
// 没有要index位置的字符(path没变)
process1(str, index + 1, ans, path);
// 要了index位置的字符(path变化了)
process1(str, index + 1, ans, path + str[index]);
}
打印一个字符串的全部子序列,不出现重复
public static List<String> subsNoRepeat(String s) {
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
String path = "";
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
process2(str, 0, set, path);
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (String cur : set) {
ans.add(cur);
}
return ans;
}
public static void process2(char[] str, int index, HashSet<String> set, String path) {
if (index == str.length) {
set.add(path);
return;
}
String no = path;
process2(str, index + 1, set, no);
String yes = path + str[index];
process2(str, index + 1, set, yes);
}
打印一个字符串的全排列
全排列就是所有的字符都得要,只是说顺序可以不一样。
a,b,c,d 分别代表0-3位置,0位置是四个字符中选一个,
1位置是3种字符选一个,2位置是2种字符选一个,3位置只剩下一个字符。

绘制成如上图,将所有路都摊开。
暴力解法:
public static List<String> permutation1(String s) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
ArrayList<Character> rest = new ArrayList<Character>();
for (char cha : str) {
rest.add(cha);
}
String path = "";
f(rest, path, ans);
return ans;
}
//剩下的字符全在rest里面
//答案在ans里面
public static void f(ArrayList<Character> rest, String path, List<String> ans) {
//之前的所有决定都做完了
if (rest.isEmpty()) {
ans.add(path);
} else {
int N = rest.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
char cur = rest.get(i);
rest.remove(i);
f(rest, path + cur, ans);
//恢复现场
rest.add(i, cur);
}
}
}
如上方法不够好,下面再演示另一个版本的方法:

依次做交换,
public static List<String> permutation2(String s) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
g1(str, 0, ans);
return ans;
}
//所有的结果在str里面
public static void g1(char[] str, int index, List<String> ans) {
if (index == str.length) {
ans.add(String.valueOf(str));
} else {
//如果有的换
for (int i = index; i < str.length; i++) {
//index的值跟i换,然后跑所有的支路,最后再换回来。
swap(str, index, i);
g1(str, index + 1, ans);
//下一个支路到来前恢复现场
swap(str, index, i);
}
}
}
public static void swap(char[] chs, int i, int j) {
char tmp = chs[i];
chs[i] = chs[j];
chs[j] = tmp;
}
打印字符串的全排列并去重
根据ascii码作为一个boolean数组来确定是否需要交换位置
从而进行去重
public static List<String> permutation3(String s) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
g2(str, 0, ans);
return ans;
}
public static void g2(char[] str, int index, List<String> ans) {
if (index == str.length) {
ans.add(String.valueOf(str));
} else {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[256];
for (int i = index; i < str.length; i++) {
//这个字符是否试过的,试过的则不管
if (!visited[str[i]]) {
visited[str[i]] = true;
swap(str, index, i);
g2(str, index + 1, ans);
swap(str, index, i);
}
}
}
}
public static void swap(char[] chs, int i, int j) {
char tmp = chs[i];
chs[i] = chs[j];
chs[j] = tmp;
}
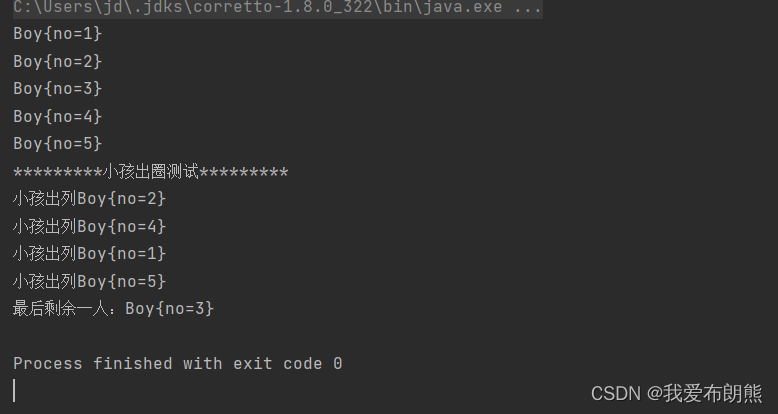
给你一个栈,请你逆序这个栈,不能申请额外的数据结构,只能使用递归函数
public static void reverse(Stack<Integer> stack) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
int i = f(stack);
reverse(stack);
stack.push(i);
}
// 栈底元素移除掉
// 上面的元素盖下来
// 返回移除掉的栈底元素
public static int f(Stack<Integer> stack) {
int result = stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return result;
} else {
int last = f(stack);
stack.push(result);
return last;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> test = new Stack<Integer>();
test.push(1);
test.push(2);
test.push(3);
test.push(4);
test.push(5);
reverse(test);
while (!test.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(test.pop());
}
}
f函数流程
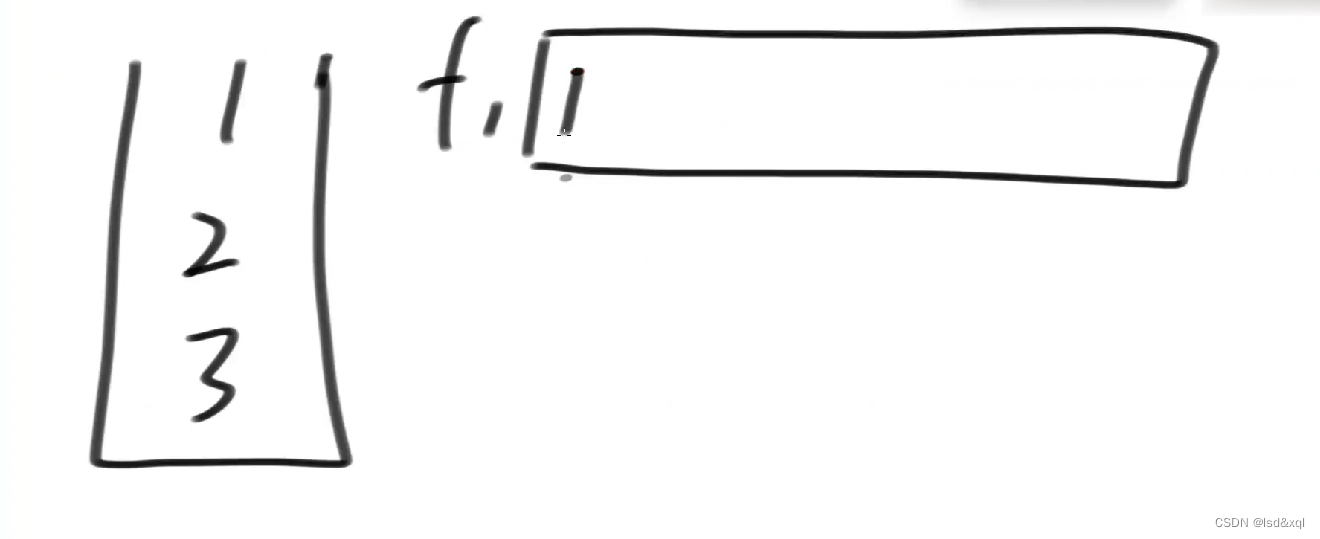
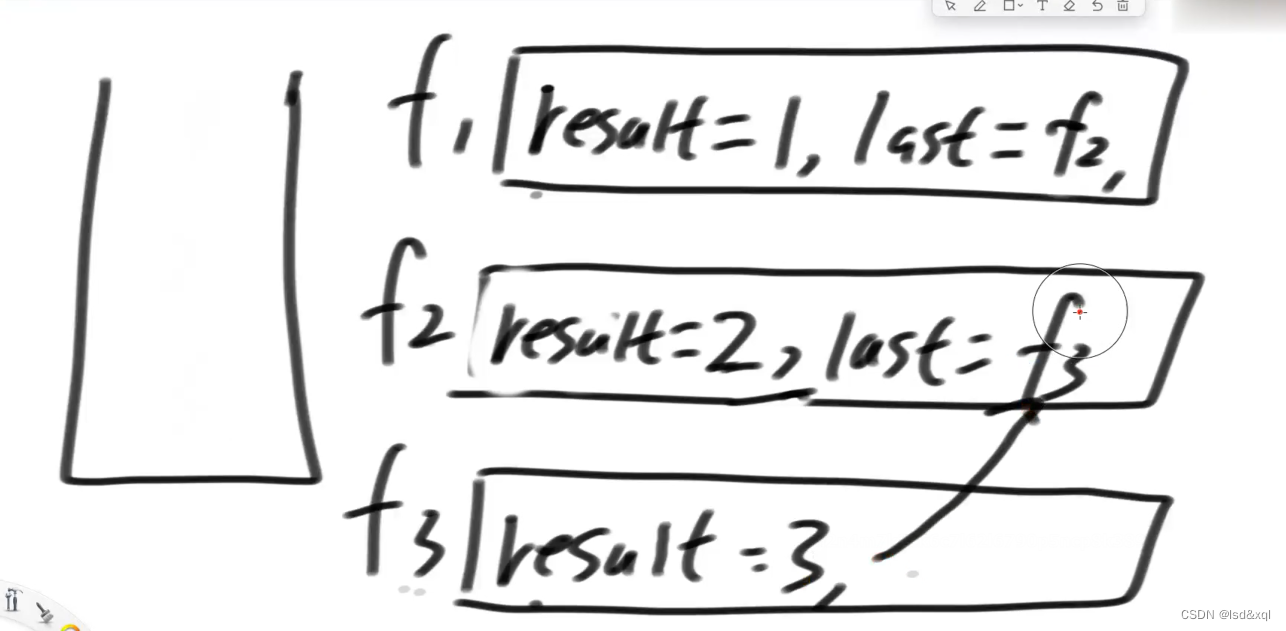
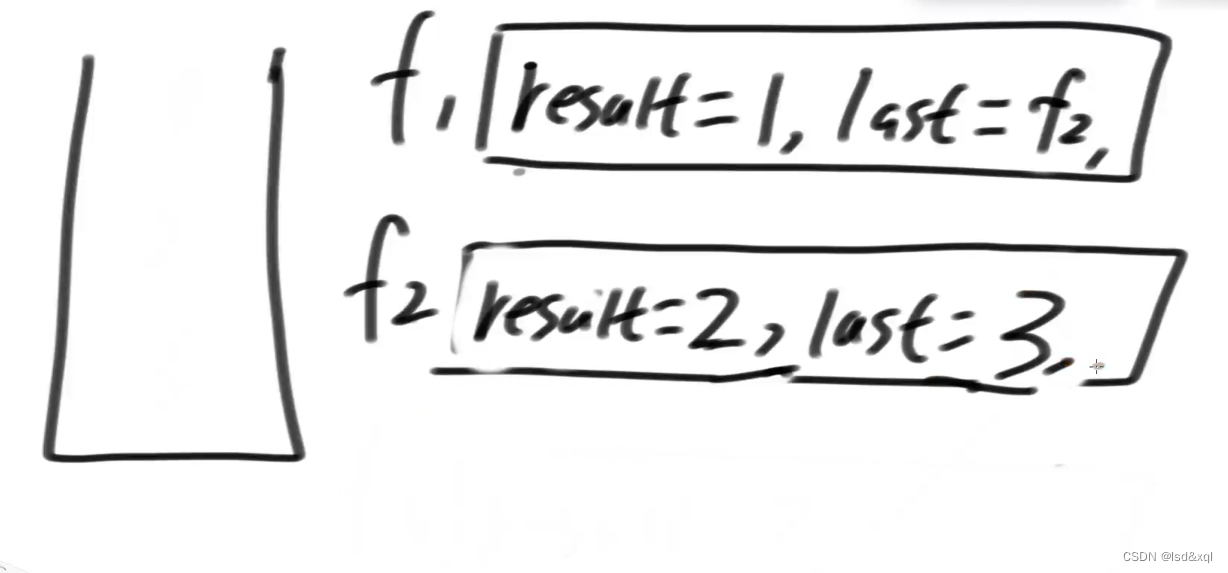
将2压栈回去,返回我接住的last到f1
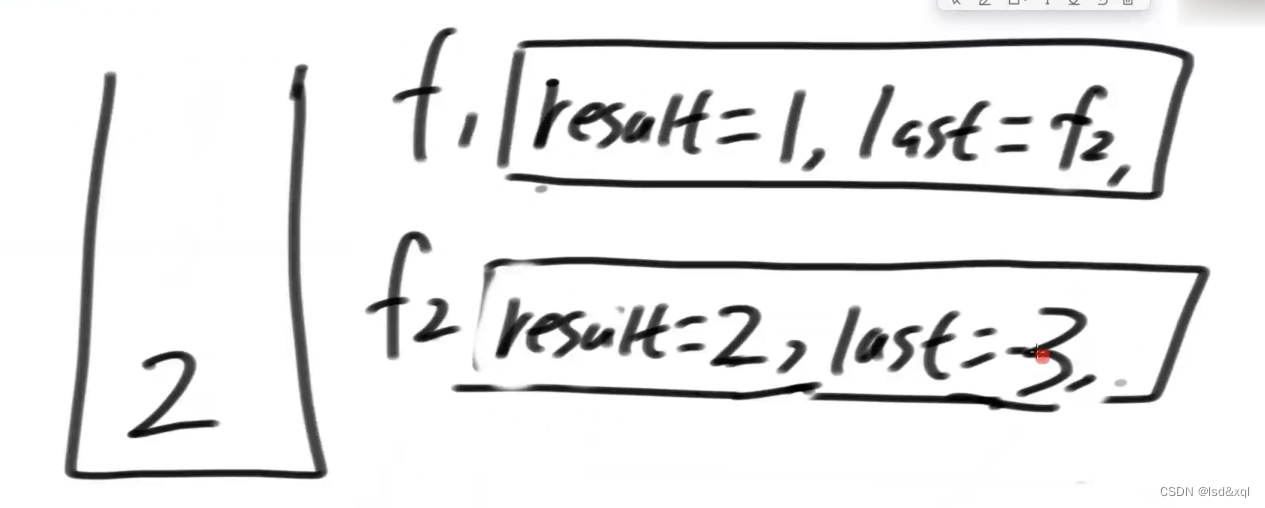
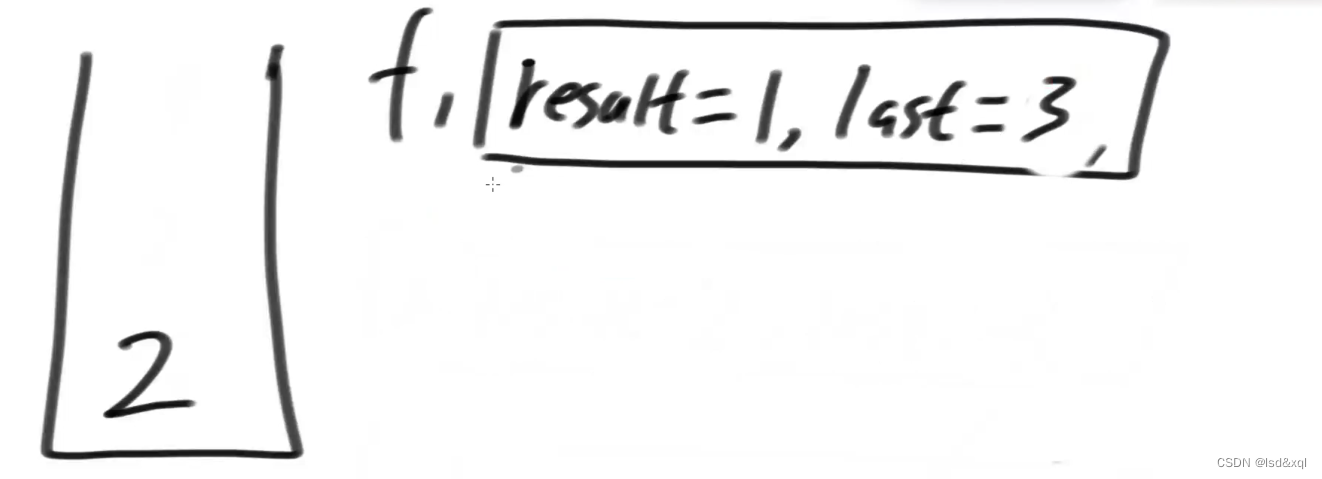
最后返回3:
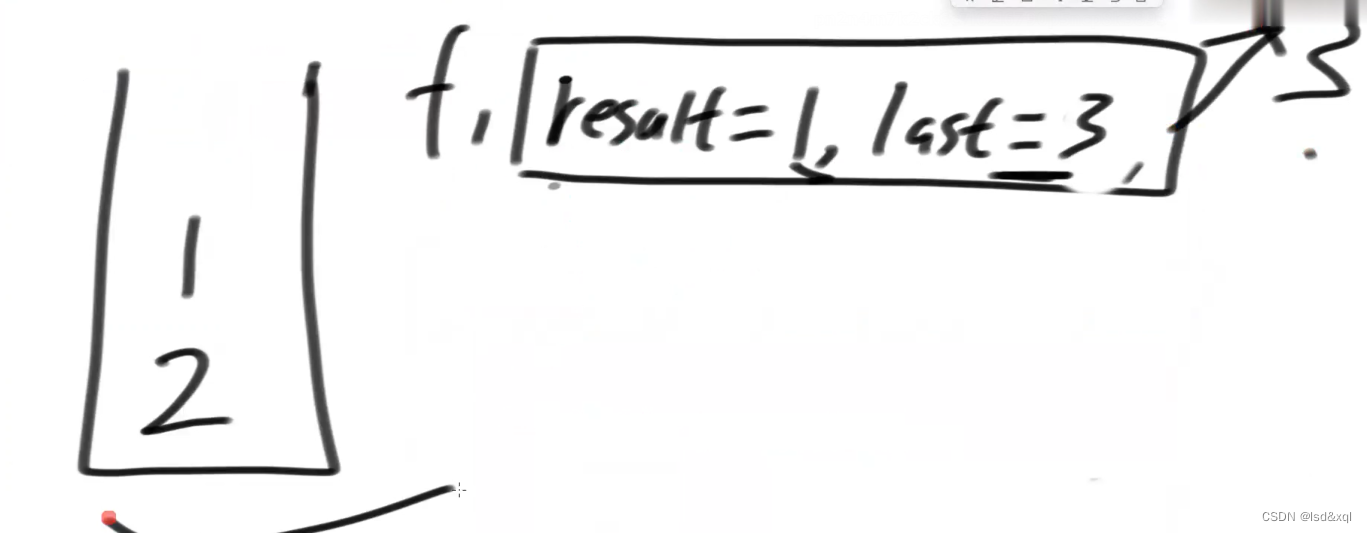
reverse函数流程:
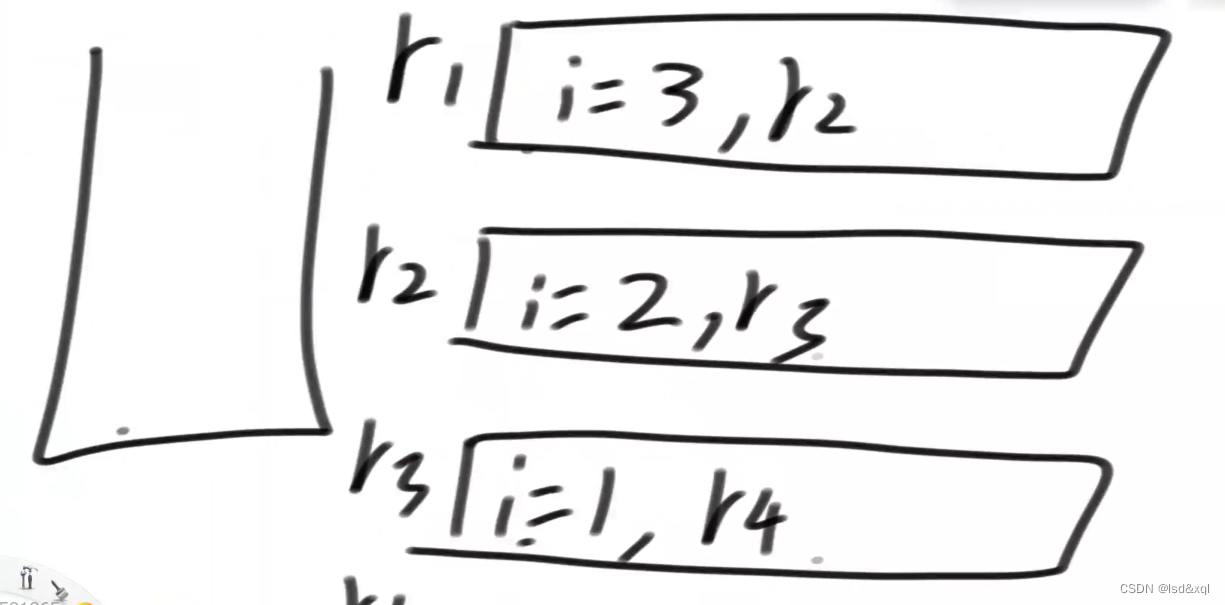
import java.util.Stack;
// 栈只提供push、pop、isEmpty三个方法
// 请完成无序栈的排序,要求排完序之后,从栈顶到栈底从小到大
// 只能使用栈提供的push、pop、isEmpty三个方法、以及递归函数
// 除此之外不能使用任何的容器,任何容器都不许,连数组也不行
// 也不能自己定义任何结构体
// 就是只用:
// 1) 栈提供的push、pop、isEmpty三个方法
// 2) 简单返回值的递归函数
public class Code01_SortStackUsingRecursive {
public static void sort(Stack<Integer> stack) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
int deep = size(stack);
while (deep > 0) {
int max = findMax(stack, deep);
int k = findMaxTimes(stack, deep, max);
maxDown(stack, deep, max, k);
deep -= k;
}
}
// 求栈的大小
// 但是不改变栈的任何数据状况
public static int size(Stack<Integer> stack) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
int hold = stack.pop();
int size = size(stack) + 1;
stack.push(hold);
return size;
}
// 从stack顶部出发,只往下找deep层
// 返回最大值
// 完全不改变stack的任何数据状况
public static int findMax(Stack<Integer> stack, int deep) {
if (deep == 0) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
int num = stack.pop();
int restMax = findMax(stack, deep - 1);
int ans = Math.max(num, restMax);
stack.push(num);
return ans;
}
// 已知从stack顶部出发,只往下找deep层,最大值是max
// 返回这个最大值出现了几次,只找到deep层!再往下不找了!
// 完全不改变stack的任何数据状况
public static int findMaxTimes(Stack<Integer> stack, int deep, int max) {
if (deep == 0) {
return 0;
}
int num = stack.pop();
int times = findMaxTimes(stack, deep - 1, max);
times += num == max ? 1 : 0;
stack.push(num);
return times;
}
// 已知从stack顶部出发,只往下找deep层,最大值是max
// 并且这个max出现了k次
// 请把这k个max沉底,不是沉到stack整体的底部,而是到deep层
// stack改变数据状况,但是只在从顶部到deep层的范围上改变
public static void maxDown(Stack<Integer> stack, int deep, int max, int k) {
if (deep == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
stack.push(max);
}
} else {
int cur = stack.pop();
maxDown(stack, deep - 1, max, k);
if (cur < max) {
stack.push(cur);
}
}
}
// 为了测试
// 生成随机栈
public static Stack<Integer> generateRandomStack(int n, int v) {
Stack<Integer> ans = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans.add((int) (Math.random() * v));
}
return ans;
}
// 为了测试
// 检测栈是不是有序的
public static boolean isSorted(Stack<Integer> stack) {
int step = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (step > stack.peek()) {
return false;
}
step = stack.pop();
}
return true;
}
// 为了测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> test = new Stack<Integer>();
test.add(1);
test.add(5);
test.add(4);
test.add(5);
test.add(3);
test.add(2);
test.add(3);
test.add(1);
test.add(4);
test.add(2);
// 1 5 4 5 3 2 3 1 4 2
sort(test);
while (!test.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(test.pop());
}
int n = 10;
int v = 20;
int testTimes = 2000;
System.out.println("测试开始");
for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {
Stack<Integer> stack = generateRandomStack(n, v);
sort(stack);
if (!isSorted(stack)) {
System.out.println("出错了!");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束");
}
}











![[036]基于Vue+Nodejs的网上作业批改系统(含源码、数据库、万字课设报告)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9b1b3923f13d4601ab4f0d3a3549b9ce.png)