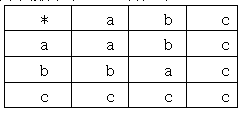
关系型数据库存储在磁盘当中,非关系型数据库存储在内存中
Jedis
第一步:导入依赖包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>5.7.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-nop</artifactId>
<version>1.7.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>第二步:建立连接
private Jedis jedis;
@BeforeEach
void setUp(){
//建立连接
jedis=new Jedis("localhost",6379);
//设置密码(window端我没有设置密码)
//jedis.auth("123456");
//选择库
jedis.select(0);
}第三步:操作库
@Test
void testString(){
//插入数据
String result = jedis.set("name", "张三");
System.out.println("result="+result);
//获取数据
String name = jedis.get("name");
System.out.println("name="+name);
}第四步:关闭资源
@AfterEach
void tearDown(){
//释放资源
if (jedis!=null){
jedis.close();
}
}jedis本身线程不安全,频繁的创建和销毁连接是有性能损耗的,推荐使用Jedis连接池代替Jedis直连方式
Jedis连接池
public class JedisConnectionFactory {
private static final JedisPool jedisPool;
static {
//配置连接池
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
//最大连接
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(8);
//设置最大空闲连接
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(8);
//设置最小空闲连接
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(0);
//设置无连接时等待时间
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(1000);
//创建连接池
jedisPool=new JedisPool("localhost",6379);
}
//获取对象
public static Jedis getJedis(){
return jedisPool.getResource();
}
}上面第二步中建立连接修改为
//建立连接
//jedis=new Jedis("localhost",6379);
jedis= JedisConnectionFactory.getJedis();SpringDataRedis
第一步:引入spring-boot-starter-data-redis依赖
<!--redis依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--commons-pool依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency><parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.7</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>第二步:在application.yaml配置Redis信息,需要把版本号降低为2.5.7
spring:
redis:
port: 6379
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
max-wait: 1000ms
host: 127.0.0.1
第三步:注入RedisTemplate
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void testString() {
//写入一条String数据
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "胡歌");
//获取String数据
Object name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("name=" + name);
}执行成功通过,但是redis数据获取name,并不是胡歌,而是Jack,实际上它存进去了,只不过name被序列化了
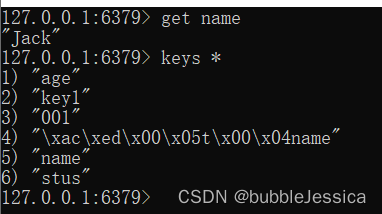
RedisTemplate可以接收任意Object作为值写入Redis,只不过写入前会把Object序列化为字节形式,默认采用JDK序列化,得到结果如下:
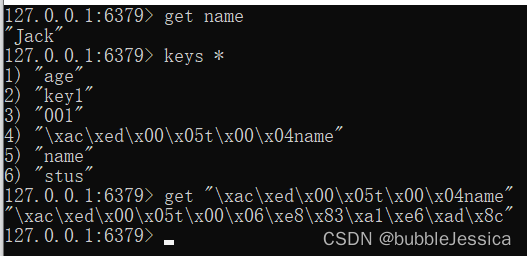
缺点:可读性差、内存占用较大
解决方法:定义RedisConfig类
package com.huhu.redis.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory){
//创建RedisTemplate对象
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
//设置连接工厂
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
//创建JSON序列化工具
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer jsonRedisSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
//设置Key的序列化
template.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
template.setHashKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
//设置Value的序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(jsonRedisSerializer);
//返回
return template;
}
}
package com.huhu;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
class RedisDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void testString() {
//写入一条String数据
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "胡歌");
//获取String数据
Object name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("name=" + name);
}
}
运行报错原因:没有导入Jackson依赖
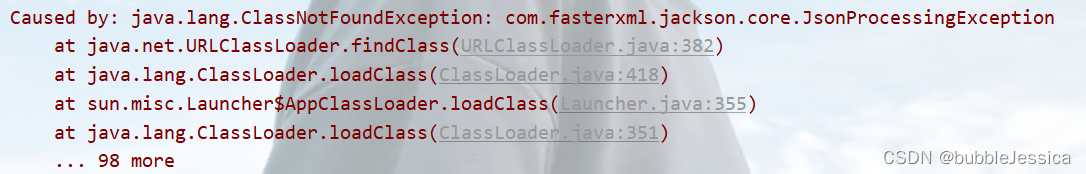
<!--Jackson依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>导入依赖后运行成功,并且之前name的值Jack已经被替代了
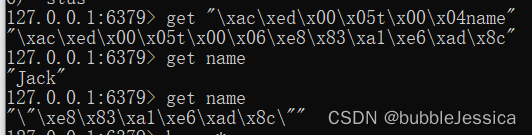
StringRedisTemplate
Java序列化就是指把Java对象转换为字节序列的过程 Java反序列化就是指把字节序列恢复为Java对象的过程。
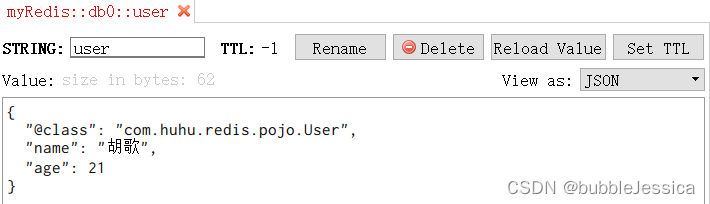
为了在反序列化时知道对象的类型,JSON序列化器会将类的class类型写入json结果中,存入Redis,会带来额外的内存开销
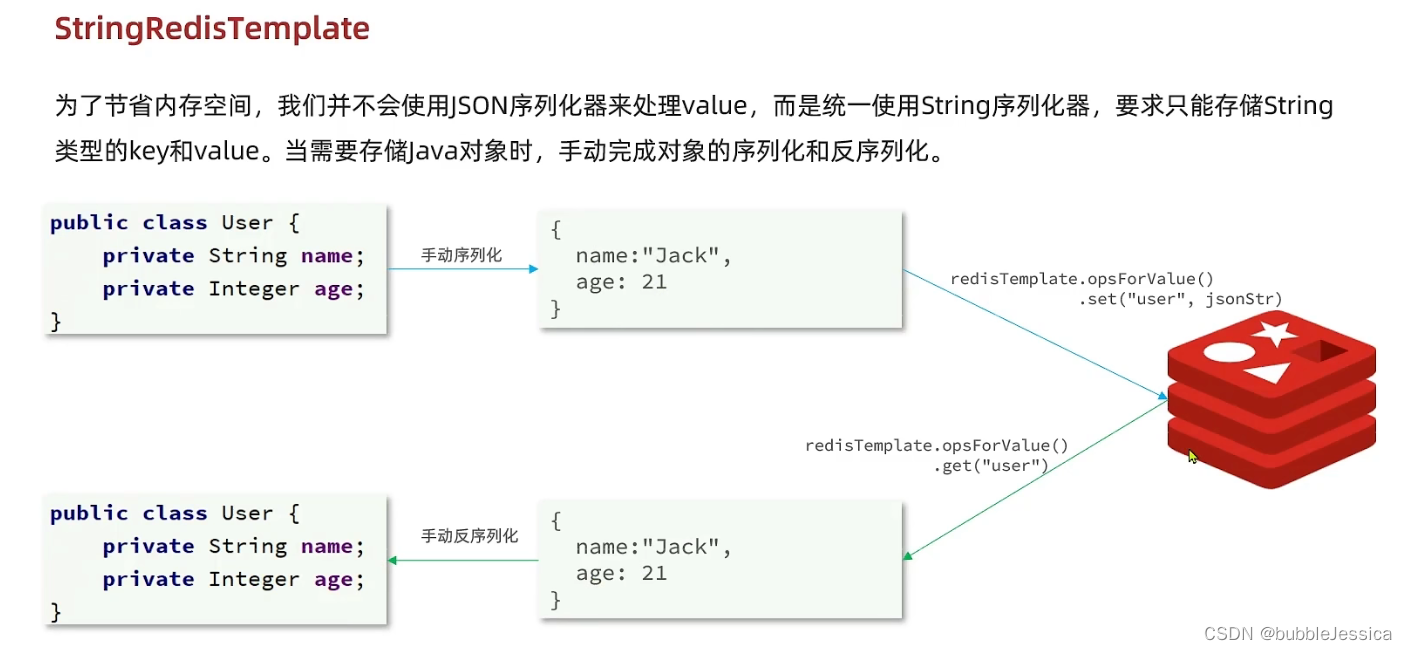
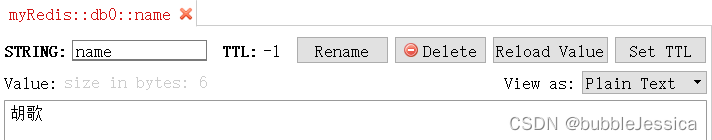
Spring默认提供了一个StringRedisTemplate类,它的key和value的序列化方式默认就是string方式
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
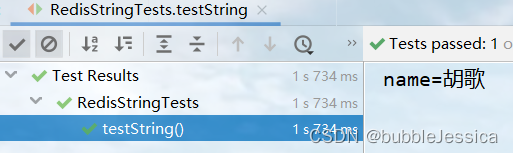
@Test
void testString() {
//写入一条String数据
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "胡歌");
//获取String数据
Object name = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("name=" + name);
}
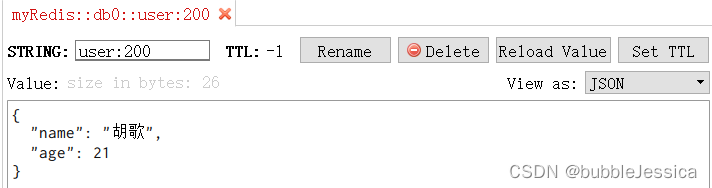
手动序列化和手动反序列化
private static final ObjectMapper mapper=new ObjectMapper();
@Test
void testSaveUser() throws JsonProcessingException {
//创建对象
User user=new User("胡歌",21);
//手动序列化
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
//写入数据
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user:200",json);
//获取数据
String jsonUser = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user:200");
//手动反序列化
User user1 = mapper.readValue(jsonUser, User.class);
System.out.println("use1r="+user1);
}
RedisTemplate操作hash类型(注意方法)
@Test
void testHash(){
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user:400","name","虎哥");
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user:400","age","21");
Map<Object, Object> entries = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("user:400");
System.out.println("entries="+entries);
}