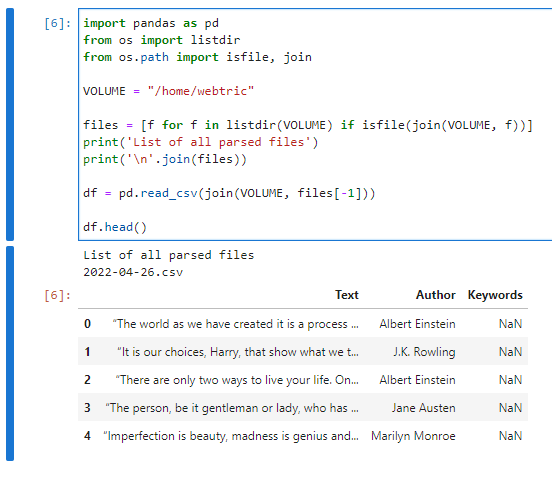
文章目录
- list的模拟实现
- 默认成员函数
- 构造函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值运算符重载
- 析构函数
- 迭代器
- 迭代器为什么要存在?
- const_iterator
- begin和end
- insert
- erase
- push_back && pop_back
- push_front &&pop_front
- swap
- 完整代码
list的模拟实现
默认成员函数
构造函数
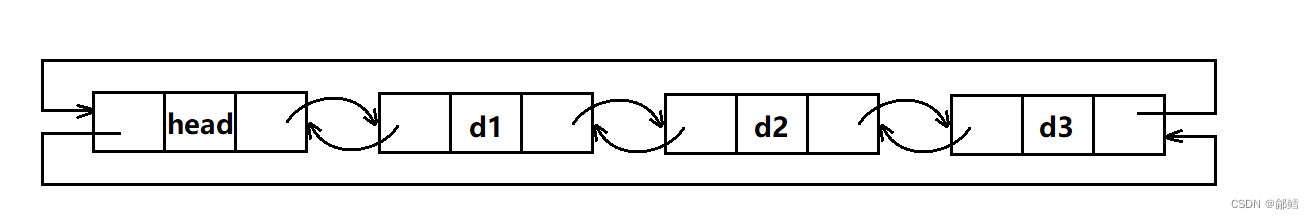
list是一个带头双向循环链表,在构造一个list对象时,new一个头结点,并让其prev和next都指向自己即可。
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
//默认构造
list()
{
empty_init();
}
拷贝构造函数
//拷贝构造函数
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
_head = new node; //申请一个头结点
_head->_next = _head; //头结点的后继指针指向自己
_head->_prev = _head; //头结点的前驱指针指向自己
for (auto & e : lt) //两个 e都是同一个
{
push_back(e); //将容器lt当中的数据一个个尾插到新构造的容器后面
}
}
赋值运算符重载
版本一(推荐):
参数不使用引用,让编译器自动调用list的拷贝构造函数构造出来一个list对象,然后调用swap函数将原容器与该list对象进行交换
这样做相当于将应该用clear清理的数据,通过交换函数交给了容器lt,而当赋值运算符重载函数调用结束时,容器lt会自动销毁,并调用其析构函数进行清理。
list<T> & operator= (list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造
//list<T>& operator= ( list<T> * this, list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造
// lt1 = lt2
{
this->swap(lt);
return *this;
}
版本二:
先调用clear函数将原容器清空,然后将容器lt当中的数据,通过遍历的方式一个个尾插到清空后的容器当中即可。
list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt)
{
if (this != <) //避免自己给自己赋值
{
clear(); //清空容器
for (const auto& e : lt)
{
push_back(e); //将容器lt当中的数据一个个尾插到链表后面
}
}
return *this; //支持连续赋值
}
析构函数
对对象进行析构时,首先调用clear函数清理容器当中的数据,然后将头结点释放,最后将头指针置空
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it!= end() )
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
迭代器
迭代器为什么要存在?
string 和vector的迭代器
string和vector将数据存储在一段连续的内存空间,那么可以通过指针进行自增、自减以及解引用等操作,就可以对相应位置的数据进行一系列操作,所以string和vector是天然的迭代器
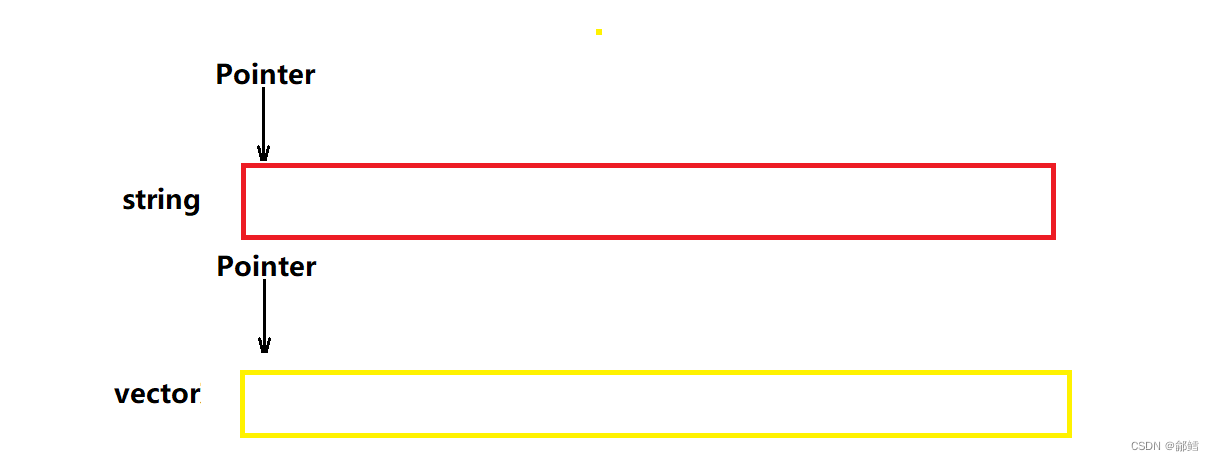

list的迭代器
list中各个结点在内存当中的位置是随机的,不一定是连续的,我们不能仅通过结点指针的自增、自减以及解引用等操作对相应结点的数据进行操作 ,采用类封装迭代器,在迭代器类的内部,重载 ++ 、 --、 *、 -> 、 !=、 == 这些迭代器会用到的运算符
const_iterator
在const迭代器中,const迭代器指向的内容不能被修改。也就是解引用返回的值不能被修改。迭代器本身是可以修改的,有两种解决方案 :
1 再封装一个const迭代器类
template< class T>
//const 迭代器 ,让迭代器指向的内容不能修改, 迭代器本身可以修改
struct __list_const_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
//构造函数
__list_const_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{
}
const T& operator*()//出了作用域,节点的值还在,用引用
//const: 返回节点的值,不能修改
{
return _node->_val;
}
//前置++,返回++之后的值
__list_const_iterator& operator++()
//__list_const_iterator& operator++(__list_const_iterator * this )
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++ ,返回++之前的值
__list_const_iterator operator++(int)
{
__list_const_iterator tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;// tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回
}
bool operator==(const __list_iterator<T>& it)
{
return *this == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)//传值返回,返回的是拷贝,是一个临时对象,临时对象具有常性
{
return *this != it._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
2 选择增加模板参数,复用代码(推荐)
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>

c++库就是用的这种解决方案
//template<class T> //list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数
//普通迭代器
//Ref是引用 ,Ptr是指针
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
//构造函数
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_val;
}
//前置++,返回++之后的值
self & operator++()
//__list_iterator<T> & operator++(__list_iterator<T> * this )
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++ ,返回++之前的值
self operator++(int)
// __list_iterator<T> operator++( __list_iterator<T> * this ,int)
{
self tmp(*this);//拷贝构造
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp; // tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回
}
bool operator!= (const self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator== (const self & it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
template<class T>//list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T ,T&,T* > iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T * > const_iterator;
//迭代器
//能直接显示构造最好显式构造,不要把决定权给编译器进行单参数的隐式类型转换
iterator end() //最后一个数据的下一个位置,即头节点
{
//return _head; // _head的类型是list_node<T>* ,iterator的类型是__list_iterator<T> ,类型不一致,涉及到单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
//还可以写成 return iterator(_head);
return iterator(_head);
}
iterator begin()//第一个数据的位置,即头节点的下一个位置
{
//return _head->_next;//单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
//还可以写成 return iterator(_head->_next)
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
//默认构造
list()
{
empty_init();
}
// lt2(lt1)
//还没有实现const_iterator
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
//拷贝数据
for (auto & e :lt )//遍历lt
{
push_back(e);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
void swap(list<T> & lt)
{
std:: swap(_head,lt._head );
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T> & operator= (list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造
//list<T>& operator= ( list<T> * this, list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造
// lt1 = lt2
{
this->swap(lt);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it!= end() )
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);//在最后一个数据的下一个位置插入
}
//pos位置之前插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
// prev newnode cur 链接关系
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
iterator erase (iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* next = cur->_next;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
//prev next
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
--_size;
return next;
}
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
void push_front( const T & x )//T可能是vector ,用引用,减少拷贝
{
insert(begin(),x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());//end是最后一个数据的下一个位置,需要--,到达最后一个数据,这样才是尾删
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
当我们定义const对象时,会自动调用const修饰的迭代器。当调用const修饰的迭代器时,__list_iterator的模板参数就会实例化为const T&。实际上在实例化时,const和非const修饰的还是两个不同类,只不过是实例化的代码工作交给了编译器处理了。
begin和end
对于list,第一个有效数据的迭代器就是头结点后一个结点
begin函数返回的是第一个有效数据的迭代器,即头节点的下一个位置
end函数返回的是最后一个有效数据的下一个位置的迭代器,即头节点
iterator end() //最后一个数据的下一个位置,即头节点
{
return _head; // _head的类型是list_node<T>* ,iterator的类型是__list_iterator<T> ,类型不一致,涉及到单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
//还可以写成 return iterator(_head);
}
iterator begin()//第一个数据的位置,即头节点的下一个位置
{
return _head->_next;//单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
//还可以写成 return iterator(_head->_next)
}
const对象的begin函数和end函数
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);//返回使用头结点后一个结点
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);//返回使用头结点
}
insert
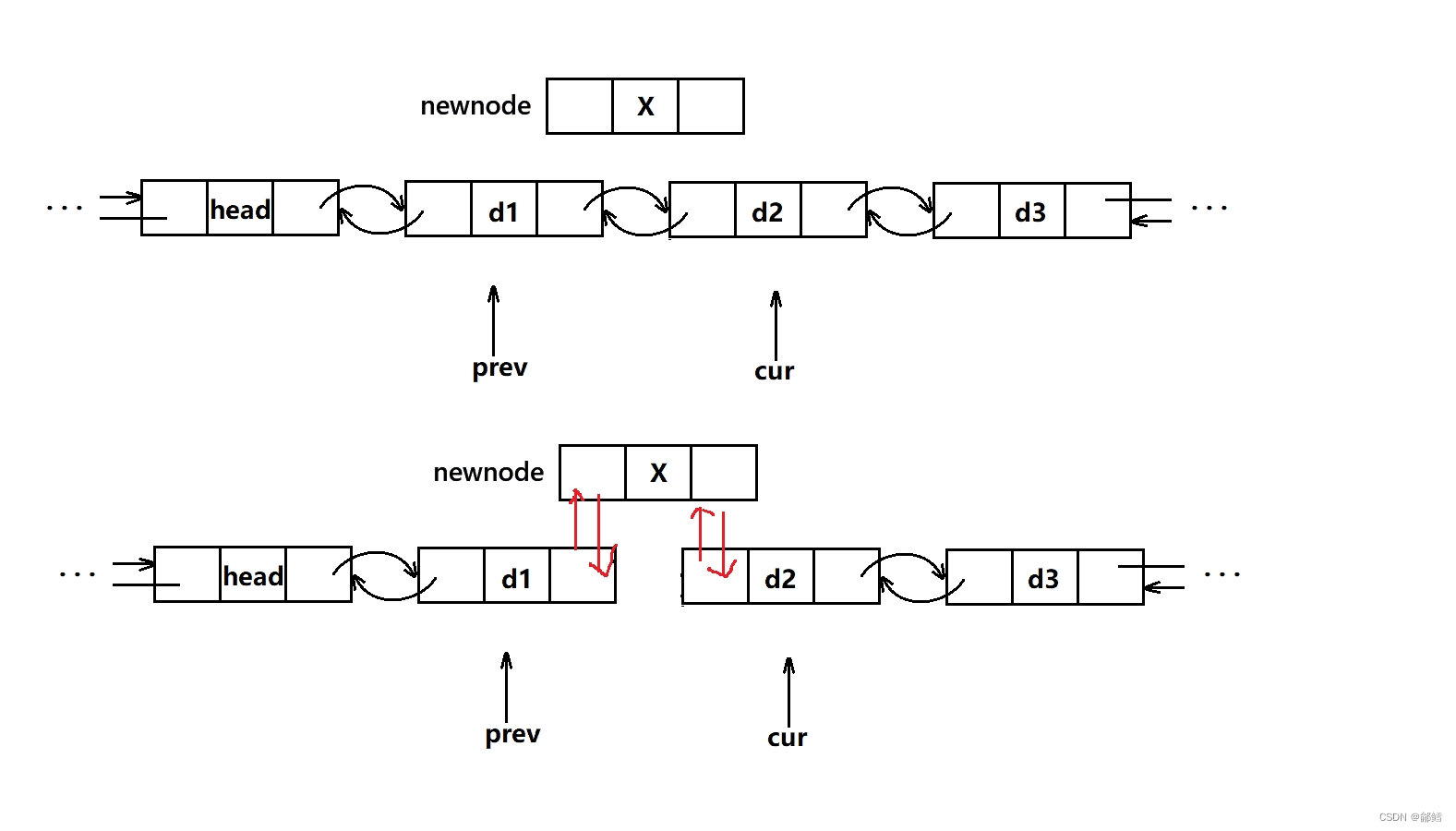
重新改变prev newnode cur 三者之间的链接关系
//pos位置之前插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
// prev newnode cur 链接关系
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
erase
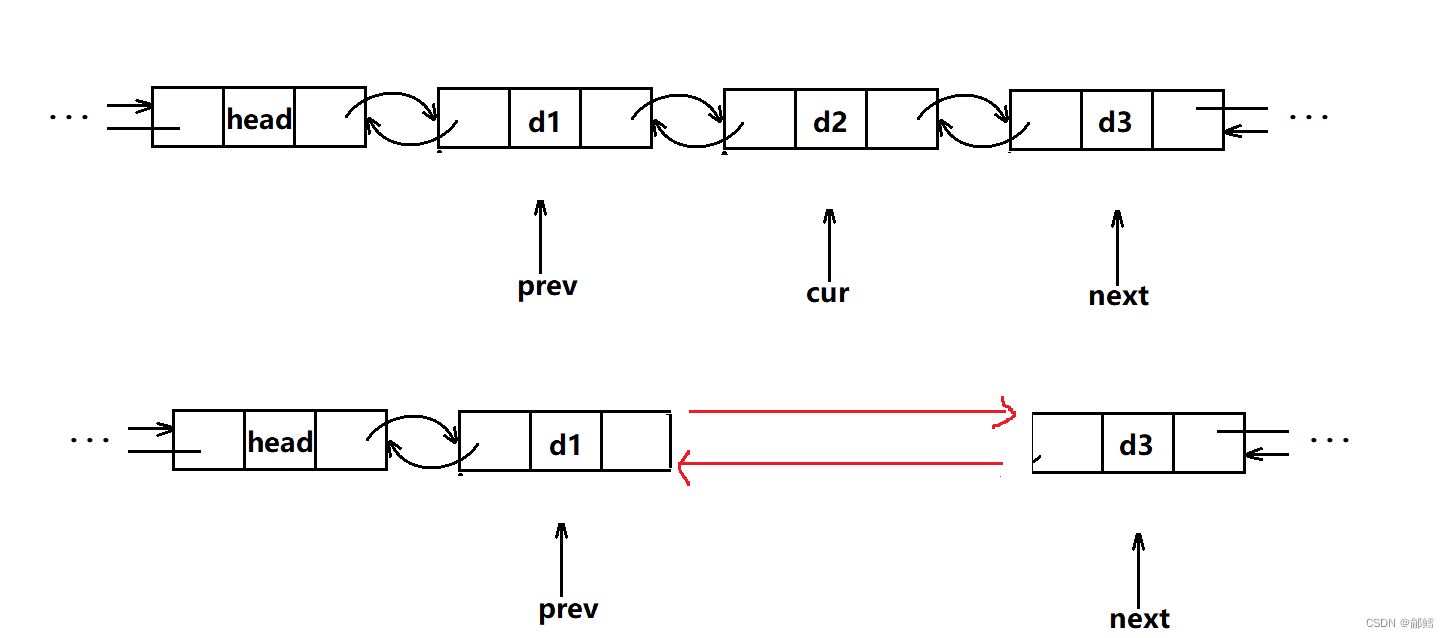
改变prev和next之间的链接关系,然后释放cur
iterator erase (iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* next = cur->_next;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
//prev next
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur ;
--_size;
return next;
}
push_back && pop_back
void push_back(const T& x)
{
insert(end(), x);//在最后一个数据的下一个位置插入
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());//end是最后一个数据的下一个位置,需要--,到达最后一个数据,这样才是尾删
}
push_front &&pop_front
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
void push_front( const T & x )//T可能是vector ,用引用,减少拷贝
{
insert(begin(),x);
}
swap
swap函数用于交换两个容器,list容器当中存储的是链表的头指针和size,我们将这两个容器当中的头指针和size交换
void swap(list<T> & lt)
{
std:: swap(_head,lt._head );
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
注意: 这里调用库里的swap模板函数,需要在swap函数之前加上“std::”,告诉编译器在c++标准库寻找swap函数,否则编译器编译时会认为你调用的是正在实现的swap函数(就近原则)
总结

完整代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
namespace cxq
{
//list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数
template<class T>
//节点
struct list_node
{
//构造函数
list_node(const T& val = T()) //缺省值是匿名对象,c++对内置类型进行了升级
:_prev(nullptr)
, _next(nullptr)
, _val(val)
{
}
list_node<T>* _prev;
list_node<T>* _next;
T _val;
};
//template<class T> //list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数
//普通迭代器
//Ref是引用 ,Ptr是指针
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
//构造函数
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_val;
}
//前置++,返回++之后的值
self & operator++()
//__list_iterator<T> & operator++(__list_iterator<T> * this )
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++ ,返回++之前的值
self operator++(int)
// __list_iterator<T> operator++( __list_iterator<T> * this ,int)
{
self tmp(*this);//拷贝构造
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp; // tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回
}
bool operator!= (const self& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator== (const self & it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
//template< class T>
const 迭代器 ,让迭代器指向的内容不能修改, 迭代器本身可以修改
//struct __list_const_iterator
//{
// typedef list_node<T> Node;
// //构造函数
// __list_const_iterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {
// }
// const T& operator*()//出了作用域,节点的值还在,用引用
// //const: 返回节点的值,不能修改
// {
// return _node->_val;
// }
// //前置++,返回++之后的值
// __list_const_iterator& operator++()
// //__list_const_iterator& operator++(__list_const_iterator * this )
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// //后置++ ,返回++之前的值
// __list_const_iterator operator++(int)
// {
// __list_const_iterator tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;// tmp出了作用域就被销毁 ,用传值返回
// }
// bool operator==(const __list_iterator<T>& it)
// {
// return *this == it._node;
// }
// bool operator!=(const __list_iterator<T>& it)//传值返回,返回的是拷贝,是一个临时对象,临时对象具有常性
// {
// return *this != it._node;
// }
// Node* _node;
//};
template<class T>//list类存储的数据是任意类型,所以需要设置模板参数
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T ,T&,T* > iterator;//普通迭代器
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T * > const_iterator;//const 迭代器
//迭代器
//能直接显示构造最好显式构造,不要把决定权给编译器进行单参数的隐式类型转换
iterator end() //最后一个数据的下一个位置,即头节点
{
//return _head; // _head的类型是list_node<T>* ,iterator的类型是__list_iterator<T> ,类型不一致,涉及到单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
//还可以写成 return iterator(_head);
return iterator(_head);
}
iterator begin()//第一个数据的位置,即头节点的下一个位置
{
//return _head->_next;//单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
//还可以写成 return iterator(_head->_next)
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(_head);
}
//默认构造
list()
{
empty_init();
}
// lt2(lt1)
//还没有实现const_iterator
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
//拷贝数据
for (auto & e :lt )//遍历lt
{
push_back(e);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
void swap(list<T> & lt)
{
std:: swap(_head,lt._head );
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
list<T> & operator= (list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造
//list<T>& operator= ( list<T> * this, list<T> lt)//右值没有引用传参,间接调用拷贝构造
// lt1 = lt2
{
this->swap(lt);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it!= end() )
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
找尾
//Node* tail = _head->_prev;
//Node* newnode = new Node(x);
改变链接关系
///*newnode = tail->next;*/
//tail->_next = newnode;
//newnode->_prev = tail;
//_head->_prev = newnode;
//newnode->_next = _head;
insert(end(), x);//在最后一个数据的下一个位置插入
}
//pos位置之前插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
// prev newnode cur 链接关系
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
iterator erase (iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* next = cur->_next;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
//prev next
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
--_size;
return next;
}
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
void push_front( const T & x )//T可能是vector ,用引用,减少拷贝
{
insert(begin(),x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());//end是最后一个数据的下一个位置,需要--,到达最后一个数据,这样才是尾删
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();//拷贝构造
while (it != lt1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list2()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
list<int> lt2 (lt1);
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
如果你觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,不妨动动手指给点赞收藏加转发,给鄃鳕一个大大的关注你们的每一次支持都将转化为我前进的动力!!!
![SpringBoot 底层机制分析[上]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f32bf6f72df7ae50a20d0c0d93ad6b4d.png)