往期博客👉
【Matlab】BP神经网络遗传算法(BP-GA)函数极值寻优——非线性函数求极值
【Matlab】GRNN神经网络遗传算法(GRNN-GA)函数极值寻优——非线性函数求极值
【Matlab】RBF神经网络遗传算法(RBF-GA)函数极值寻优——非线性函数求极值
【Matlab】Elman神经网络遗传算法(Elman-GA)函数极值寻优——非线性函数求极值
本篇博客将主要介绍ELM(极限学习机),希望能帮助大家快速入门ELM。
1.背景条件
要求:对于未知模型(函数表达式未知)求解极值。
条件:已知模型的一些输入输出数据。
程序的示例是根据用神经网络遗传算法寻优非线性函数 y = x 1 2 + x 2 2 y = x_1^2+x_2^2 y=x12+x22 的极值,输入参数有2个,输出参数有1个,易知函数有极小值0,极小值点为(0, 0)。已知的只有一些输入输出数据(用rand函数生成输入,然后代入表达式生成输出):
for i=1:4000
input(i,:)=10*rand(1,2)-5;
output(i)=input(i,1)^2+input(i,2)^2;
end
2.完整代码
data.m
用于生成神经网络拟合的原始数据。
for i=1:4000
input(i,:)=10*rand(1,2)-5;
output(i)=input(i,1)^2+input(i,2)^2;
end
output=output';
save data input output
ELM.m
用函数输入输出数据训练ELM,使训练后的网络能够拟合非线性函数输出,保存训练好的网络用于计算个体适应度值。根据非线性函数方程随机得到该函数的4000组输入输出数据,存储于data中,其中input为函数输入数据,output为函数对应输出数据,从中随机抽取3900组训练数据训练网络,100组测试数据测试网络拟合性能。最后保存训练好的网络。
%% 清空环境变量
clc
tic
%% 训练数据预测数据提取及归一化
%从1到4000间随机排序
k=rand(1,4000);
[m,n]=sort(k);
%划分训练数据和预测数据
input_train=input(n(1:3900),:)';
output_train=output(n(1:3900),:)';
input_test=input(n(3901:4000),:)';
output_test=output(n(3901:4000),:)';
[inputn_train,inputps]=mapminmax(input_train,-1,1);
[outputn_train,outputps]=mapminmax(output_train,-1,1);
inputn_test = mapminmax('apply',input_test,inputps);
outputn_test = mapminmax('apply',output_test,outputps);
%% ELM创建/训练
[IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(inputn_train,outputn_train,20,'sig',0);
%% ELM仿真测试
outputn_ELM = elmpredict(inputn_test,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE);
output_ELM = mapminmax('reverse',outputn_ELM,outputps);
%% 结果分析
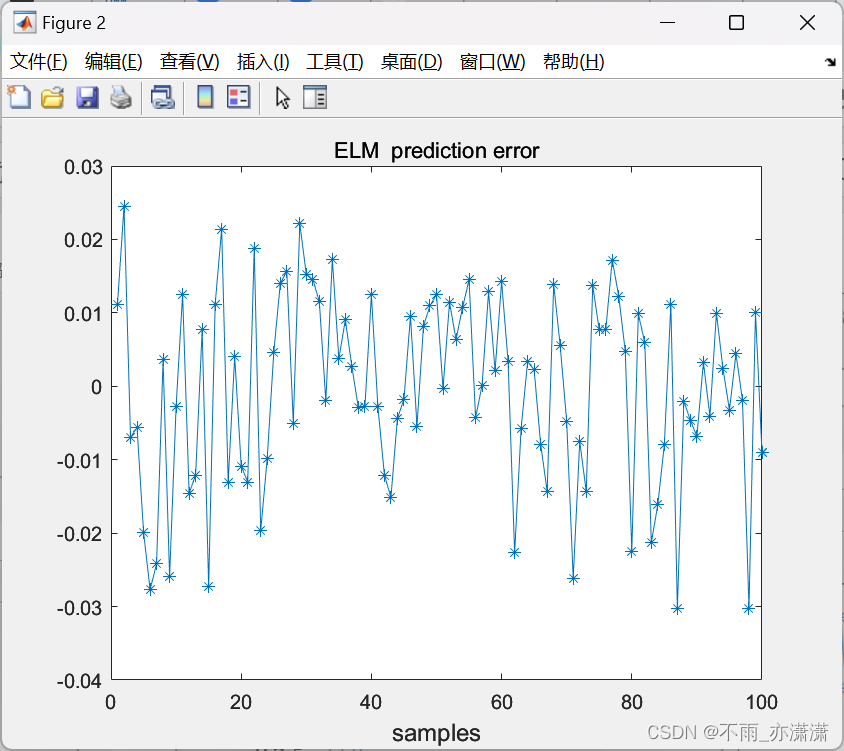
error=output_test-output_ELM;
errorsum=sum(abs(error))
figure(1);
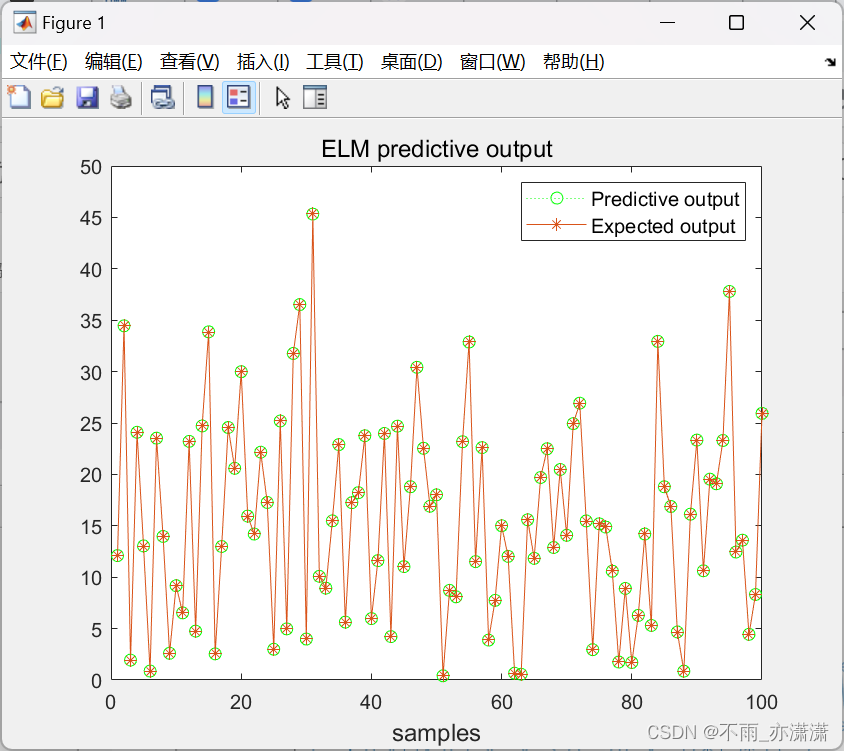
plot(output_ELM,':og');
hold on
plot(output_test,'-*');
legend('Predictive output','Expected output','fontsize',10);
title('ELM predictive output','fontsize',12);
xlabel("samples",'fontsize',12);
figure(2);
plot(error,'-*');
title('ELM prediction error');
xlabel("samples",'fontsize',12);
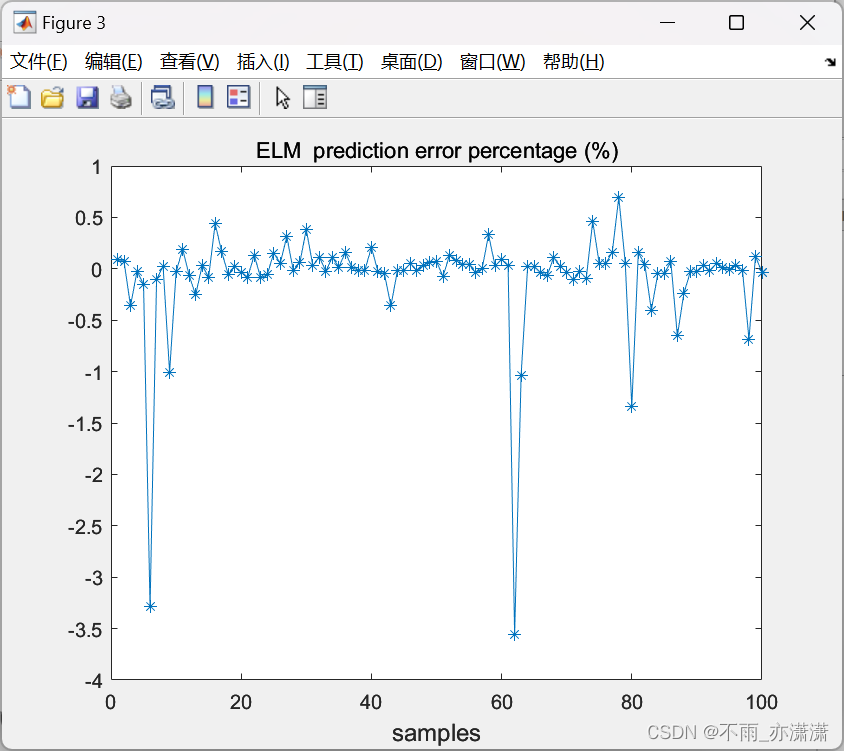
figure(3);
plot(100*(output_test-output_ELM)./output_test,'-*');
title('ELM prediction error percentage (%)');
xlabel("samples",'fontsize',12);
toc
save data inputps outputps
save net IW B LW TF TYPE
elmtrain.m
ELM训练函数。
function [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,N,TF,TYPE)
% ELMTRAIN Create and Train a Extreme Learning Machine
% Syntax
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,N,TF,TYPE)
% Description
% Input
% P - Input Matrix of Training Set (R*Q)
% T - Output Matrix of Training Set (S*Q)
% N - Number of Hidden Neurons (default = Q)
% TF - Transfer Function:
% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function (default)
% 'sin' for Sine function
% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function
% TYPE - Regression (0,default) or Classification (1)
% Output
% IW - Input Weight Matrix (N*R)
% B - Bias Matrix (N*1)
% LW - Layer Weight Matrix (N*S)
% Example
% Regression:
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',0)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% Classification
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',1)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% See also ELMPREDICT
% Yu Lei,11-7-2010
% Copyright www.matlabsky.com
% $Revision:1.0 $
if nargin < 2
error('ELM:Arguments','Not enough input arguments.');
end
if nargin < 3
N = size(P,2);
end
if nargin < 4
TF = 'sig';
end
if nargin < 5
TYPE = 0;
end
if size(P,2) ~= size(T,2)
error('ELM:Arguments','The columns of P and T must be same.');
end
[R,Q] = size(P);
if TYPE == 1
T = ind2vec(T);
end
[S,Q] = size(T);
% Randomly Generate the Input Weight Matrix
IW = rand(N,R) * 2 - 1;
% Randomly Generate the Bias Matrix
B = rand(N,1);
BiasMatrix = repmat(B,1,Q);
% Calculate the Layer Output Matrix H
tempH = IW * P + BiasMatrix;
switch TF
case 'sig'
H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));
case 'sin'
H = sin(tempH);
case 'hardlim'
H = hardlim(tempH);
end
% Calculate the Output Weight Matrix
LW = pinv(H') * T';
elmpredict.m
ELM预测函数。
function Y = elmpredict(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% ELMPREDICT Simulate a Extreme Learning Machine
% Syntax
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% Description
% Input
% P - Input Matrix of Training Set (R*Q)
% IW - Input Weight Matrix (N*R)
% B - Bias Matrix (N*1)
% LW - Layer Weight Matrix (N*S)
% TF - Transfer Function:
% 'sig' for Sigmoidal function (default)
% 'sin' for Sine function
% 'hardlim' for Hardlim function
% TYPE - Regression (0,default) or Classification (1)
% Output
% Y - Simulate Output Matrix (S*Q)
% Example
% Regression:
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',0)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% Classification
% [IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE] = elmtrain(P,T,20,'sig',1)
% Y = elmtrain(P,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE)
% See also ELMTRAIN
% Yu Lei,11-7-2010
% Copyright www.matlabsky.com
% $Revision:1.0 $
if nargin < 6
error('ELM:Arguments','Not enough input arguments.');
end
% Calculate the Layer Output Matrix H
Q = size(P,2);
BiasMatrix = repmat(B,1,Q);
tempH = IW * P + BiasMatrix;
switch TF
case 'sig'
H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH));
case 'sin'
H = sin(tempH);
case 'hardlim'
H = hardlim(tempH);
end
% Calculate the Simulate Output
Y = (H' * LW)';
if TYPE == 1
temp_Y = zeros(size(Y));
for i = 1:size(Y,2)
[max_Y,index] = max(Y(:,i));
temp_Y(index,i) = 1;
end
Y = vec2ind(temp_Y);
end
Code.m
编码成染色体。
function ret=Code(lenchrom,bound)
%本函数将变量编码成染色体,用于随机初始化一个种群
% lenchrom input : 染色体长度
% bound input : 变量的取值范围
% ret output: 染色体的编码值
flag=0;
while flag==0
pick=rand(1,length(lenchrom));
ret=bound(:,1)'+(bound(:,2)-bound(:,1))'.*pick; %线性插值,编码结果以实数向量存入ret中
flag=test(lenchrom,bound,ret); %检验染色体的可行性
end
fun.m
把训练好的ELM预测输出作为个体适应度值。
function fitness = fun(x)
% 函数功能:计算该个体对应适应度值
% x input 个体
% fitness output 个体适应度值
load data inputps outputps
load net IW B LW TF TYPE
%数据归一化
x=x';
inputn_test=mapminmax('apply',x,inputps);
%网络预测输出
outputn_ELM = elmpredict(inputn_test,IW,B,LW,TF,TYPE);
%网络输出反归一化
fitness=mapminmax('reverse',outputn_ELM,outputps);
对于求极小值的函数,适应度可以设为ELM预测结果,如果需要求极大值,可以对适应度取反。
Select.m
选择操作采用轮盘赌法从种群中选择适应度好的个体组成新种群。
function ret=select(individuals,sizepop)
% 本函数对每一代种群中的染色体进行选择,以进行后面的交叉和变异
% individuals input : 种群信息
% sizepop input : 种群规模
% ret output : 经过选择后的种群
fitness1=1./individuals.fitness;
sumfitness=sum(fitness1);
sumf=fitness1./sumfitness;
index=[];
for i=1:sizepop %转sizepop次轮盘
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
for i=1:sizepop
pick=pick-sumf(i);
if pick<0
index=[index i];
break; %寻找落入的区间,此次转轮盘选中了染色体i,注意:在转sizepop次轮盘的过程中,有可能会重复选择某些染色体
end
end
end
individuals.chrom=individuals.chrom(index,:);
individuals.fitness=individuals.fitness(index);
ret=individuals;
Cross.m
交叉操作从种群中选择两个个体,按一定概率交叉得到新个体。
function ret=Cross(pcross,lenchrom,chrom,sizepop,bound)
%本函数完成交叉操作
% pcorss input : 交叉概率
% lenchrom input : 染色体的长度
% chrom input : 染色体群
% sizepop input : 种群规模
% ret output : 交叉后的染色体
for i=1:sizepop %每一轮for循环中,可能会进行一次交叉操作,染色体是随机选择的,交叉位置也是随机选择的,%但该轮for循环中是否进行交叉操作则由交叉概率决定(continue控制)
% 随机选择两个染色体进行交叉
pick=rand(1,2);
while prod(pick)==0
pick=rand(1,2);
end
index=ceil(pick.*sizepop);
% 交叉概率决定是否进行交叉
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
if pick>pcross
continue;
end
flag=0;
while flag==0
% 随机选择交叉位
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
pos=ceil(pick.*sum(lenchrom)); %随机选择进行交叉的位置,即选择第几个变量进行交叉,注意:两个染色体交叉的位置相同
pick=rand; %交叉开始
v1=chrom(index(1),pos);
v2=chrom(index(2),pos);
chrom(index(1),pos)=pick*v2+(1-pick)*v1;
chrom(index(2),pos)=pick*v1+(1-pick)*v2; %交叉结束
flag1=test(lenchrom,bound,chrom(index(1),:)); %检验染色体1的可行性
flag2=test(lenchrom,bound,chrom(index(2),:)); %检验染色体2的可行性
if flag1*flag2==0
flag=0;
else flag=1;
end %如果两个染色体不是都可行,则重新交叉
end
end
ret=chrom;
test.m
检验染色体的可行性。
function flag=test(lenchrom,bound,code)
% lenchrom input : 染色体长度
% bound input : 变量的取值范围
% code output: 染色体的编码值
x=code; %先解码
flag=1;
if (x(1)<bound(1,1))&&(x(2)<bound(2,1))&&(x(1)>bound(1,2))&&(x(2)>bound(2,2))
flag=0;
end
Mutation.m
变异操作从种群中随机选择一个个体,按一定概率变异得到新个体。
function ret=Mutation(pmutation,lenchrom,chrom,sizepop,pop,bound)
% 本函数完成变异操作
% pcorss input : 变异概率
% lenchrom input : 染色体长度
% chrom input : 染色体群
% sizepop input : 种群规模
% opts input : 变异方法的选择
% pop input : 当前种群的进化代数和最大的进化代数信息
% ret output : 变异后的染色体
for i=1:sizepop %每一轮for循环中,可能会进行一次变异操作,染色体是随机选择的,变异位置也是随机选择的,
%但该轮for循环中是否进行变异操作则由变异概率决定(continue控制)
% 随机选择一个染色体进行变异
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
index=ceil(pick*sizepop);
% 变异概率决定该轮循环是否进行变异
pick=rand;
if pick>pmutation
continue;
end
flag=0;
while flag==0
% 变异位置
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
pos=ceil(pick*sum(lenchrom)); %随机选择了染色体变异的位置,即选择了第pos个变量进行变异
v=chrom(i,pos);
v1=v-bound(pos,1);
v2=bound(pos,2)-v;
pick=rand; %变异开始
if pick>0.5
delta=v2*(1-pick^((1-pop(1)/pop(2))^2));
chrom(i,pos)=v+delta;
else
delta=v1*(1-pick^((1-pop(1)/pop(2))^2));
chrom(i,pos)=v-delta;
end %变异结束
flag=test(lenchrom,bound,chrom(i,:)); %检验染色体的可行性
end
end
ret=chrom;
Genetic.m
%% 清空环境变量
clc
% clear
%% 初始化遗传算法参数
%初始化参数
maxgen=100; %进化代数,即迭代次数
sizepop=20; %种群规模
pcross=[0.4]; %交叉概率选择,0和1之间
pmutation=[0.2]; %变异概率选择,0和1之间
lenchrom=[1 1]; %每个变量的字串长度,如果是浮点变量,则长度都为1
bound=[-5 5;-5 5]; %数据范围
individuals=struct('fitness',zeros(1,sizepop), 'chrom',[]); %将种群信息定义为一个结构体
avgfitness=[]; %每一代种群的平均适应度
bestfitness=[]; %每一代种群的最佳适应度
bestchrom=[]; %适应度最好的染色体
%% 初始化种群计算适应度值
% 初始化种群
for i=1:sizepop
%随机产生一个种群
individuals.chrom(i,:)=Code(lenchrom,bound);
x=individuals.chrom(i,:);
%计算适应度
individuals.fitness(i)=fun(x); %染色体的适应度
end
%找最好的染色体
[bestfitness bestindex]=min(individuals.fitness);
bestchrom=individuals.chrom(bestindex,:); %最好的染色体
avgfitness=sum(individuals.fitness)/sizepop; %染色体的平均适应度
% 记录每一代进化中最好的适应度和平均适应度
trace=[avgfitness bestfitness];
%% 迭代寻优
% 进化开始
for i=1:maxgen
i
% 选择
individuals=Select(individuals,sizepop);
avgfitness=sum(individuals.fitness)/sizepop;
% 交叉
individuals.chrom=Cross(pcross,lenchrom,individuals.chrom,sizepop,bound);
% 变异
individuals.chrom=Mutation(pmutation,lenchrom,individuals.chrom,sizepop,[i maxgen],bound);
% 计算适应度
for j=1:sizepop
x=individuals.chrom(j,:); %解码
individuals.fitness(j)=fun(x);
end
%找到最小和最大适应度的染色体及它们在种群中的位置
[newbestfitness,newbestindex]=min(individuals.fitness);
[worestfitness,worestindex]=max(individuals.fitness);
% 代替上一次进化中最好的染色体
if bestfitness>newbestfitness
bestfitness=newbestfitness;
bestchrom=individuals.chrom(newbestindex,:);
end
individuals.chrom(worestindex,:)=bestchrom;
individuals.fitness(worestindex)=bestfitness;
avgfitness=sum(individuals.fitness)/sizepop;
trace=[trace;avgfitness bestfitness]; %记录每一代进化中最好的适应度和平均适应度
end
%进化结束
%% 结果分析
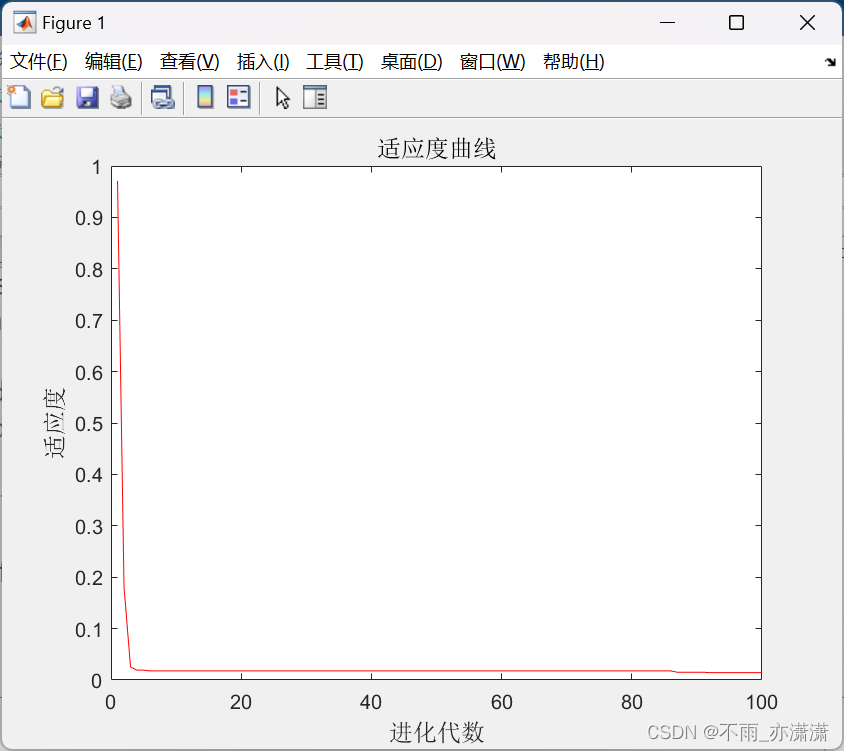
[r c]=size(trace);
plot([1:r]',trace(:,2),'r-');
title('适应度曲线','fontsize',12);
xlabel('进化代数','fontsize',12);ylabel('适应度','fontsize',12);
disp('适应度 变量');
x=bestchrom;
xlim([0, 100]);
% 窗口显示
disp([bestfitness x]);
3.代码使用说明
上述代码运行顺序
data.m 生成数据(如果已有 input output 数据可跳过),
ELM.m 进行ELM训练及函数拟合,
Genetic.m(主函数)利用遗传算法求极值。
求最大值的方法
上述代码用于求解最小值,对于求解最大值的需求,可以在适应度函数里面,对适应度计算结果求反,把求解最大值的问题转化为求解最小值的问题。
例如:对于非线性函数 y = − ( x 1 2 + x 2 2 ) + 4 y = -(x_1^2+x_2^2)+4 y=−(x12+x22)+4 :
for i=1:4000
input(i,:)=10*rand(1,2)-5;
output(i)=-(input(i,1)^2+input(i,2)^2)+4;
end
求最大值时,需要在 fun.m 里面,修改最后一行代码:
fitness=-mapminmax('reverse',an,outputps);
注意:每次运行结果不尽相同。
4.代码运行结果
对 y = x 1 2 + x 2 2 y = x_1^2+x_2^2 y=x12+x22 求极小值
ELM神经网络拟合
运行ELM.m之后:
输出:
errorsum =
1.0758
历时 0.169951 秒。
注意:每次运行结果不尽相同。
遗传算法寻优
运行主函数 Genetic.m之后:
输出:
...
i =
100
适应度 变量
0.0142 -0.0038 -0.0103
最终结果最优个体为(-0.0038,-0.0103),适应度为 0.0142。
注意:每次运行结果不尽相同。
参考
《MATLAB神经网络43个案例分析》