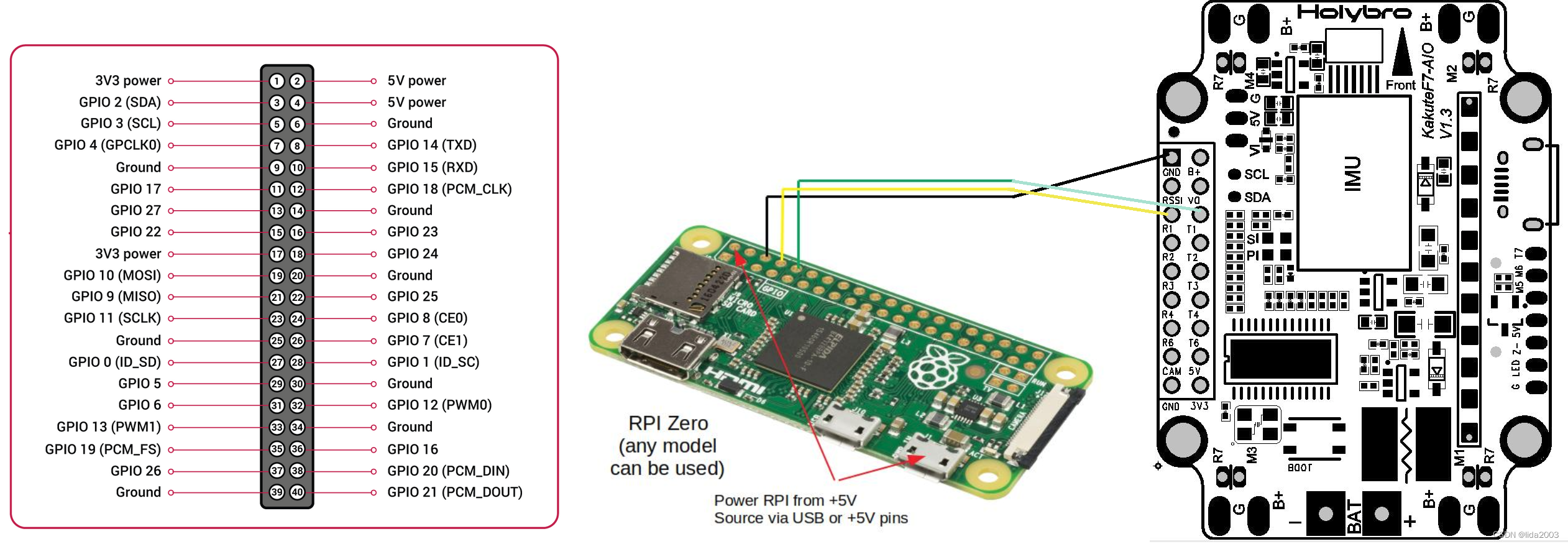
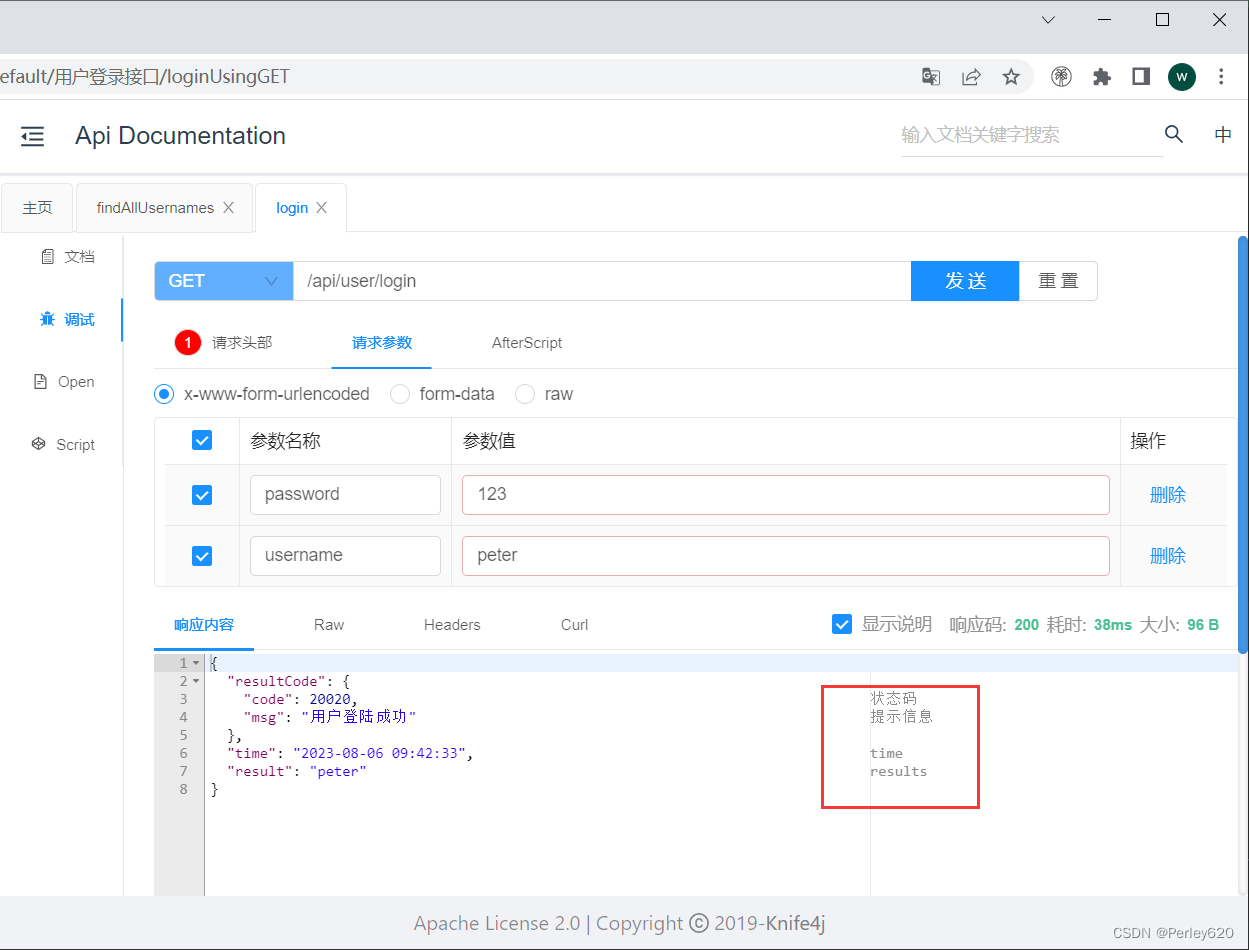
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char * * argv){
printf("输入了参数个数:%d \n",argc);
if (argc !=3 )
{
printf("参数不对,useage %s file newfile \n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
//打开源文件
int oldfile = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
if (oldfile == -1)
{
printf("文件%s不存在!\n",argv[1]);
}
/* 3. 创建新文件 */
int fd_new = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH);
if (fd_new == -1)
{
printf("can not creat file %s \n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
char buf[1024];
int len = 0;
//获取输入流
while ((len = read(oldfile,buf,1024)) > 0 )
{
if (write(fd_new, buf, len) != len)
{
printf("can not write %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
}
/* 5. 关闭文件 */
close(oldfile);
close(fd_new);
printf("复制文件成功!\n");
return 1;
}
主要函数:open、read、write
在linux使用: man 2 open...查看调用函数api
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
/*
* ./copy 1.txt 2.txt
* argc = 3
* argv[0] = "./copy"
* argv[1] = "1.txt"
* argv[2] = "2.txt"
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd_old, fd_new;
struct stat stat;
char *buf;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s <old-file> <new-file>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开老文件 */
fd_old = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fd_old == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 3. 确定老文件的大小 */
if (fstat(fd_old, &stat) == -1)
{
printf("can not get stat of file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 4. 映射老文件 */
buf = mmap(NULL, stat.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd_old, 0);
if (buf == MAP_FAILED)
{
printf("can not mmap file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 5. 创建新文件 */
fd_new = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH);
if (fd_new == -1)
{
printf("can not creat file %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
/* 6. 写新文件 */
if (write(fd_new, buf, stat.st_size) != stat.st_size)
{
printf("can not write %s\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
/* 5. 关闭文件 */
close(fd_old);
close(fd_new);
return 0;
}
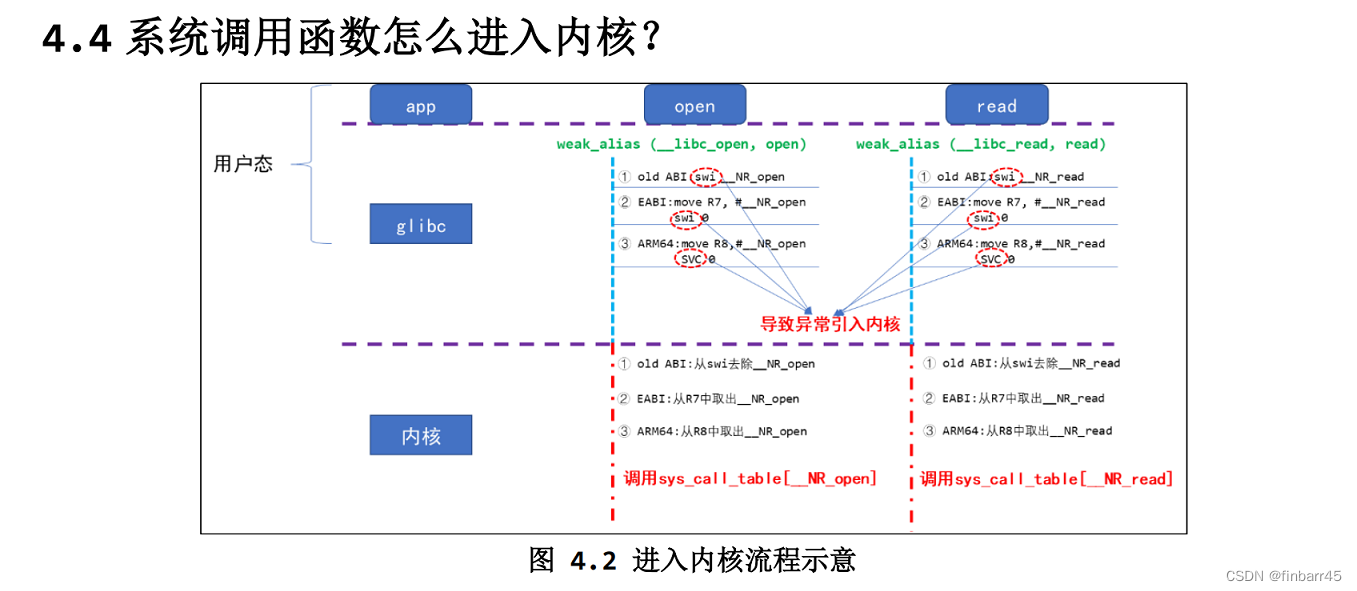
linux调用内核的原理图