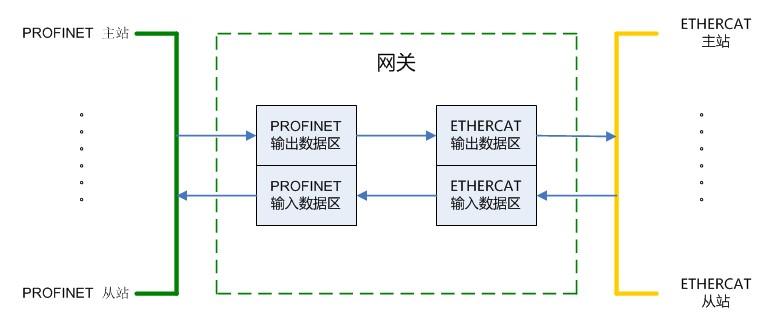
1.简述
linprog函数主要用来求线型规划中的最小值问题(最大值的镜像问题,求最大值只需要加个“-”)
2. 算法结构及使用方法
针对约束条件为Ax=b或Ax≤b的问题
2.1 linprog函数
x=linprog(f,A,b)
x=linprog(f,A,b,Aeq,beq)
x=linprog(f,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub)
x=linprog(f,A,b,Aeq,beq,lb,ub,x0)
2.2 参数简介
f:目标函数
A:不等式约束条件矩阵
b:对应不等式右侧的矩阵
Aeq:等式约束条件矩阵
beq:不等式右侧的矩阵
Aeq:等式约束条件矩阵
beq:对应等式右侧的矩阵
lb:x的下界
ub:x的上界
x0:设置初始点x0,这个选择项只是对medium-scale算法有效。默认的large-scale算法和简单的算法忽略任何初始点。(一般用不到)
2.3 常用linprog函数及用法举例
linprog函数常用形式为:
x=linprog(f,A,b,Aep,beq,lb,ub);
例子: 学习目标:有约束条件多元变量函数最小值
适合 计划生产盈利最大 的模式求解,
最大值解法可转化为求解最小值算法,非常容易
求最大值转化为求最小值 f=70*x1+120*x2 的最大值,当然x1,x2是有约束的。
转化为求 f=-(70*x1+120*x2) 的最小值。
约束条件:9*x1+4*x2<=3600;4*x1+5*x2<=2000;3*x1+10*x2<=3000;-x1,-x2<
2.代码
主函数:
clc
clear
f=[-70 -120];
A=[9 4;4 5;3 10];
B=[3600;2000;3000];
Aeq=[]; Beq=[];
lb=[0 0];ub=[inf inf];
x0=[1 1];
options=optimset('display','iter','Tolx',1e-8);
[x,f,exitflag]=linprog(f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,x0,options)
%[xmincon,fval,exitflag,output] = fmincon(@(x)-(70*x(1)+120*x(2)),x0,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,[],options)
子函数:
function [x,fval,exitflag,output,lambda]=linprog(f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,x0,options)
%LINPROG Linear programming.
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b) attempts to solve the linear programming problem:
%
% min f'*x subject to: A*x <= b
% x
%
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b,Aeq,beq) solves the problem above while additionally
% satisfying the equality constraints Aeq*x = beq. (Set A=[] and B=[] if
% no inequalities exist.)
%
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b,Aeq,beq,LB,UB) defines a set of lower and upper
% bounds on the design variables, X, so that the solution is in
% the range LB <= X <= UB. Use empty matrices for LB and UB
% if no bounds exist. Set LB(i) = -Inf if X(i) is unbounded below;
% set UB(i) = Inf if X(i) is unbounded above.
%
% X = LINPROG(f,A,b,Aeq,beq,LB,UB,X0) sets the starting point to X0. This
% option is only available with the active-set algorithm. The default
% interior point algorithm will ignore any non-empty starting point.
%
% X = LINPROG(PROBLEM) finds the minimum for PROBLEM. PROBLEM is a
% structure with the vector 'f' in PROBLEM.f, the linear inequality
% constraints in PROBLEM.Aineq and PROBLEM.bineq, the linear equality
% constraints in PROBLEM.Aeq and PROBLEM.beq, the lower bounds in
% PROBLEM.lb, the upper bounds in PROBLEM.ub, the start point
% in PROBLEM.x0, the options structure in PROBLEM.options, and solver
% name 'linprog' in PROBLEM.solver. Use this syntax to solve at the
% command line a problem exported from OPTIMTOOL.
%
% [X,FVAL] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns the value of the objective function
% at X: FVAL = f'*X.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns an EXITFLAG that describes
% the exit condition. Possible values of EXITFLAG and the corresponding
% exit conditions are
%
% 3 LINPROG converged to a solution X with poor constraint feasibility.
% 1 LINPROG converged to a solution X.
% 0 Maximum number of iterations reached.
% -2 No feasible point found.
% -3 Problem is unbounded.
% -4 NaN value encountered during execution of algorithm.
% -5 Both primal and dual problems are infeasible.
% -7 Magnitude of search direction became too small; no further
% progress can be made. The problem is ill-posed or badly
% conditioned.
% -9 LINPROG lost feasibility probably due to ill-conditioned matrix.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns a structure OUTPUT
% with the number of iterations taken in OUTPUT.iterations, maximum of
% constraint violations in OUTPUT.constrviolation, the type of
% algorithm used in OUTPUT.algorithm, the number of conjugate gradient
% iterations in OUTPUT.cgiterations (= 0, included for backward
% compatibility), and the exit message in OUTPUT.message.
%
% [X,FVAL,EXITFLAG,OUTPUT,LAMBDA] = LINPROG(f,A,b) returns the set of
% Lagrangian multipliers LAMBDA, at the solution: LAMBDA.ineqlin for the
% linear inequalities A, LAMBDA.eqlin for the linear equalities Aeq,
% LAMBDA.lower for LB, and LAMBDA.upper for UB.
%
% NOTE: the interior-point (the default) algorithm of LINPROG uses a
% primal-dual method. Both the primal problem and the dual problem
% must be feasible for convergence. Infeasibility messages of
% either the primal or dual, or both, are given as appropriate. The
% primal problem in standard form is
% min f'*x such that A*x = b, x >= 0.
% The dual problem is
% max b'*y such that A'*y + s = f, s >= 0.
%
% See also QUADPROG.
% Copyright 1990-2018 The MathWorks, Inc.
% If just 'defaults' passed in, return the default options in X
% Default MaxIter, TolCon and TolFun is set to [] because its value depends
% on the algorithm.
defaultopt = struct( ...
'Algorithm','dual-simplex', ...
'Diagnostics','off', ...
'Display','final', ...
'LargeScale','on', ...
'MaxIter',[], ...
'MaxTime', Inf, ...
'Preprocess','basic', ...
'TolCon',[],...
'TolFun',[]);
if nargin==1 && nargout <= 1 && strcmpi(f,'defaults')
x = defaultopt;
return
end
% Handle missing arguments
if nargin < 9
options = [];
% Check if x0 was omitted and options were passed instead
if nargin == 8
if isa(x0, 'struct') || isa(x0, 'optim.options.SolverOptions')
options = x0;
x0 = [];
end
else
x0 = [];
if nargin < 7
ub = [];
if nargin < 6
lb = [];
if nargin < 5
Beq = [];
if nargin < 4
Aeq = [];
end
end
end
end
end
end
% Detect problem structure input
problemInput = false;
if nargin == 1
if isa(f,'struct')
problemInput = true;
[f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,x0,options] = separateOptimStruct(f);
else % Single input and non-structure.
error(message('optim:linprog:InputArg'));
end
end
% No options passed. Set options directly to defaultopt after
allDefaultOpts = isempty(options);
% Prepare the options for the solver
options = prepareOptionsForSolver(options, 'linprog');
if nargin < 3 && ~problemInput
error(message('optim:linprog:NotEnoughInputs'))
end
% Define algorithm strings
thisFcn = 'linprog';
algIP = 'interior-point-legacy';
algDSX = 'dual-simplex';
algIP15b = 'interior-point';
% Check for non-double inputs
msg = isoptimargdbl(upper(thisFcn), {'f','A','b','Aeq','beq','LB','UB', 'X0'}, ...
f, A, B, Aeq, Beq, lb, ub, x0);
if ~isempty(msg)
error('optim:linprog:NonDoubleInput',msg);
end
% After processing options for optionFeedback, etc., set options to default
% if no options were passed.
if allDefaultOpts
% Options are all default
options = defaultopt;
end
if nargout > 3
computeConstrViolation = true;
computeFirstOrderOpt = true;
% Lagrange multipliers are needed to compute first-order optimality
computeLambda = true;
else
computeConstrViolation = false;
computeFirstOrderOpt = false;
computeLambda = false;
end
% Algorithm check:
% If Algorithm is empty, it is set to its default value.
algIsEmpty = ~isfield(options,'Algorithm') || isempty(options.Algorithm);
if ~algIsEmpty
Algorithm = optimget(options,'Algorithm',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
OUTPUT.algorithm = Algorithm;
% Make sure the algorithm choice is valid
if ~any(strcmp({algIP; algDSX; algIP15b},Algorithm))
error(message('optim:linprog:InvalidAlgorithm'));
end
else
Algorithm = algDSX;
OUTPUT.algorithm = Algorithm;
end
% Option LargeScale = 'off' is ignored
largescaleOn = strcmpi(optimget(options,'LargeScale',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts),'on');
if ~largescaleOn
[linkTag, endLinkTag] = linkToAlgDefaultChangeCsh('linprog_warn_largescale');
warning(message('optim:linprog:AlgOptsConflict', Algorithm, linkTag, endLinkTag));
end
% Options setup
diagnostics = strcmpi(optimget(options,'Diagnostics',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts),'on');
switch optimget(options,'Display',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts)
case {'final','final-detailed'}
verbosity = 1;
case {'off','none'}
verbosity = 0;
case {'iter','iter-detailed'}
verbosity = 2;
case {'testing'}
verbosity = 3;
otherwise
verbosity = 1;
end
% Set the constraints up: defaults and check size
[nineqcstr,nvarsineq] = size(A);
[neqcstr,nvarseq] = size(Aeq);
nvars = max([length(f),nvarsineq,nvarseq]); % In case A is empty
if nvars == 0
% The problem is empty possibly due to some error in input.
error(message('optim:linprog:EmptyProblem'));
end
if isempty(f), f=zeros(nvars,1); end
if isempty(A), A=zeros(0,nvars); end
if isempty(B), B=zeros(0,1); end
if isempty(Aeq), Aeq=zeros(0,nvars); end
if isempty(Beq), Beq=zeros(0,1); end
% Set to column vectors
f = f(:);
B = B(:);
Beq = Beq(:);
if ~isequal(length(B),nineqcstr)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchRowsOfA'));
elseif ~isequal(length(Beq),neqcstr)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchRowsOfAeq'));
elseif ~isequal(length(f),nvarsineq) && ~isempty(A)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchColsOfA'));
elseif ~isequal(length(f),nvarseq) && ~isempty(Aeq)
error(message('optim:linprog:SizeMismatchColsOfAeq'));
end
[x0,lb,ub,msg] = checkbounds(x0,lb,ub,nvars);
if ~isempty(msg)
exitflag = -2;
x = x0; fval = []; lambda = [];
output.iterations = 0;
output.constrviolation = [];
output.firstorderopt = [];
output.algorithm = ''; % not known at this stage
output.cgiterations = [];
output.message = msg;
if verbosity > 0
disp(msg)
end
return
end
if diagnostics
% Do diagnostics on information so far
gradflag = []; hessflag = []; constflag = false; gradconstflag = false;
non_eq=0;non_ineq=0; lin_eq=size(Aeq,1); lin_ineq=size(A,1); XOUT=ones(nvars,1);
funfcn{1} = []; confcn{1}=[];
diagnose('linprog',OUTPUT,gradflag,hessflag,constflag,gradconstflag,...
XOUT,non_eq,non_ineq,lin_eq,lin_ineq,lb,ub,funfcn,confcn);
end
% Throw warning that x0 is ignored (true for all algorithms)
if ~isempty(x0) && verbosity > 0
fprintf(getString(message('optim:linprog:IgnoreX0',Algorithm)));
end
if strcmpi(Algorithm,algIP)
% Set the default values of TolFun and MaxIter for this algorithm
defaultopt.TolFun = 1e-8;
defaultopt.MaxIter = 85;
[x,fval,lambda,exitflag,output] = lipsol(f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,options,defaultopt,computeLambda);
elseif strcmpi(Algorithm,algDSX) || strcmpi(Algorithm,algIP15b)
% Create linprog options object
algoptions = optimoptions('linprog', 'Algorithm', Algorithm);
% Set some algorithm specific options
if isfield(options, 'InternalOptions')
algoptions = setInternalOptions(algoptions, options.InternalOptions);
end
thisMaxIter = optimget(options,'MaxIter',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if strcmpi(Algorithm,algIP15b)
if ischar(thisMaxIter)
error(message('optim:linprog:InvalidMaxIter'));
end
end
if strcmpi(Algorithm,algDSX)
algoptions.Preprocess = optimget(options,'Preprocess',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
algoptions.MaxTime = optimget(options,'MaxTime',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if ischar(thisMaxIter) && ...
~strcmpi(thisMaxIter,'10*(numberofequalities+numberofinequalities+numberofvariables)')
error(message('optim:linprog:InvalidMaxIter'));
end
end
% Set options common to dual-simplex and interior-point-r2015b
algoptions.Diagnostics = optimget(options,'Diagnostics',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
algoptions.Display = optimget(options,'Display',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
thisTolCon = optimget(options,'TolCon',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if ~isempty(thisTolCon)
algoptions.TolCon = thisTolCon;
end
thisTolFun = optimget(options,'TolFun',defaultopt,'fast',allDefaultOpts);
if ~isempty(thisTolFun)
algoptions.TolFun = thisTolFun;
end
if ~isempty(thisMaxIter) && ~ischar(thisMaxIter)
% At this point, thisMaxIter is either
% * a double that we can set in the options object or
% * the default string, which we do not have to set as algoptions
% is constructed with MaxIter at its default value
algoptions.MaxIter = thisMaxIter;
end
% Create a problem structure. Individually creating each field is quicker
% than one call to struct
problem.f = f;
problem.Aineq = A;
problem.bineq = B;
problem.Aeq = Aeq;
problem.beq = Beq;
problem.lb = lb;
problem.ub = ub;
problem.options = algoptions;
problem.solver = 'linprog';
% Create the algorithm from the options.
algorithm = createAlgorithm(problem.options);
% Check that we can run the problem.
try
problem = checkRun(algorithm, problem, 'linprog');
catch ME
throw(ME);
end
% Run the algorithm
[x, fval, exitflag, output, lambda] = run(algorithm, problem);
% If exitflag is {NaN, <aString>}, this means an internal error has been
% thrown. The internal exit code is held in exitflag{2}.
if iscell(exitflag) && isnan(exitflag{1})
handleInternalError(exitflag{2}, 'linprog');
end
end
output.algorithm = Algorithm;
% Compute constraint violation when x is not empty (interior-point/simplex presolve
% can return empty x).
if computeConstrViolation && ~isempty(x)
output.constrviolation = max([0; norm(Aeq*x-Beq, inf); (lb-x); (x-ub); (A*x-B)]);
else
output.constrviolation = [];
end
% Compute first order optimality if needed. This information does not come
% from either qpsub, lipsol, or simplex.
if exitflag ~= -9 && computeFirstOrderOpt && ~isempty(lambda)
output.firstorderopt = computeKKTErrorForQPLP([],f,A,B,Aeq,Beq,lb,ub,lambda,x);
else
output.firstorderopt = [];
end
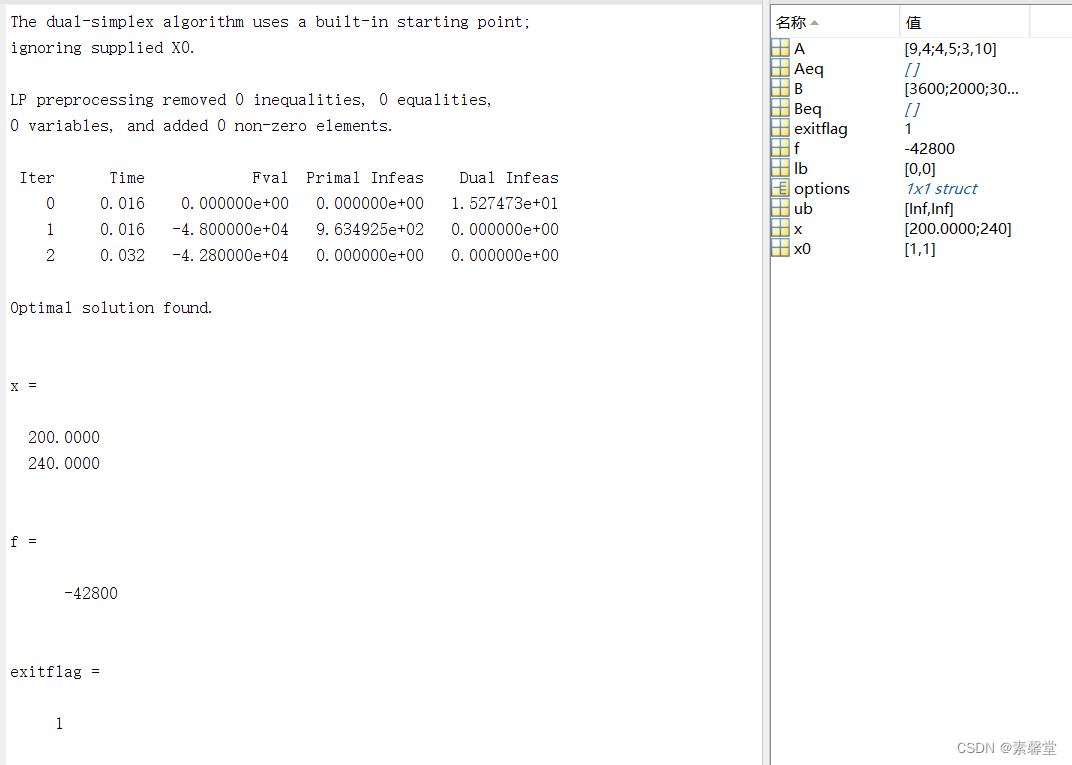
3.运行结果